Embed presentation
Downloaded 175 times


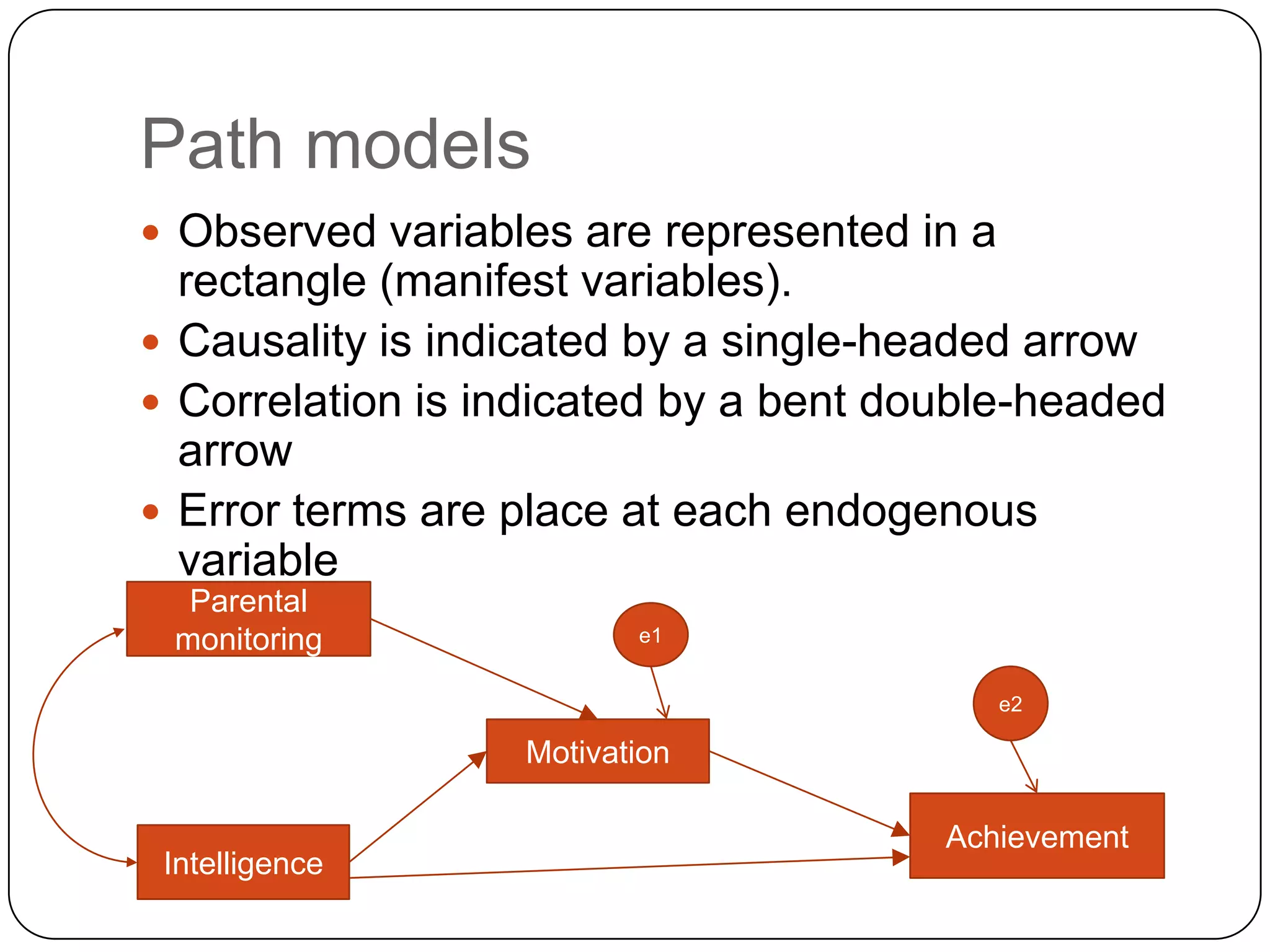


Path analysis is a technique that uses regression models to test theories of causal relationships among variables. It allows researchers to explicitly specify presumed causal relationships and determine not just associations but also potential causal relationships between variables. Path models represent variables as rectangles or ovals, with causality indicated by single-headed arrows and correlation by double-headed arrows. Path coefficients represent standardized regression weights and can be interpreted as the change in the response variable corresponding to a change in the explanatory variable while controlling for other factors.







