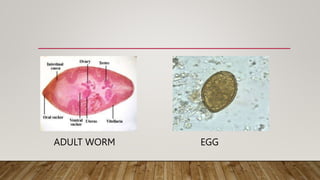
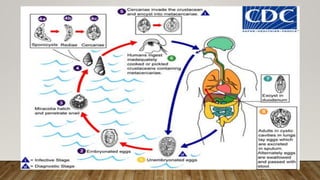
This document provides an overview of paragonimiasis, a parasitic infection of the respiratory tract caused by the trematode Paragonimus westermani. It is endemic in northeast India, especially Manipur. The life cycle involves 3 hosts - humans, snails, and crabs or crayfish. Clinical manifestations include cough with rusty sputum due to lung cysts and inflammation. Diagnosis is made by detecting eggs in sputum or antibodies/antigens in serum or stool. Prevention focuses on sanitation and health education. Treatment uses praziquantel.