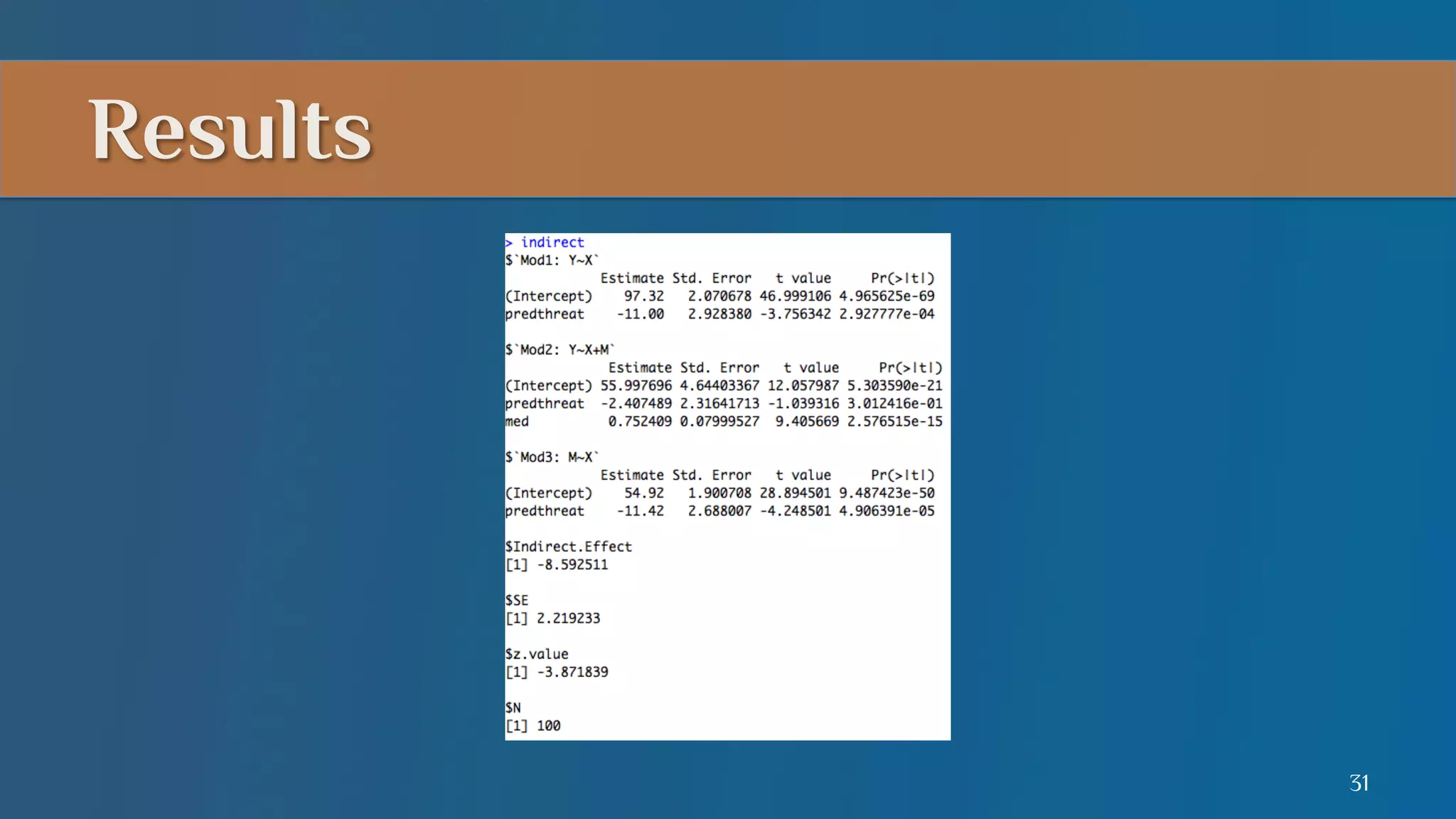
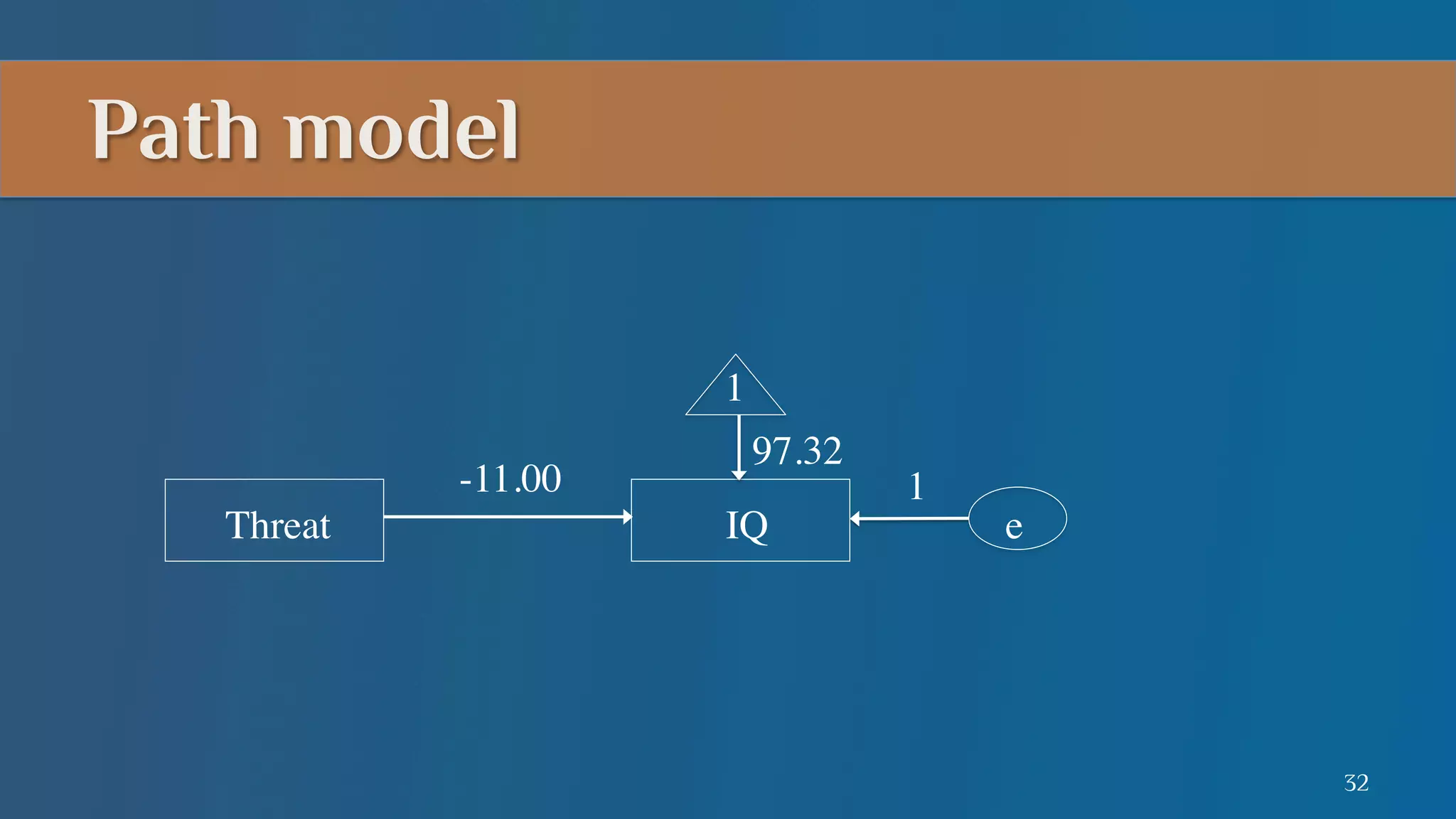
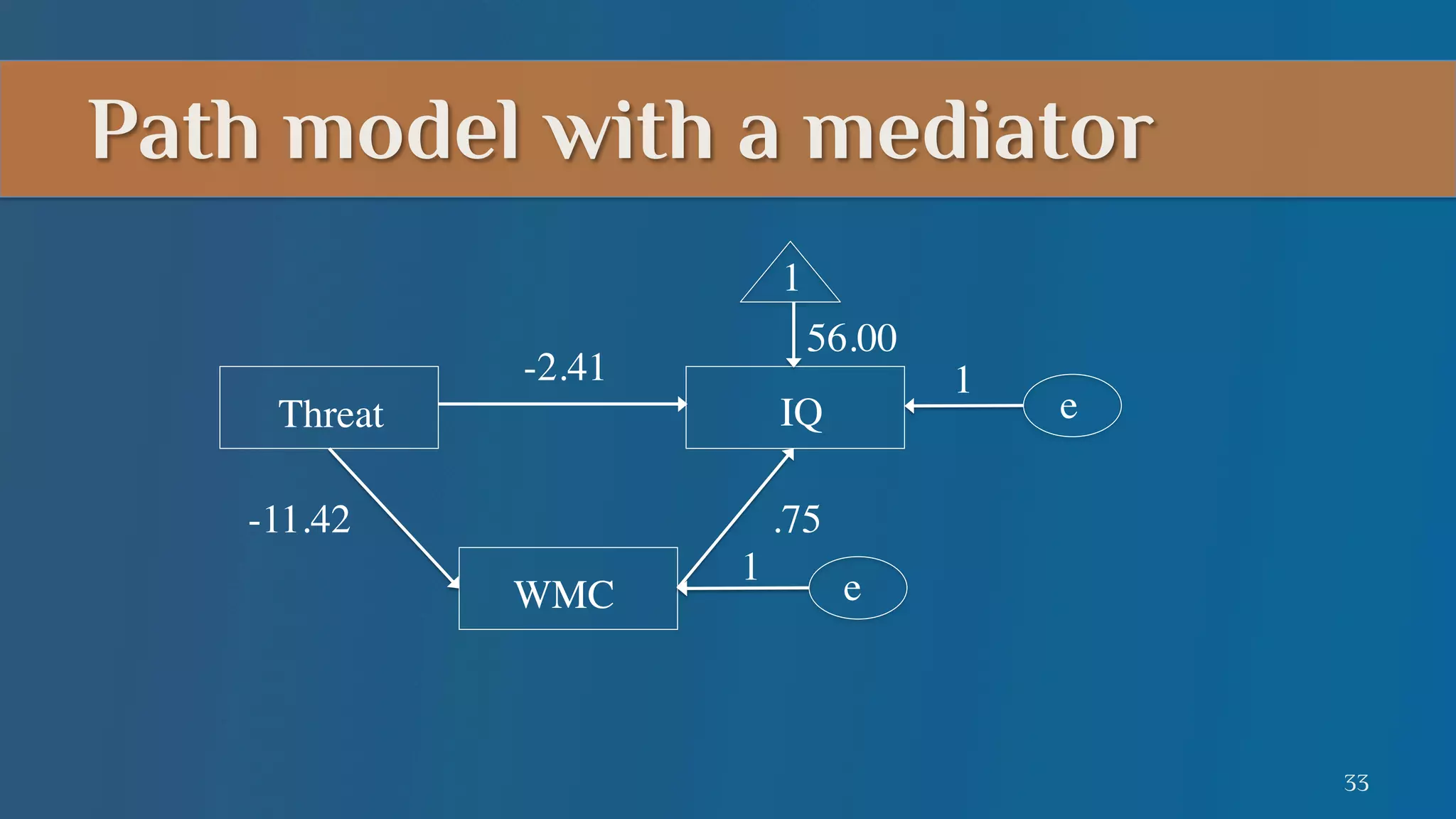
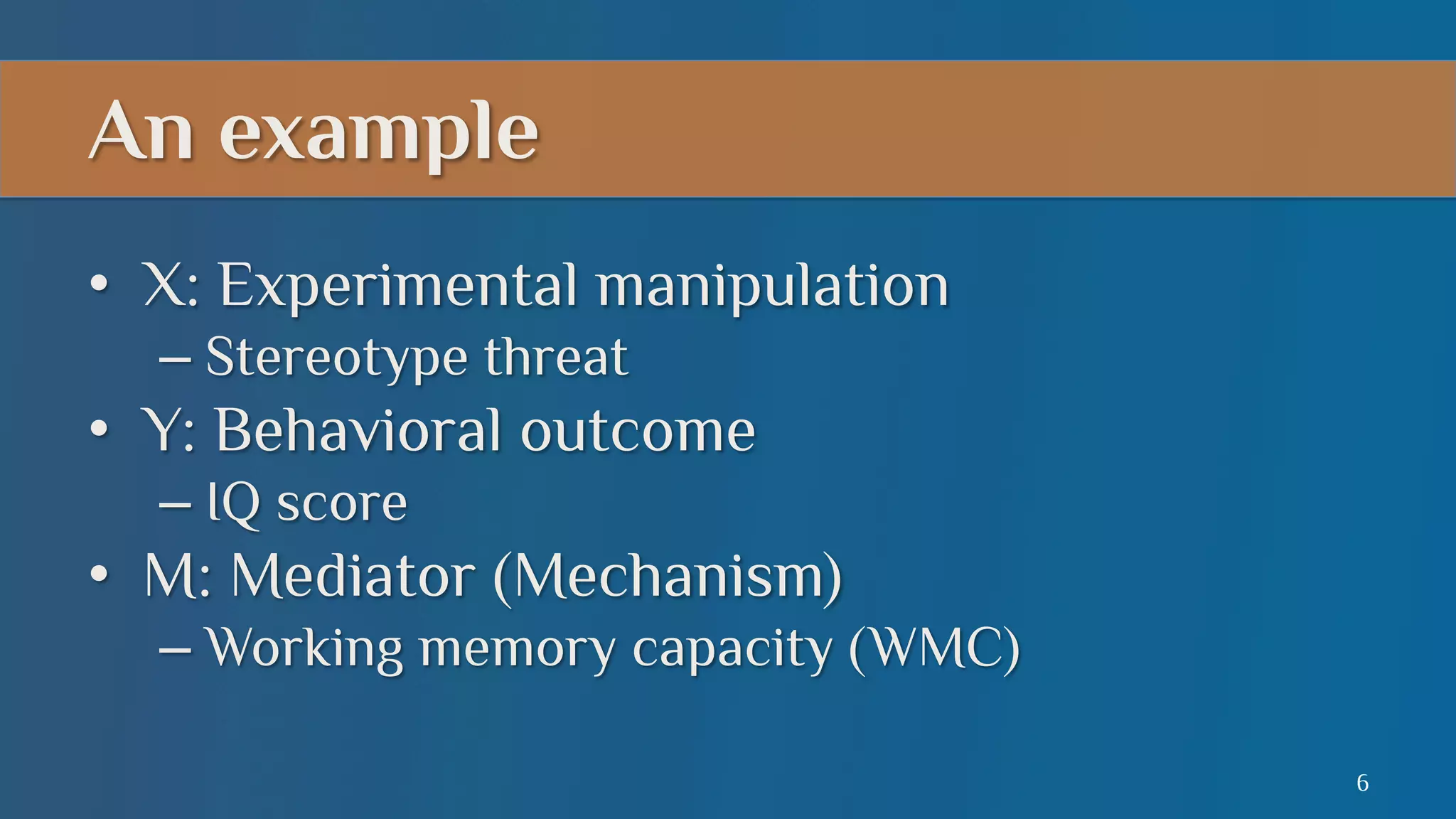
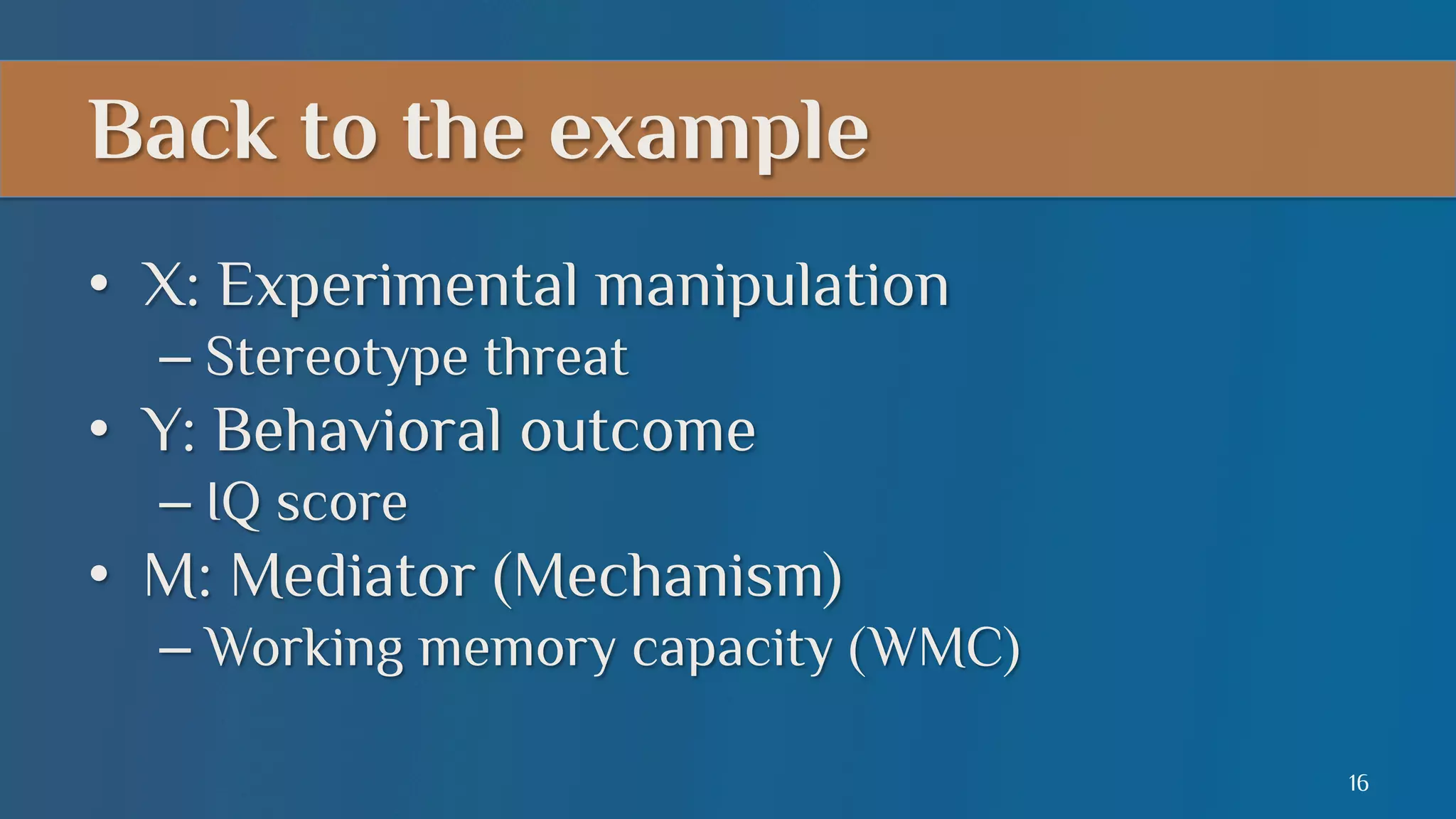
