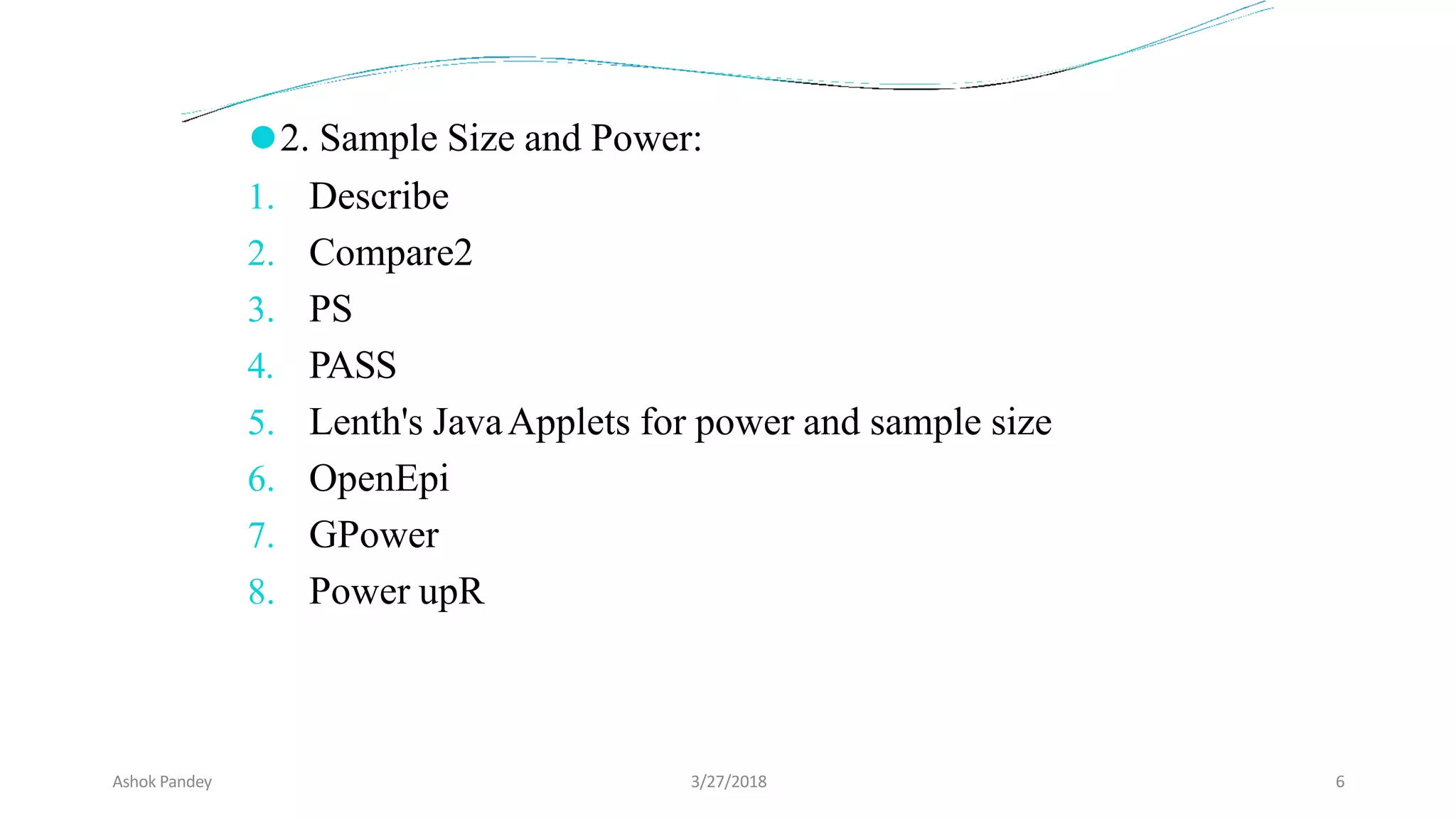
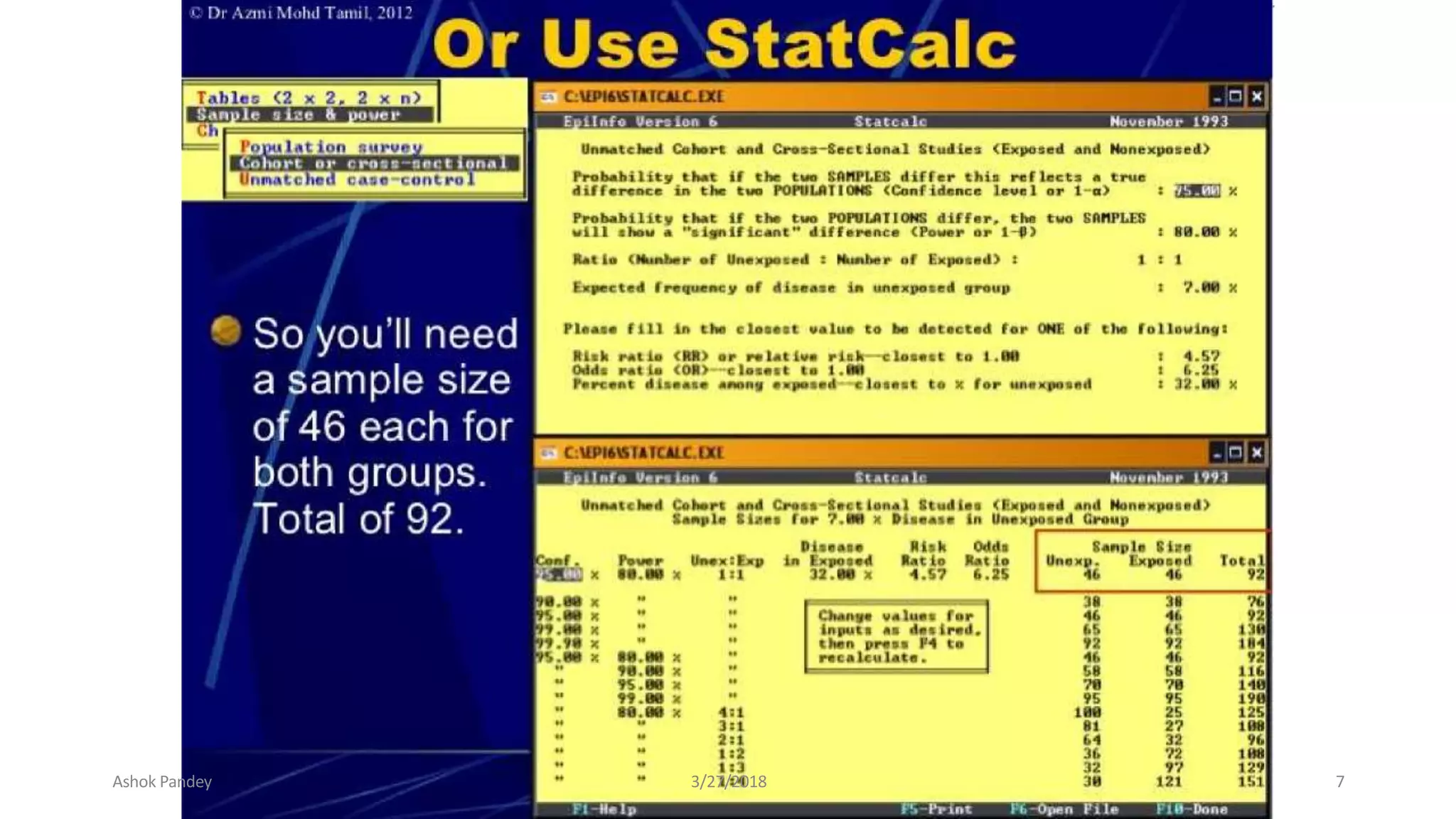
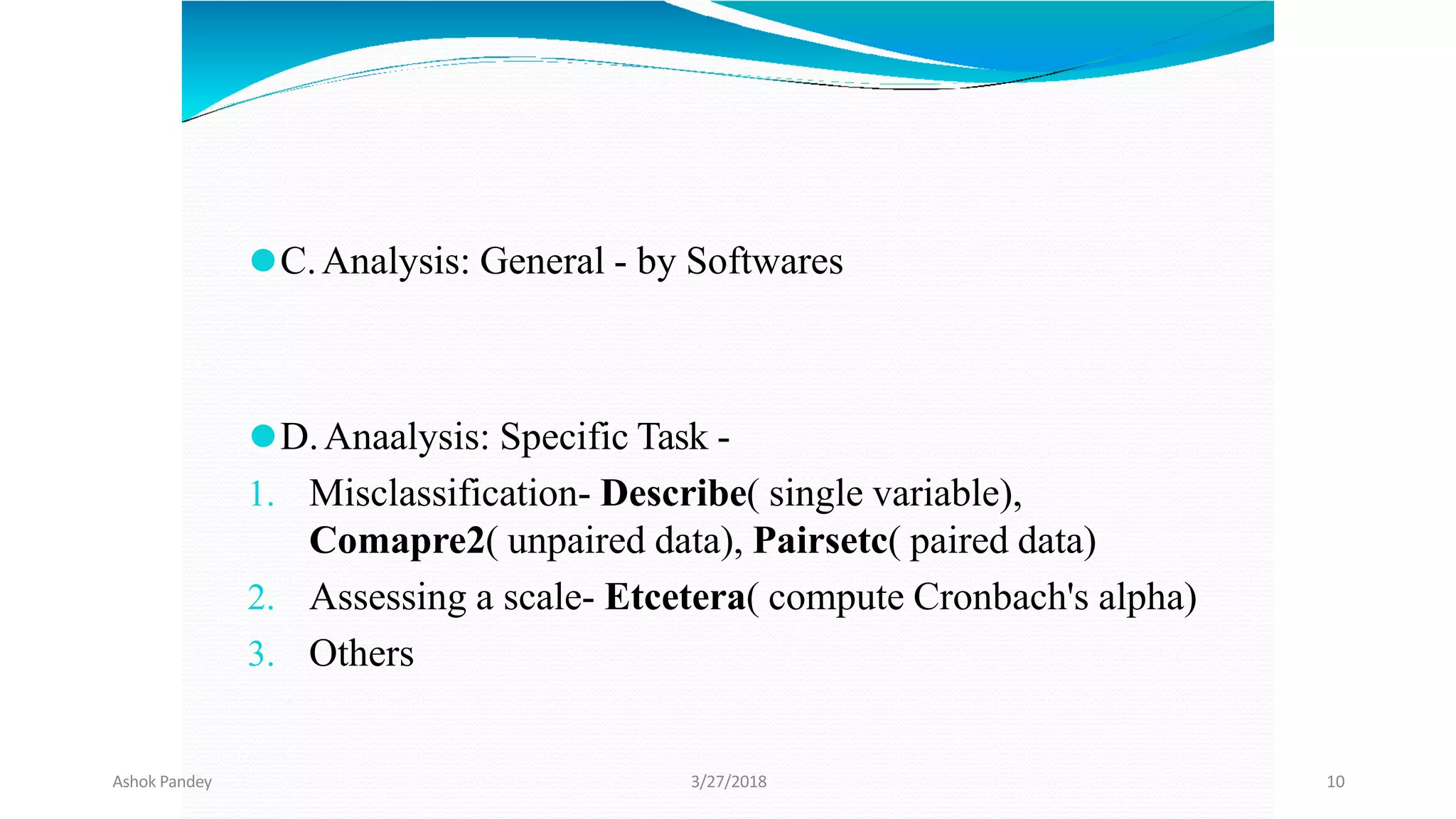
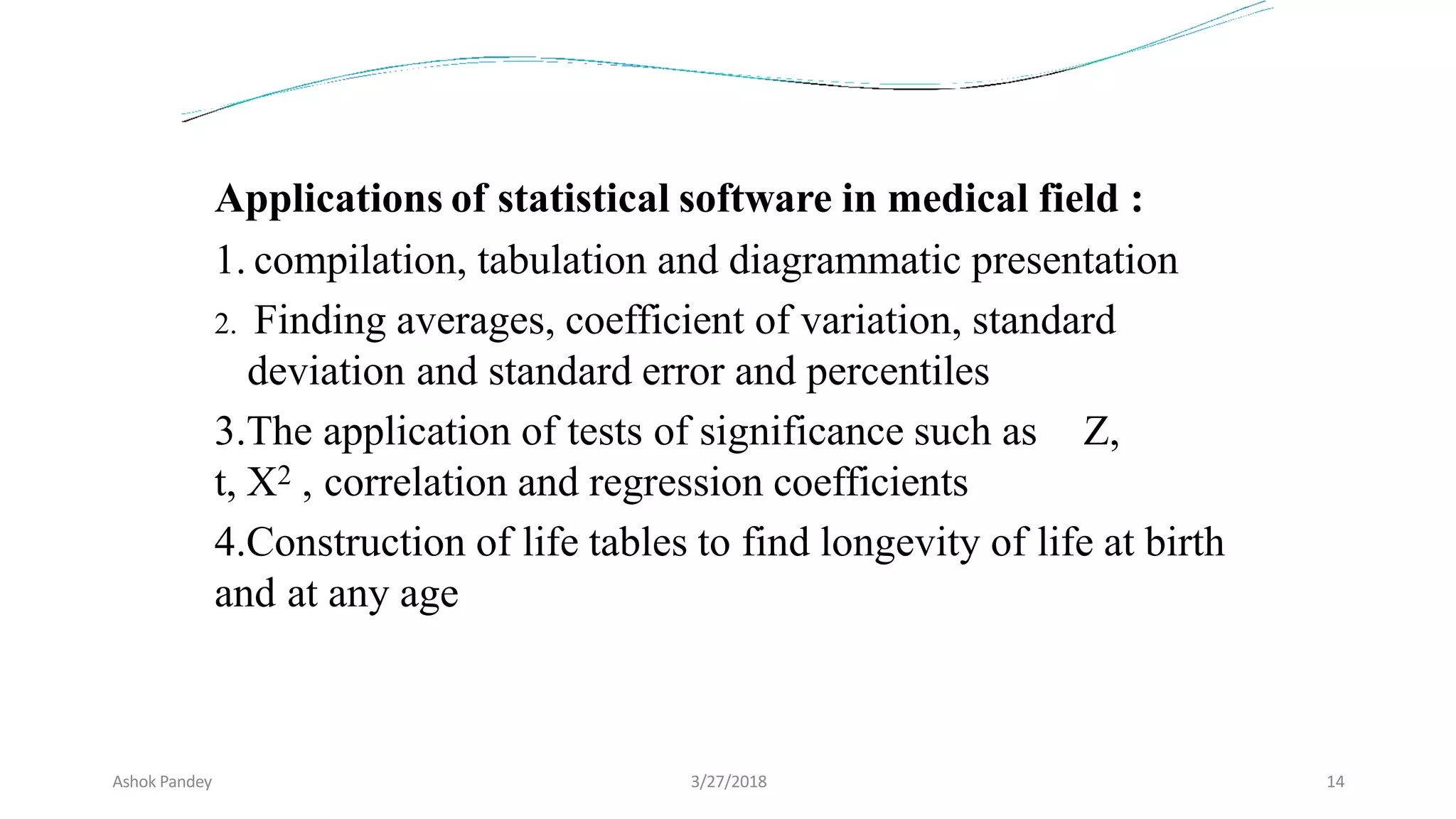
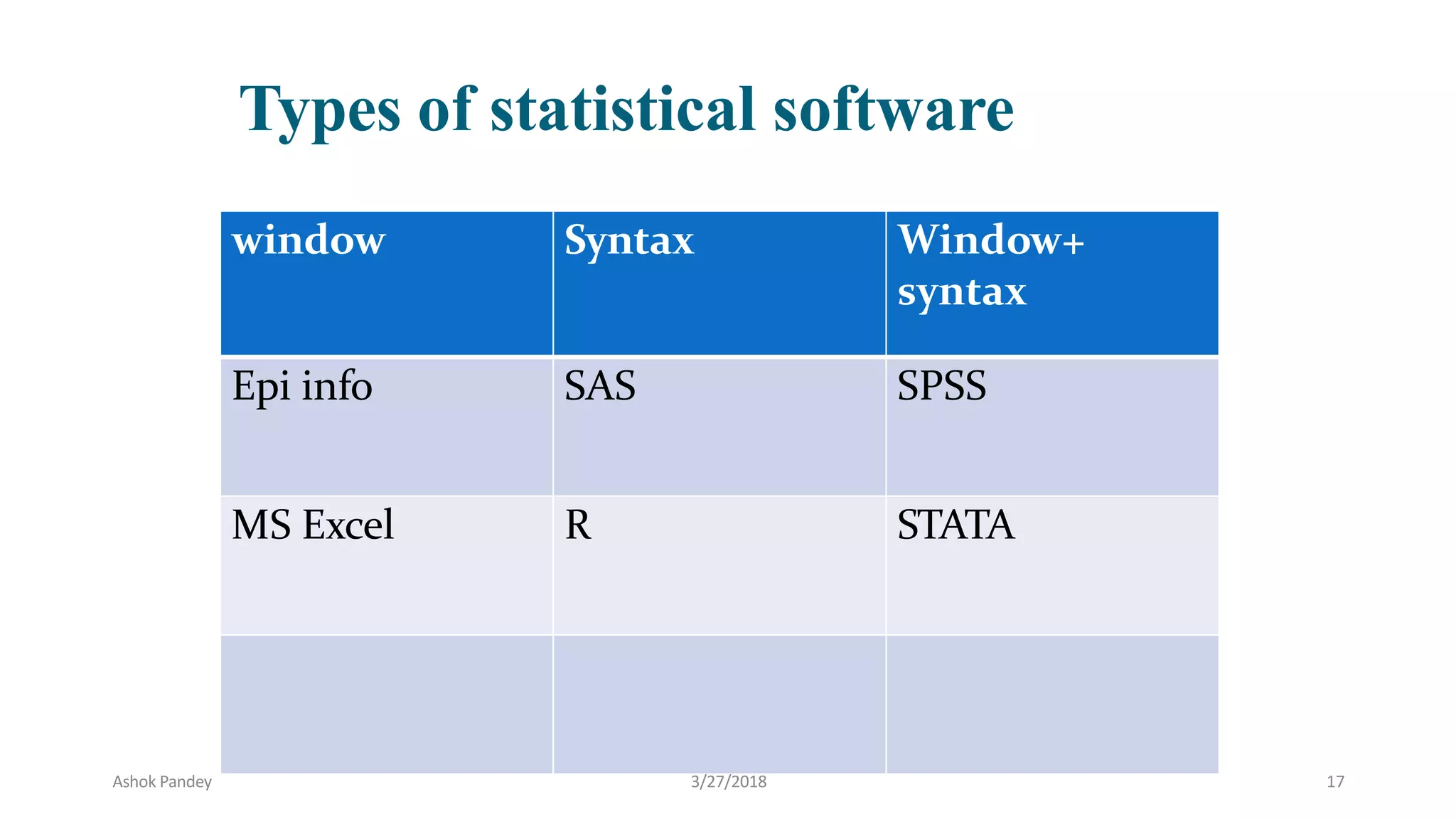
