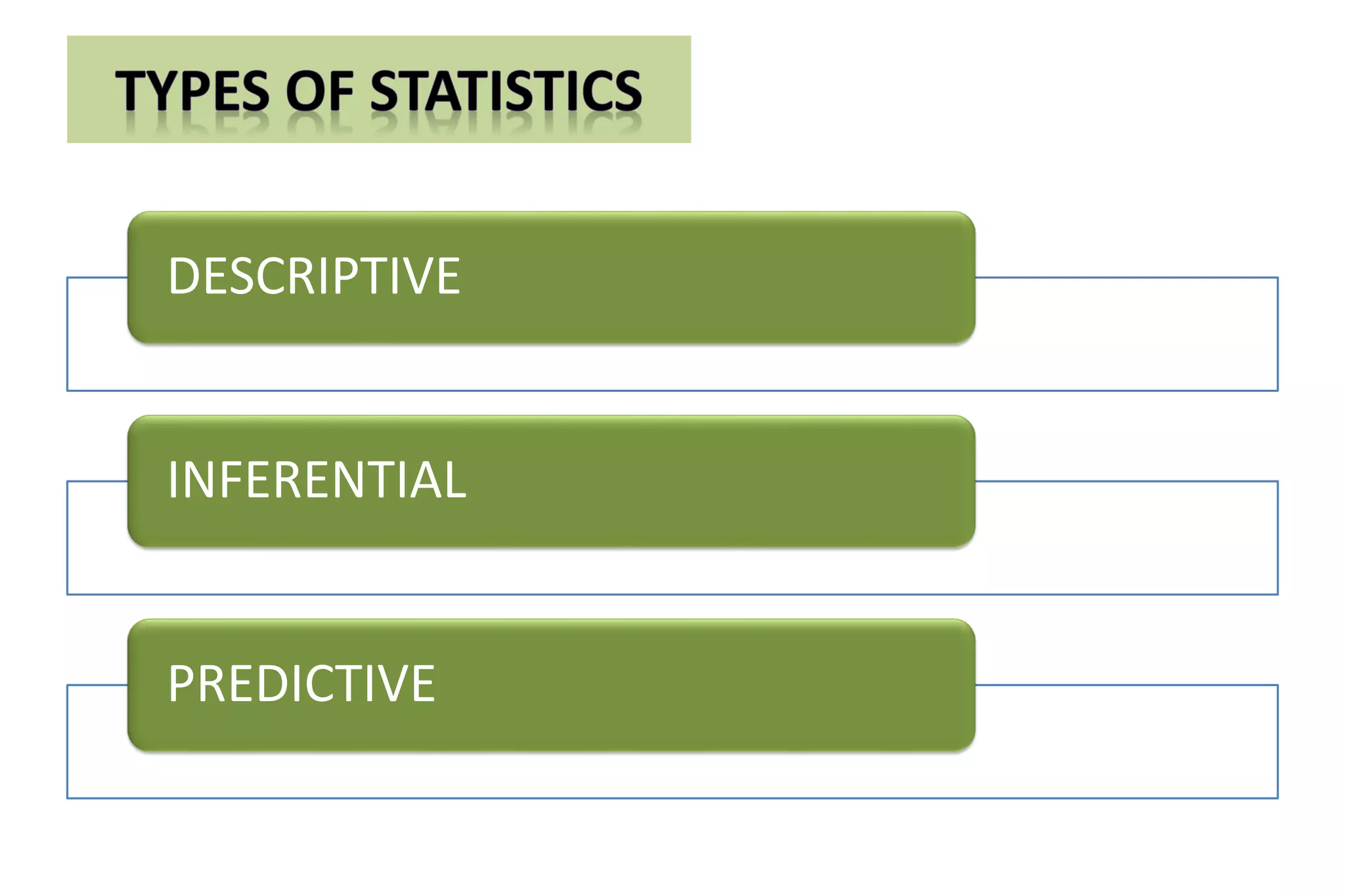
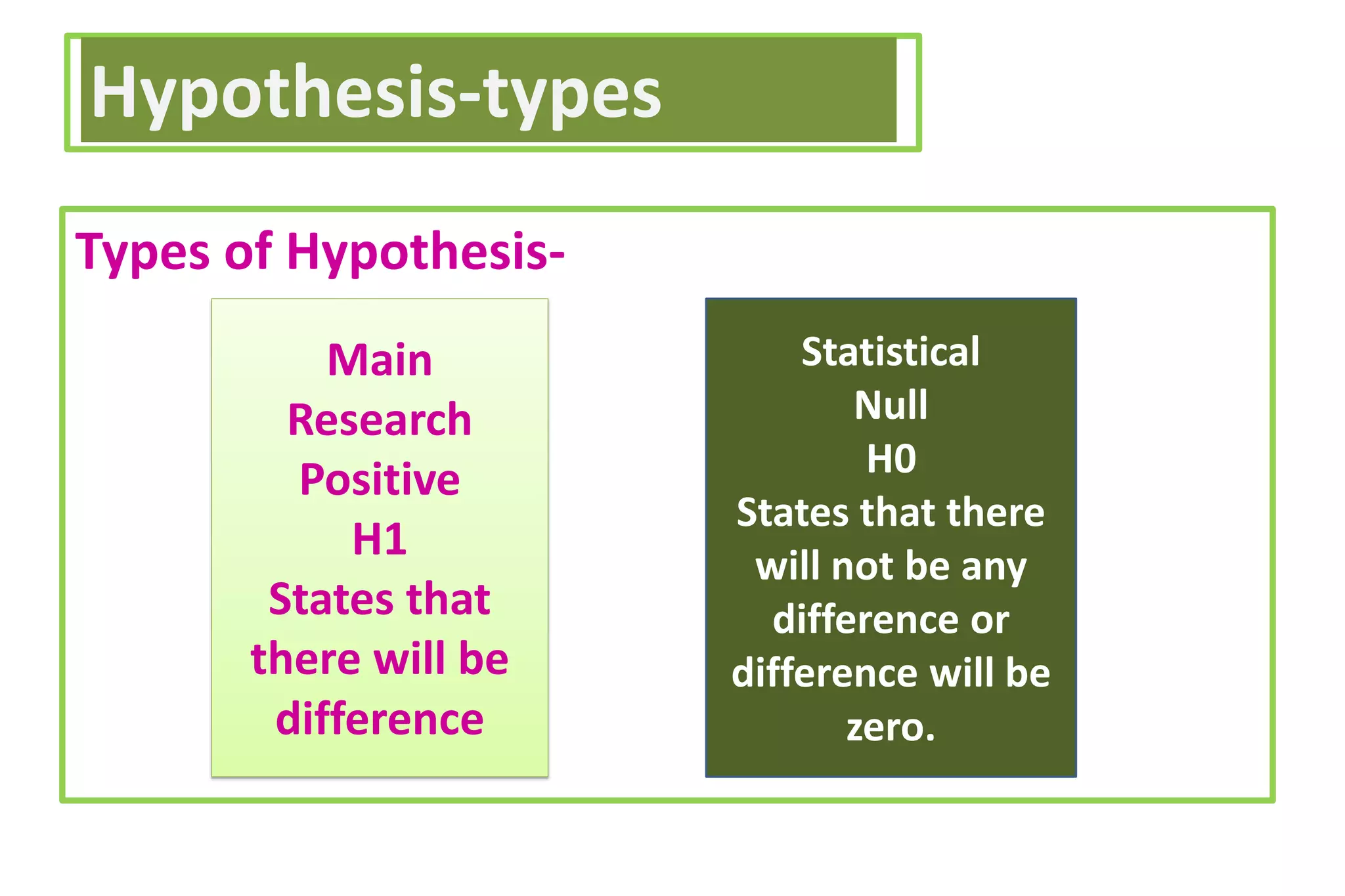
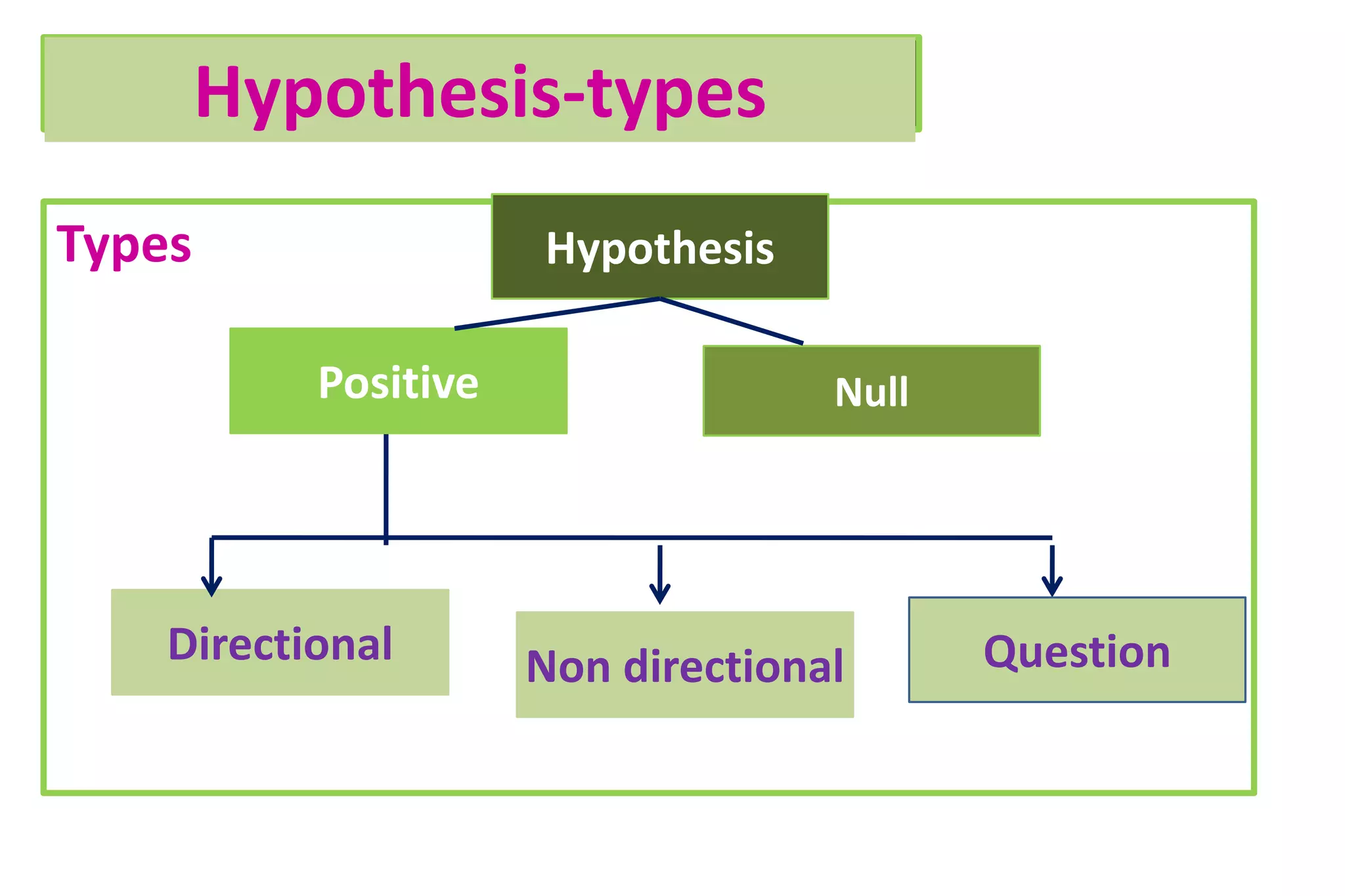
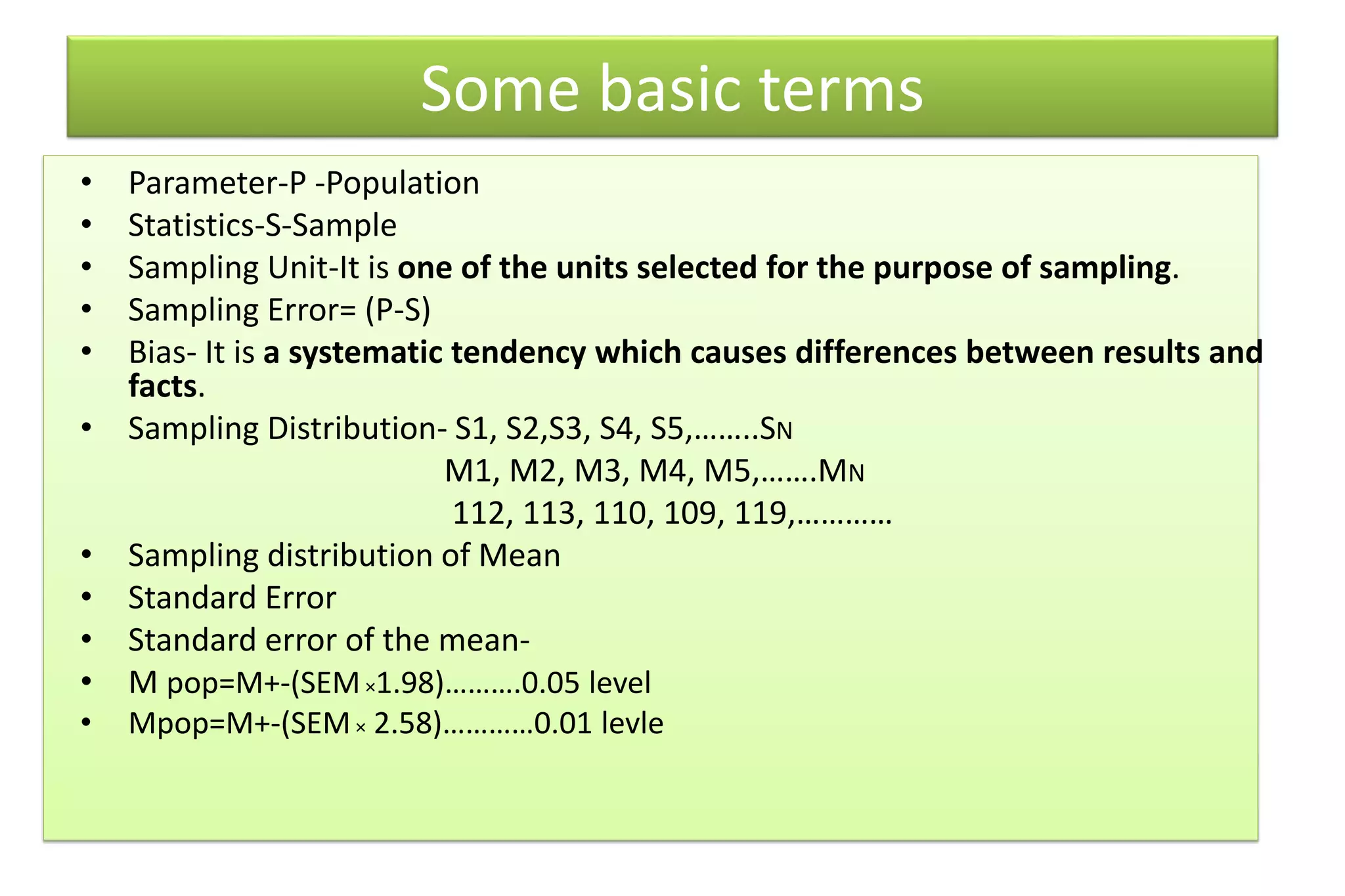
