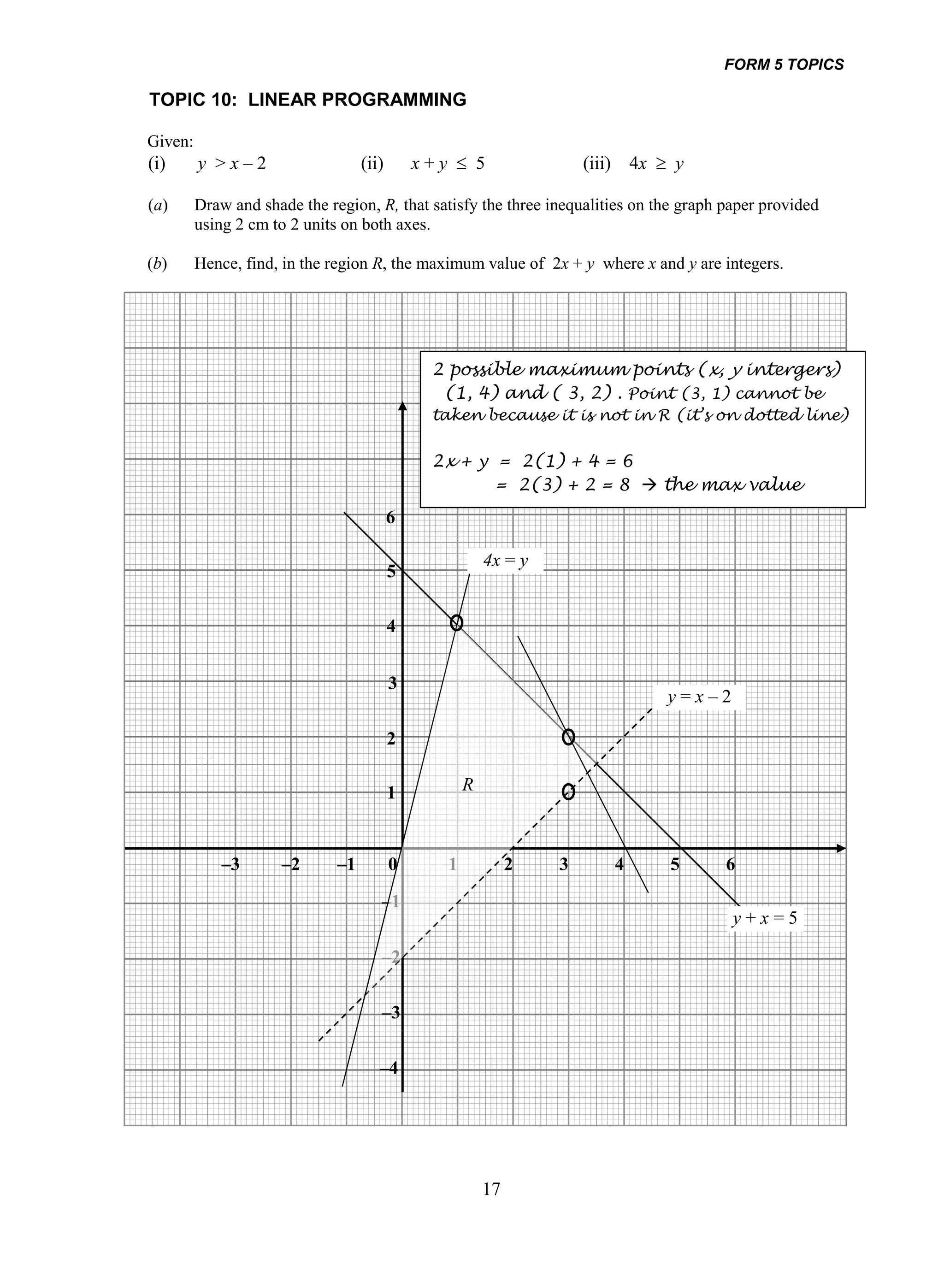
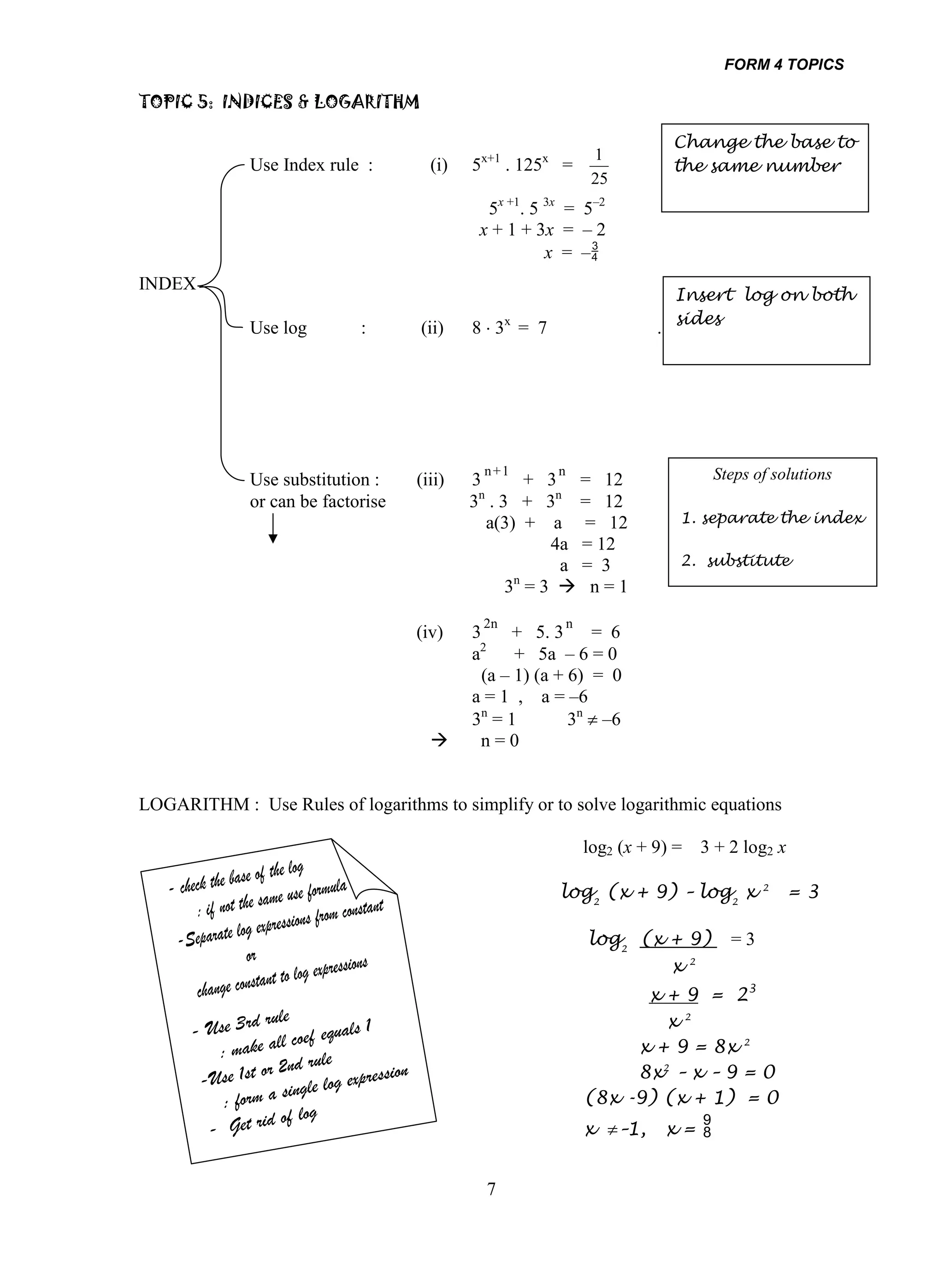
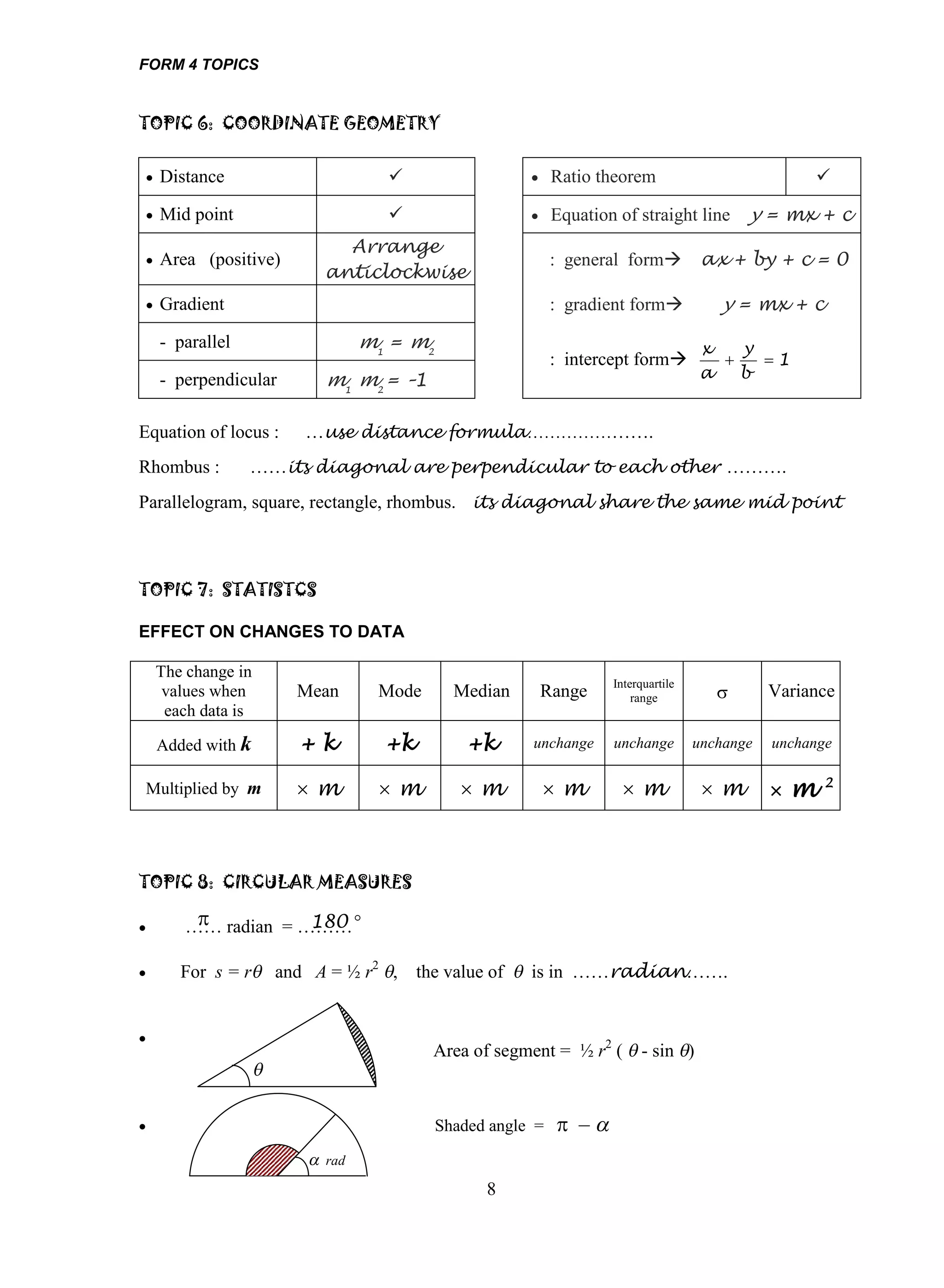
