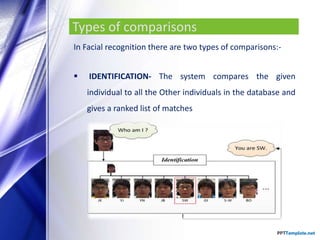
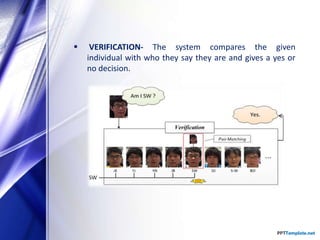
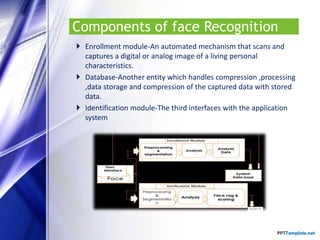
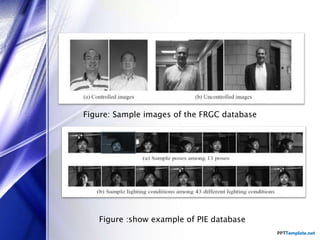
The document discusses facial recognition technology, which identifies individuals in digital images by analyzing facial features. It covers the history, applications, types of comparisons, components, and techniques used in face recognition, highlighting its use in security, banking, and social media. Additionally, it presents the advantages and disadvantages of this technology, including cost-effectiveness and issues related to accuracy.