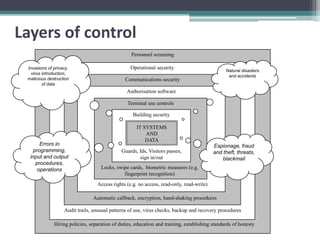
There are multiple layers of control that can help provide security for IT systems and data:
1) Physical security controls like building access restrictions, locks, ID cards help protect the physical infrastructure and limit access.
2) Technical controls include authorization software, encryption, audit trails that monitor user activity and system behavior to detect issues.
3) Operational security procedures audit transaction records and network activity to identify errors, threats, or policy violations. Personnel screening and training also help reduce security risks from internal sources.