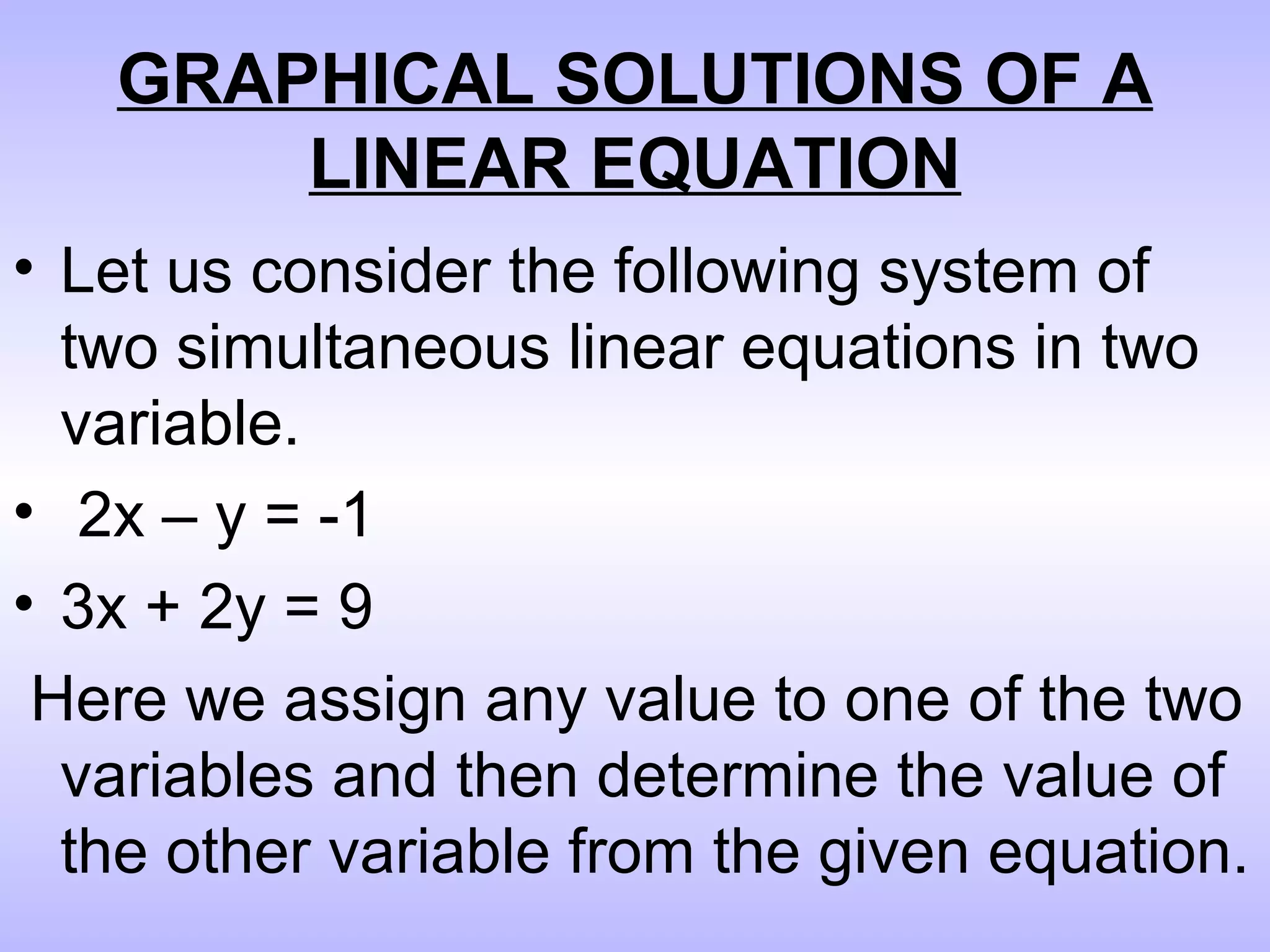
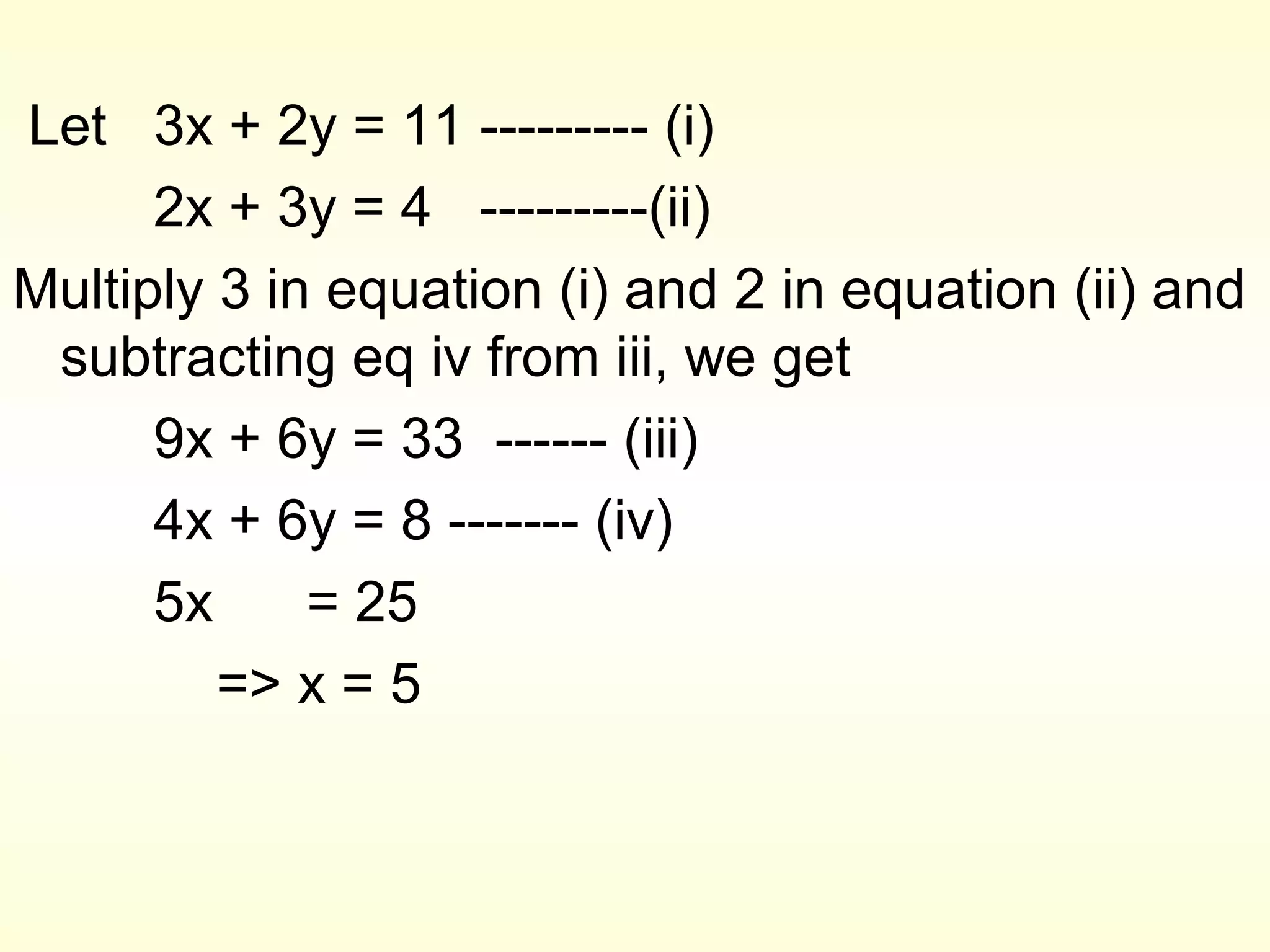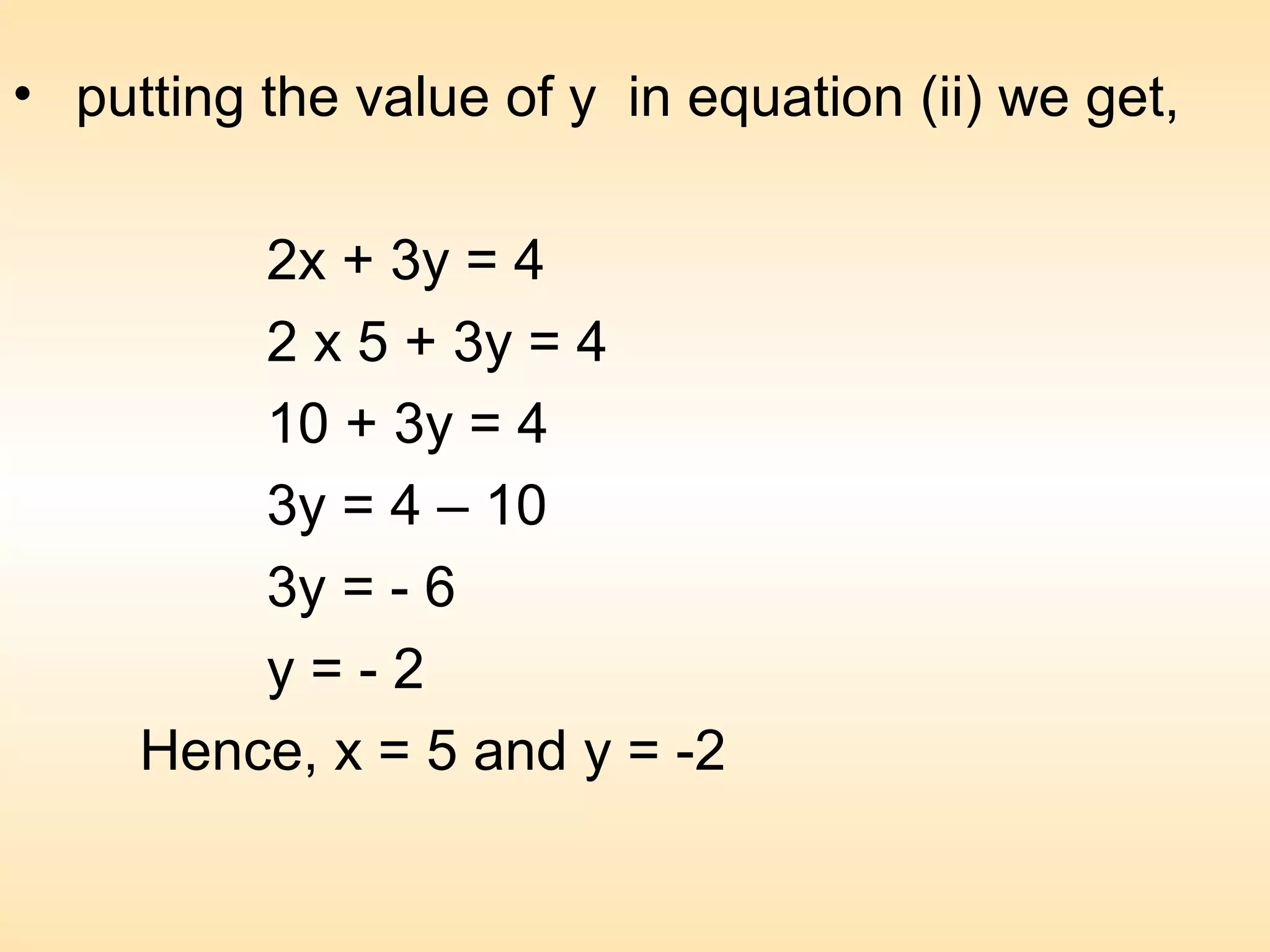