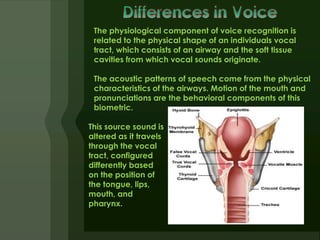
1) Speaker recognition uses characteristics extracted from voices to validate a user's claimed identity. It recognizes who is speaking, whereas speech recognition recognizes what is being said.
2) Speaker recognition technologies have evolved alongside speech recognition and synthesis since the 1960s as researchers have studied vocal tract physiology and developed systems to analyze speech acoustics and match samples to templates.
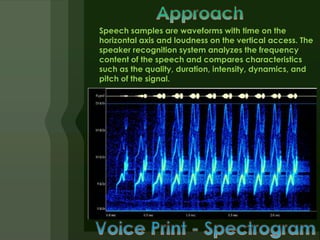
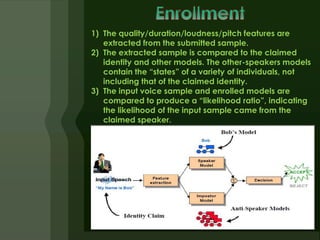
3) Speaker recognition systems extract features from speech like duration, pitch, and intensity to generate likelihood ratios comparing a sample to the claimed identity versus other speakers. Updates help models cope with voice changes over time.