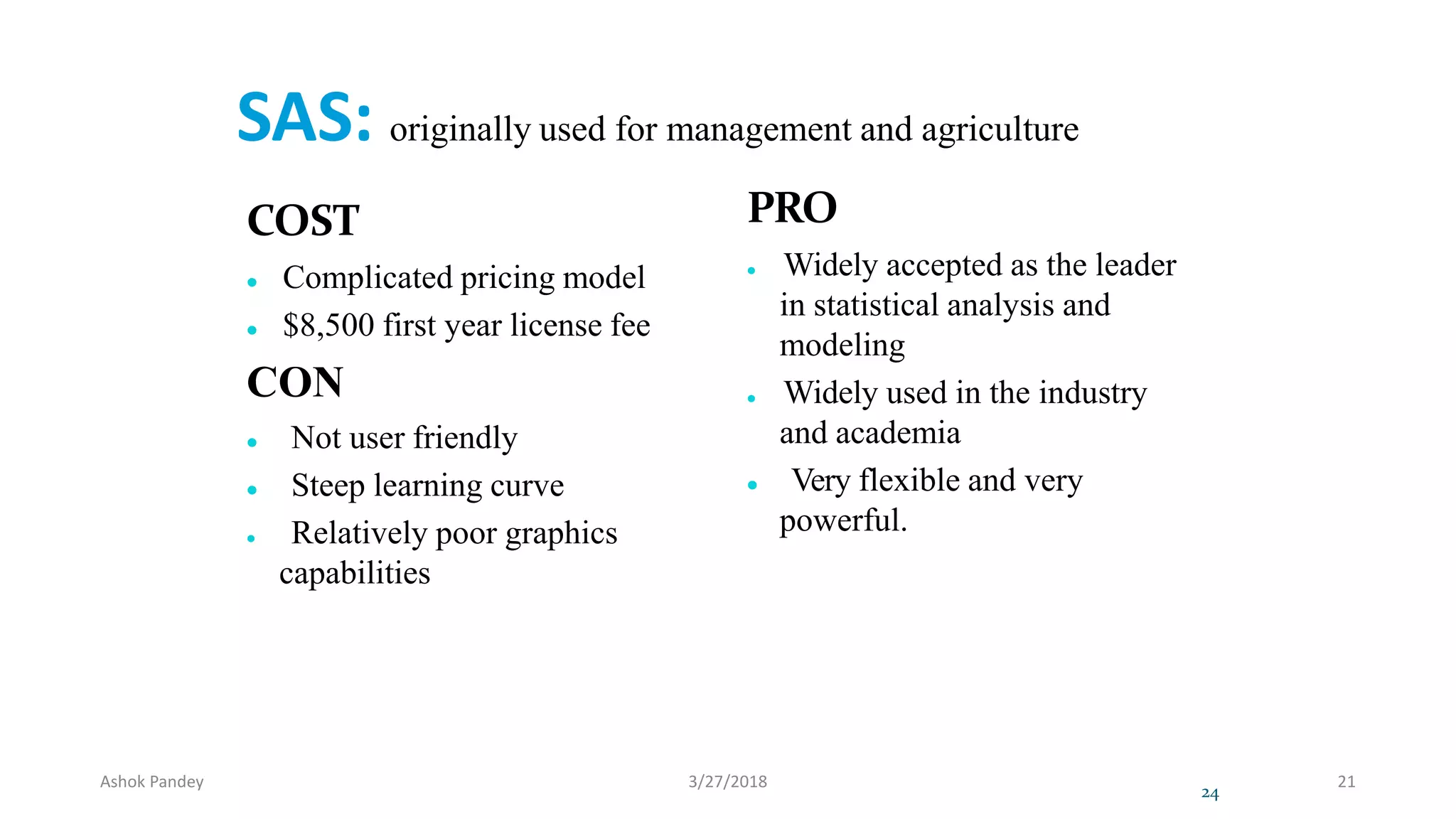
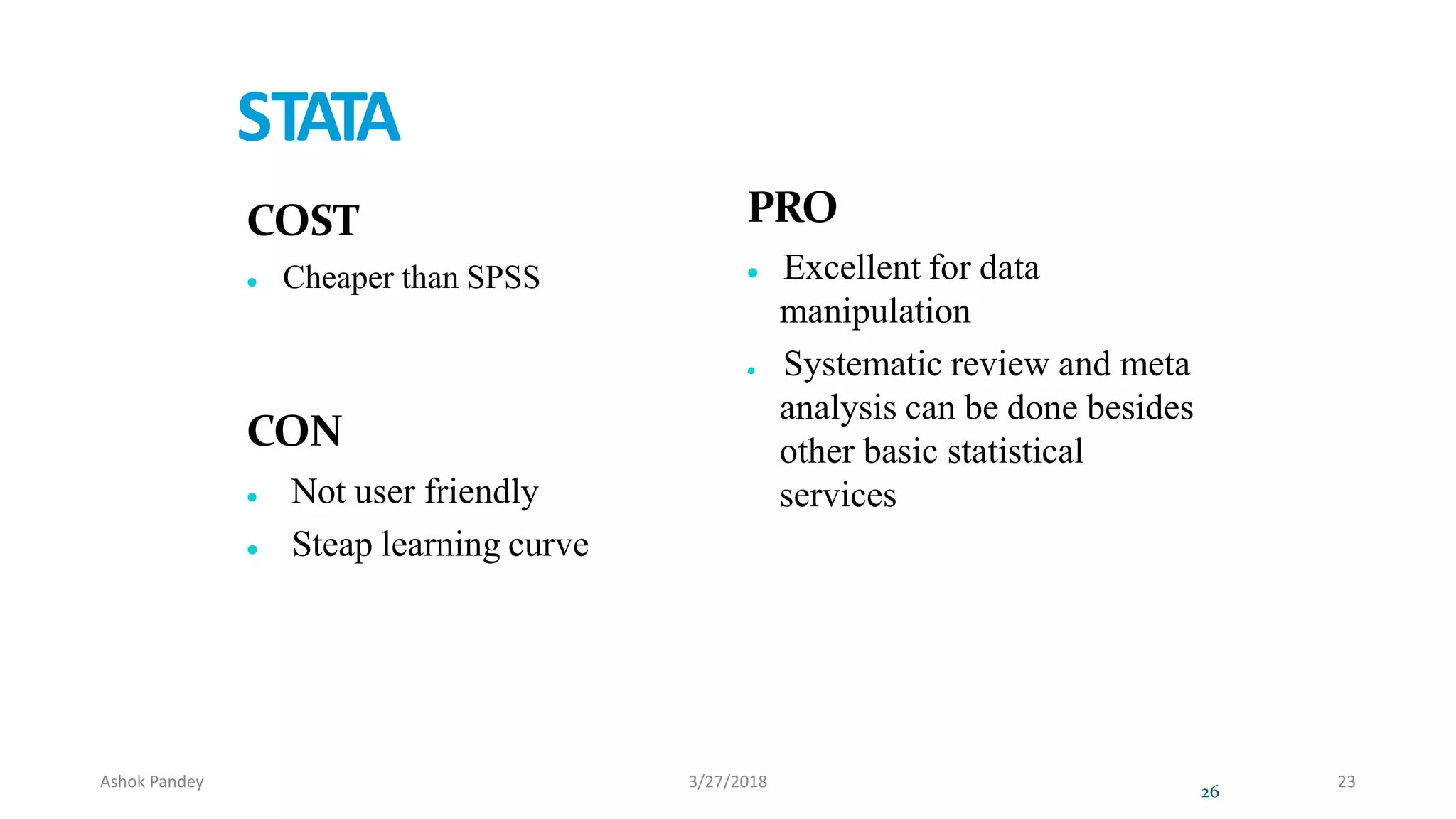
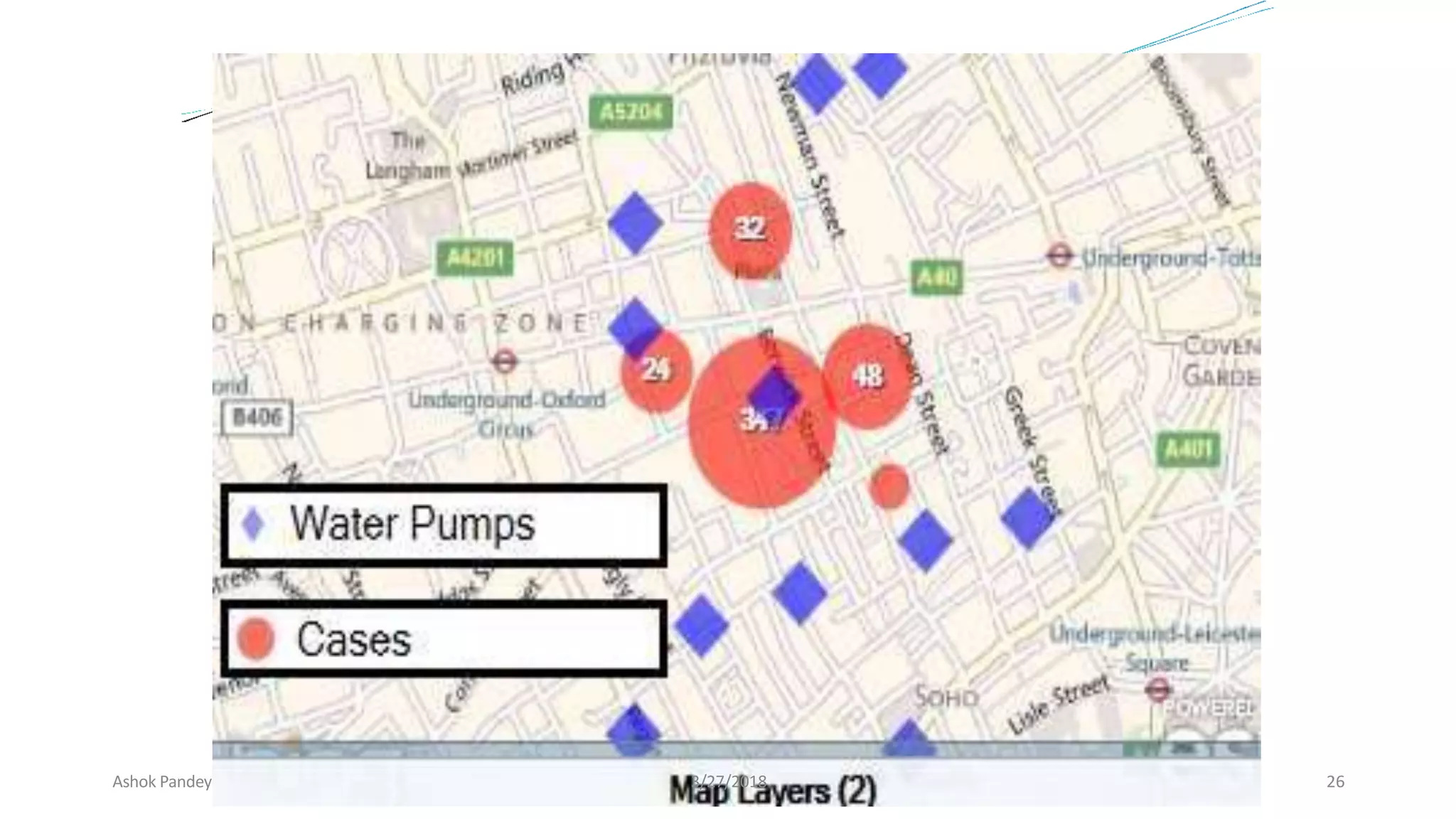
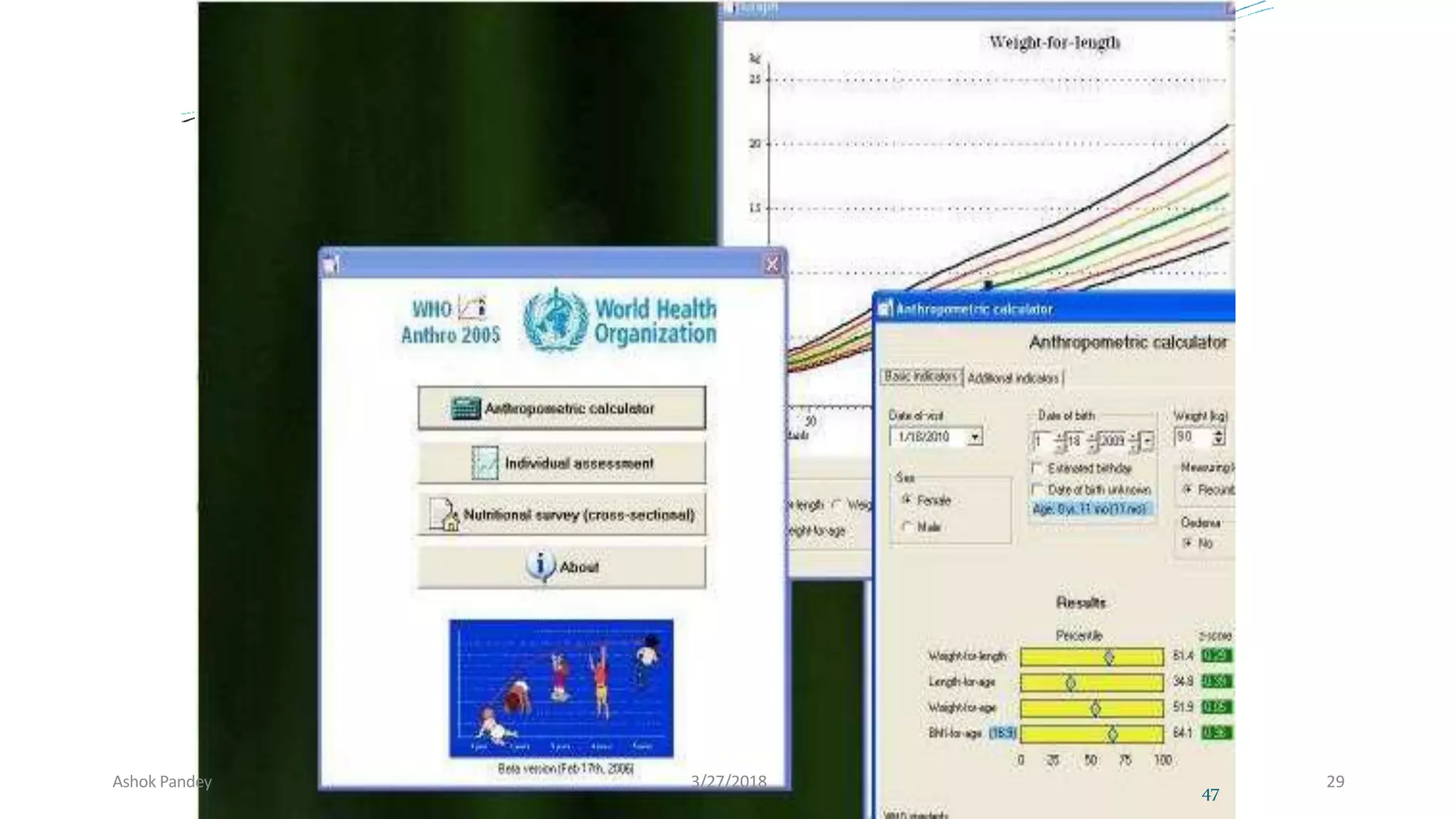
