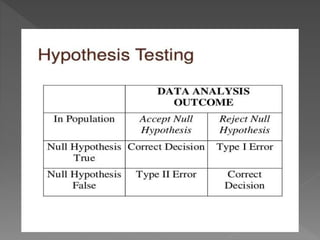
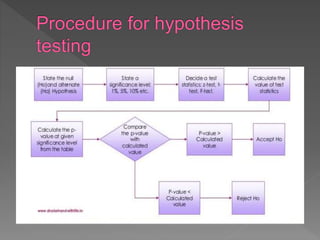
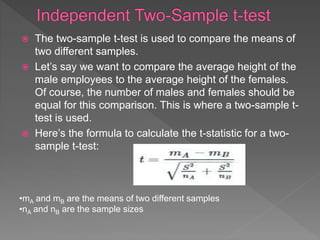
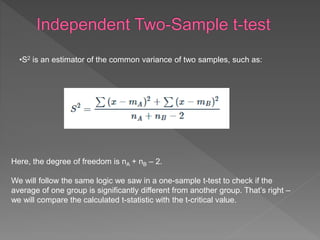
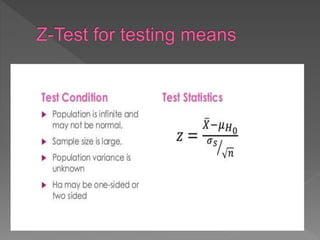
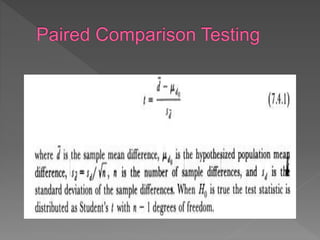
The document discusses hypotheses in research. A hypothesis is a testable statement about the relationship between two variables. Researchers propose a null hypothesis, which states there is no relationship between the variables, and an alternative or experimental hypothesis, which predicts a relationship. Statistical tests are used to analyze data and determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. The document provides examples of different types of hypotheses and statistical tests used, including t-tests and z-tests.