Introduction to the presenter and the topic of path analysis in counseling and educational psychology.
Path analysis uses regression models to test causal relationships among variables, clarifying theories of relationships.
Path models use rectangles for observed variables and arrows to indicate causality and correlation, featuring error terms.
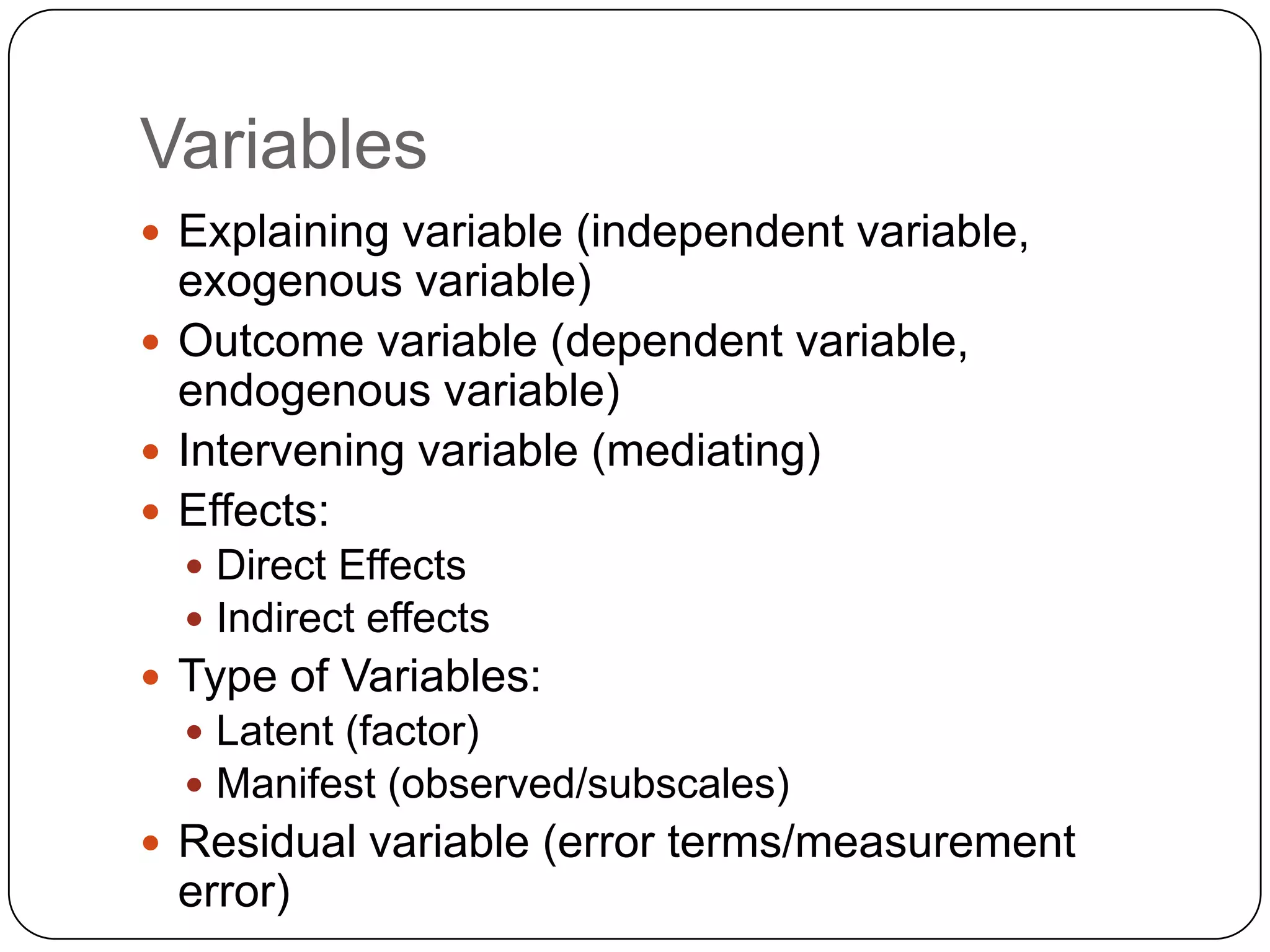
Explains different types of variables in path analysis: independent, dependent, mediating, and their effects.