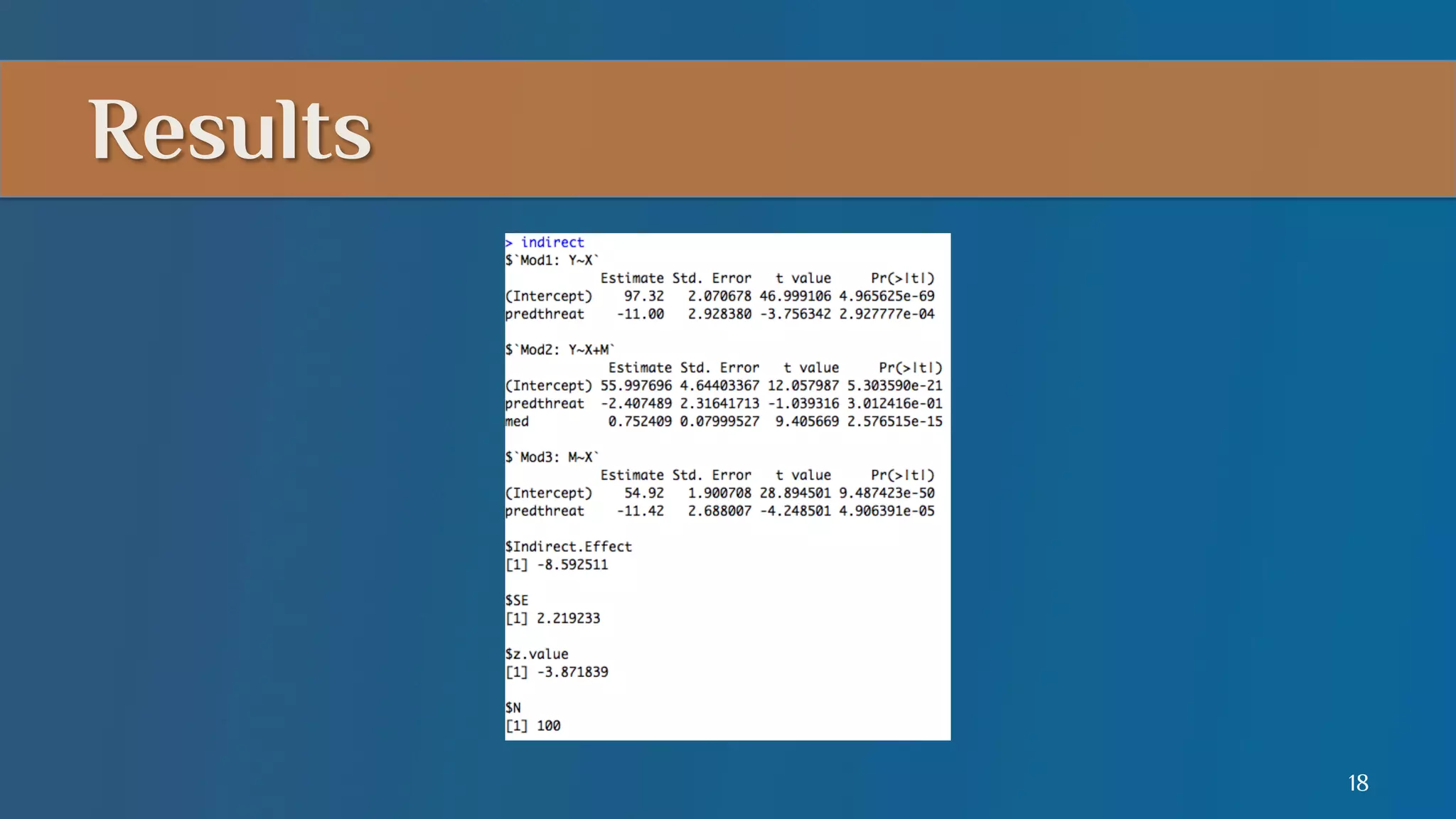
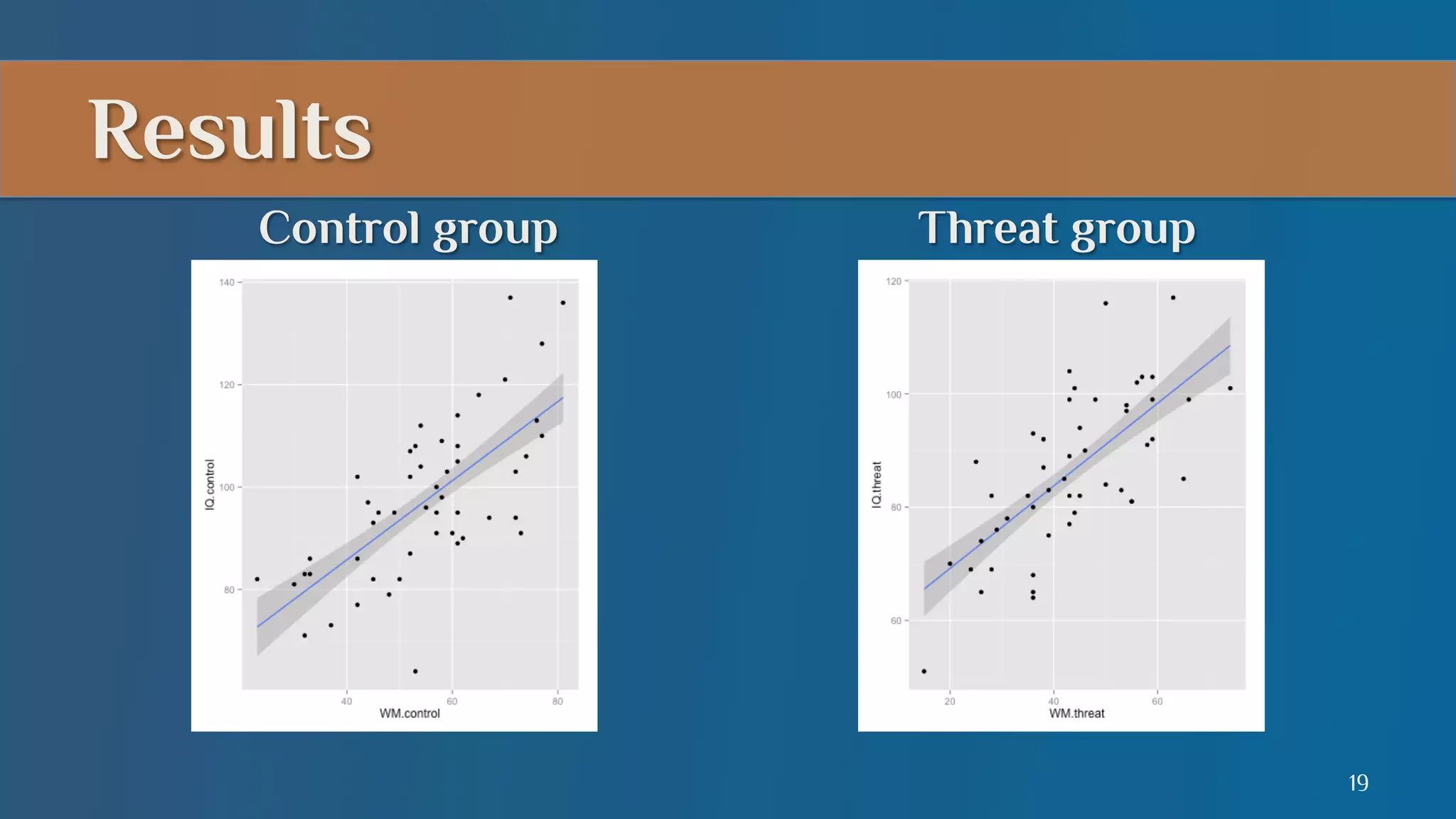
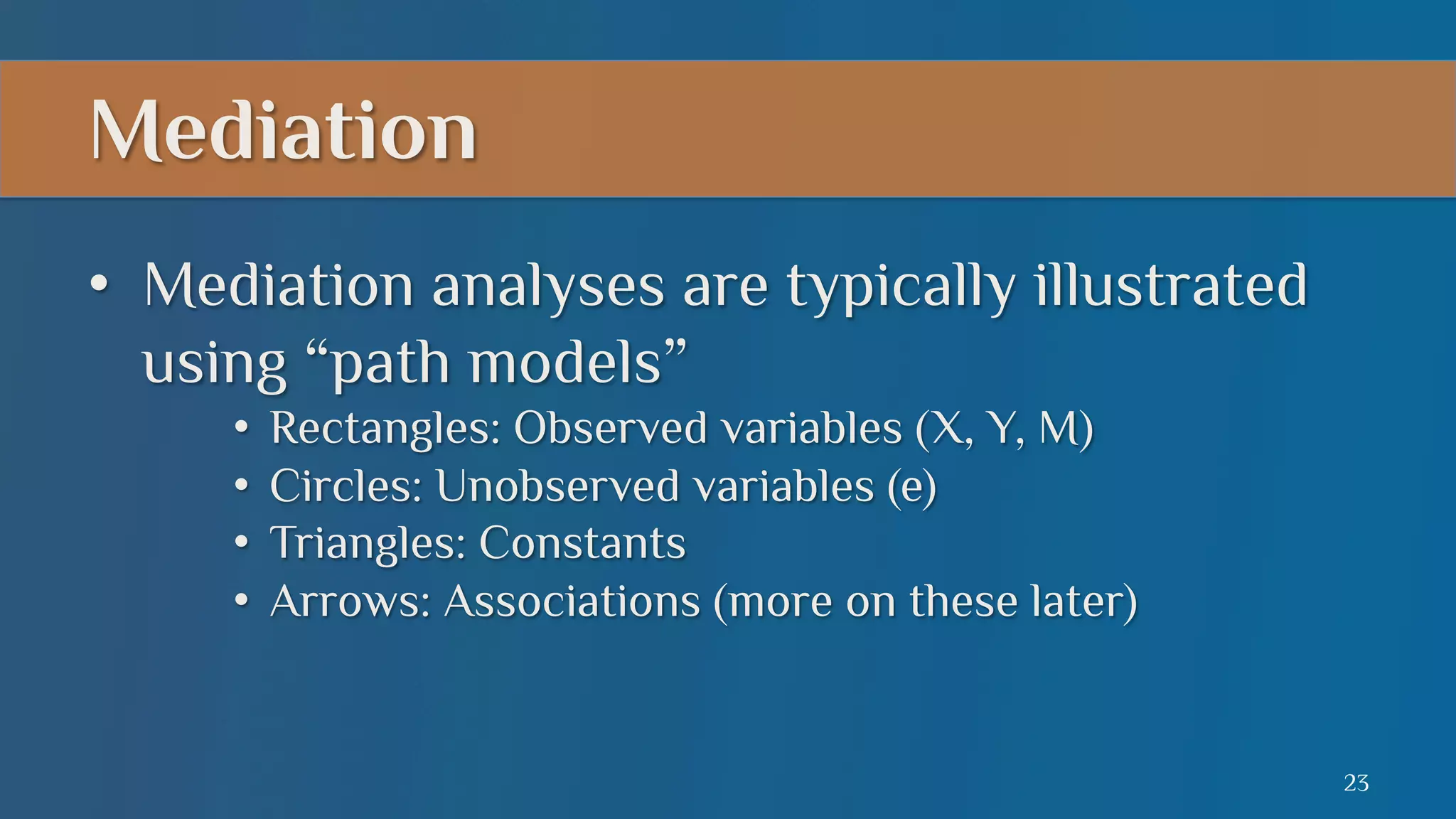
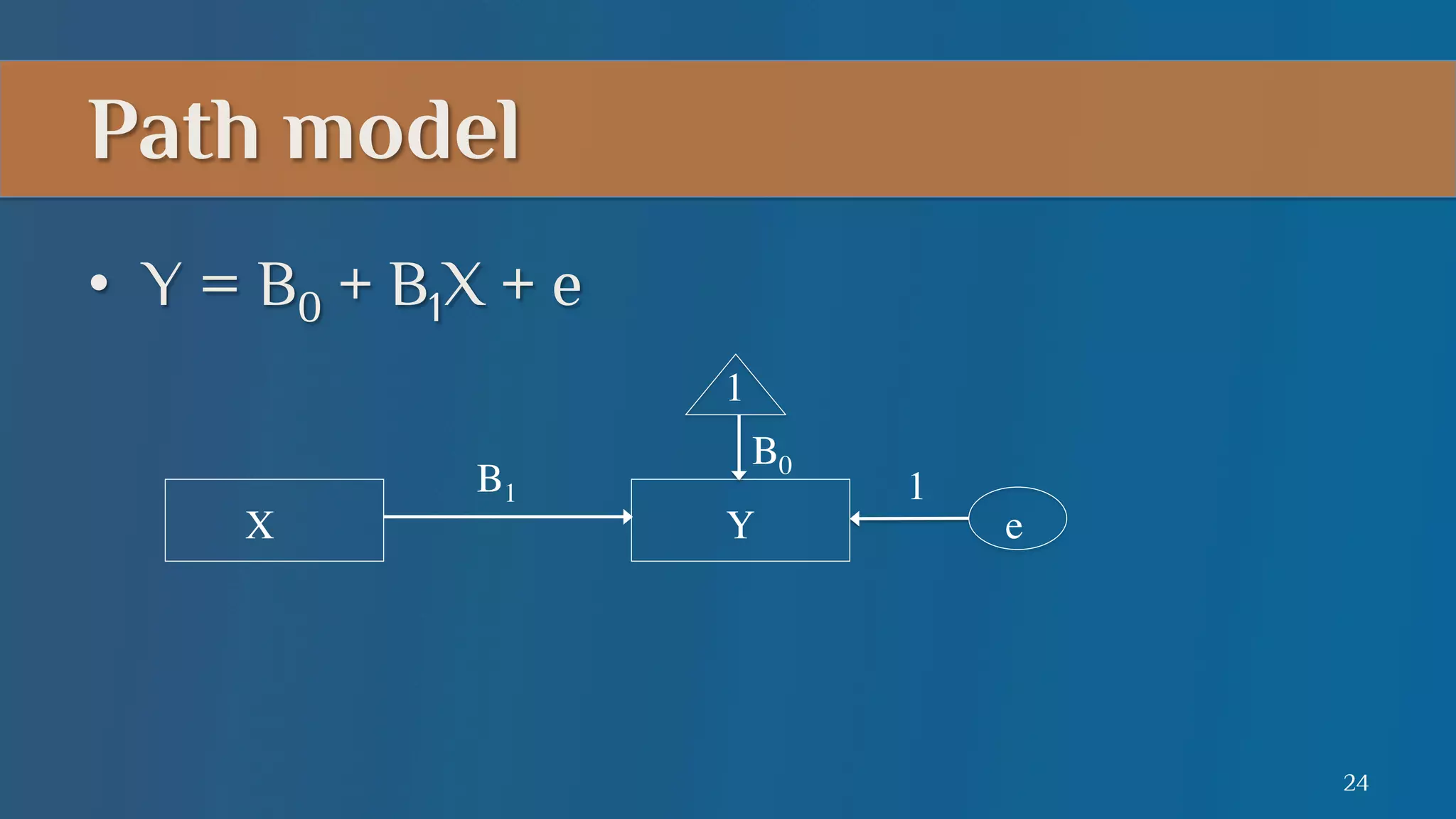
