This document discusses adsorption chromatography, which involves the adsorption of solutes onto the surface of a stationary phase. Key points include:
- Adsorption is a surface phenomenon where interaction occurs only on the surface of one substance, unlike absorption.
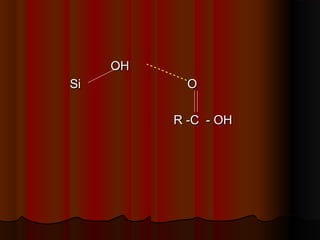
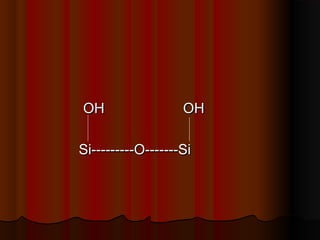
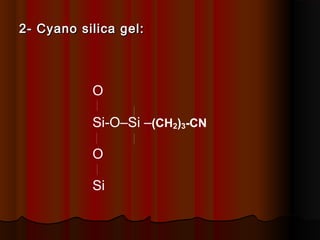
- Common stationary phases used in adsorption chromatography include silica gel, alumina, charcoal, and kieselguhr. Silica gel is the most widely used, with hydroxyl groups facilitating hydrogen bonding.
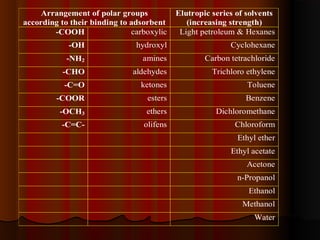
- Forces between solutes and the adsorbent like dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces determine how strongly compounds are retained on the stationary phase. Mobile phase composition impacts the balance of