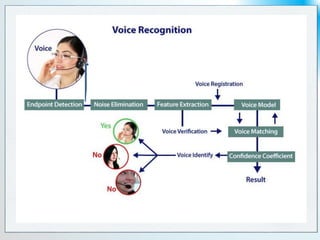
Voice biometrics offer advantages as an easily accessible biometric trait, especially for remote authentication, but are influenced by various environmental and personal factors. There are different applications of this technology, including access control and evidence gathering, utilizing unique speech characteristics for identification. However, limitations such as background noise and changes in a person's voice due to age or health can impact accuracy.