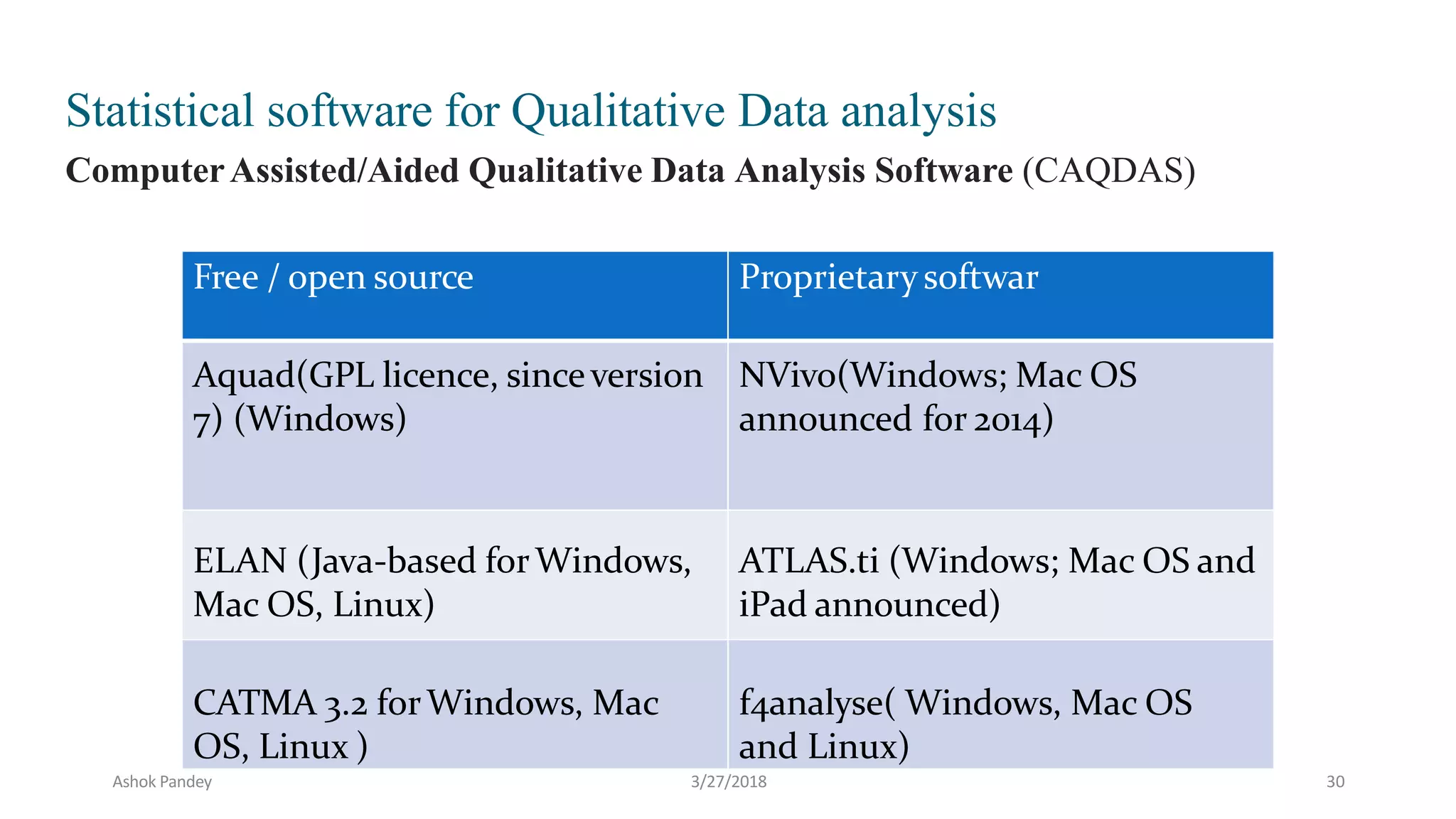
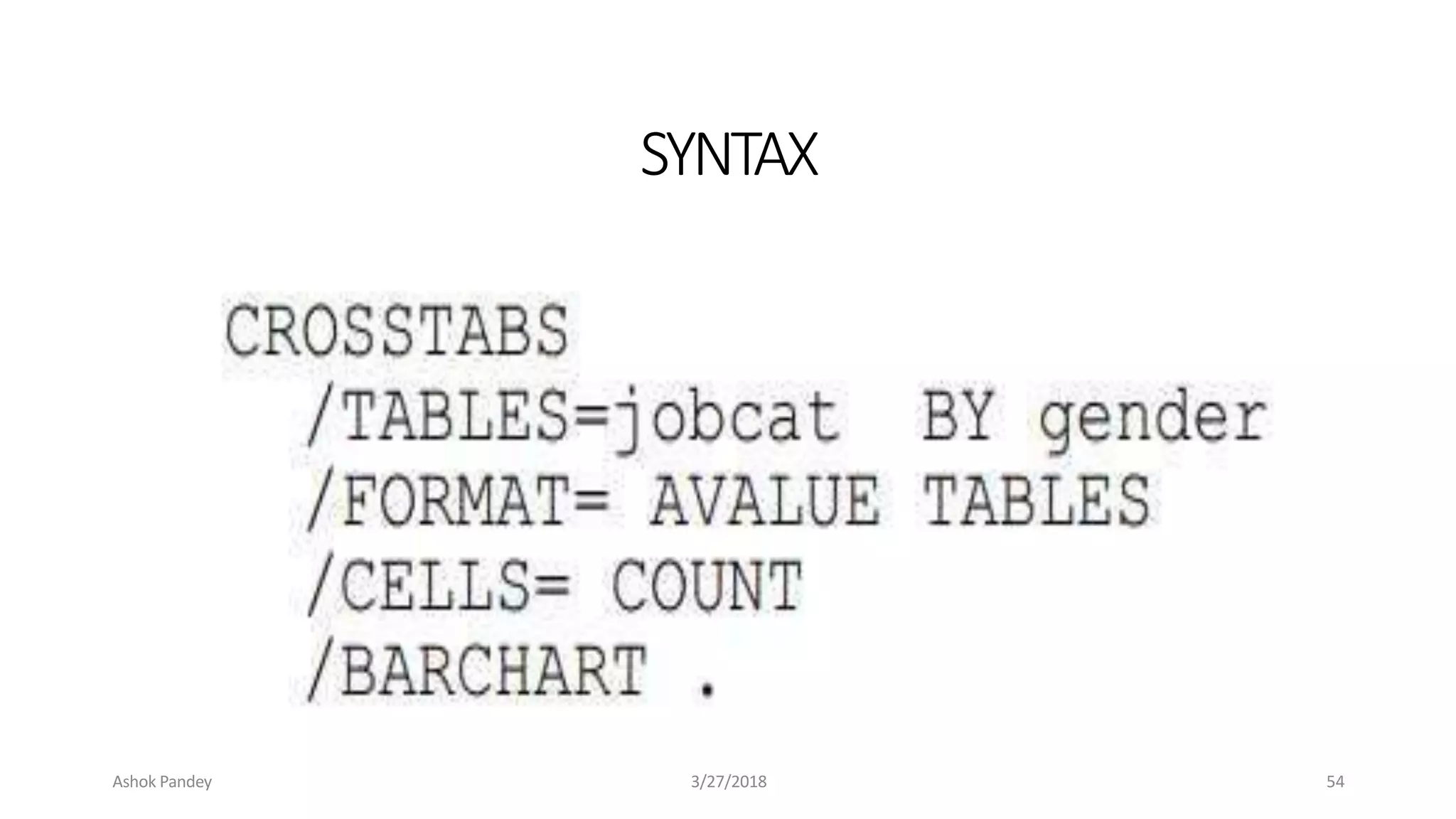
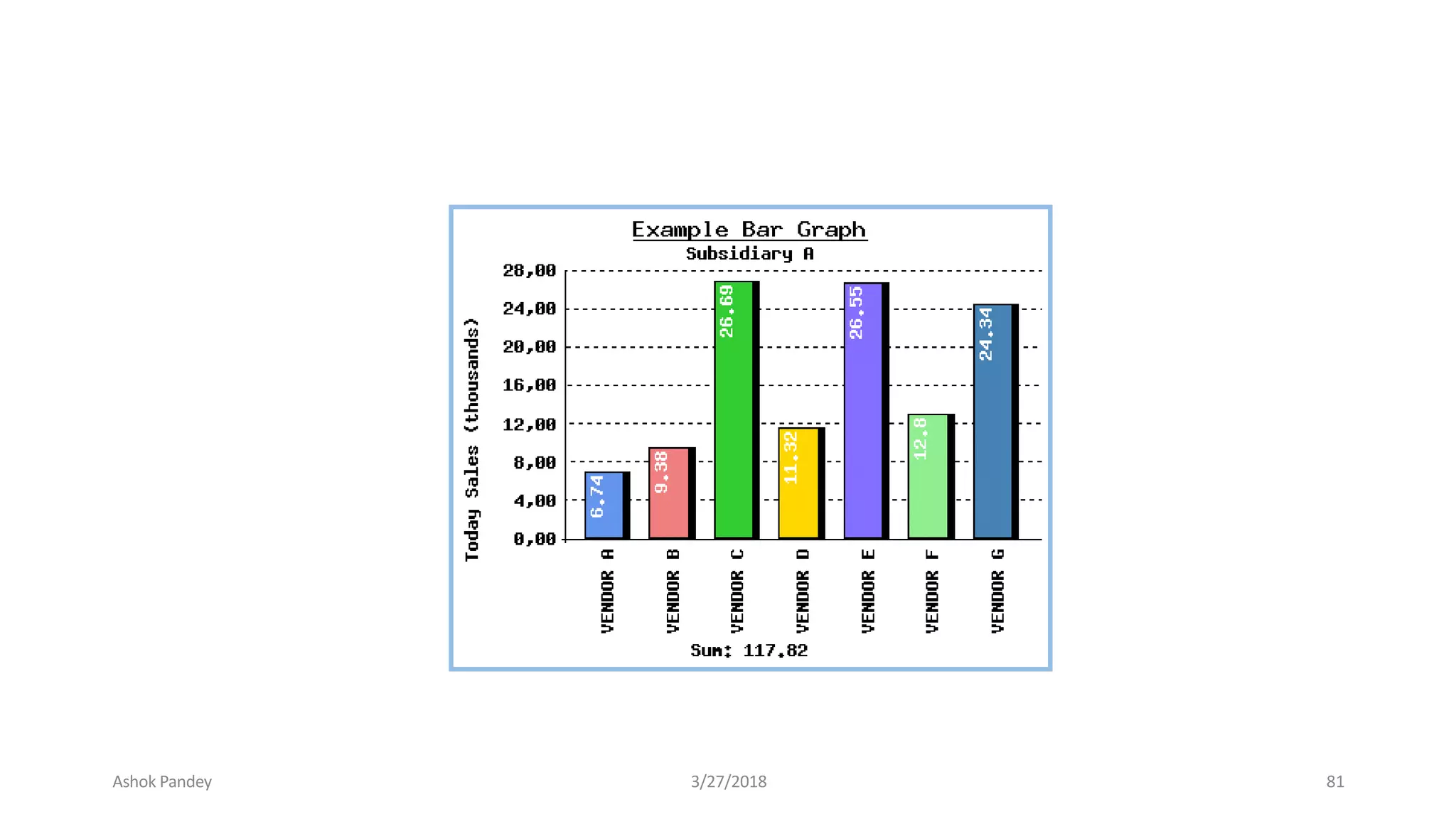
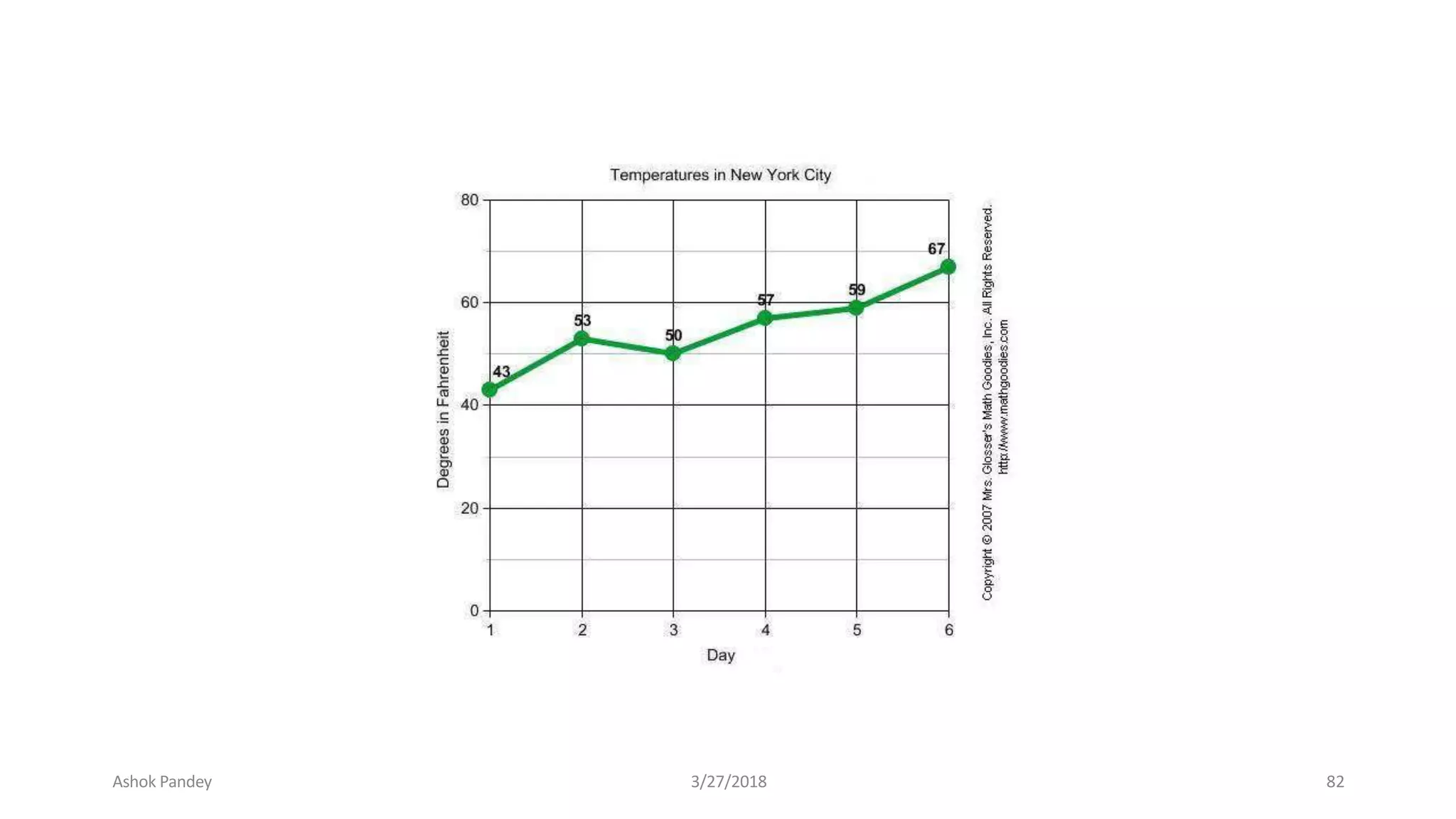
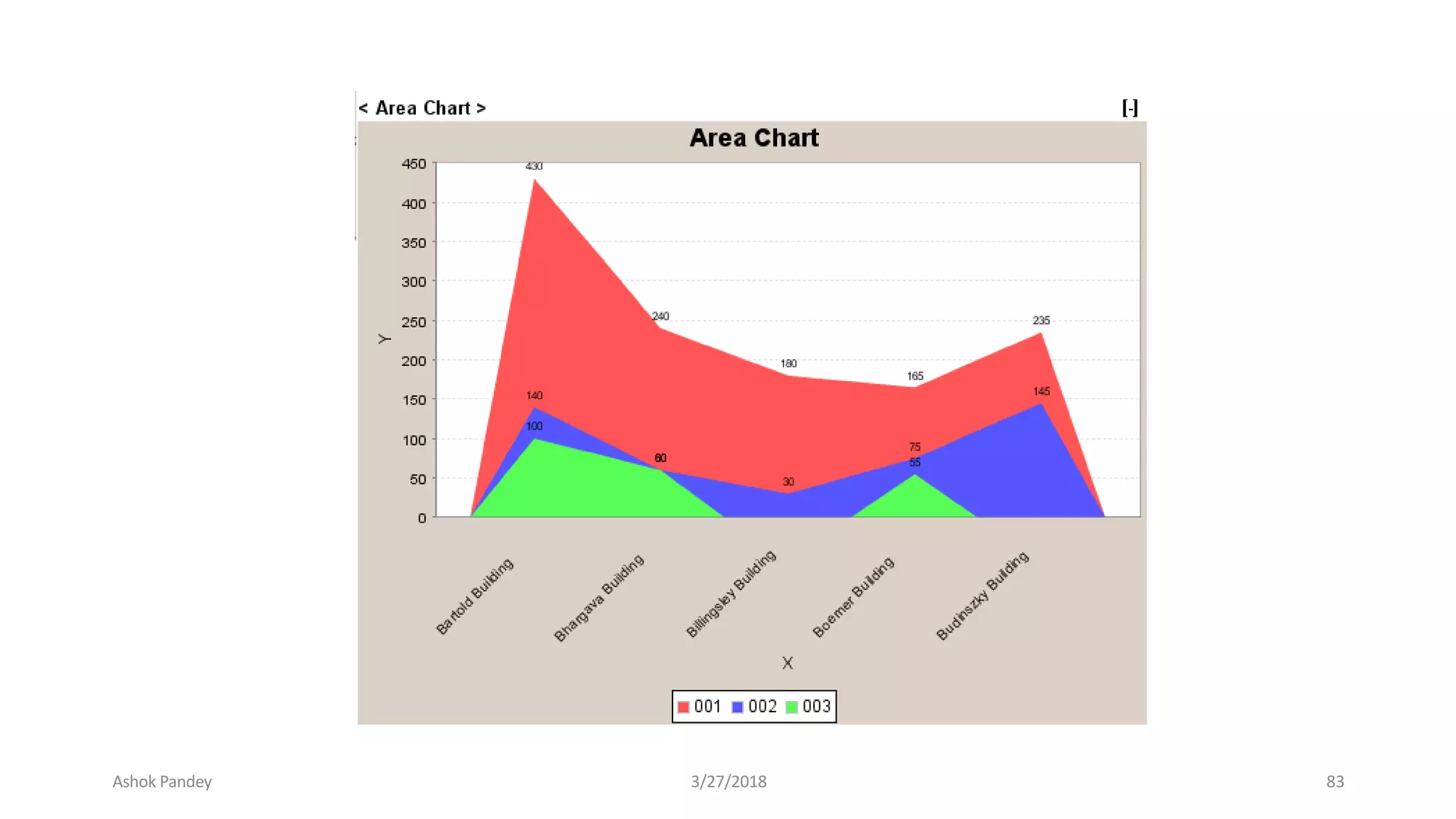
