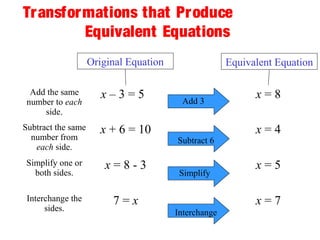
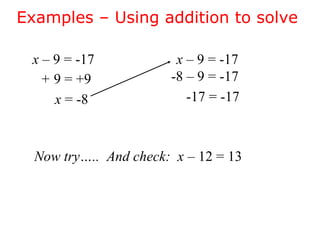
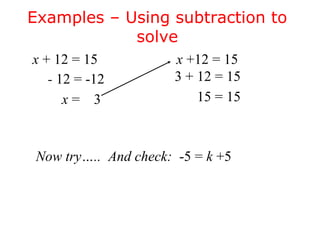
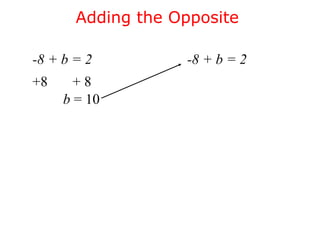
This document discusses solving one-step linear equations using addition and subtraction. It defines key terms like equations, solutions, and isolating variables. It explains that when transforming equations, the same operations must be applied to both sides to maintain equivalence. Inverse operations like addition and subtraction can isolate variables. Examples show how to isolate variables using addition or subtraction and solve equations. Students are then prompted to solve practice equations on their own. The document also discusses using equations to solve real-world problems, like finding a person's maximum heart rate based on their age.