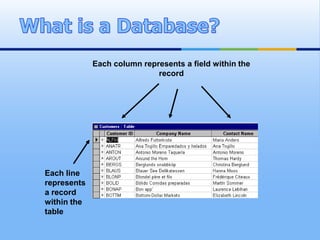
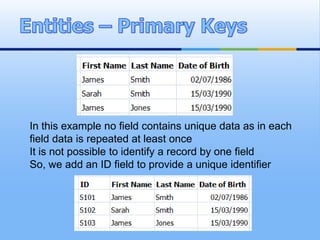
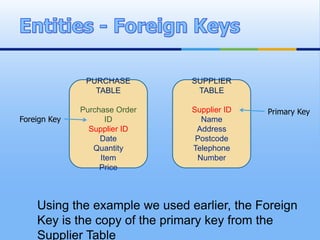
A relational database organizes data into tables with rows and columns. Each table contains records about a type of entity, with columns representing attributes. Unique identifiers called primary keys are used to link tables together through foreign keys, allowing efficient storage and retrieval of related data. Validation rules can be set on fields to ensure accurate data entry. Relational databases provide benefits like reduced data redundancy, improved data integrity, and easier querying of information.



















![ Microsoft Access gives you lots of flexibility when it
comes to naming your fields.
A field can be 64 characters long
A field can include any combination of letters,
numbers, spaces and special characters.
There are exceptions – a period (.), an exclamation
point (!), an accent grave (`) and brackets ([ ]). You
cannot begin with a space.
Ensure you give fields meaningful names – not
names internal to Access or VB as this may cause
conflicts
Create table and field names without embedded
spaces – most SQL databases to which Access can](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18databasefeatures-130324132437-phpapp01/85/18-database-features-23-320.jpg)





![Source: Microsoft
http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/create-a-validation-rule-to-validate-data-in-a-field-
HA010096312.aspx [Accessed 28/04/11]
A validation rule limits or controls what users
can enter in a table field or a control (such as
a text box) on a form.
Microsoft Office Access 2007 provides a
number of ways to validate data, and you
often use several of those techniques to
define a validation rule. You can think of
validation rules as a set of layers — you can
use some or all of the layers when you need
to ensure that your users enter data properly.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18databasefeatures-130324132437-phpapp01/85/18-database-features-29-320.jpg)


![Input masks
You can use an input mask to validate
data by forcing users to enter values in a
specific way. For example, an input mask
can force users to enter dates in a
European format, such as 2007.04.14.
Source: Microsoft
http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/create-a-validation-rule-to-validate-
data-in-a-field-HA010096312.aspx [Accessed 28/04/11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18databasefeatures-130324132437-phpapp01/85/18-database-features-32-320.jpg)