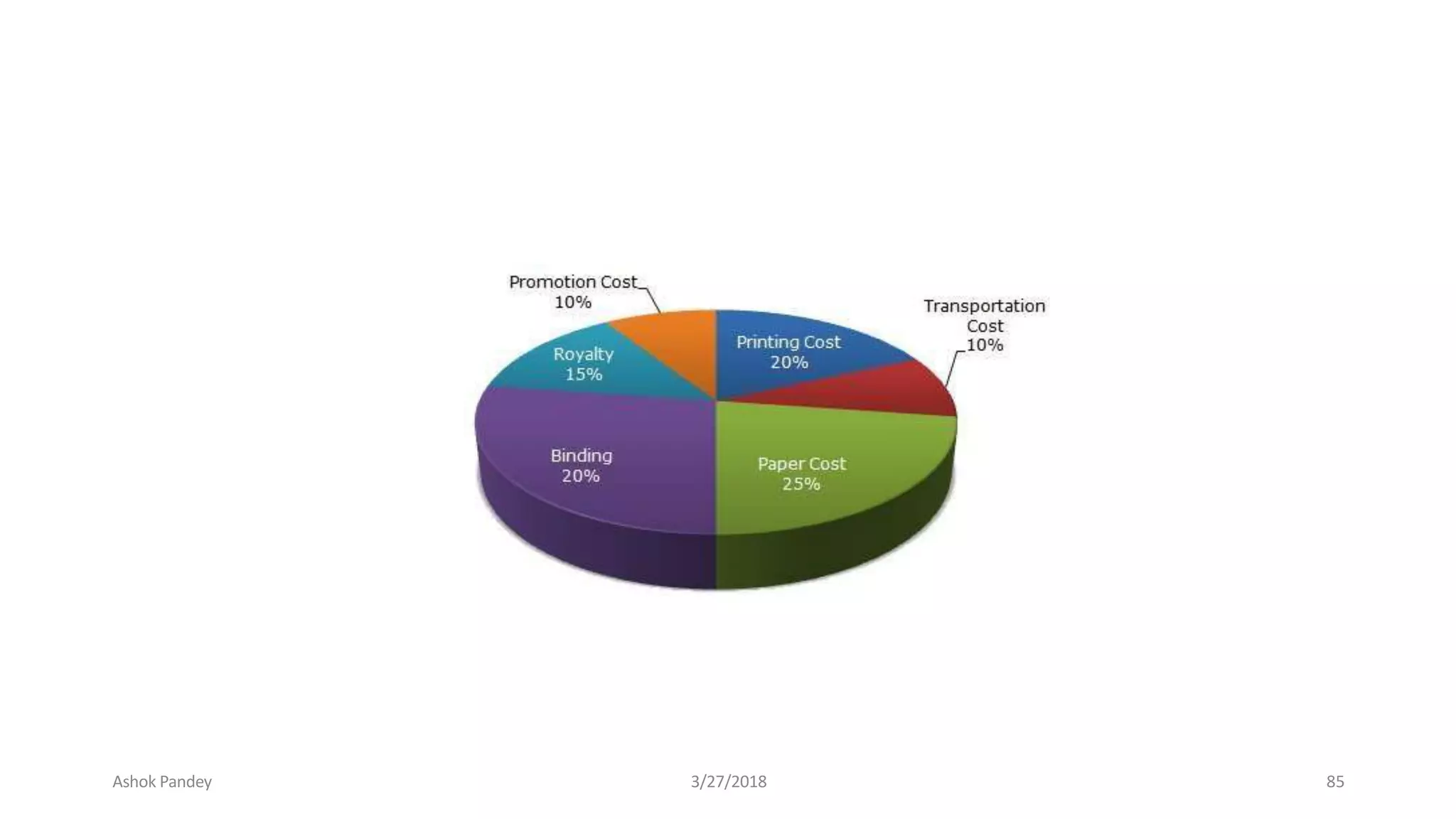
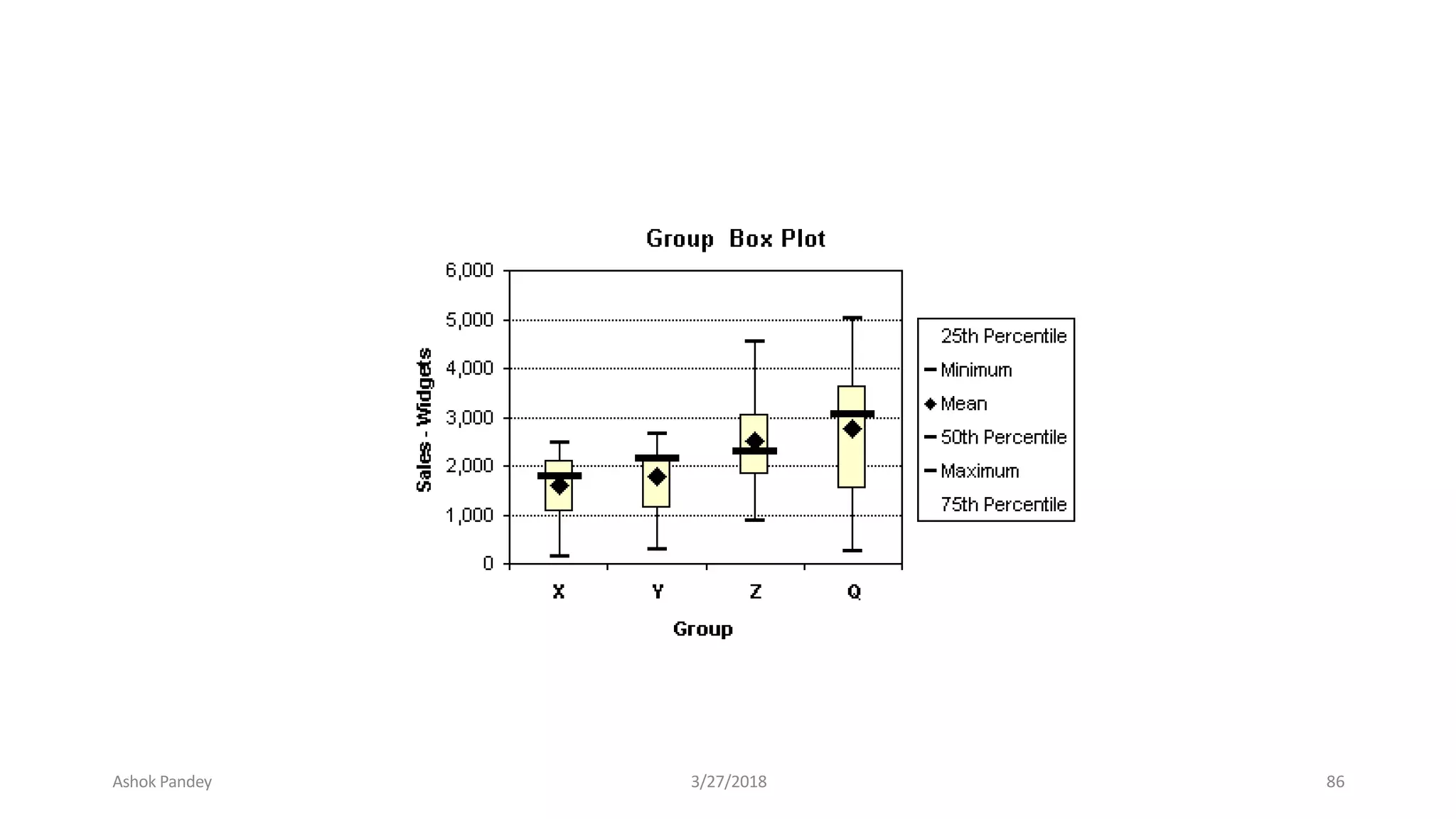
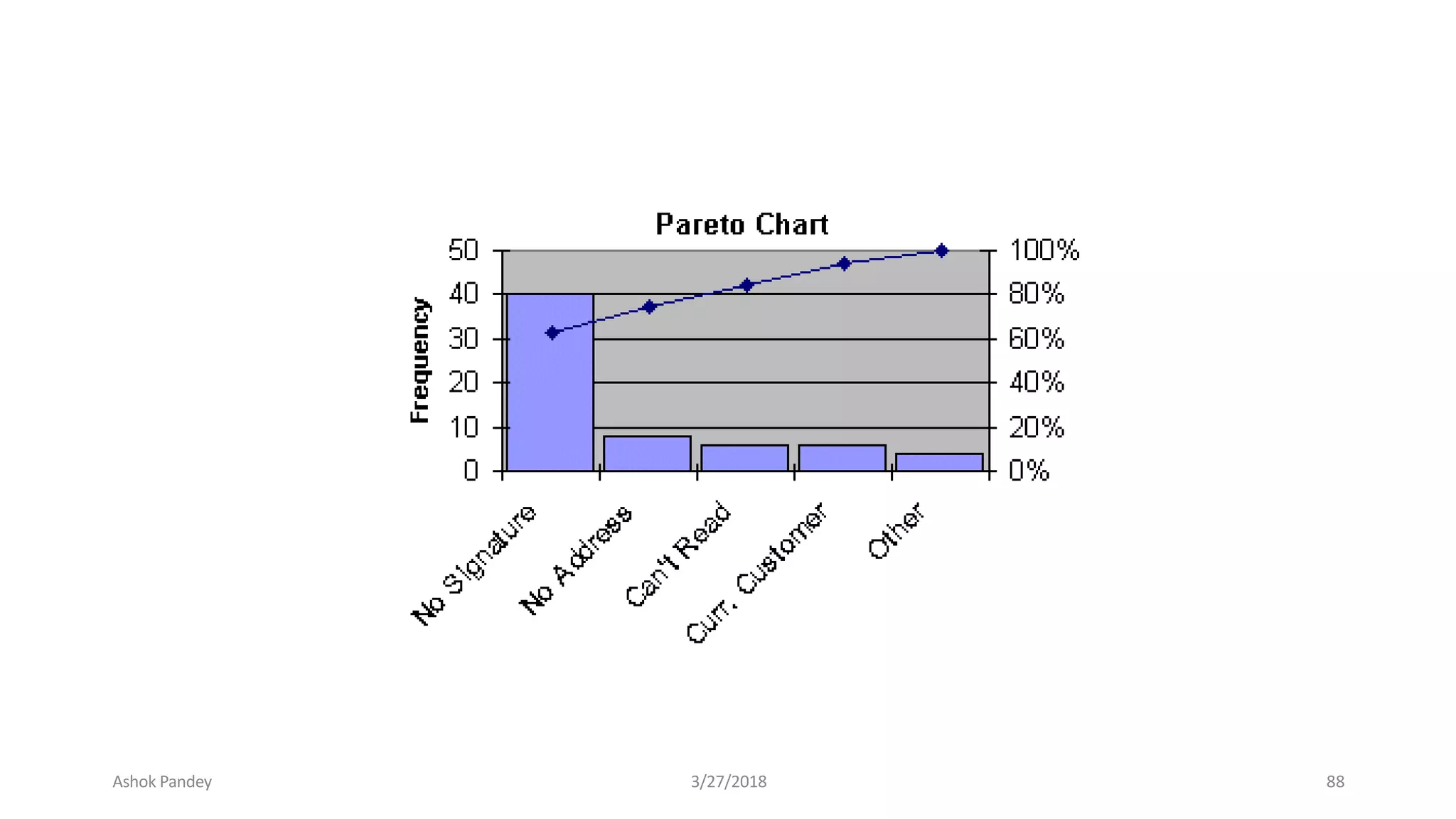
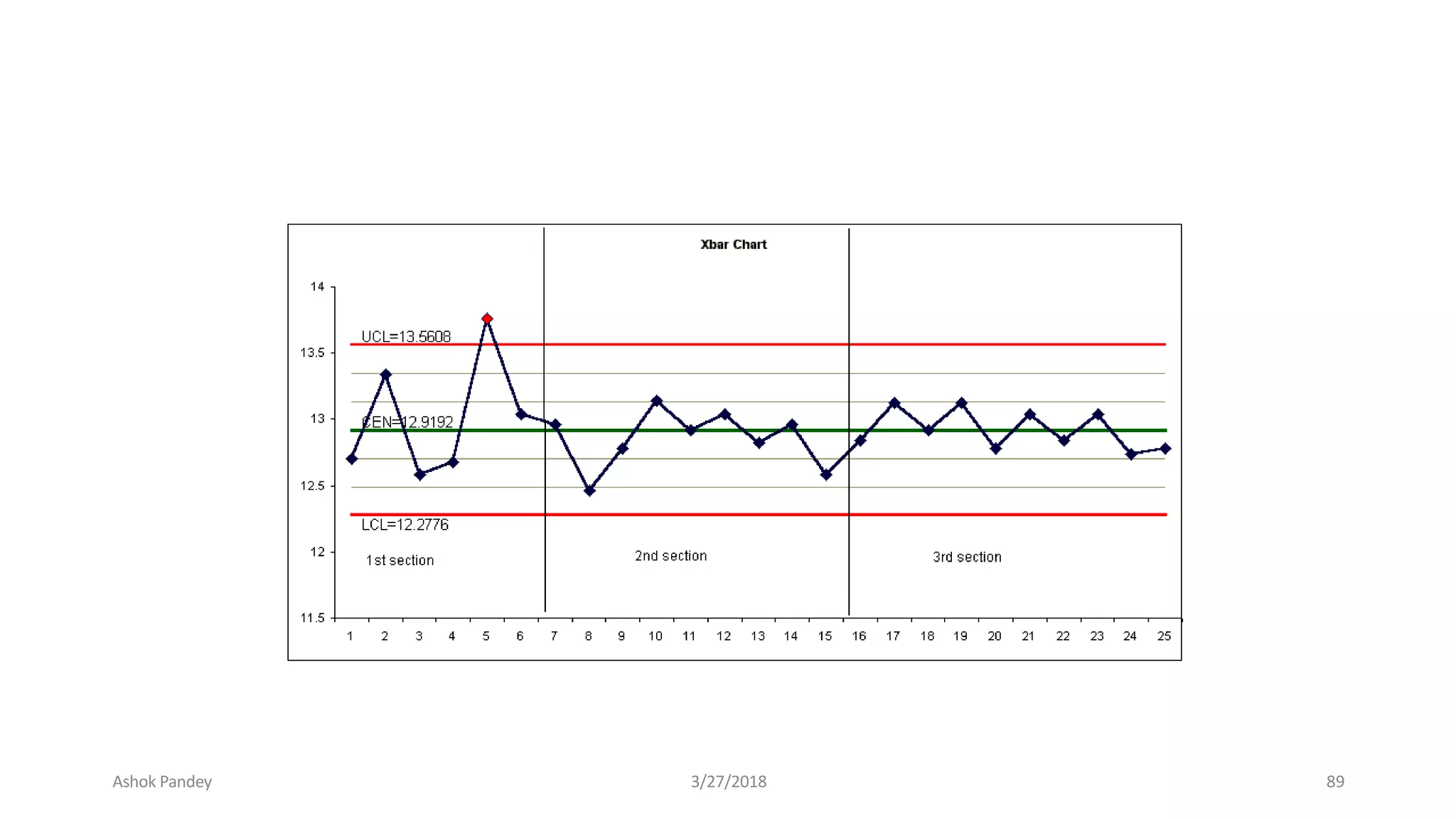
