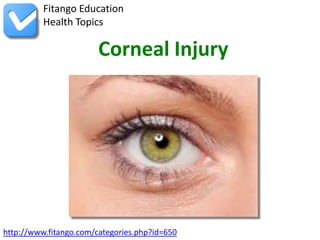
Corneal injury refers to damage to the cornea, resulting in symptoms such as pain, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light. Diagnosis involves a thorough eye exam, potentially using fluorescein staining, while treatment may include eye patches, prescribed drops, and avoiding contact lenses until healed. Prevention measures include wearing protective eyewear in hazardous situations and utilizing sunglasses against UV exposure.