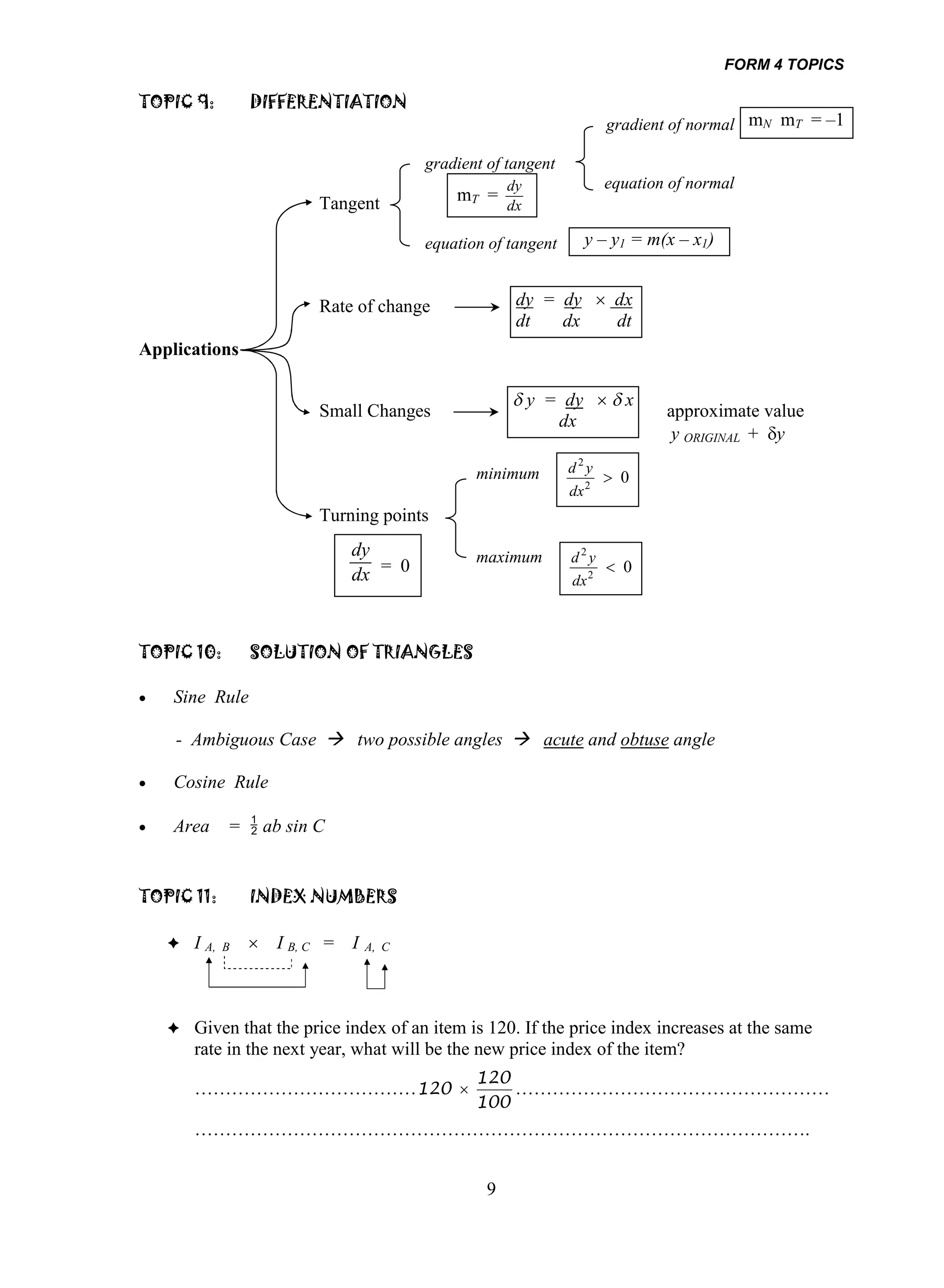
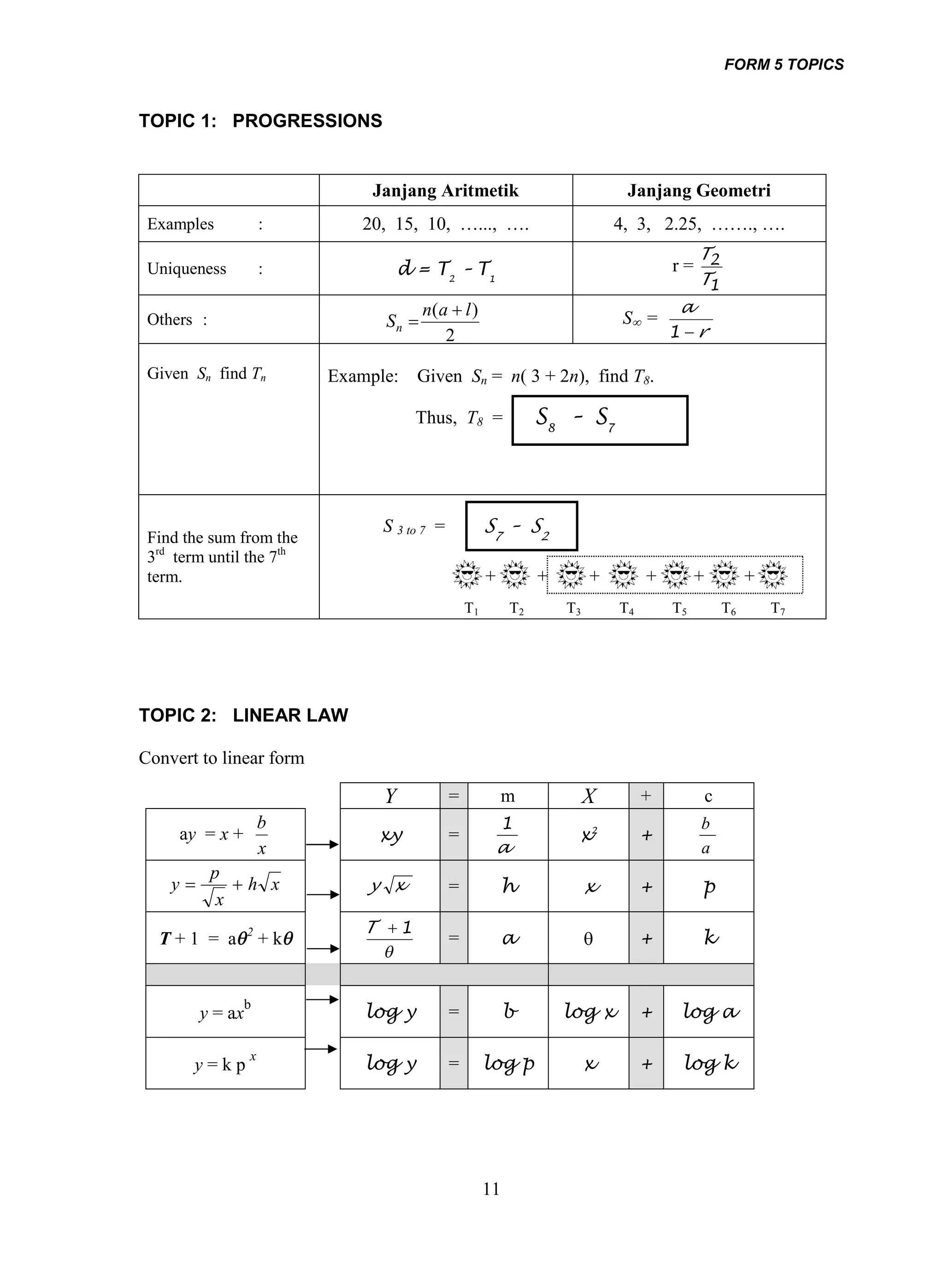
1. The document provides an overview of important topics covered in Form 4 and Form 5 mathematics. These include functions, quadratic equations, trigonometry, statistics, calculus, and coordinate geometry.