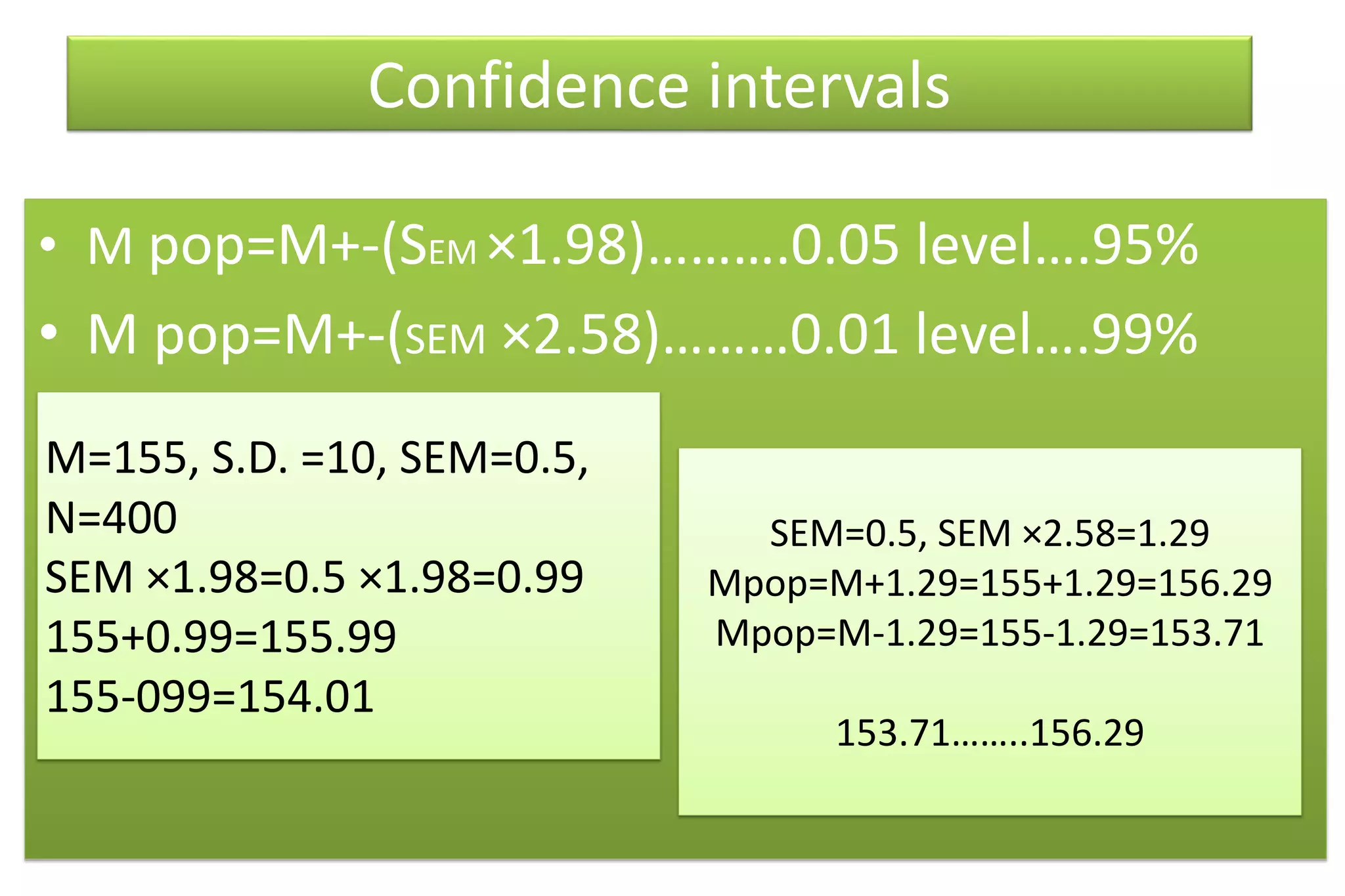
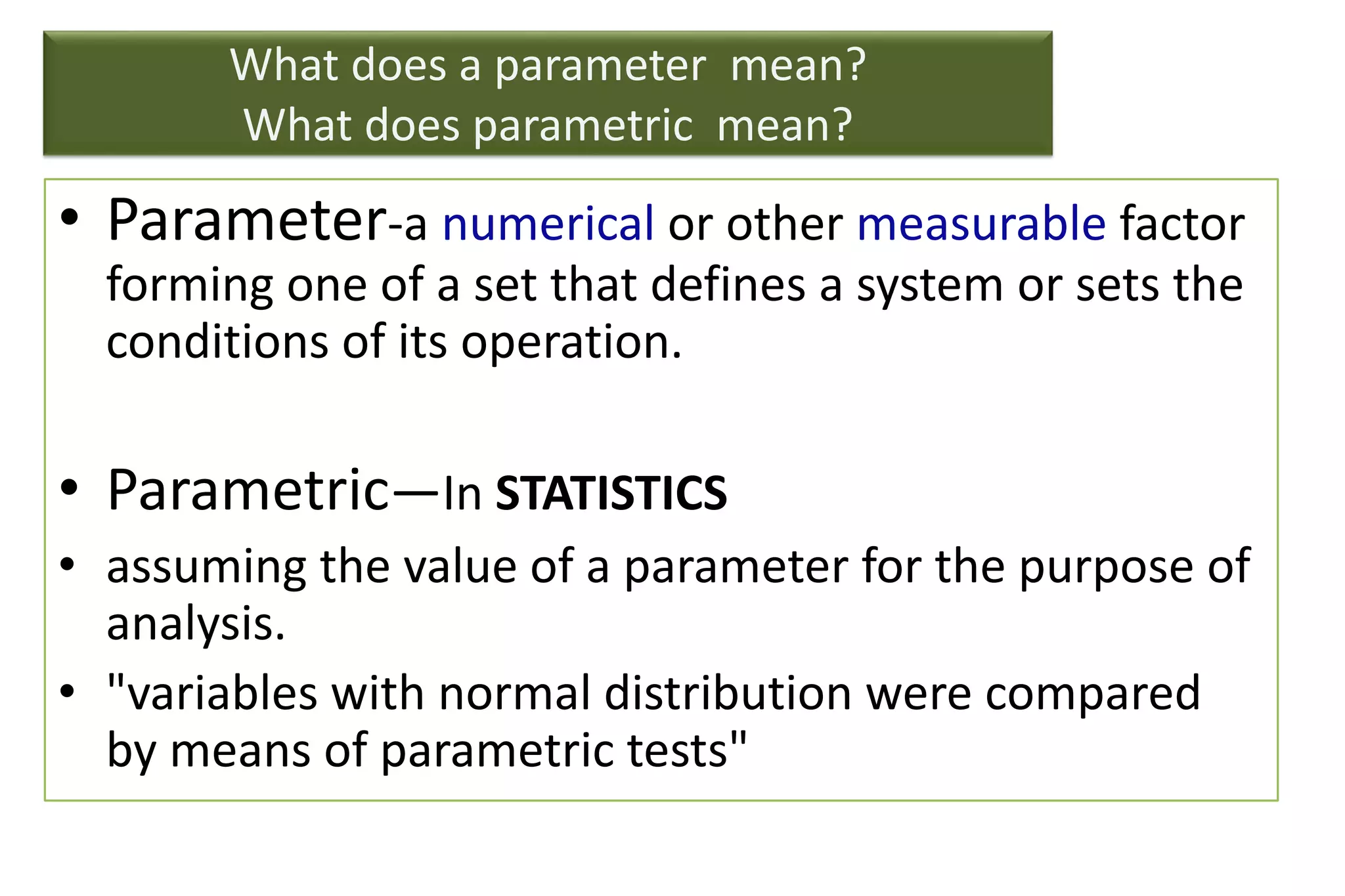
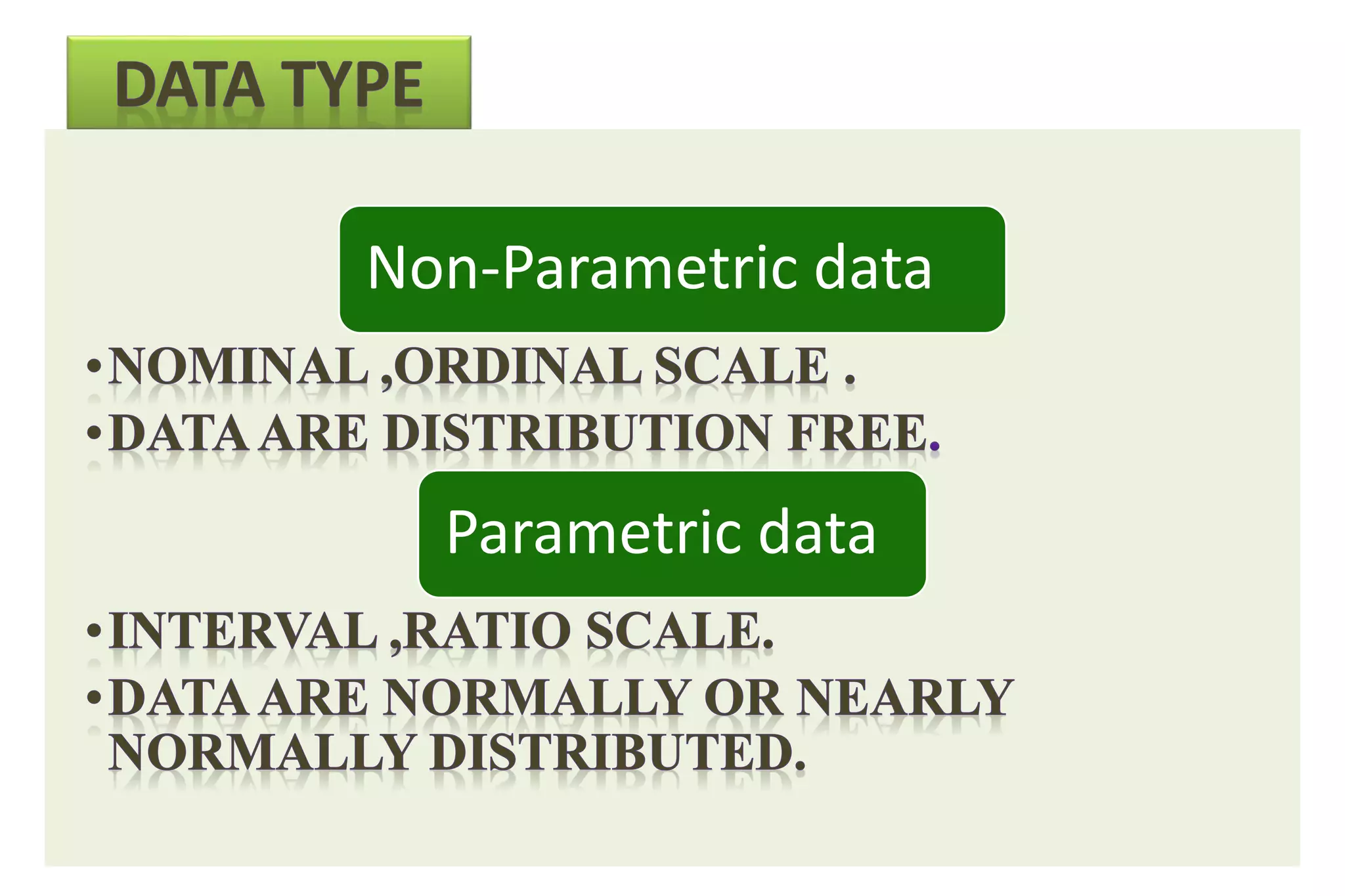