This document discusses two methods for graphically solving systems of linear equations:
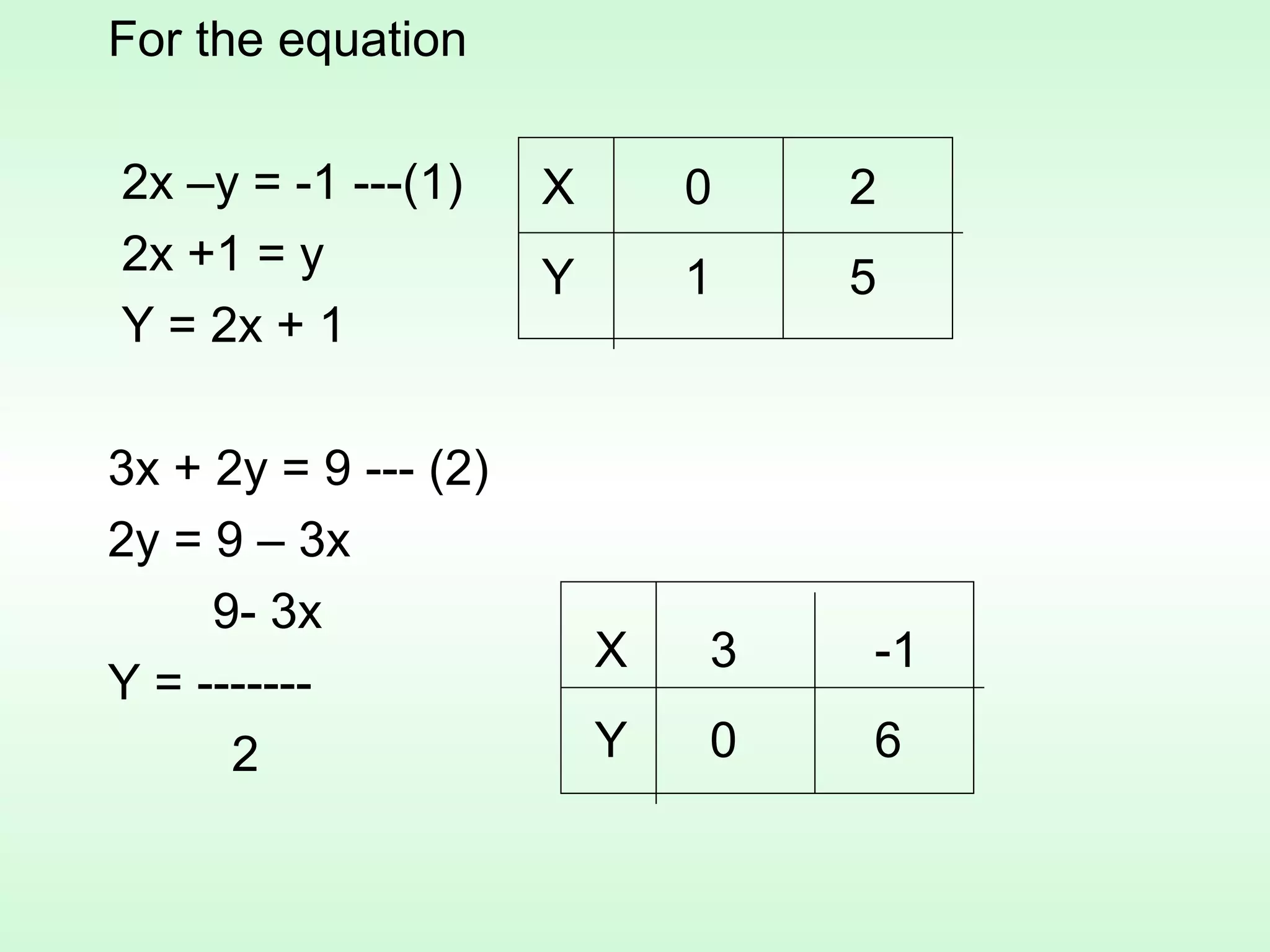
1) Assign a value to one variable and determine the value of the other variable from the given equations, plotting the points and connecting them with a line.