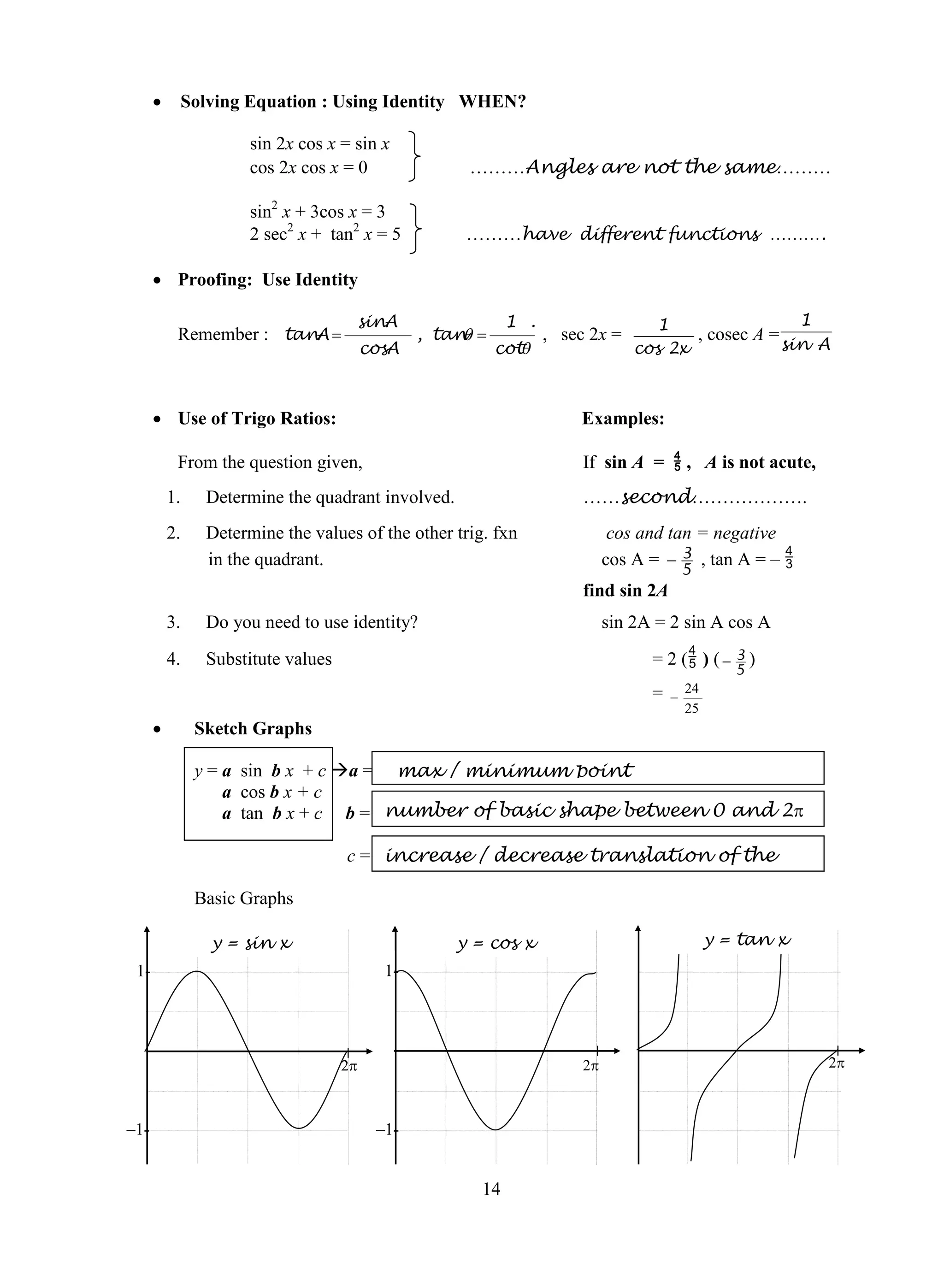
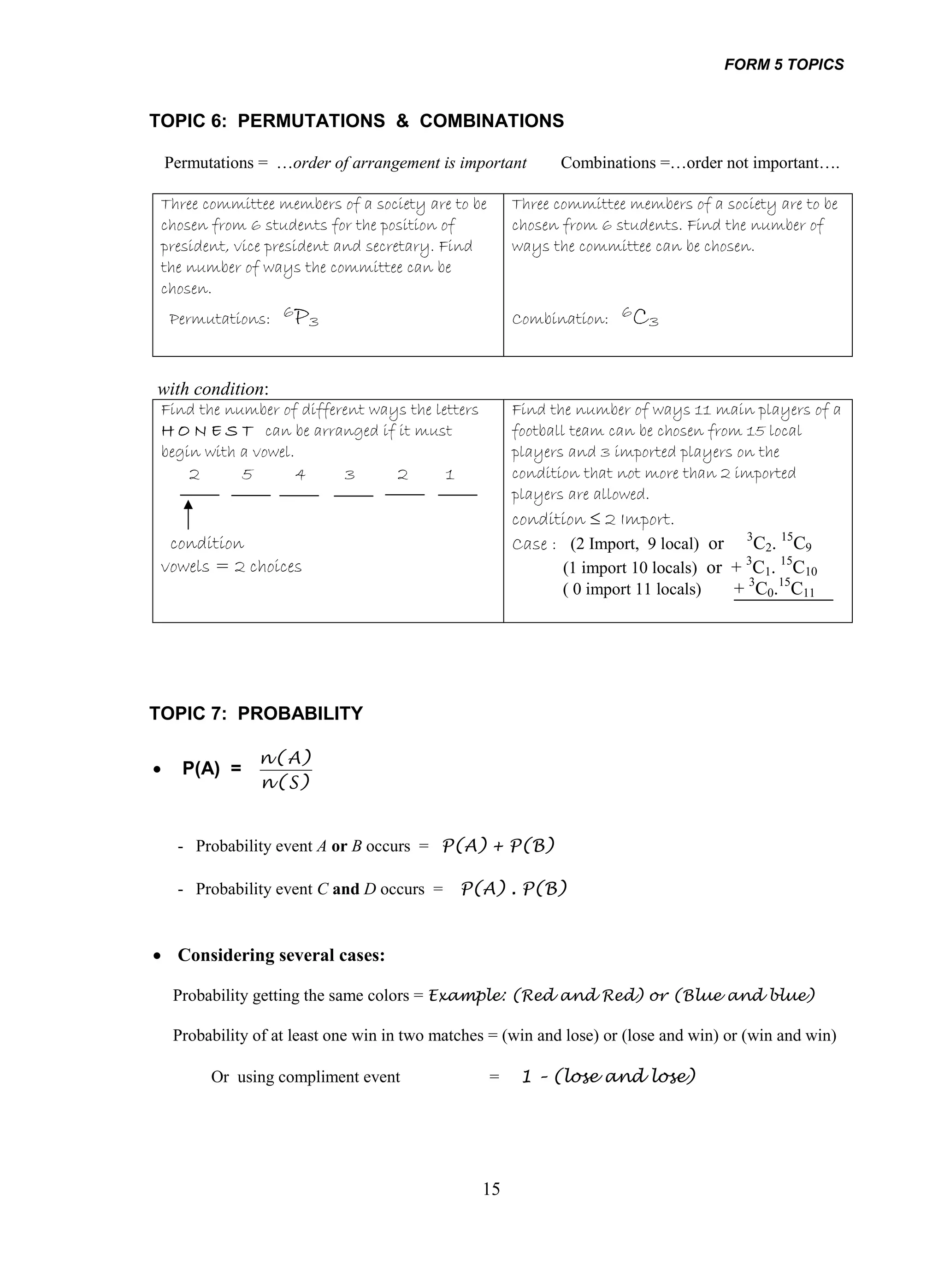
2. Examples of how to solve different types of problems are given for each topic, such as finding the sum and product of roots for quadratic equations or using rules of logarithms to simplify logarithmic expressions.