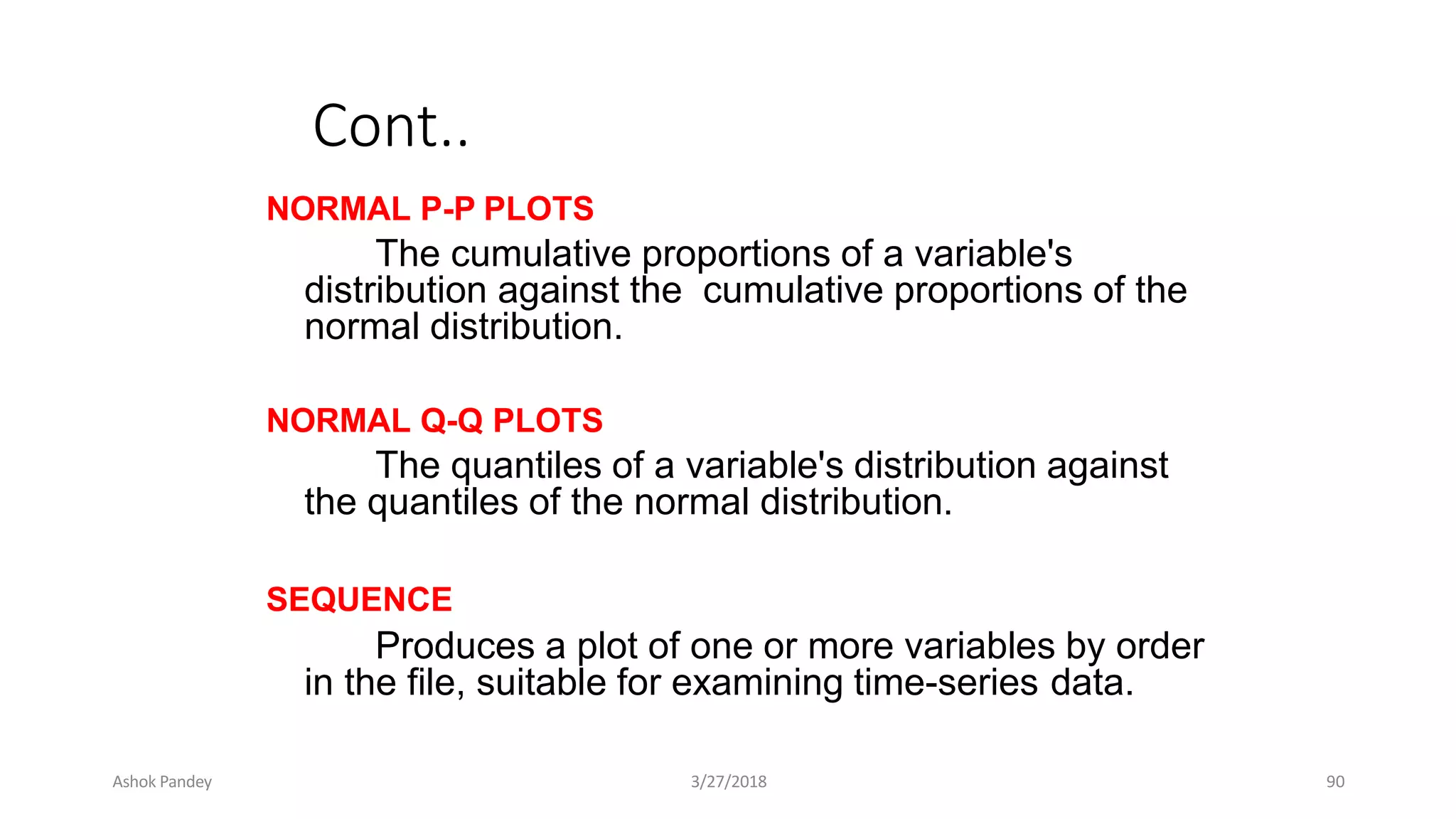
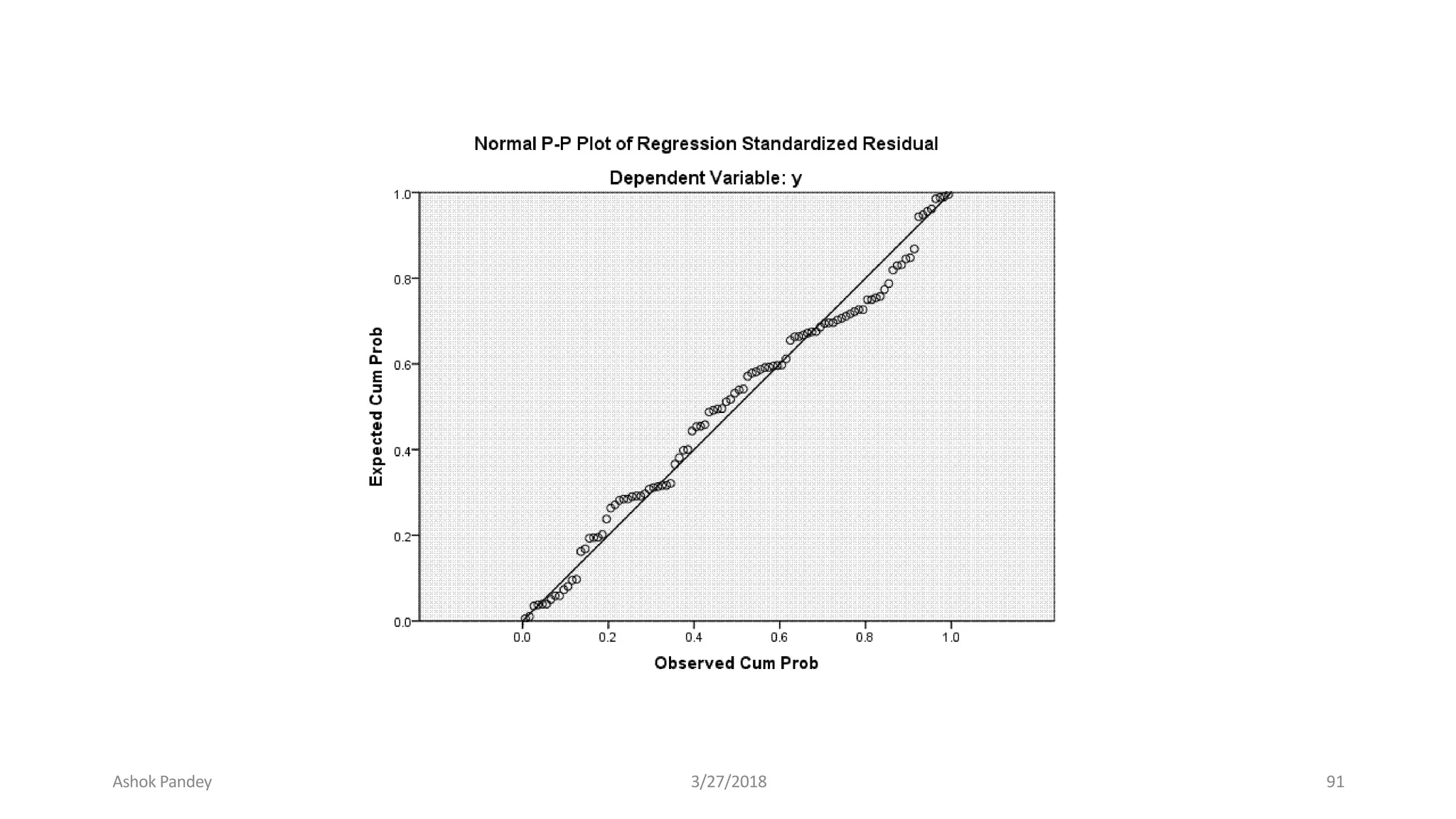
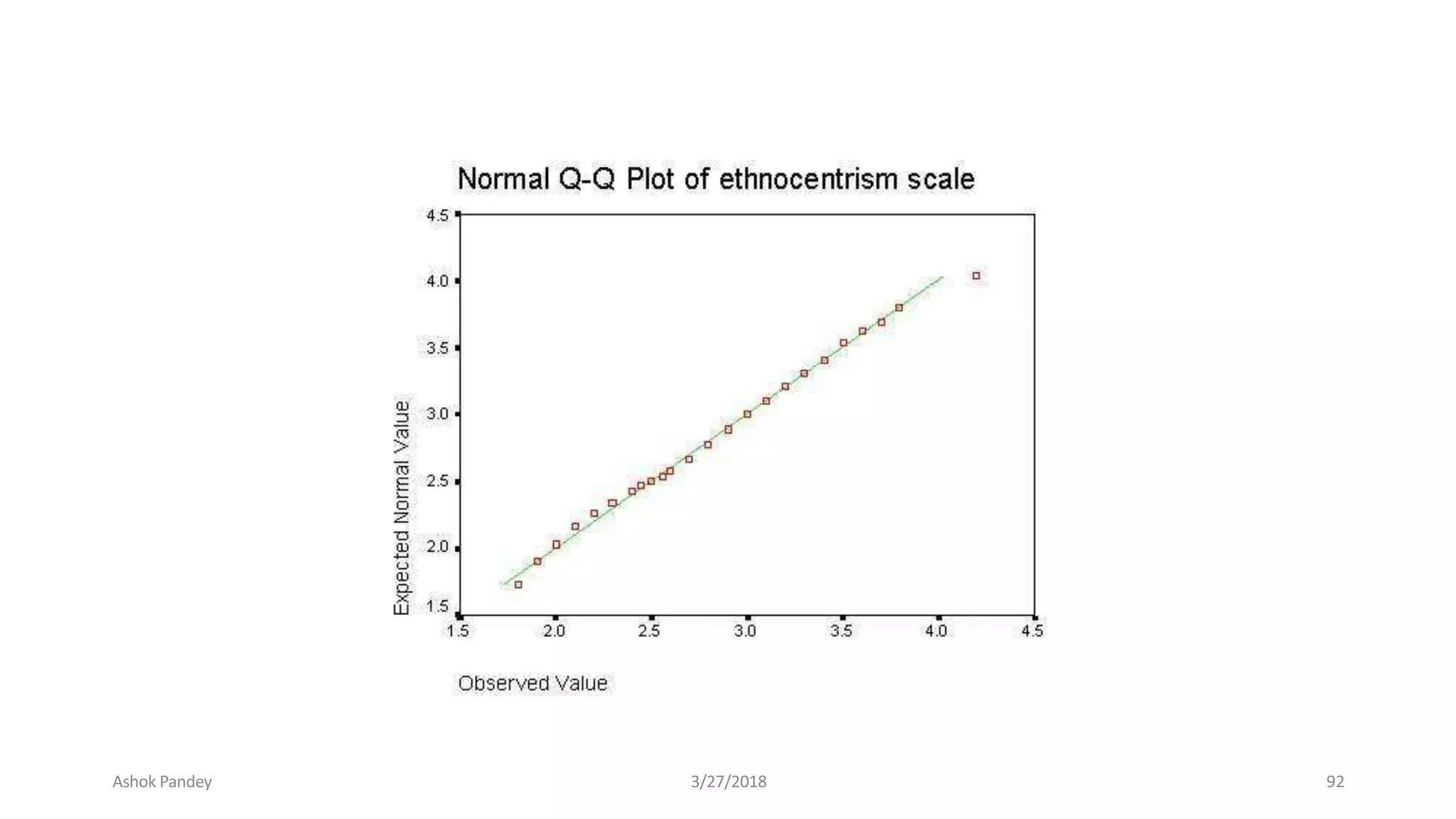
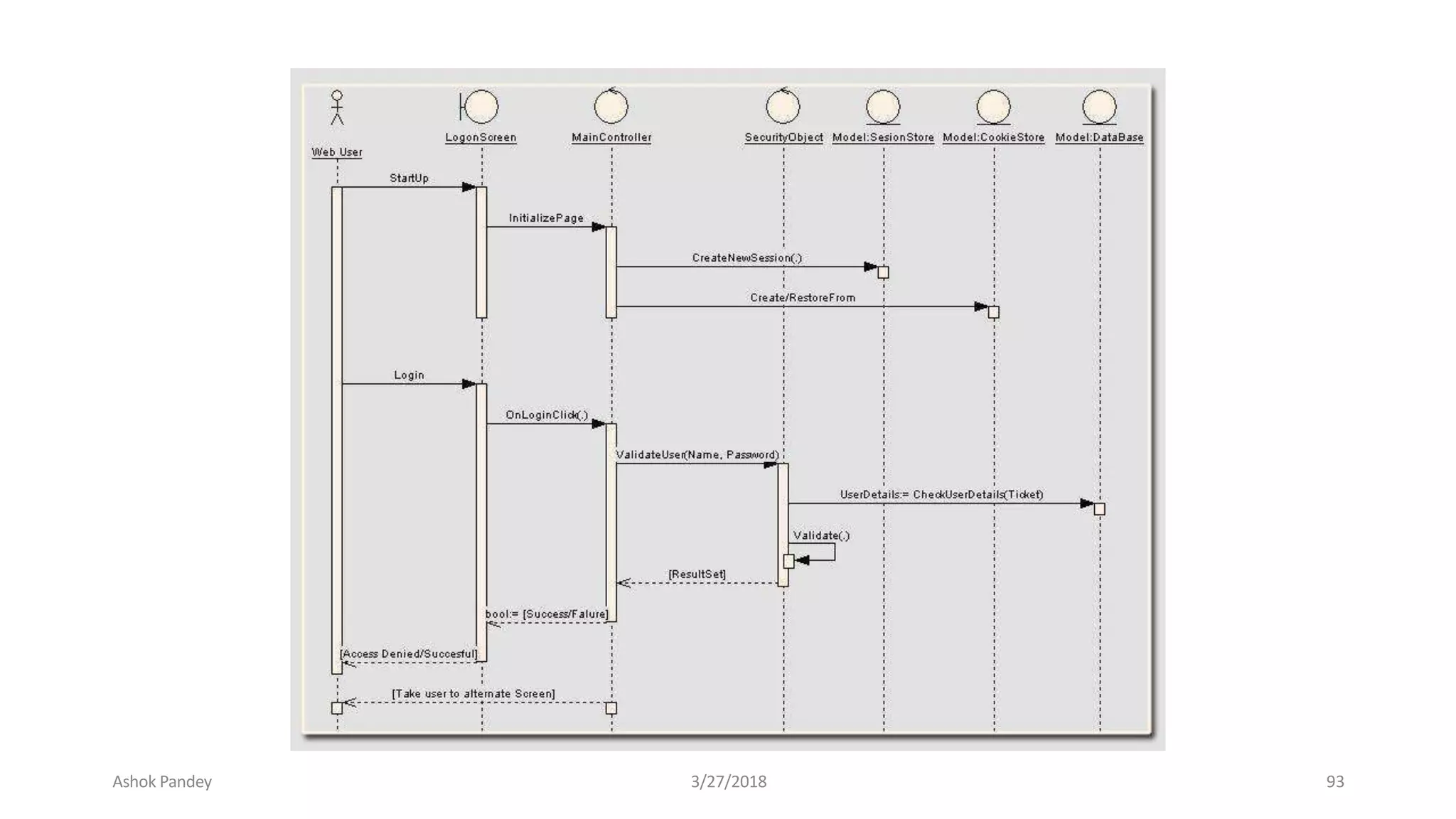
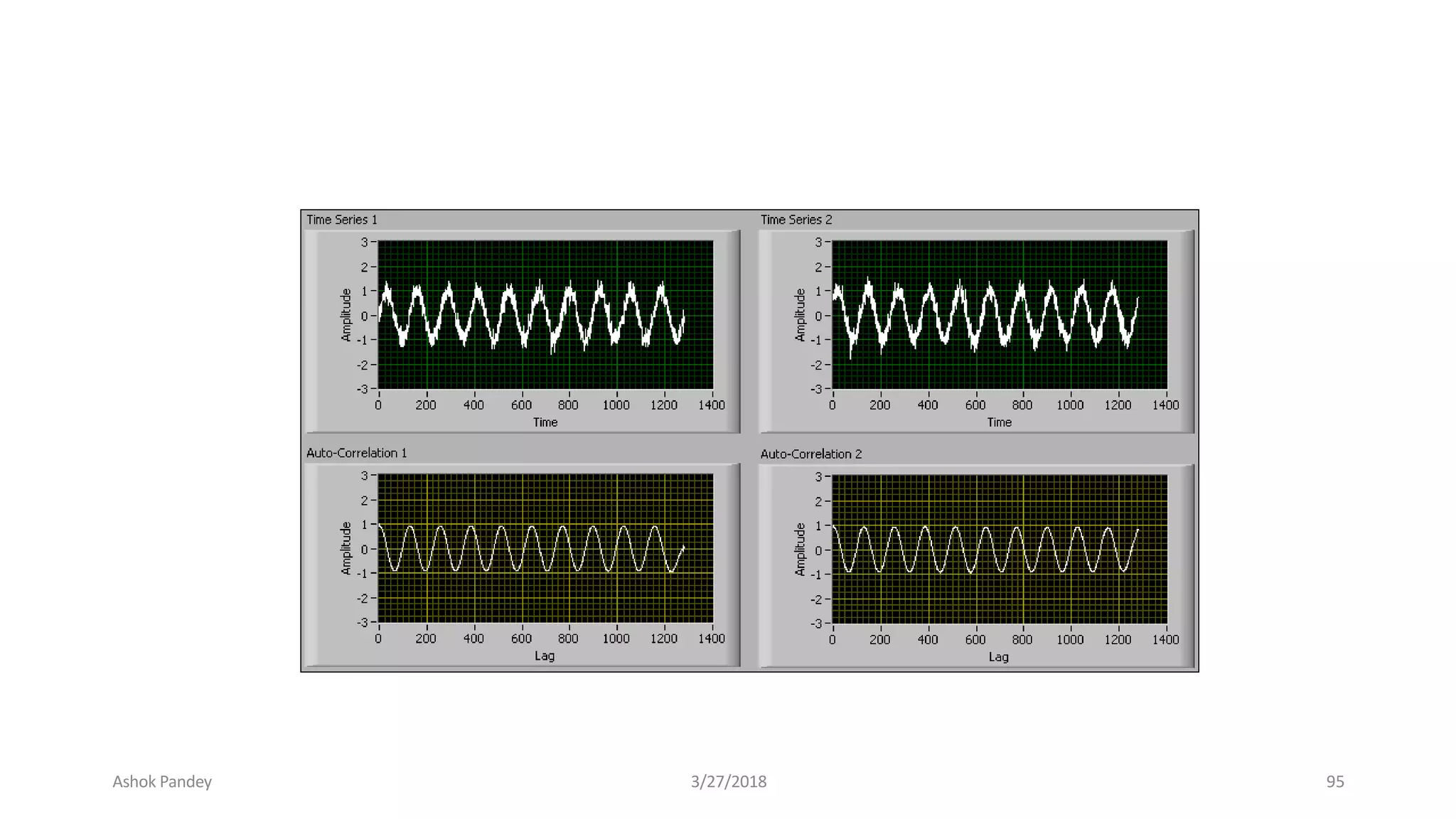