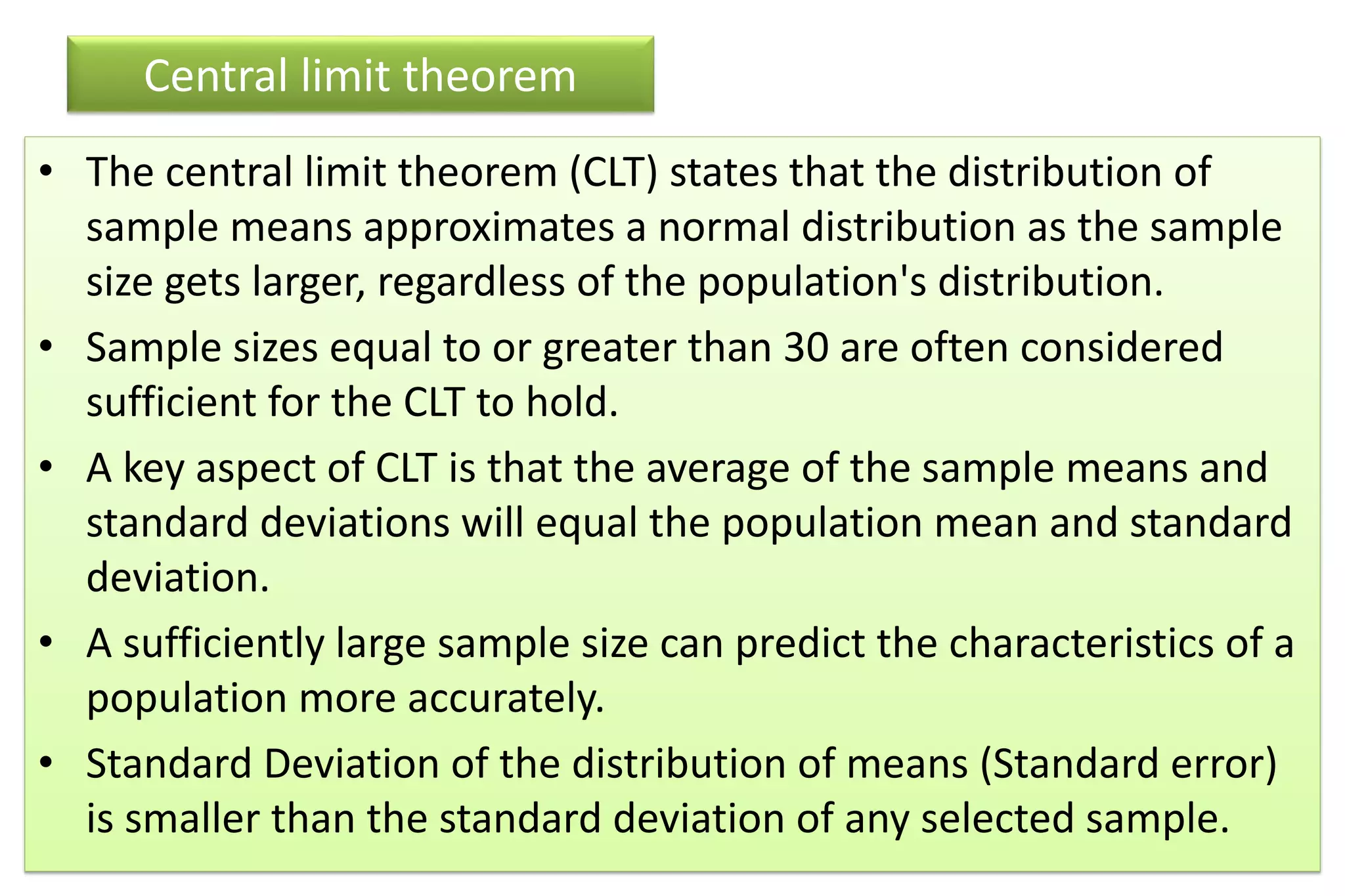
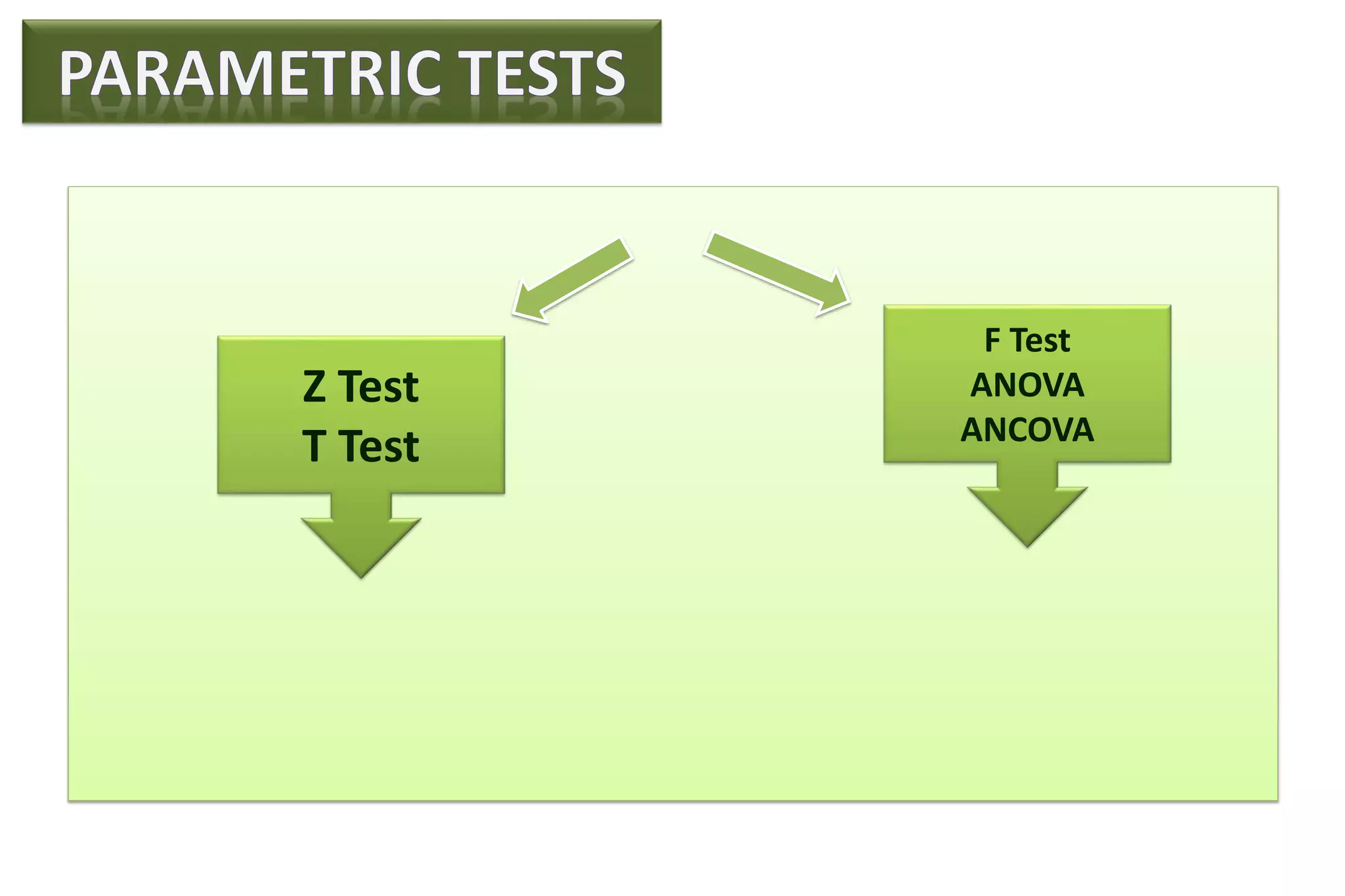
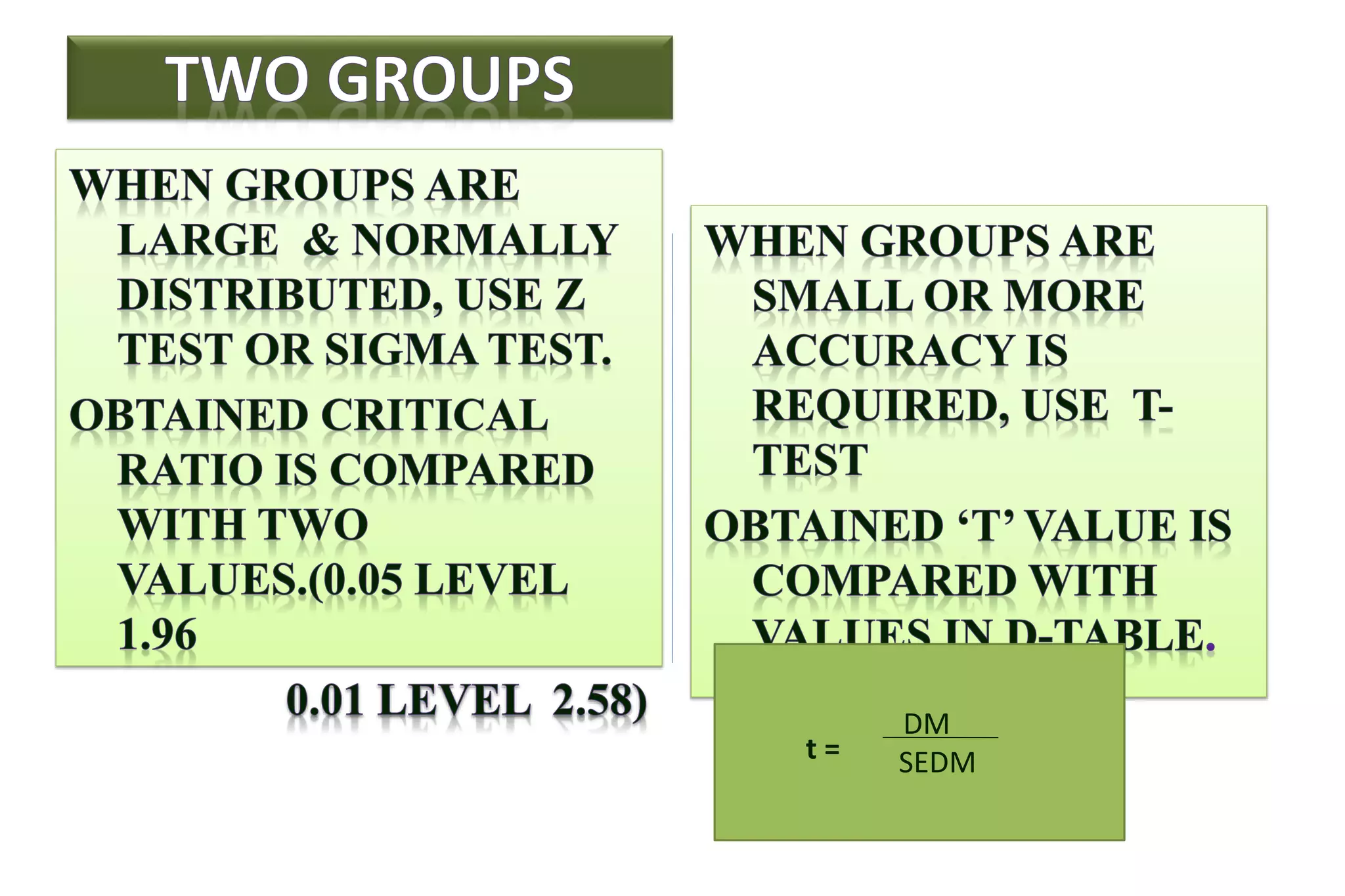
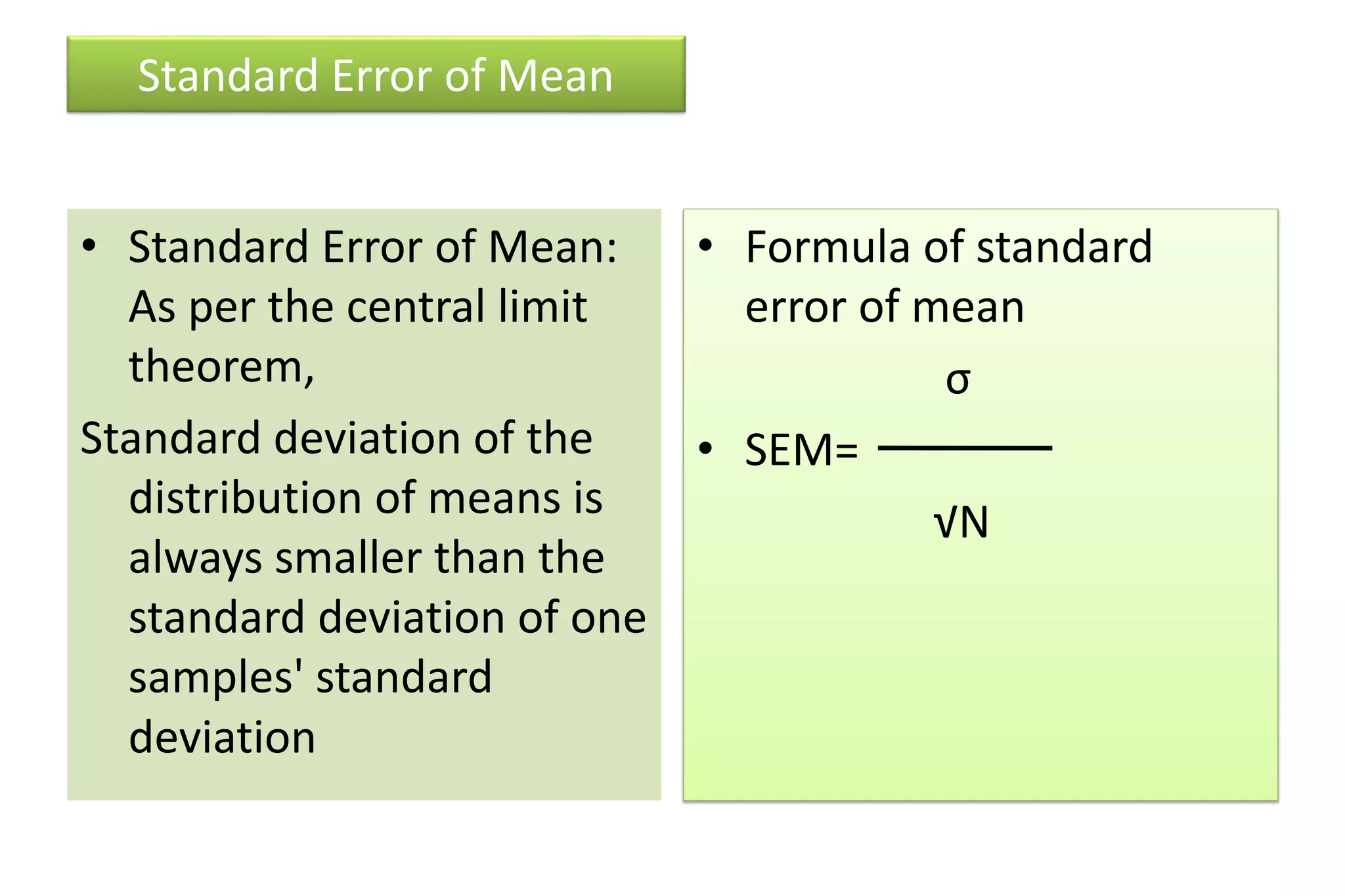