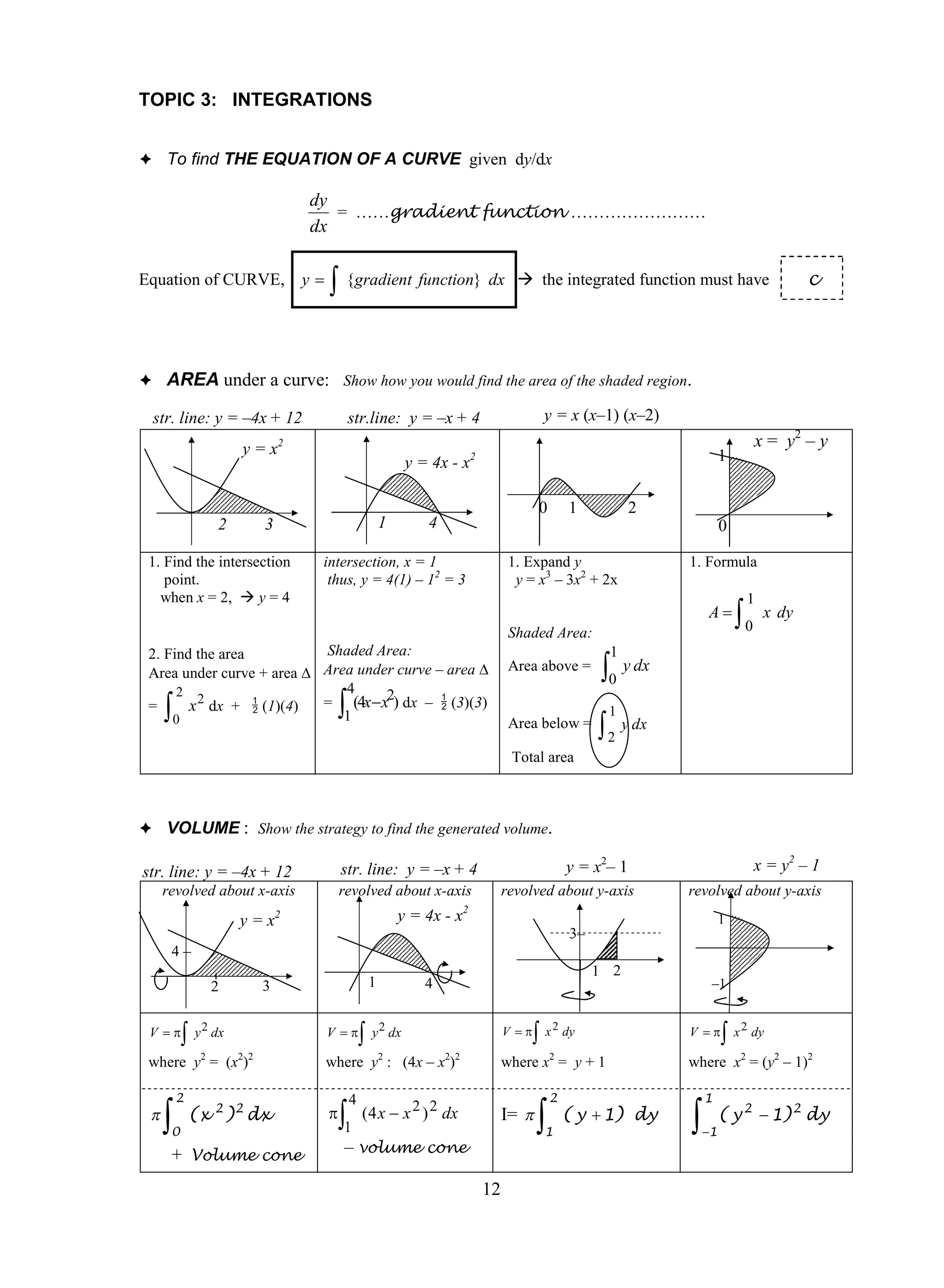
3. Strategies for solving problems involving concepts like differentiation, integration, progressions, and linear laws are outlined. Methods for finding volumes or areas under curves are also summarized briefly.