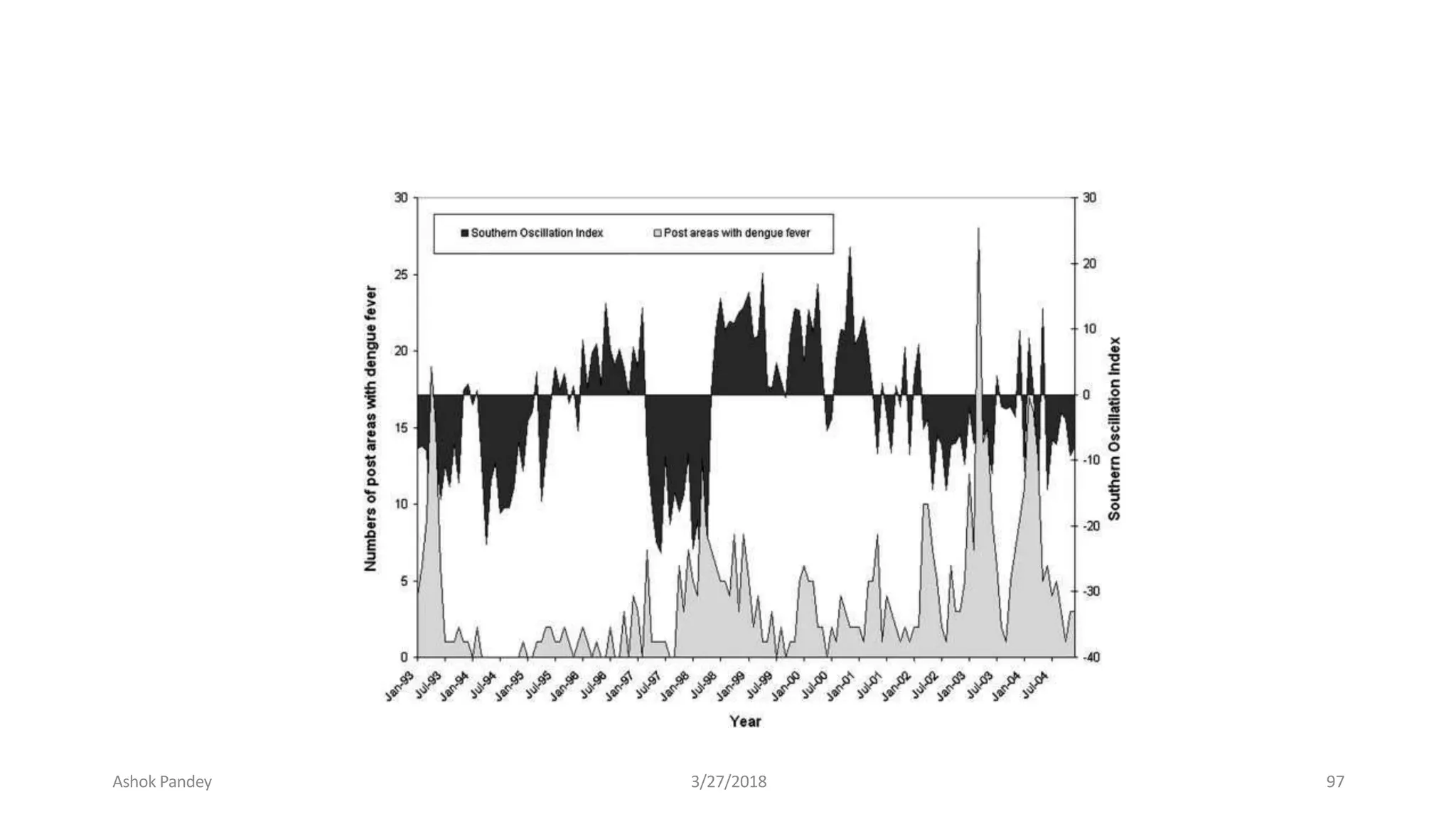
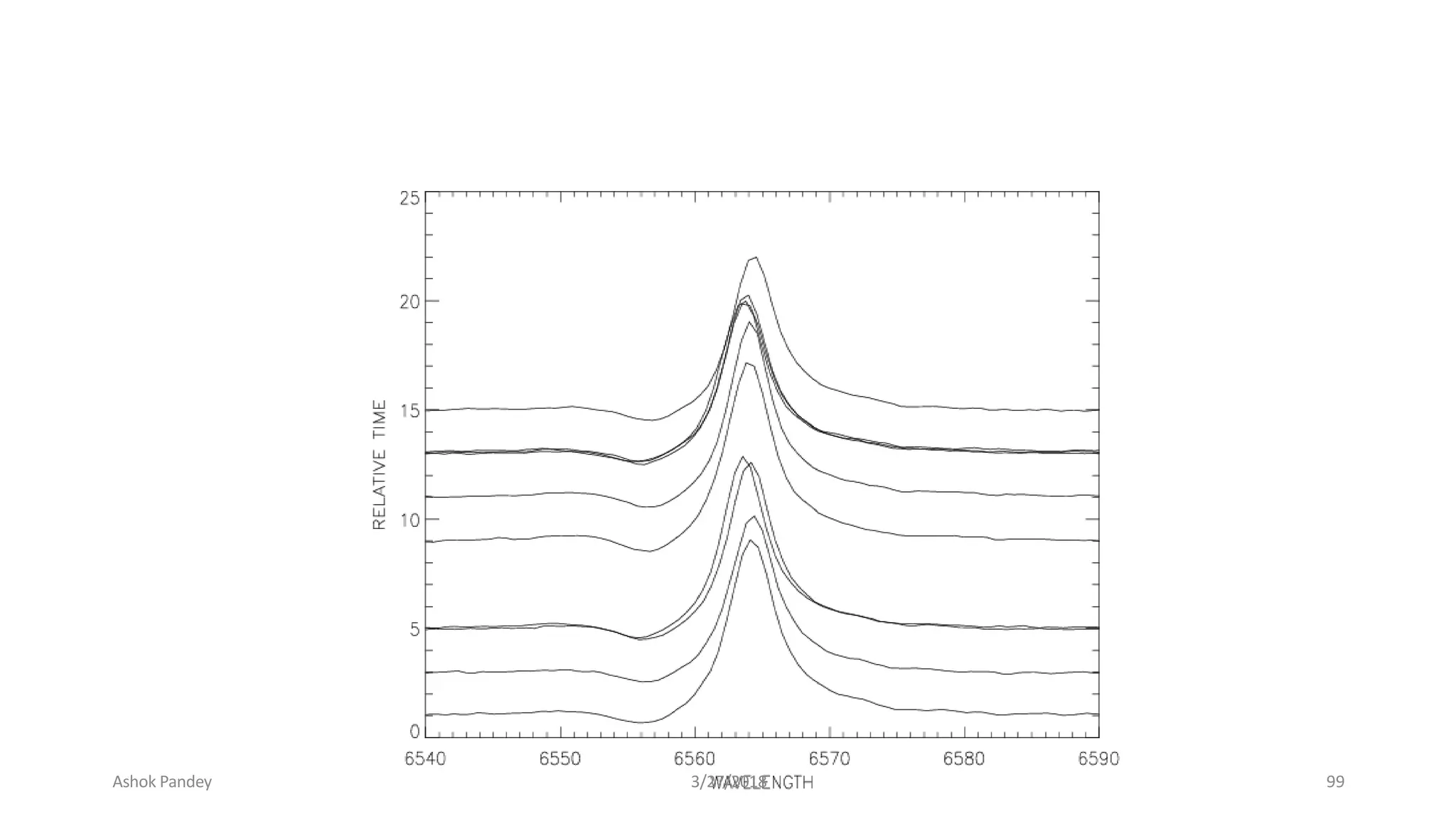
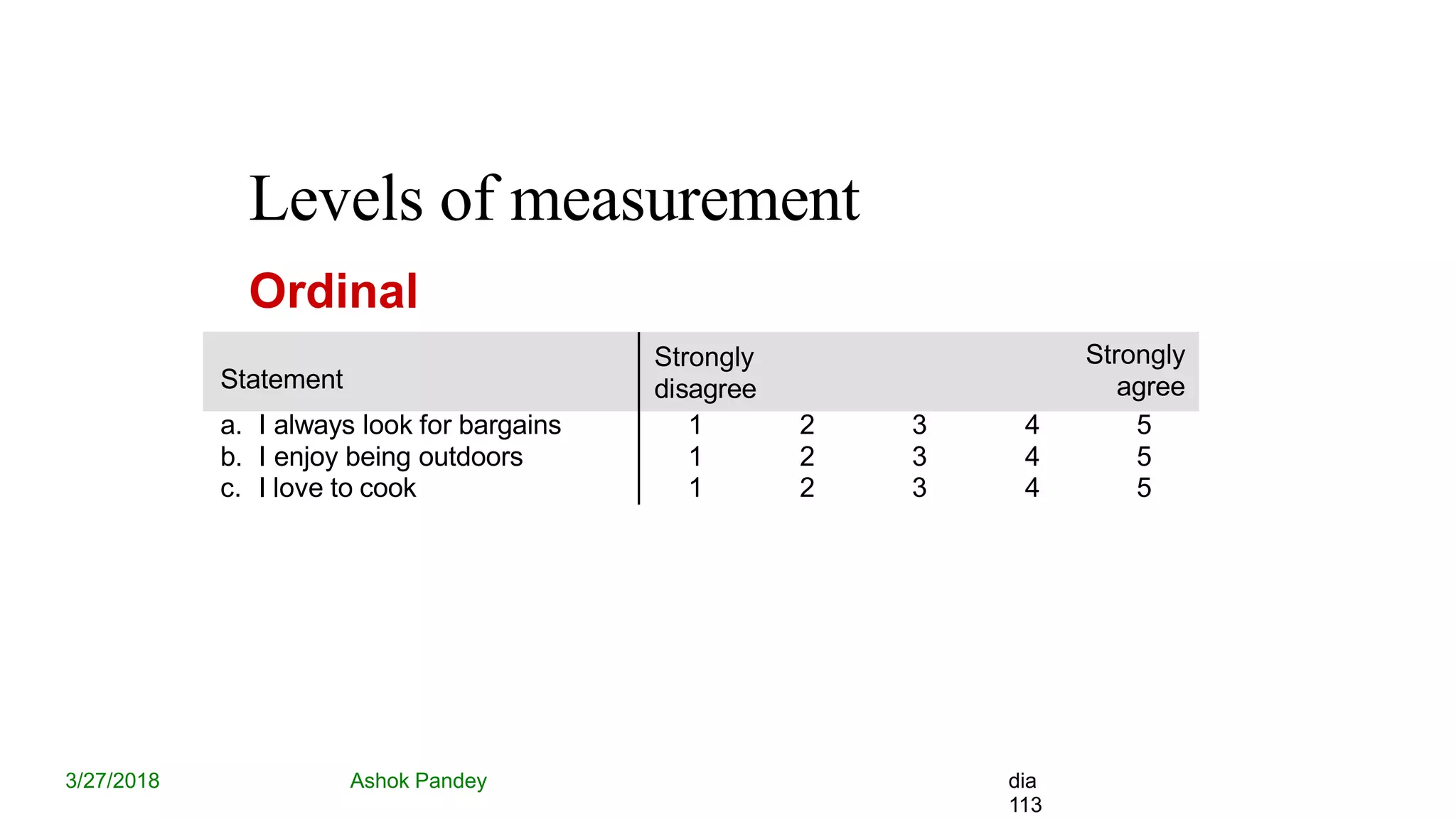
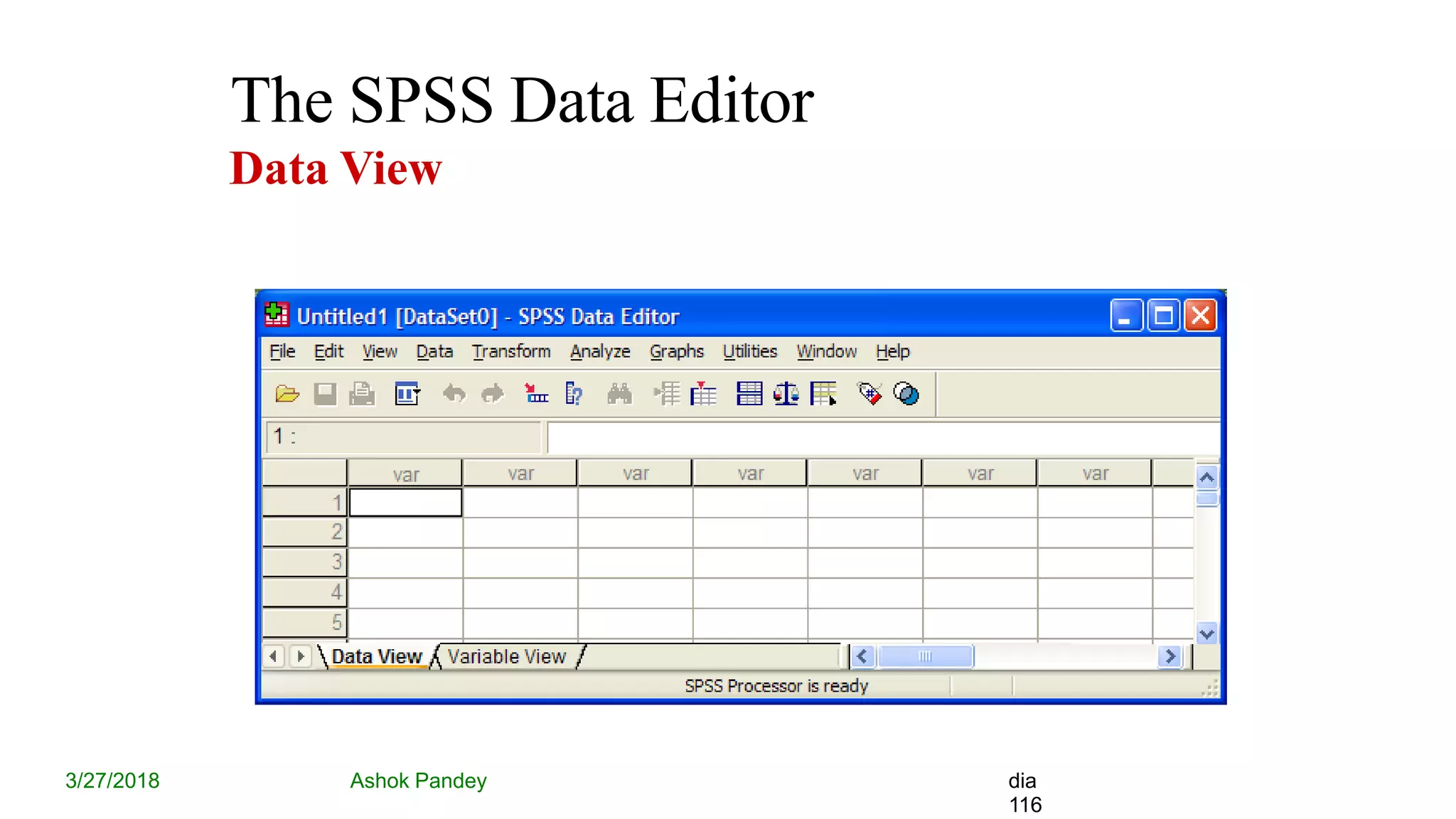
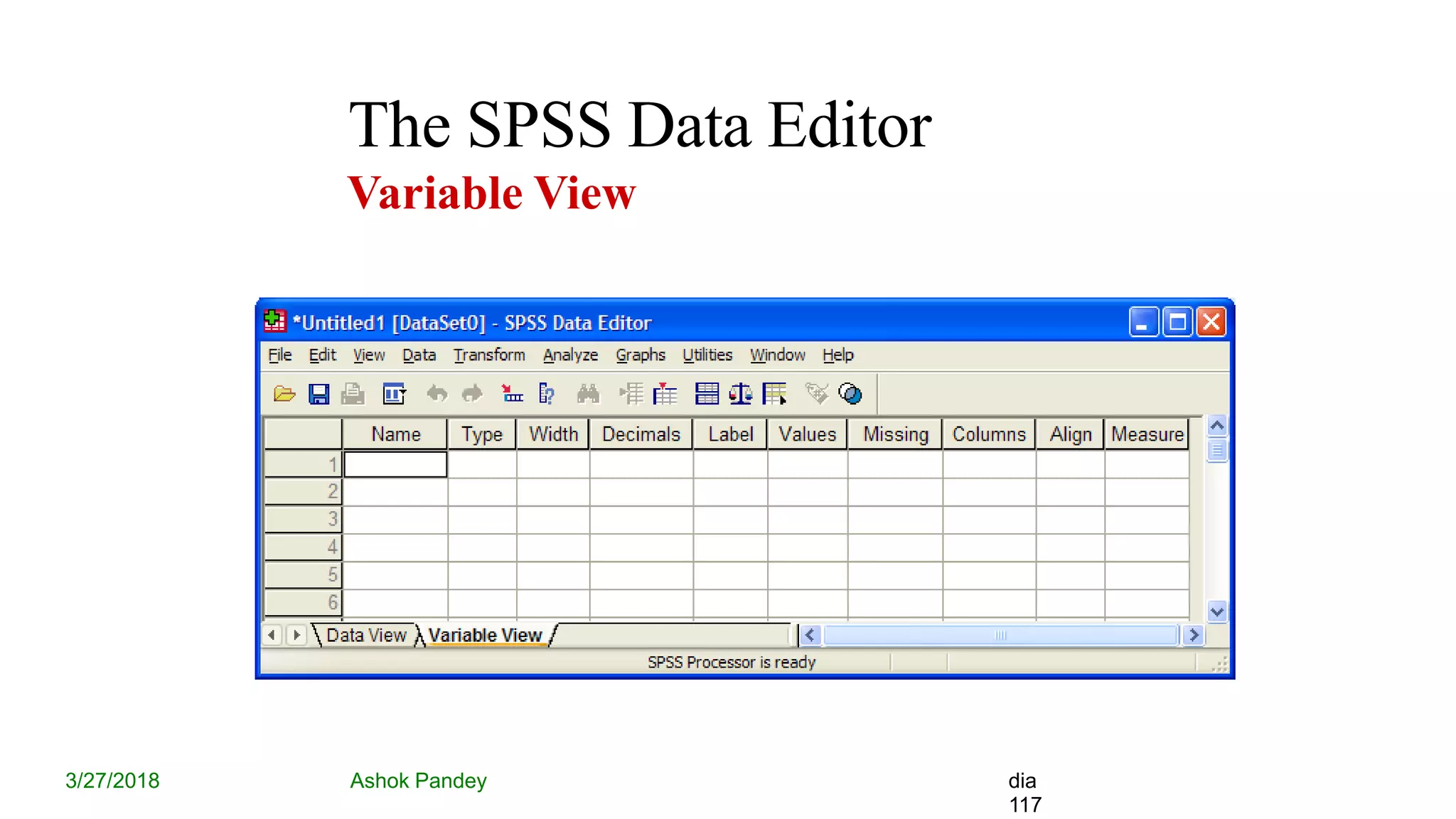
