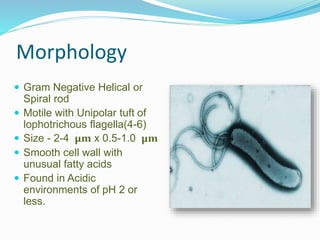
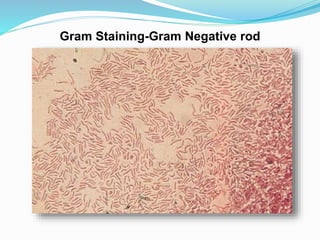
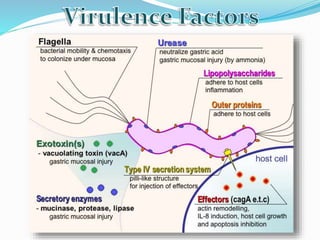
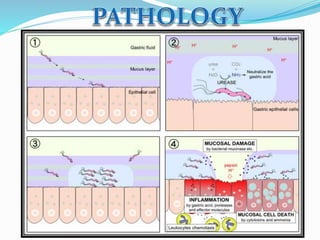
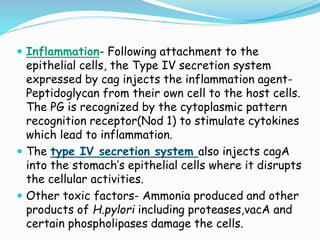
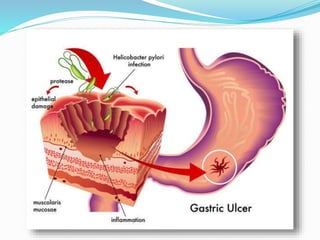
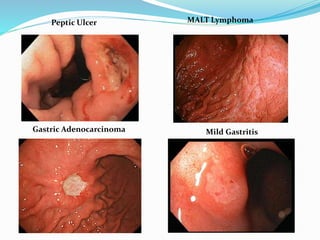
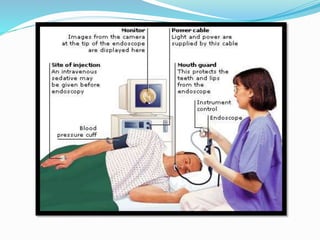
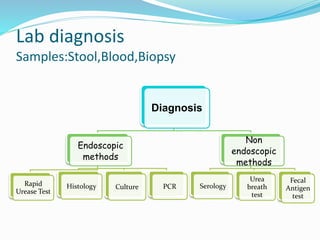
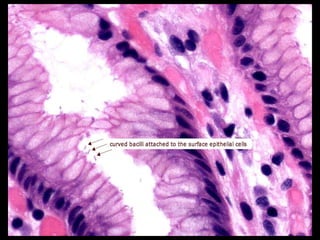
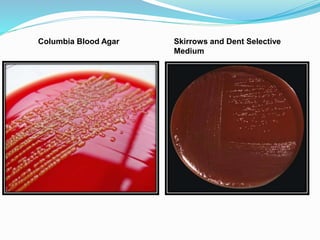
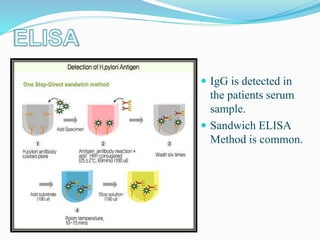
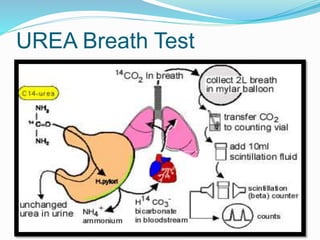
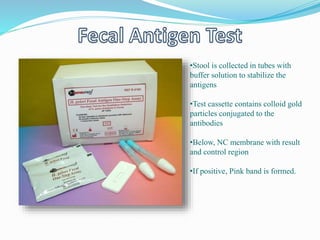
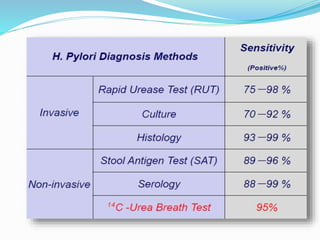
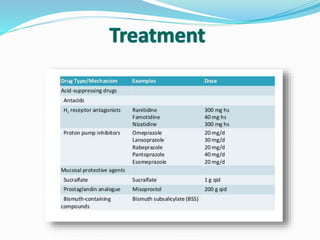
This document provides information on Helicobacter pylori, including its scientific classification, history of discovery, morphology, culture characteristics, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and methods of laboratory diagnosis. Key points include that H. pylori was identified in 1982 as the cause of chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, it is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral bacterium that colonizes the stomach, and diagnostic tests include rapid urease test, histology, culture, PCR, serology, and urea breath test.