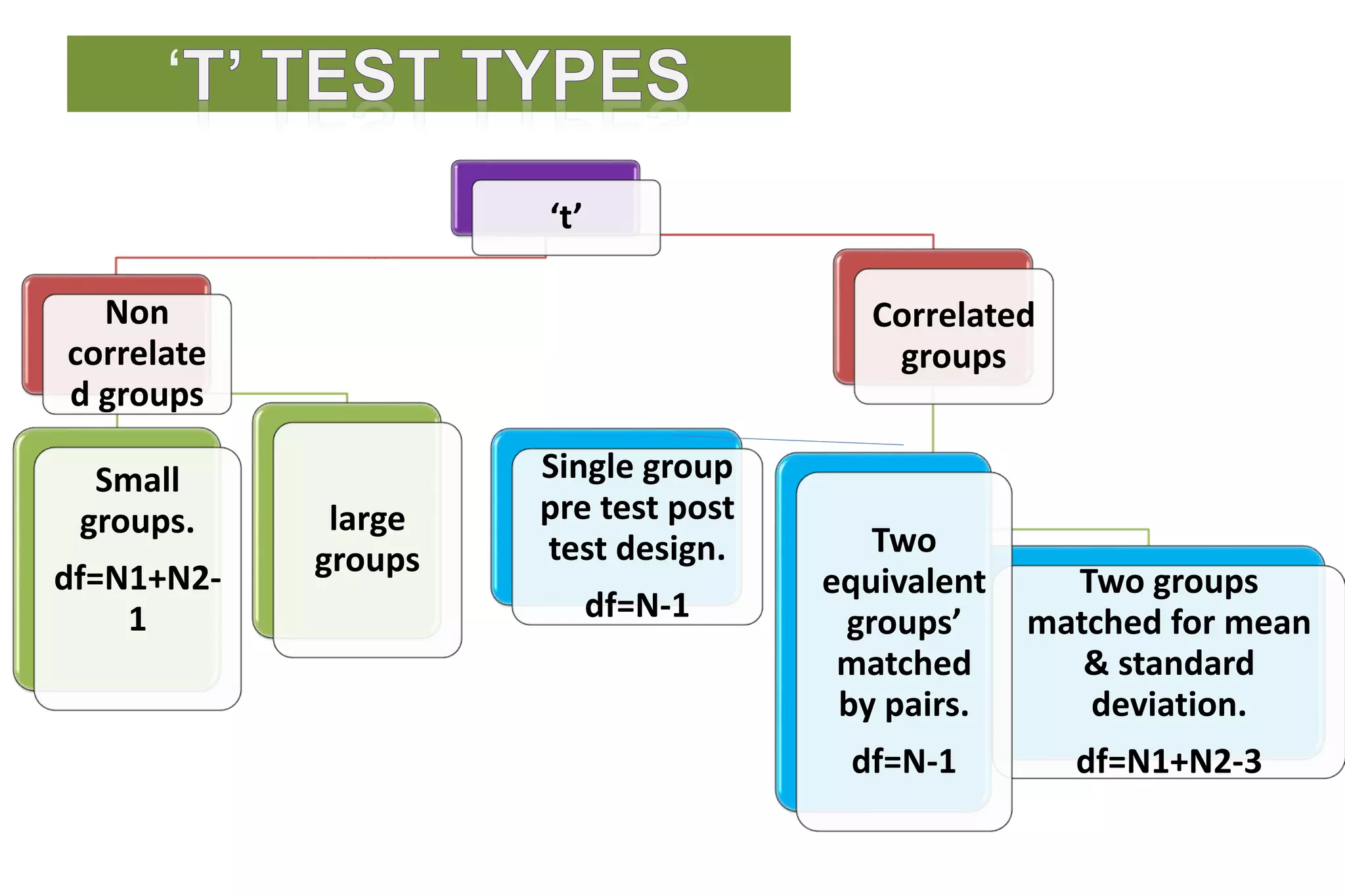
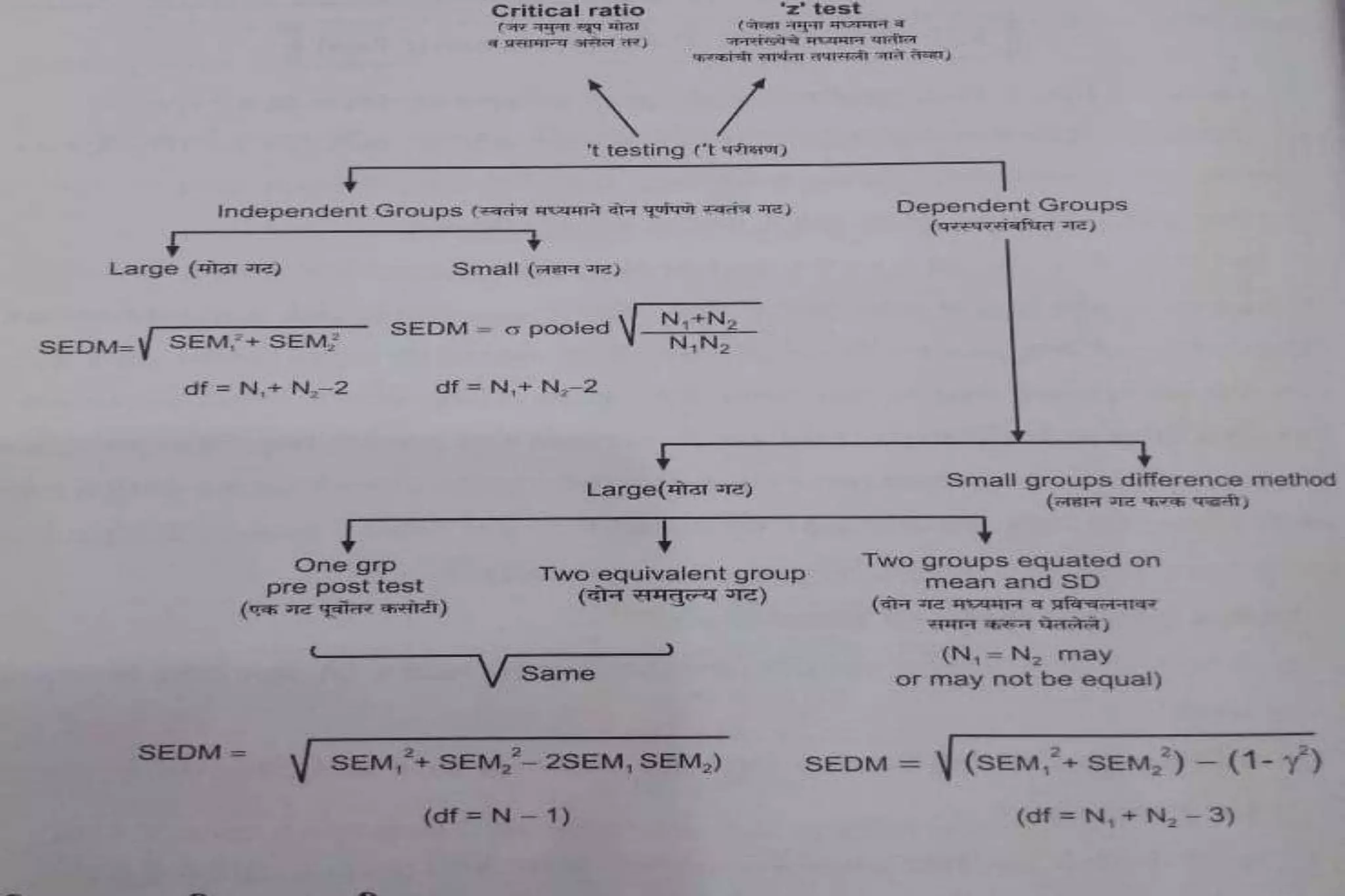
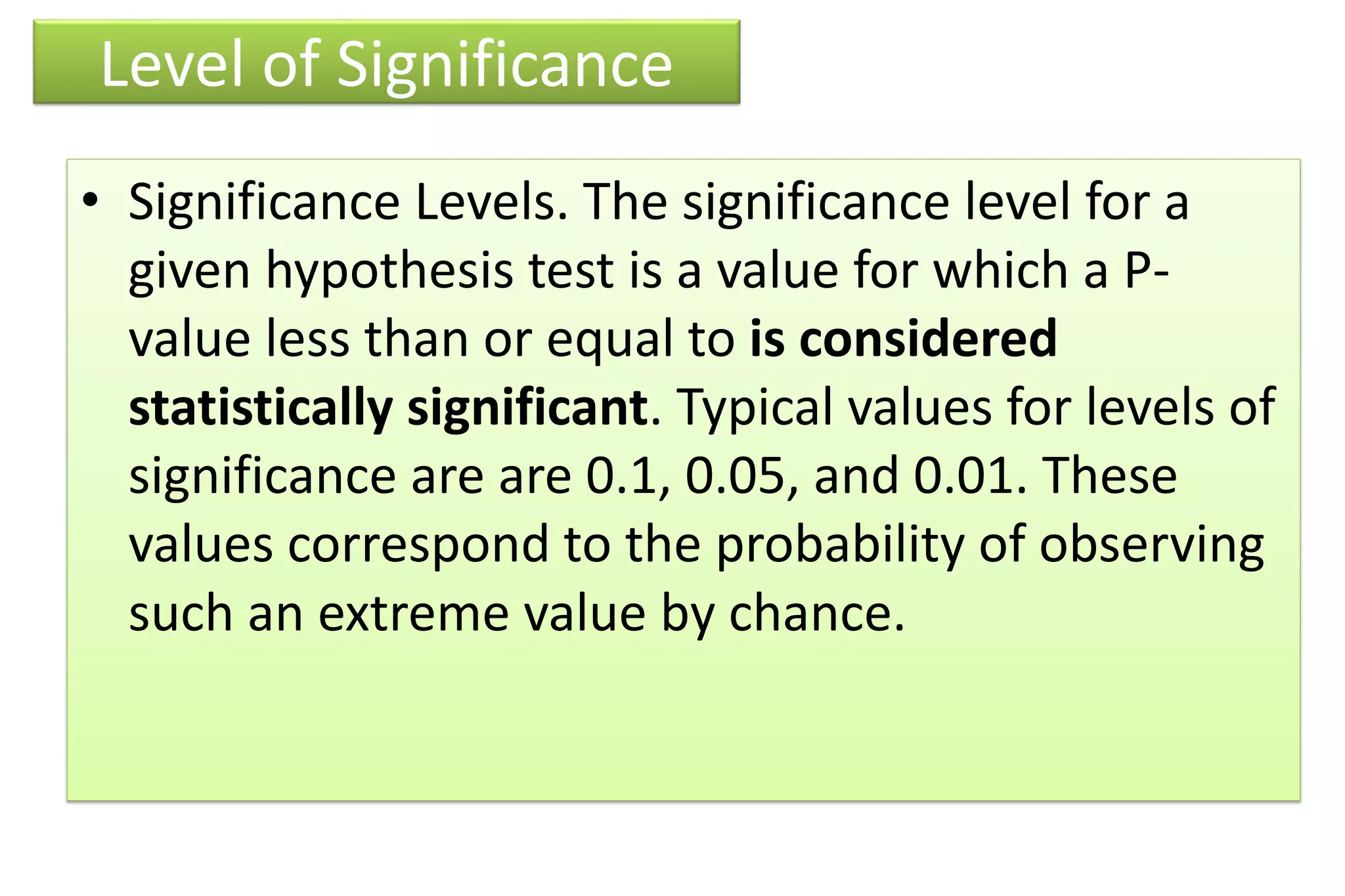
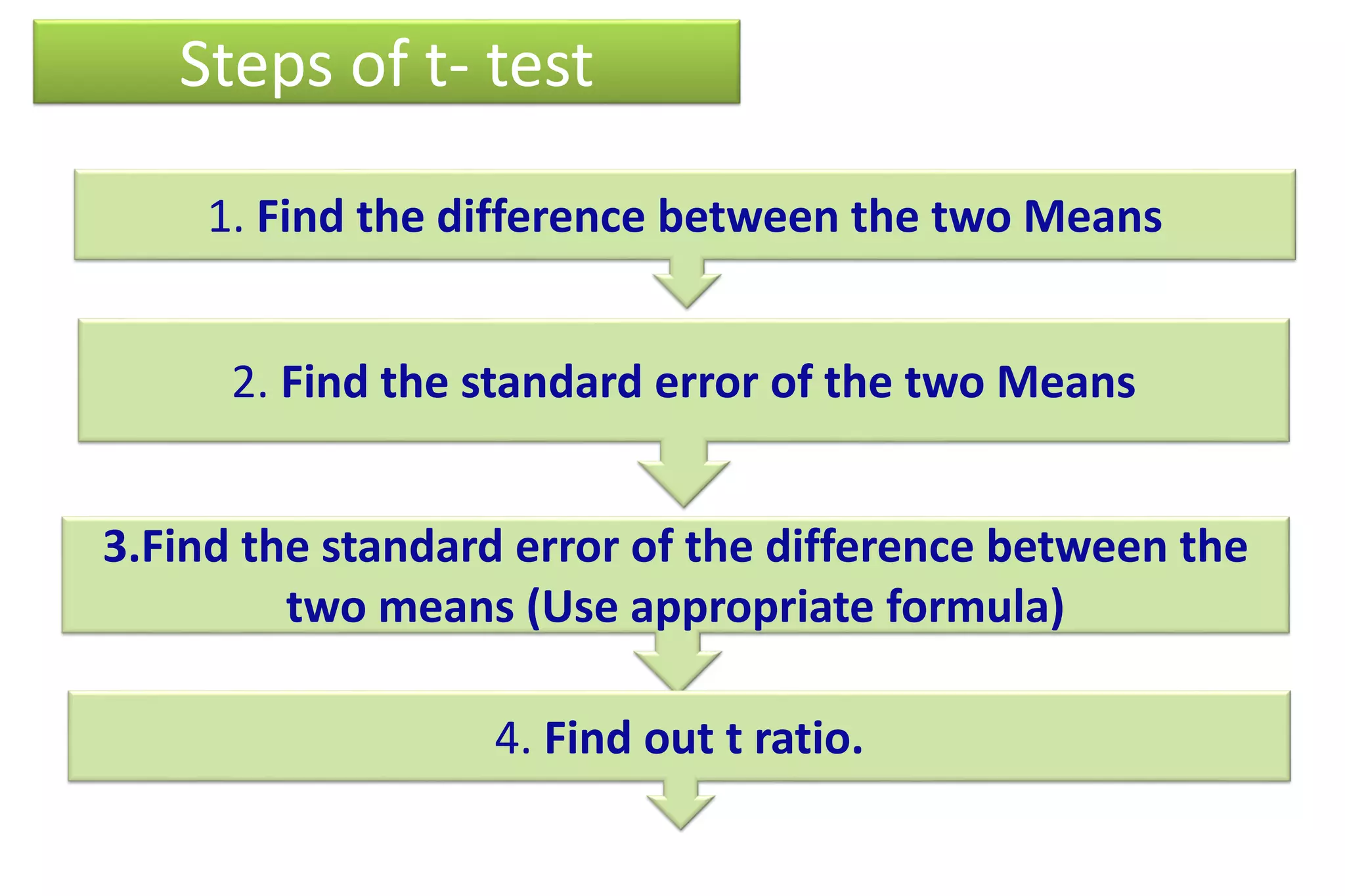
