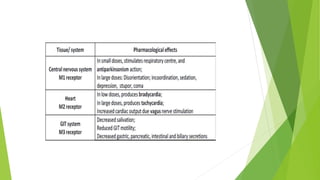
Parasympatholytics are drugs that block acetylcholine at postganglionic nerve endings and cholinergic receptors. They include natural alkaloids like atropine and hyoscine, as well as semisynthetic and synthetic compounds. Atropine is a prototypical parasympatholytic that acts as a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist. It has therapeutic uses as an antispasmodic, antisecretory agent, and in ophthalmology for mydriasis and cycloplegia. Adverse effects include dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, and hyperthermia. Overdose of atropine or related anticholinergic drugs can cause acute belladonna poisoning with