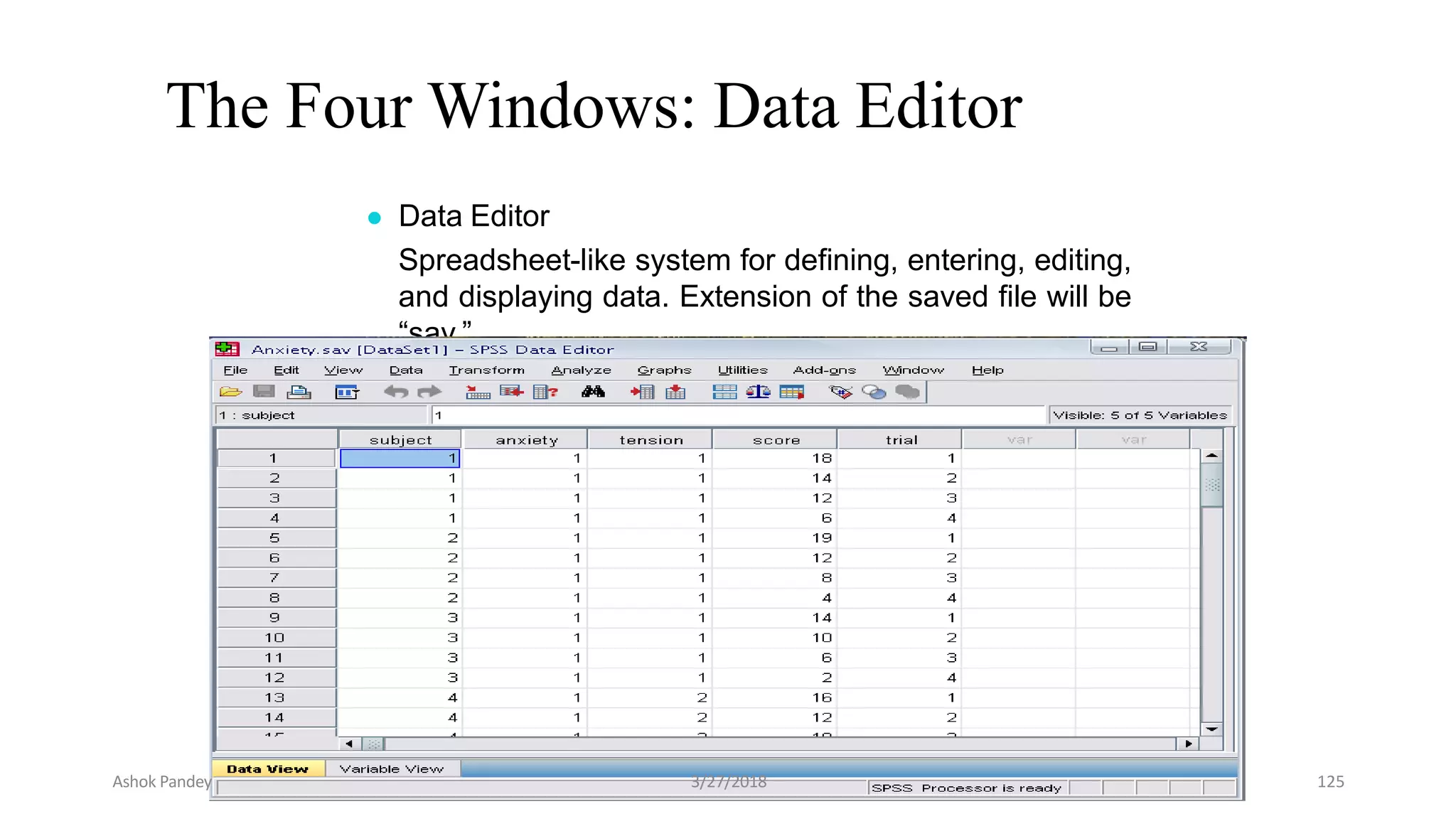
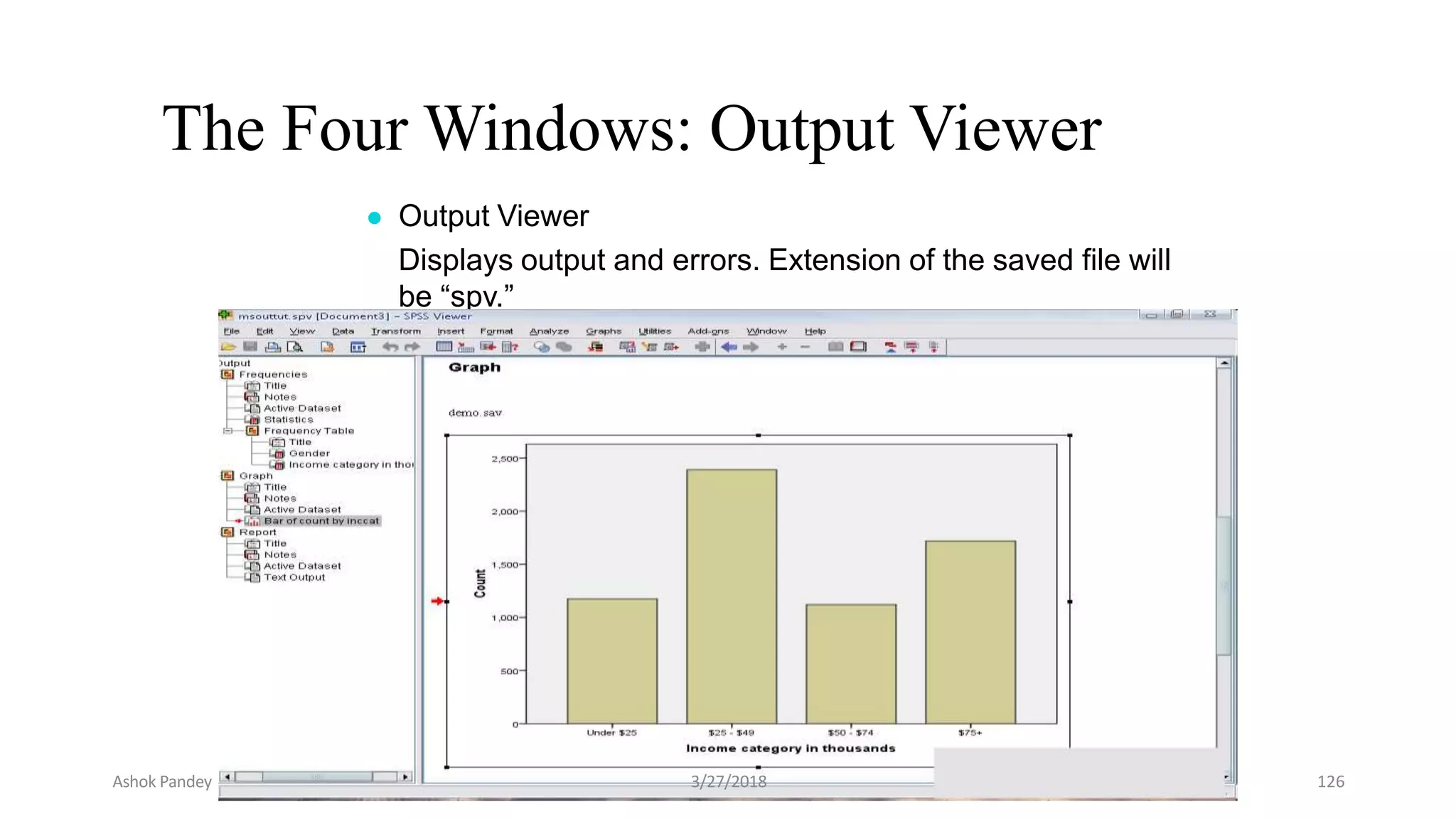
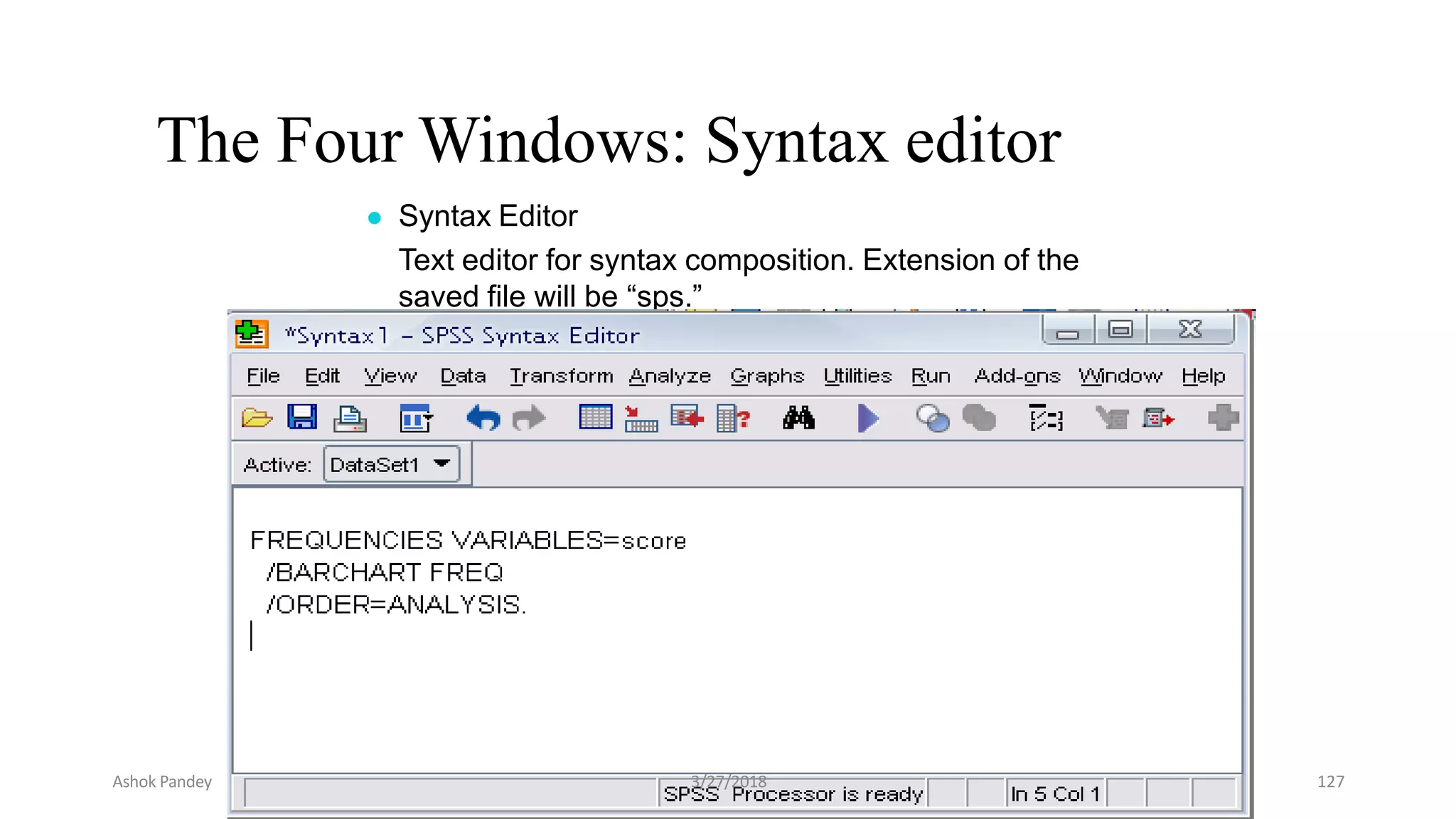
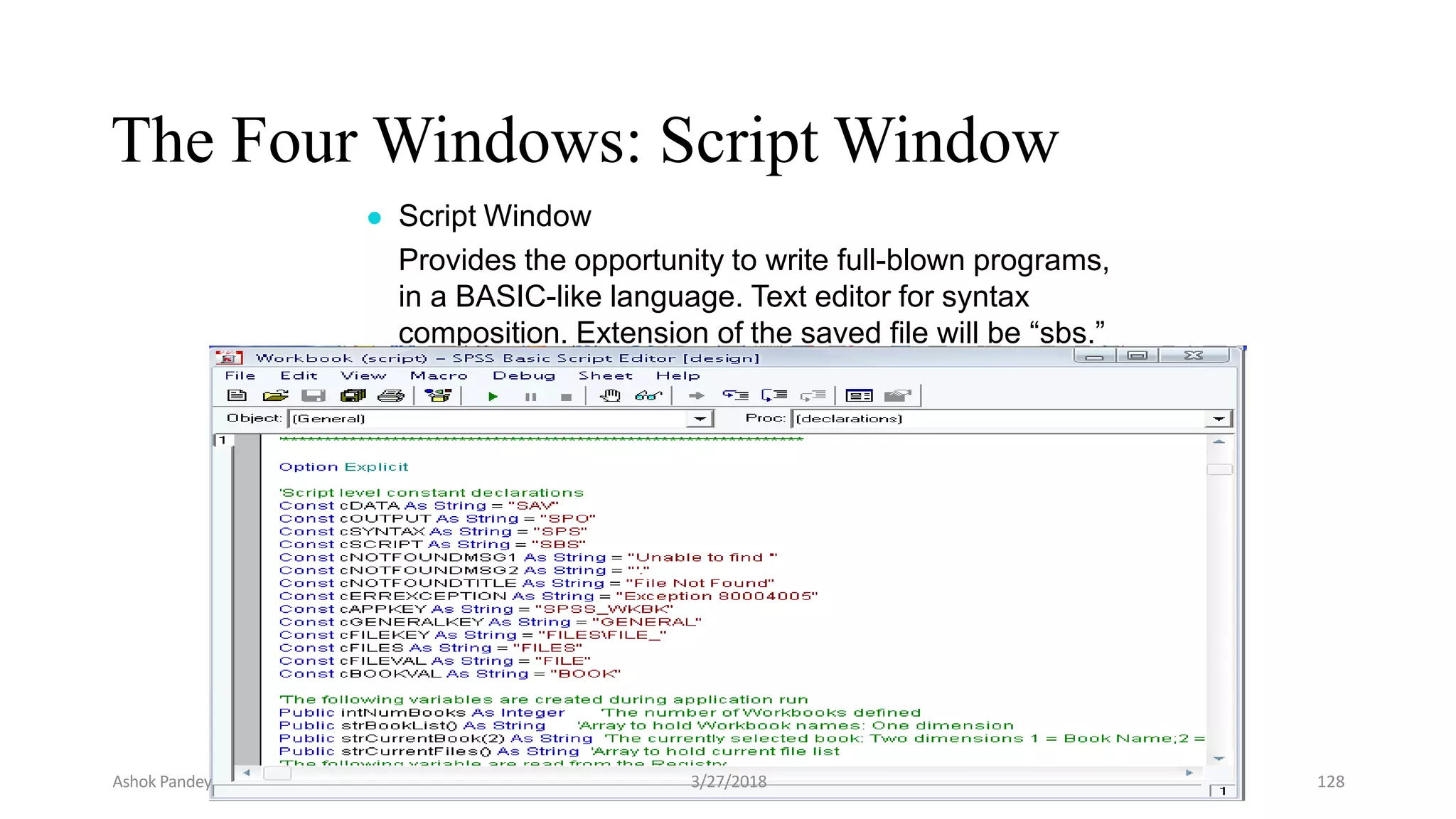
