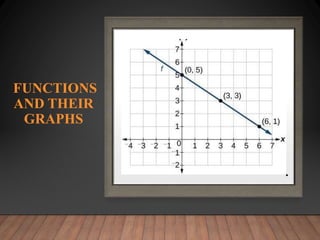
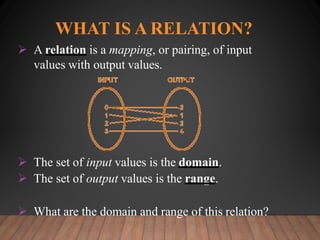
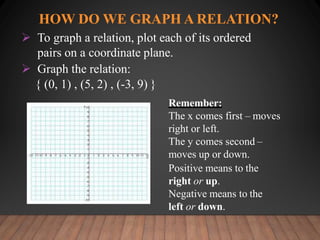
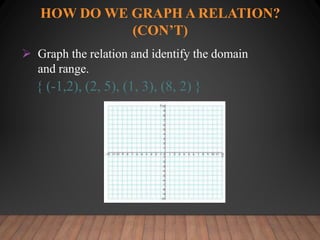
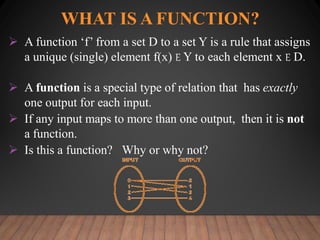
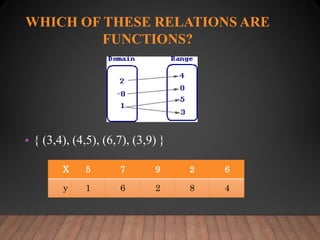
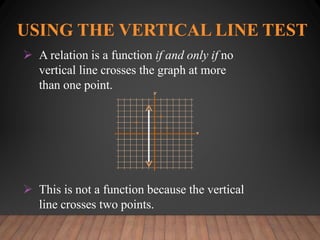
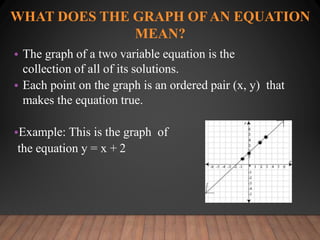
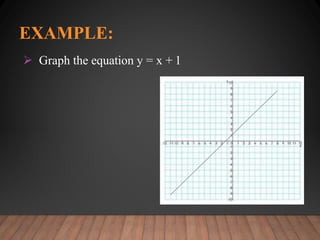
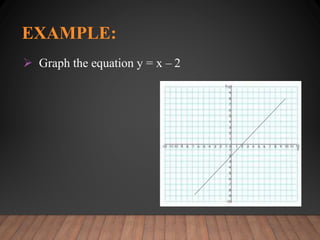
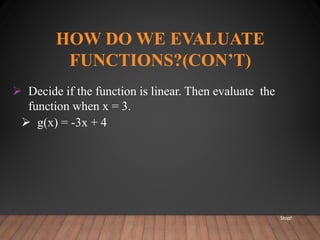
This document discusses functions and their graphs. It defines relations, functions, and how to write and graph relations and functions. It discusses domain and range, and how to identify whether a relation is a function using the vertical line test. It provides examples of how to graph linear and non-linear equations, evaluate functions, and find the domain and range of functions.