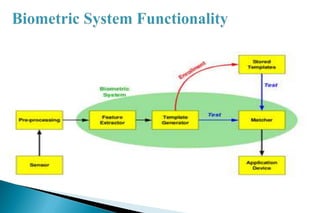
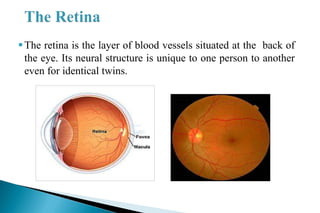
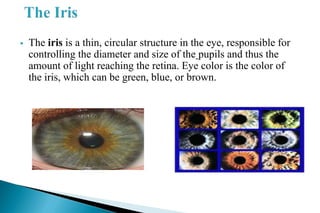
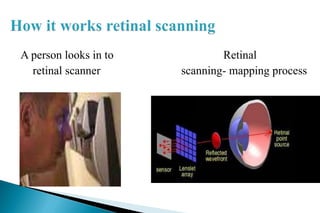
This document discusses iris and retinal scanning as biometric identification technologies. Retinal scanning analyzes the blood vessels at the back of the eye, while iris scanning reads patterns in the iris. Both are highly accurate, with almost zero false positive rates. However, retinal scanning requires more user skill and can be affected by eye conditions. Now widely used, iris scanning was developed in 1994 and has advantages over fingerprints in identifying individuals.