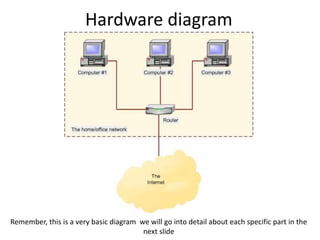
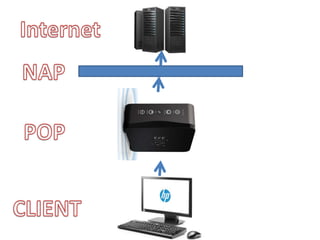
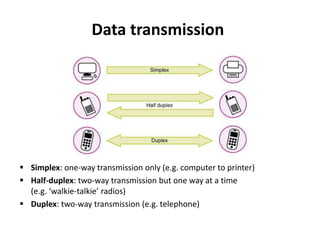
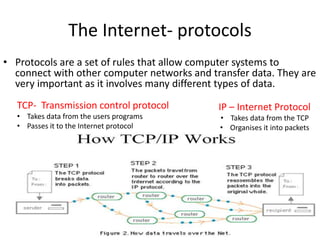
The document discusses components of the internet and how digital devices exchange and store information. It will cover understanding what the internet is and how it works, the concepts and impact of the World Wide Web, email, and different methods of data exchange and storage. Specific topics covered include internet hardware like servers, clients, routers, and ISPs; connection methods like wireless, broadband, and dial-up; transmission protocols; and concepts of the World Wide Web. Tasks are provided to define internet terms and compare connection methods.