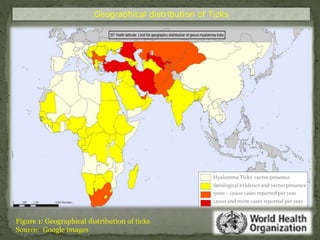
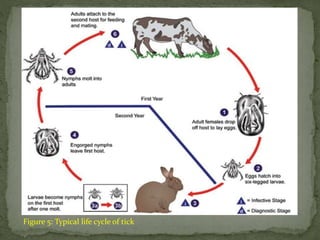
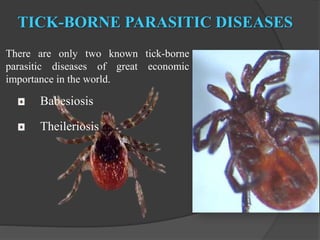
Tick-borne parasitic infections are caused by protozoan parasites transmitted through tick bites. The most common infections are babesiosis caused by Babesia parasites and theileriosis caused by Theileria species. These infections affect both animals and humans, causing symptoms ranging from fever and fatigue to enlarged lymph nodes. Diagnosis involves identifying the parasites in blood smears or tissue samples. Treatment consists of anti-parasitic drugs. Prevention strategies focus on controlling tick populations and avoiding tick bites through environmental and personal protective measures.