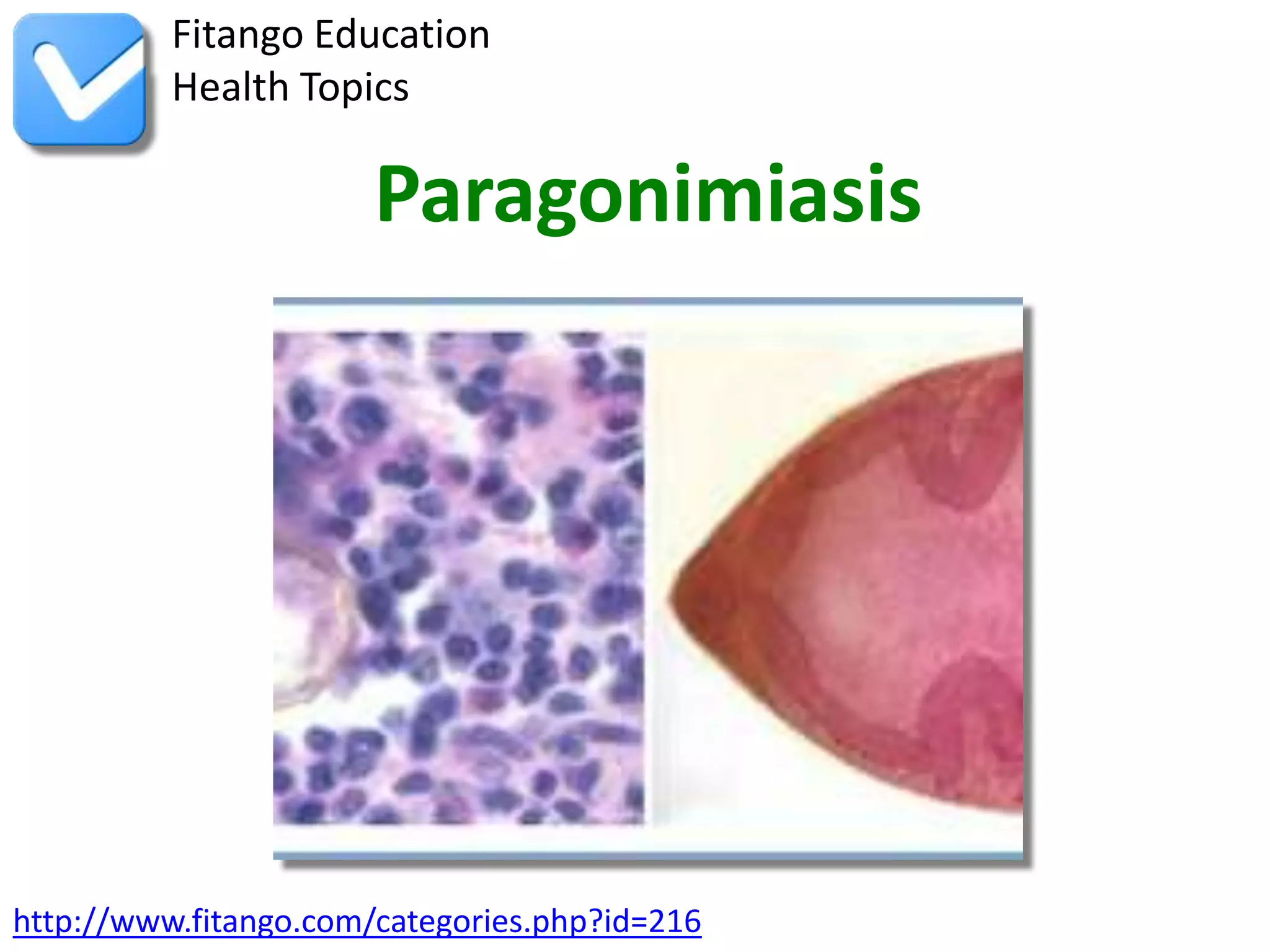
Paragonimiasis is caused by lung fluke infection from eating raw or undercooked crabs or crayfish. It typically causes lung symptoms but can spread to the brain. While rare, cases have occurred in the US Midwest from eating raw crayfish. Diagnosis involves identifying eggs in sputum or biopsy samples. Infection is treatable with prescription medication. Risk of infection comes from dishes with undercooked freshwater shellfish in Asia and Central/South America. Prevention involves thoroughly cooking crabs and crayfish before eating.