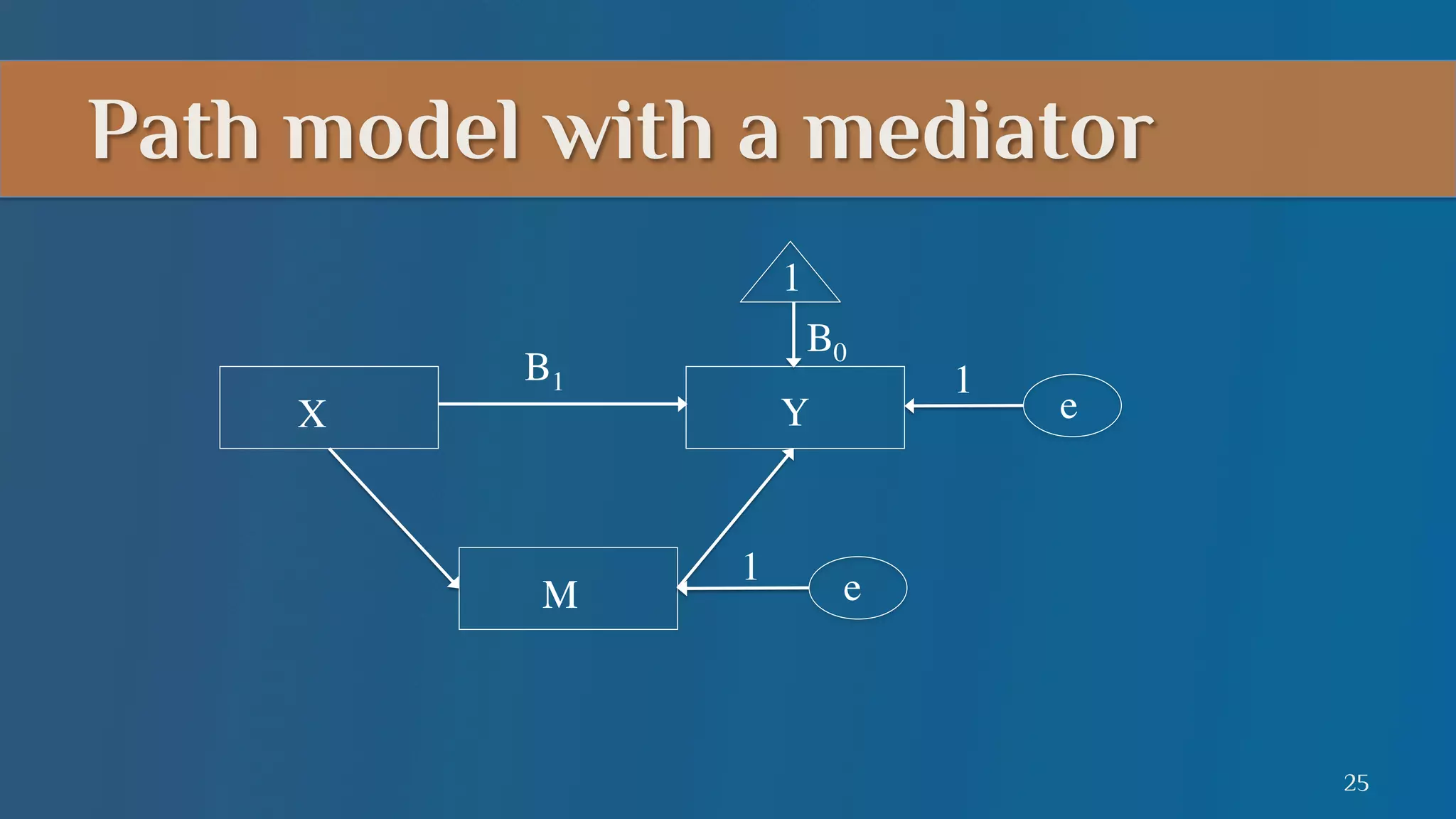
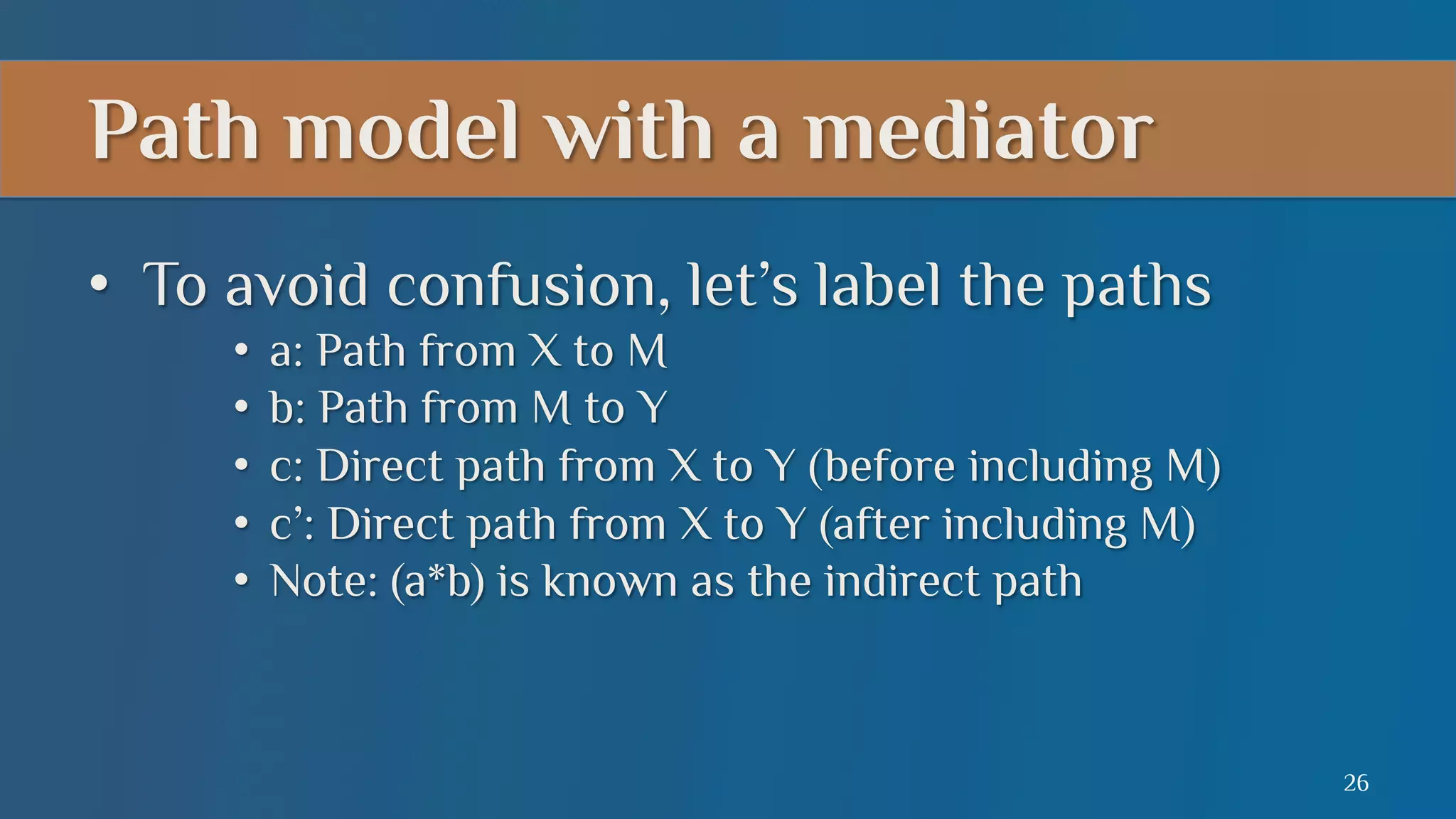
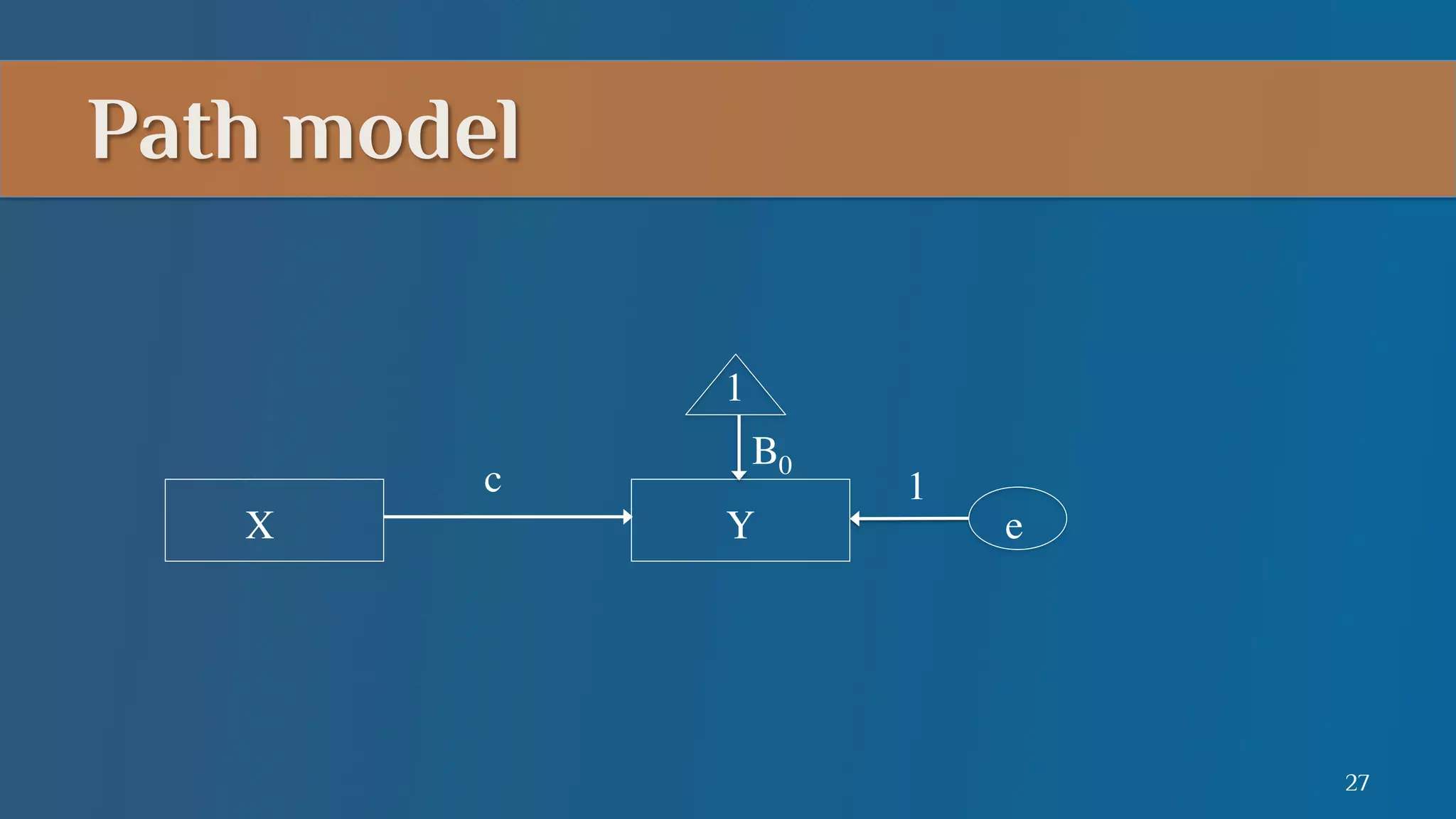
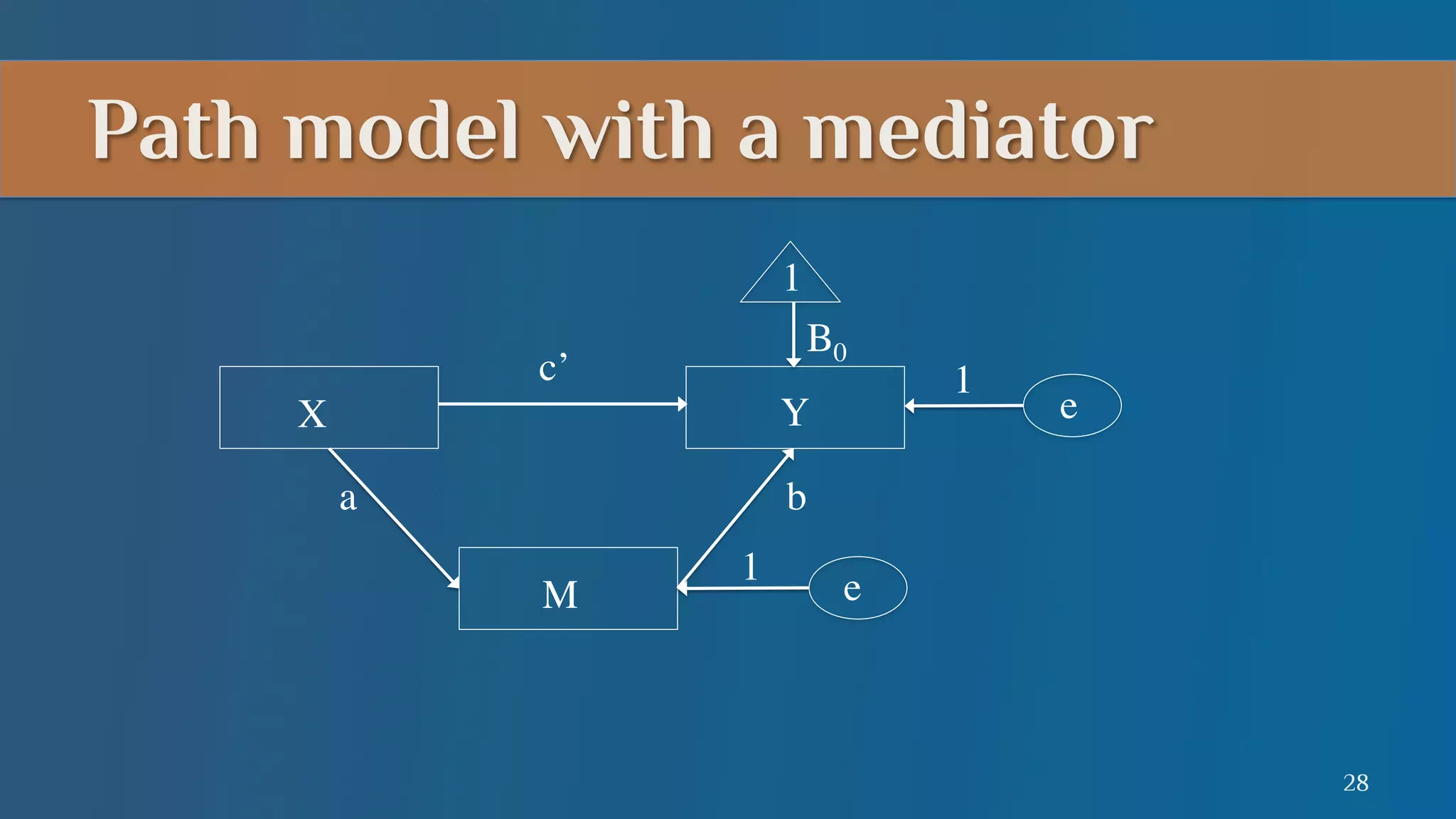
This document summarizes a lecture on