Discusses standardized regression coefficients to interpret relationships, exemplified with intelligence and motivation.
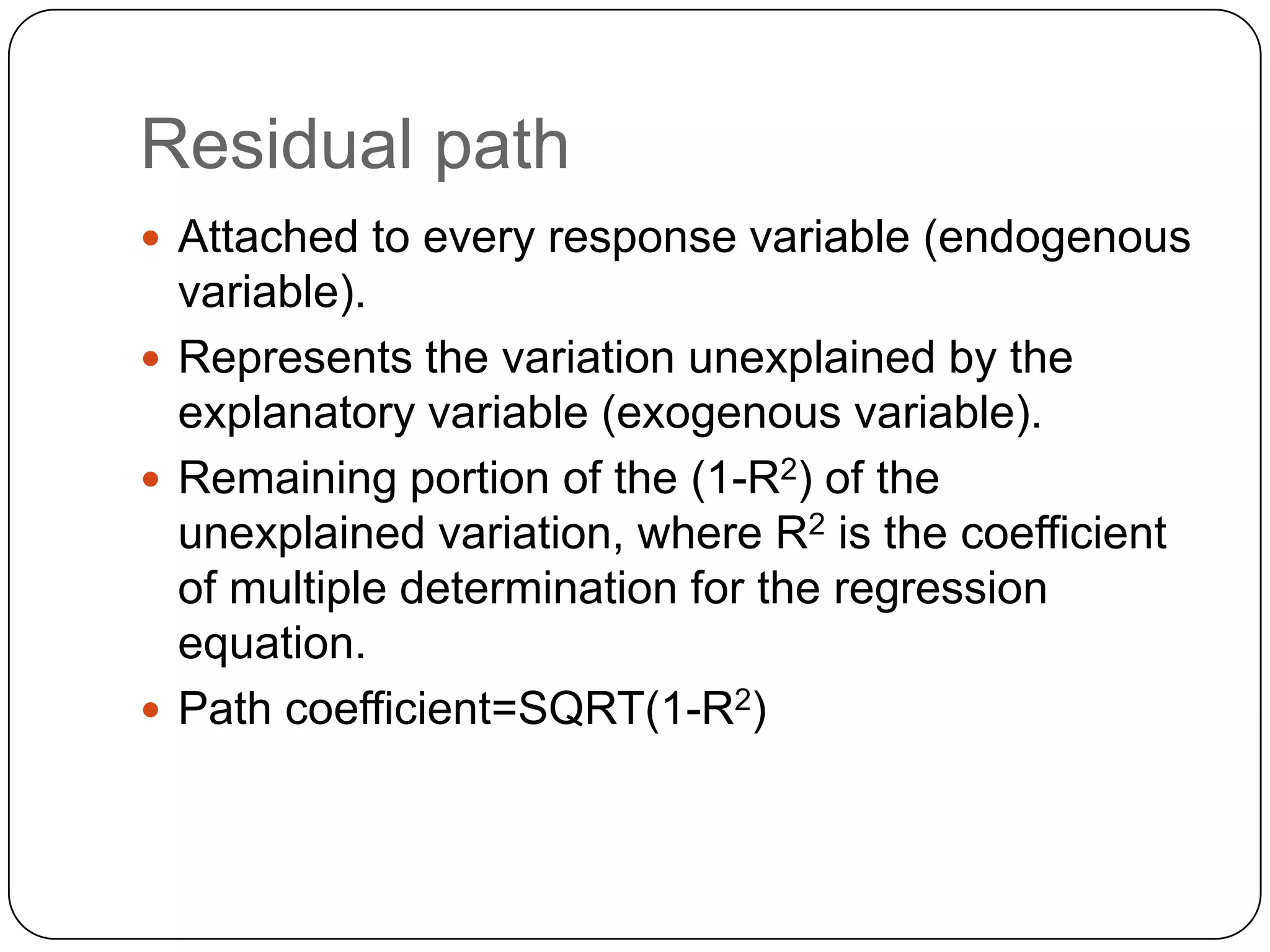
Residual paths indicate unexplained variation in models, with calculations for path coefficients due to unexplained variation.