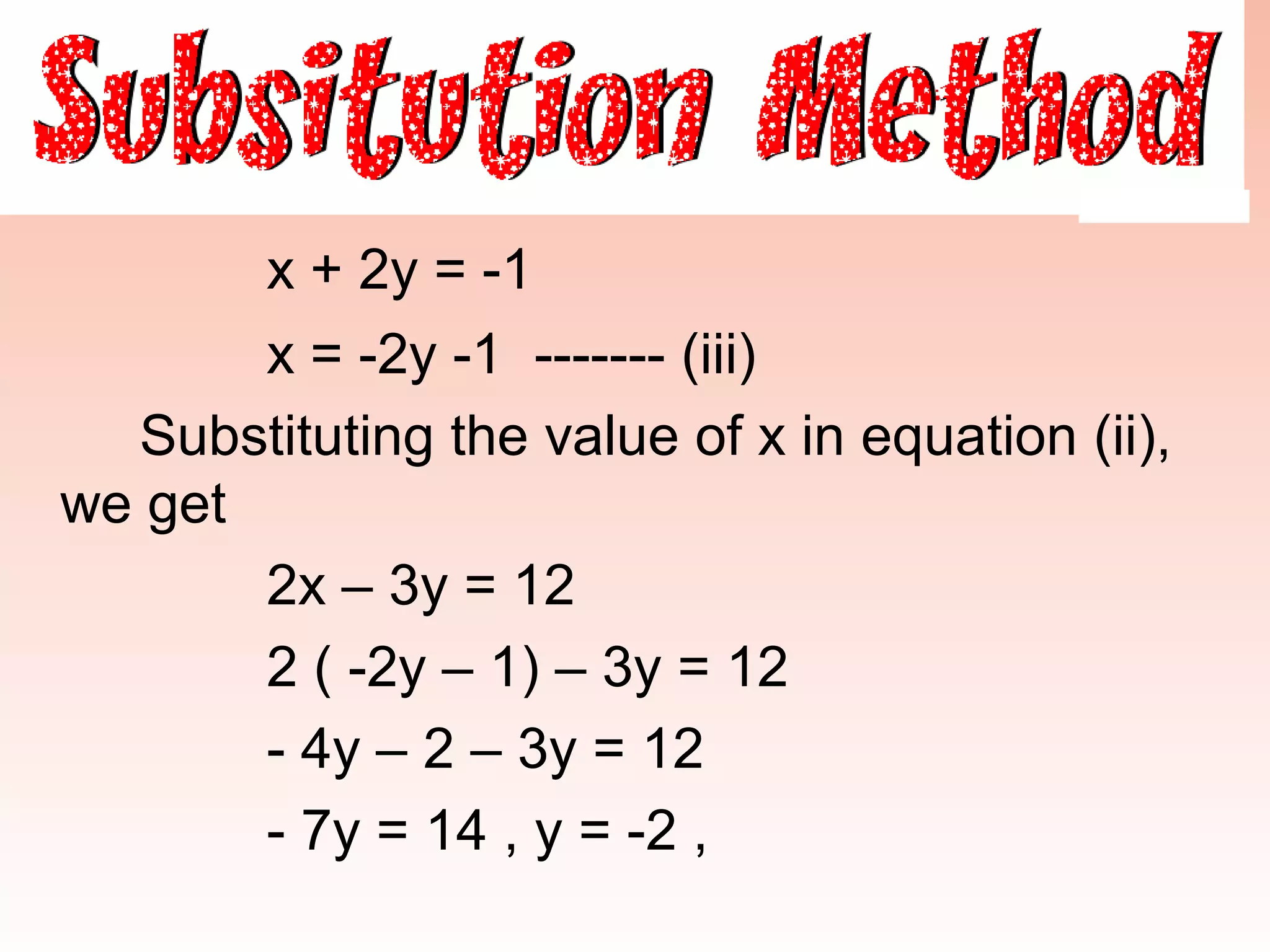
2) Eliminate one variable to obtain a single-variable equation, solve for the eliminated variable, then substitute back into one of the original equations to solve for the other variable.