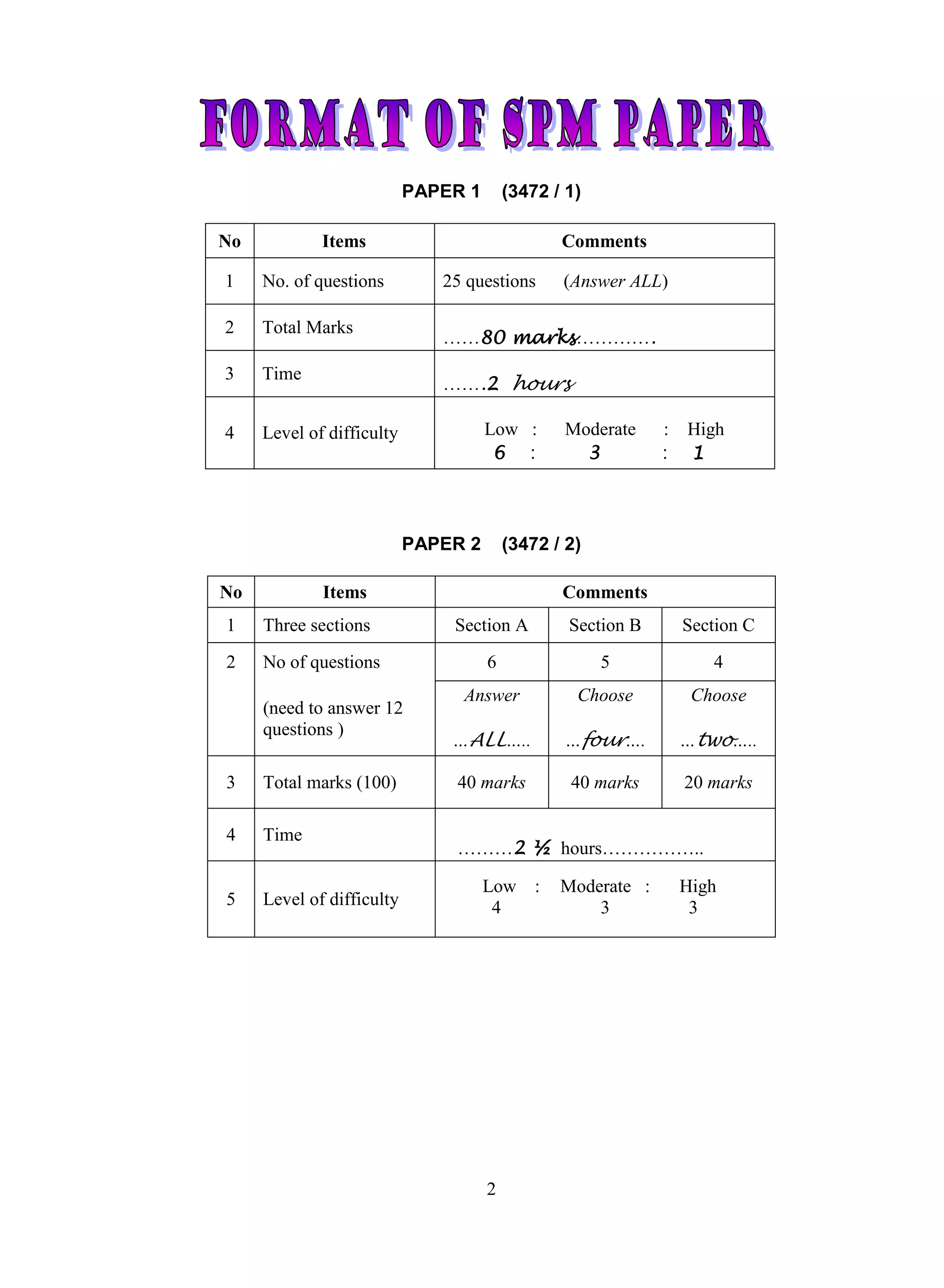

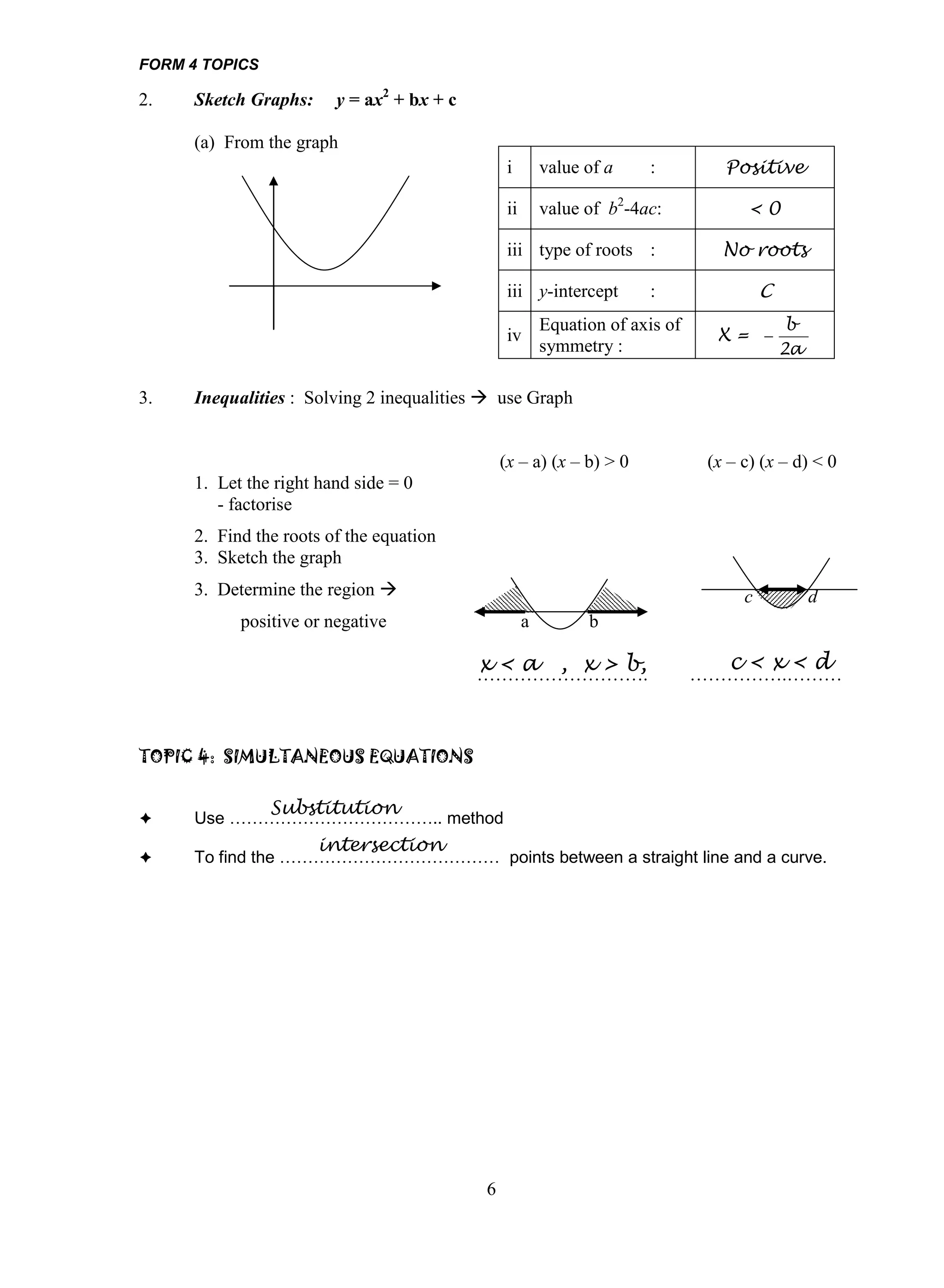
![FORM 4 TOPICS
TOPIC 1 : FUNCTIONS
a b
f(a) = b object = …………………….. image = ………………..
-1
Given f (x) and gf(x). Find g(x) . Thus, g(x) = gf f
3x 5
f ( x) , X1
x 1
TOPIC 2: QUADRATIC EQUATIONS [ ax2 + bx + c = 0 ]
Types of roots
- two distinct real roots
>0 - intersects at two points
0 Real roots
- two equal roots
b2 – 4ac =0 - touches / tangent
<0 - no root
- does not intersect
- f(x) is always positive
Sum and Product of Roots [ ax2 + bx + c = 0 ]
b c
Sum of roots, ( + ) = Product of roots ( ) = x2 – Sx + P =0
a a
TOPIC 3: QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
1. General form CTS form
f (x) = ax2 + bx + c = a( x + p)2 + q
Similarity Same value of a Same value of a
c = y-intercept. q = max/min value
Difference
of f(x)
Able to find: Able to find
Specialty - shape - turning point
- y intercept ( - p , q)
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addmathsmoduleform45-121224040622-phpapp02/75/Add-maths-module-form-4-5-5-2048.jpg)


![TOPIC 8: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
P(X)
BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION _
0.3
0.25 _
- The table shows the binomial probability distribution of
0.2 _
an event with n = 4 .
0.15 _
0.1 _
X=r r=0 r=1 r=2 r=3 r=4
0.05 _
P(X) 0.2 0.15 0.3 0.25 0.1 0 1 2 3 4 X=r
Graph of Binomial Prob Distribution
total = 1
- formula: P(X = r) = n C r p r q n – r
- mean, = np standard deviation = npq variance = npq
NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
X
- Formula : Z
- Type 1 : Given value of X find the value of Z find the probability
[use formula] [use calculator]
- Type 2 : Given the probability Find the value of Z Find its value of X .
[use log book] [use formula]
TOPIC 9: MOTION IN STRAIGHT LINES
Displacement, s Velocity, v Acceleration, a
ds dv d 2s
s= v dt v a =
dt dt dt 2
dv
Maximum velocity - 0 a=0
dt
return to O s=0 - -
stops momentarily v=0
da
max. acceleration 0
dt
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/addmathsmoduleform45-121224040622-phpapp02/75/Add-maths-module-form-4-5-16-2048.jpg)