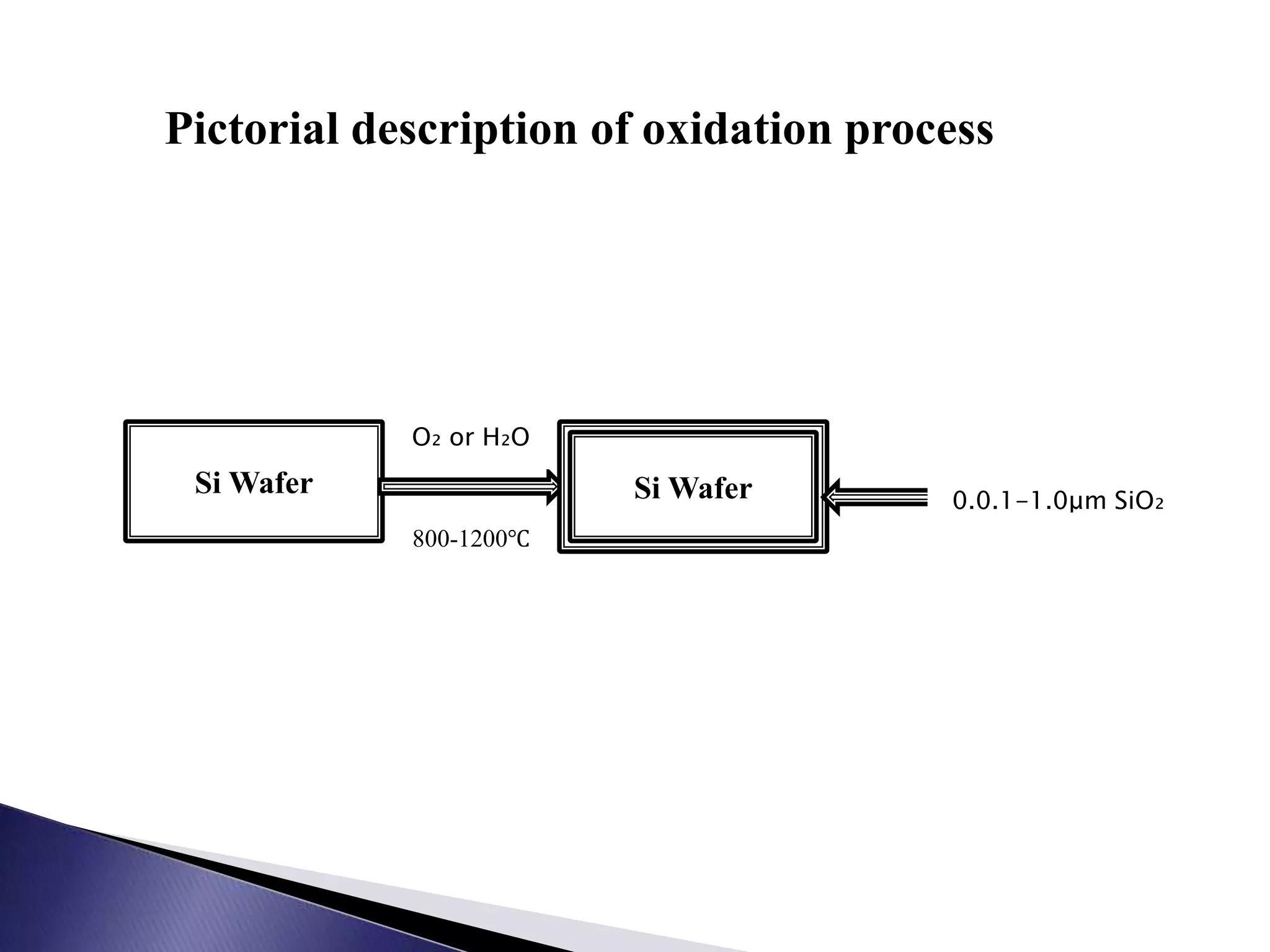
This document discusses oxidation of silicon and the thermal oxidation process. It describes how silicon is commonly oxidized using thermal oxidation in a furnace between 800-1200°C in the presence of oxygen or water vapor. Thermal oxidation grows either a dry oxide layer using oxygen or a wet oxide layer using water vapor, with wet oxidation growing faster but introducing more defects. Thermal oxidation is a key process in silicon integrated circuit fabrication for growing silicon dioxide layers.