mediation analysis. It discusses two main approaches: the standard approach using regression models and path analysis. For the standard approach, three regression models are run to test the direct and indirect effects of an independent variable on a dependent variable through a proposed mediator. For path analysis, paths are drawn between variables to represent these relationships and specific paths are tested. An example is provided of stereotype threat affecting IQ scores through working memory capacity. The results support full mediation according to the standard approach and path analysis.






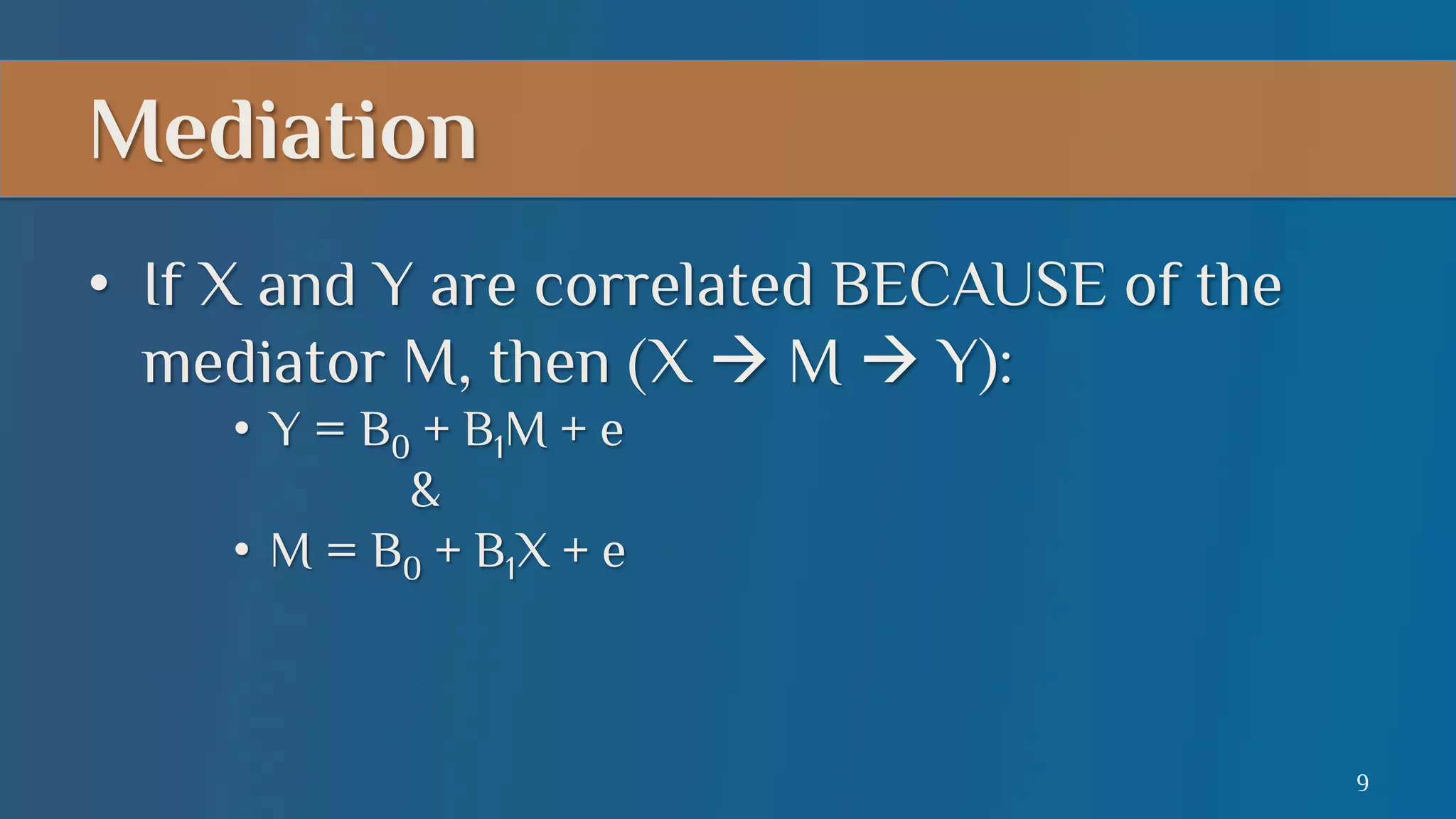











![How to test for mediation
• The Sobel test
z = (Ba* Bb) / SQRT[(Ba2 * SEb2) + (Bb2 * SEa2)]
– The null hypothesis
• The indirect effect is zero
• (Ba*Bb) = 0
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lectureslides-stats1-131228060047-phpapp01/75/Lecture-slides-stats1-13-l14-air-30-2048.jpg)