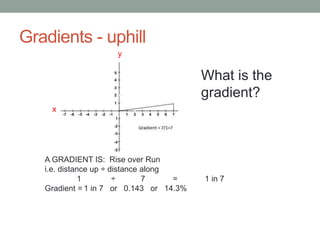
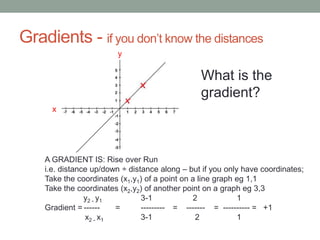
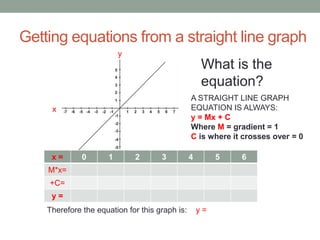
This document discusses functions and linear graphs. It defines functions as relations or expressions involving variables and explains that they are useful in computing for representing problems when all values are unknown. It also covers identifying the gradient and y-intercept of a linear graph from its equation in the form y=mx+c. Key steps shown include calculating the gradient as rise over run and using coordinates to find the equation from a graph.