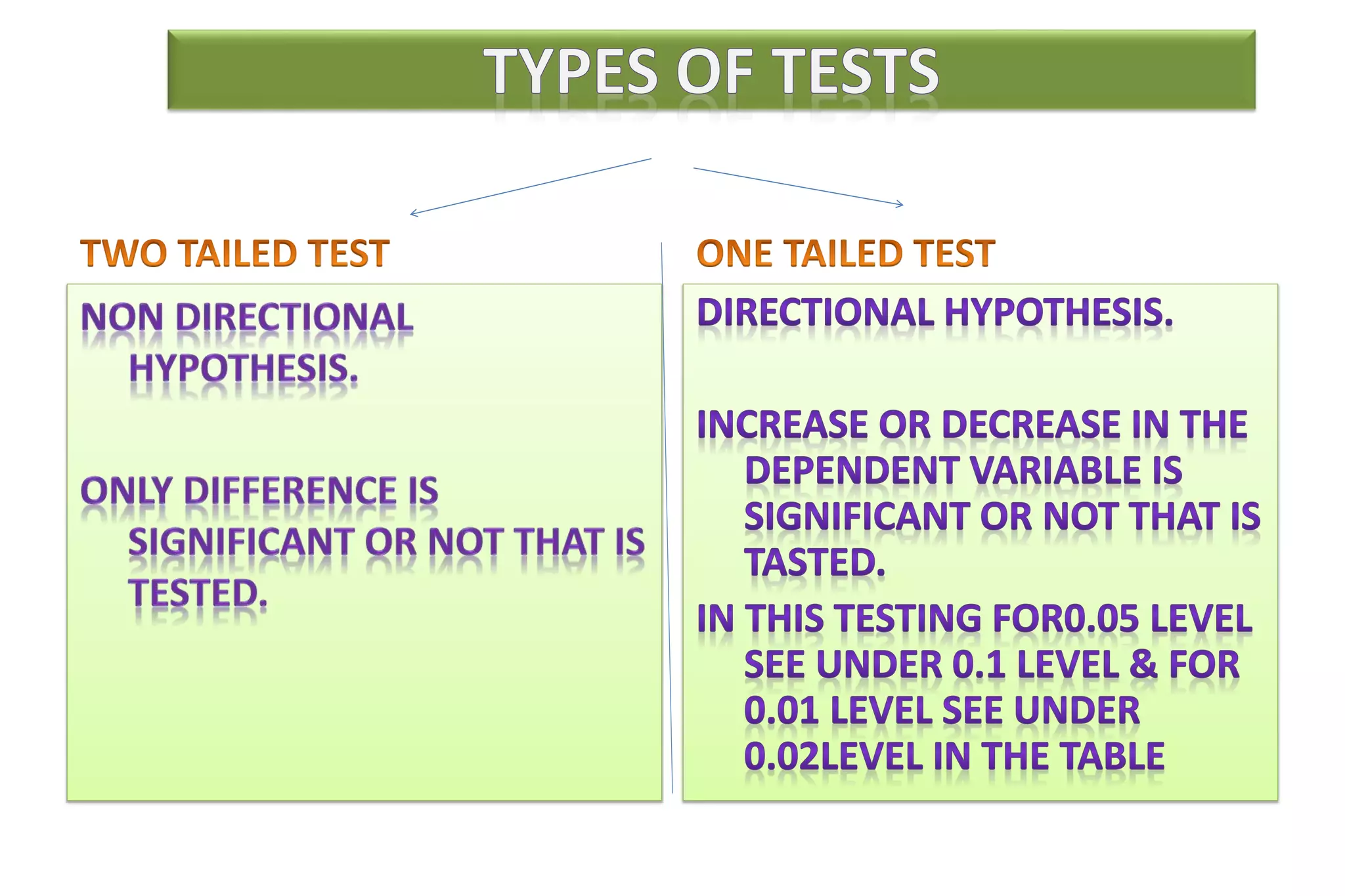
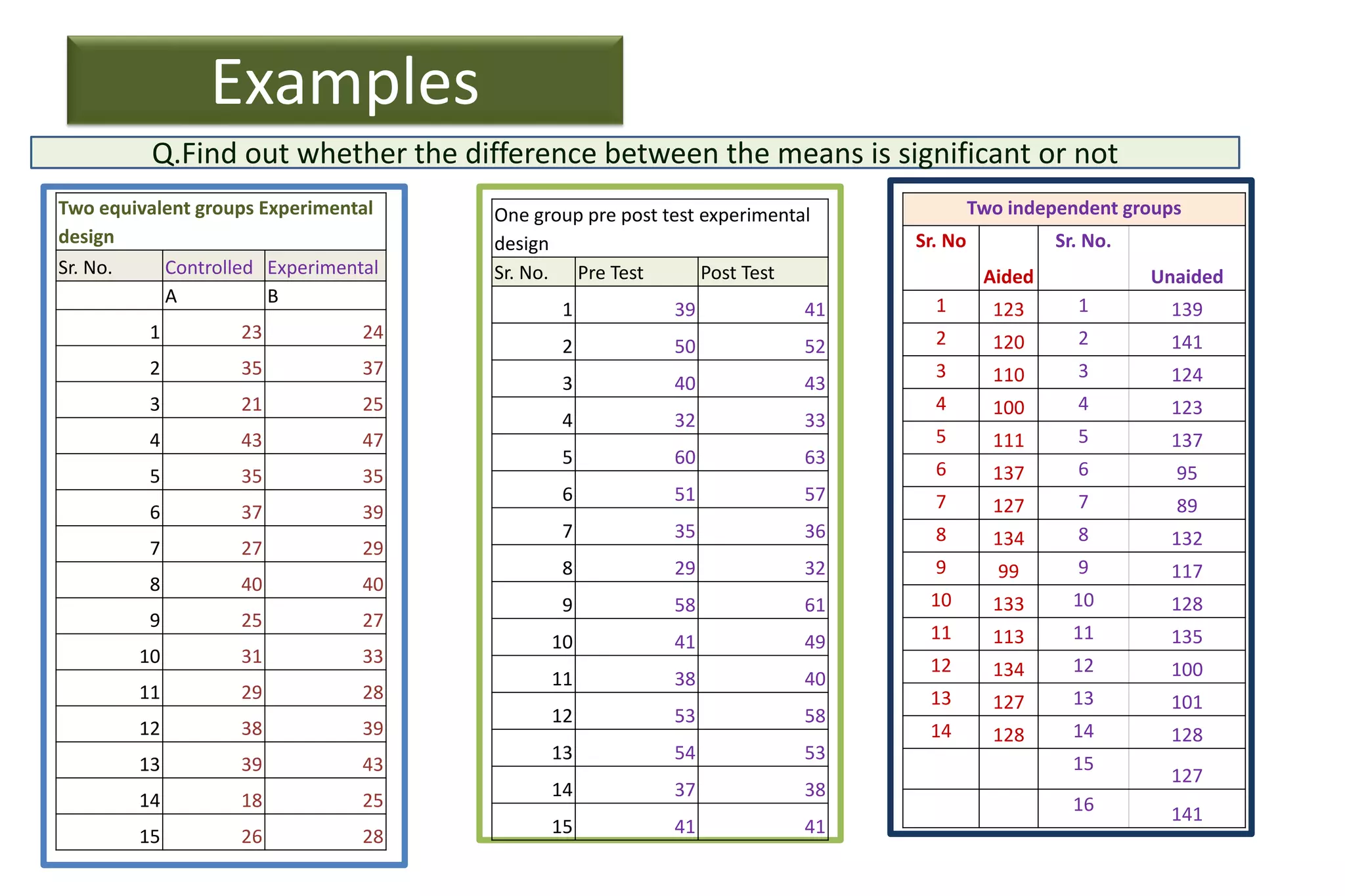
The document discusses hypothesis testing, particularly focusing on parametric tests like the t-test, explaining the role and types of hypotheses, including null and alternative hypotheses. It elaborates on concepts such as degrees of freedom, significance levels, and the steps involved in conducting t-tests for various experimental designs. Additionally, it covers statistical parameters and the Central Limit Theorem, providing formulas and examples to illustrate standard error and data distributions.