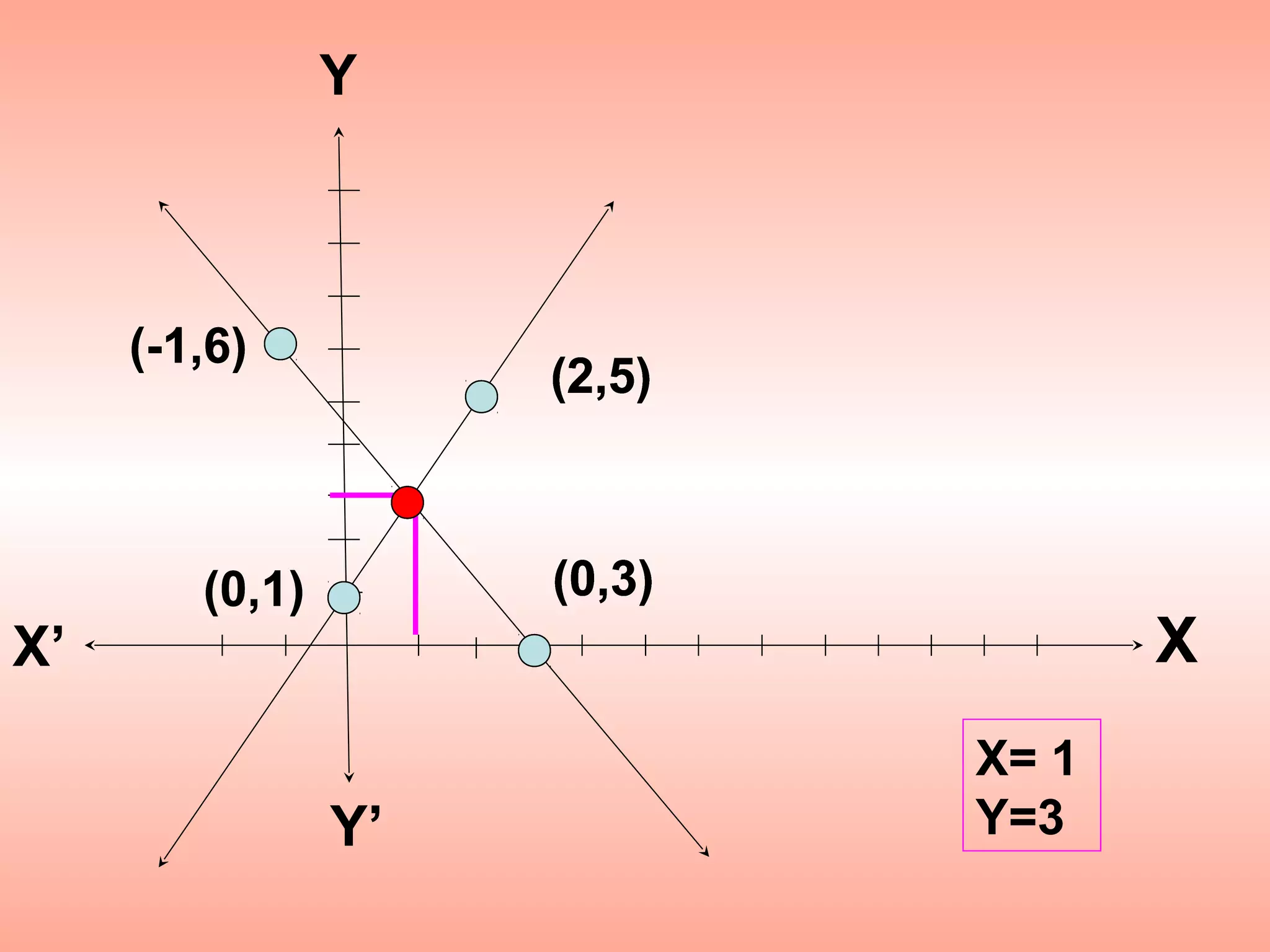
For example, a system is solved by setting x=3, solving for y, then substituting back to find x= -1. The solution is plotted as the point (-1,6).