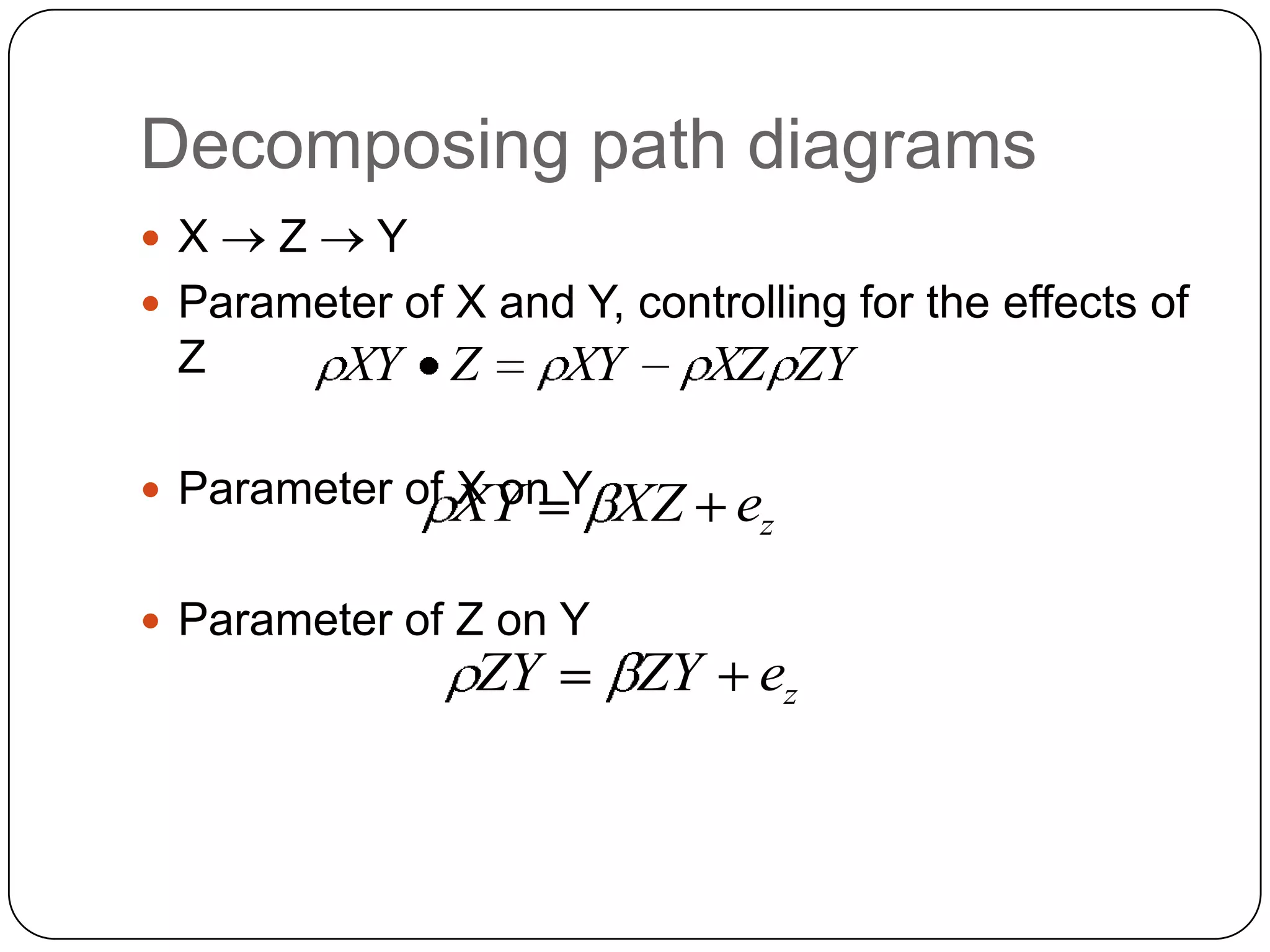
Illustrates the decomposition of path diagrams, emphasizing the parameters of X, Y, and Z and their controlled effects.