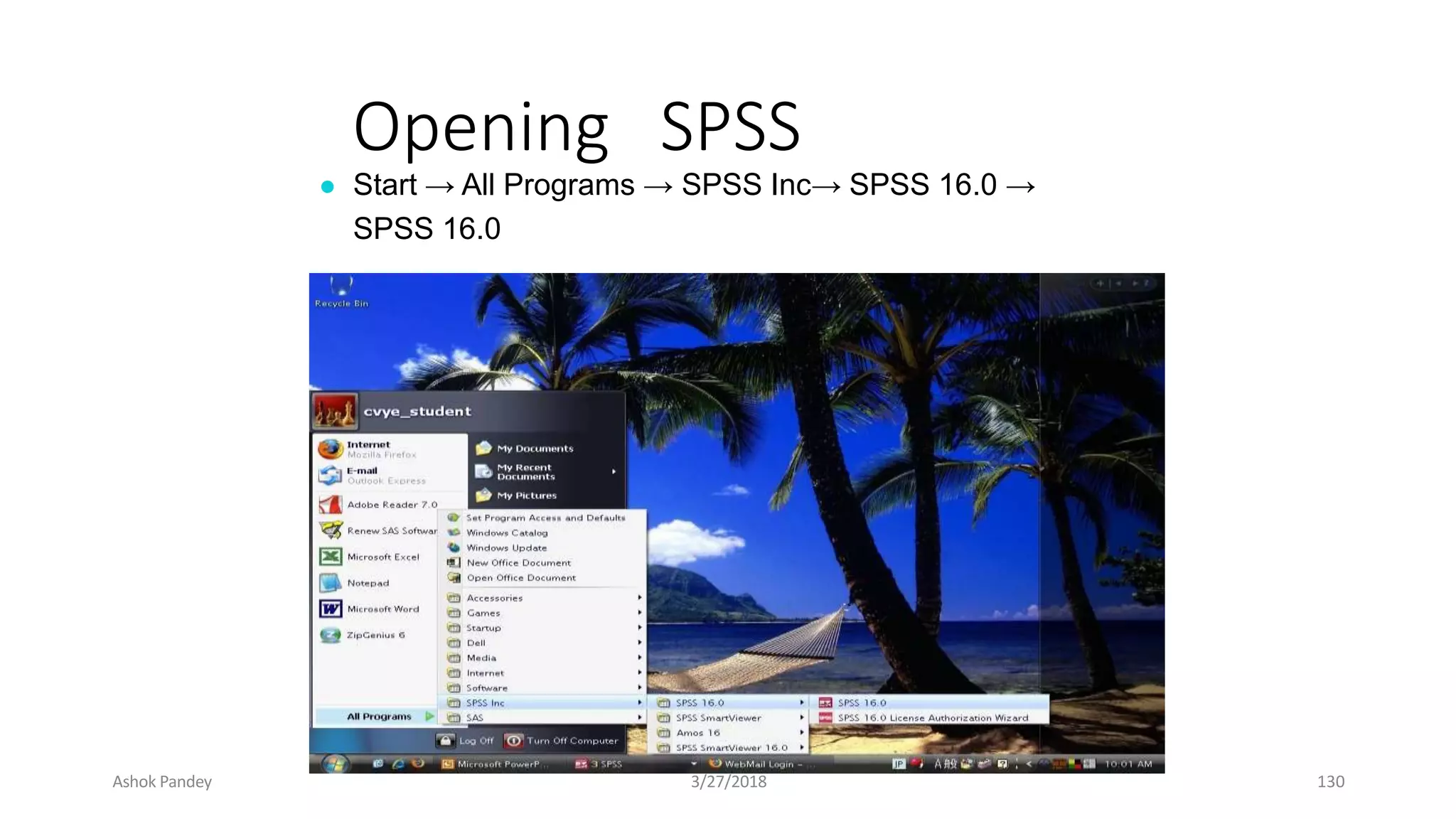
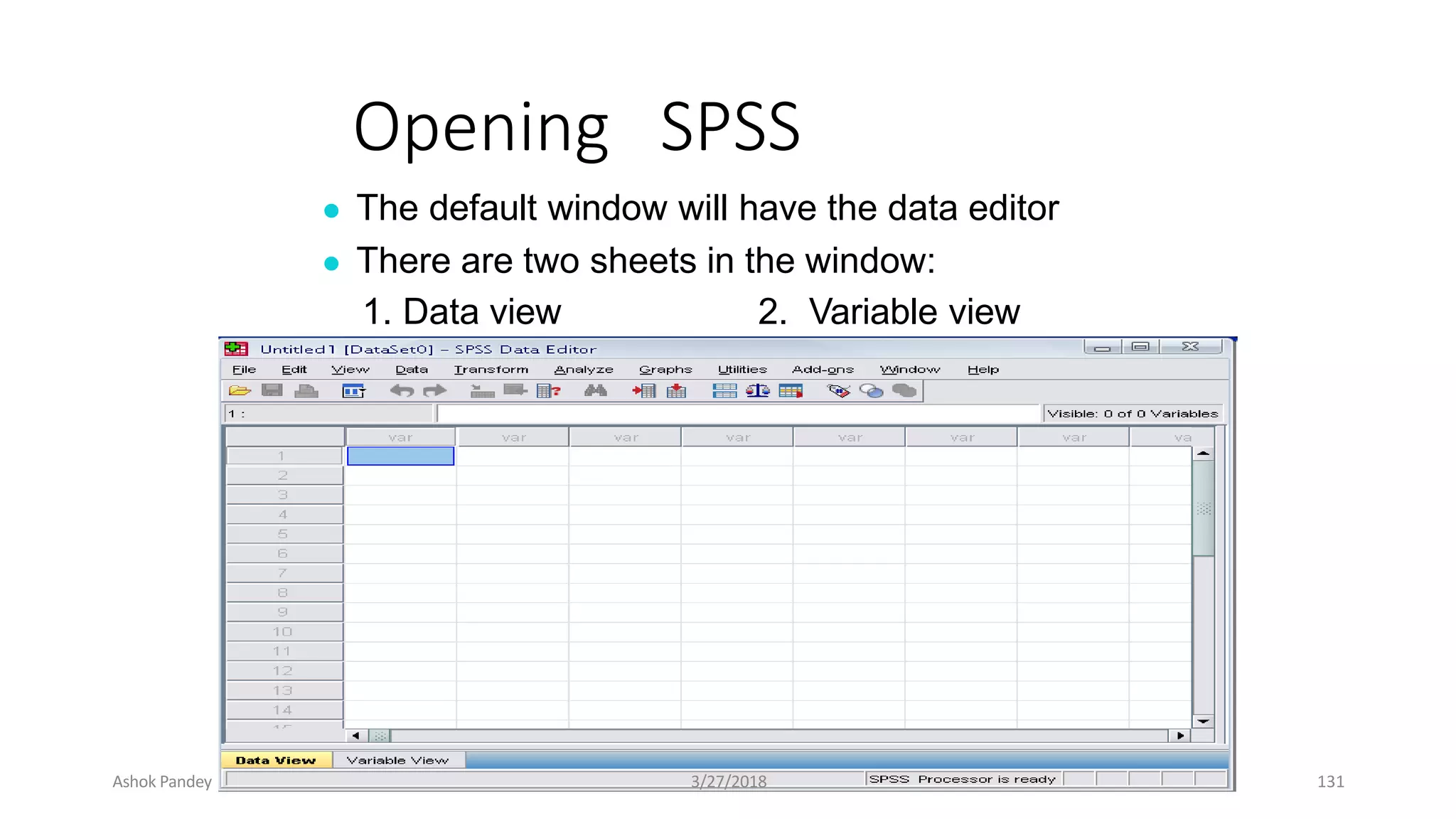
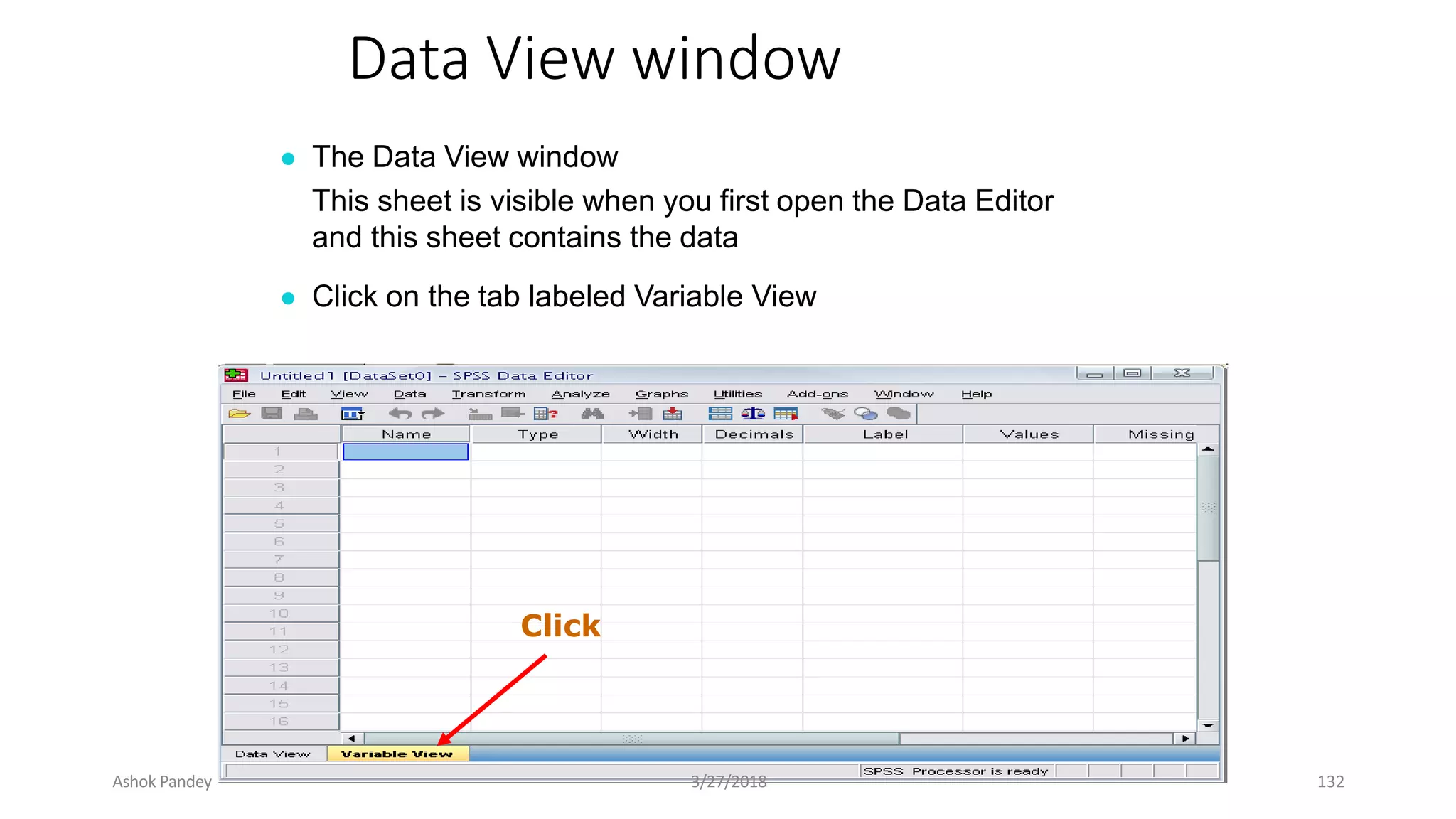
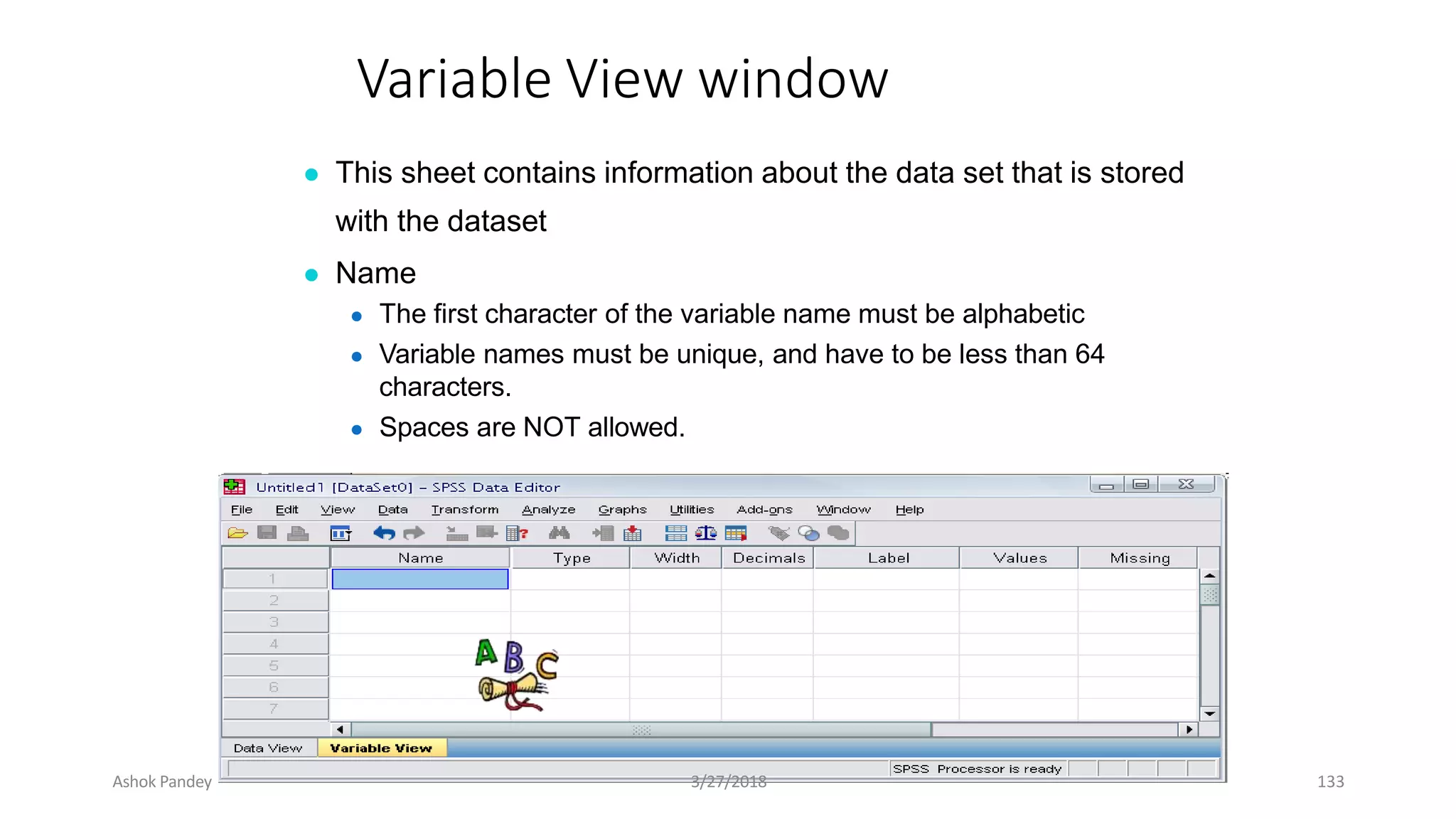
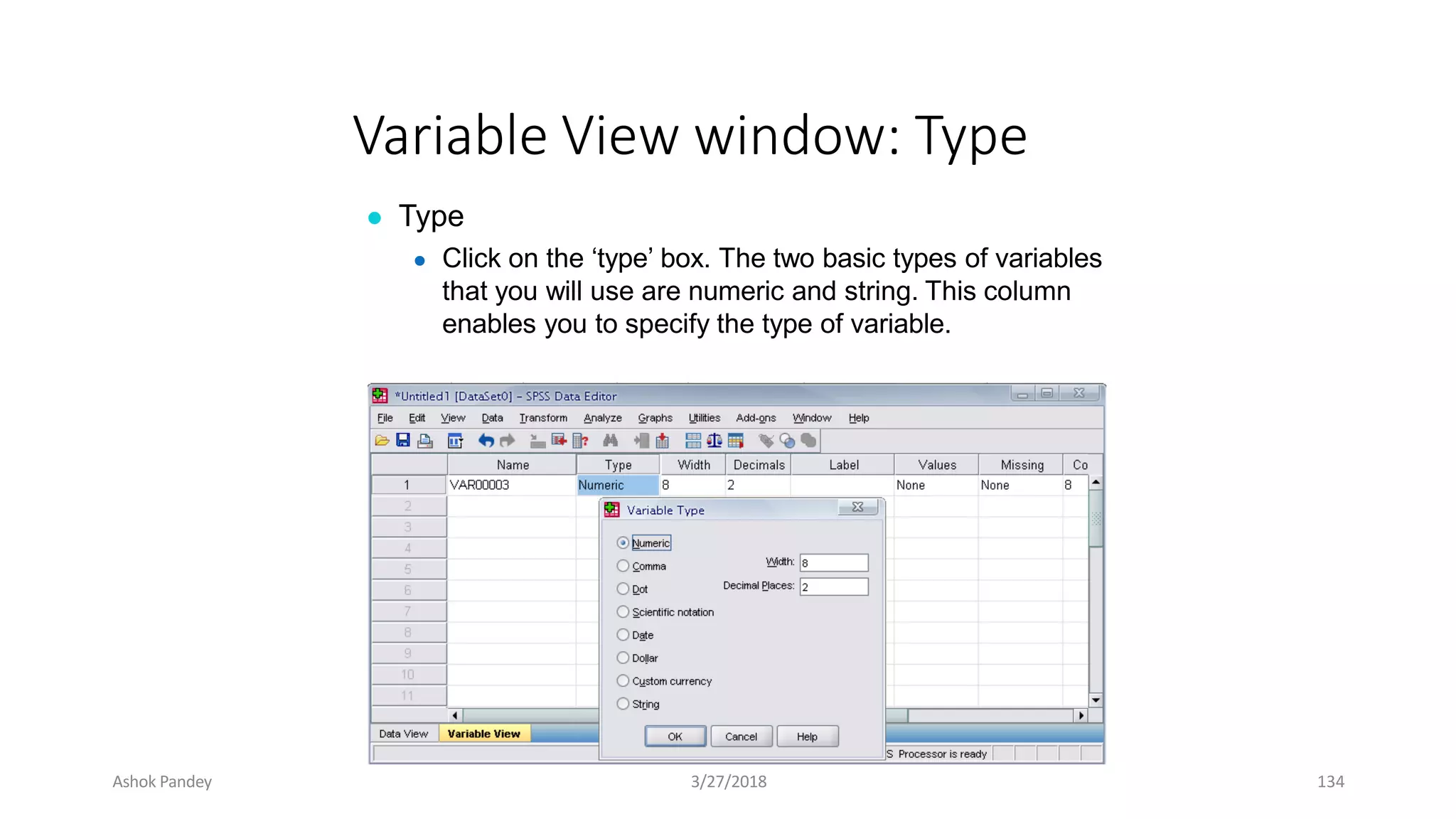
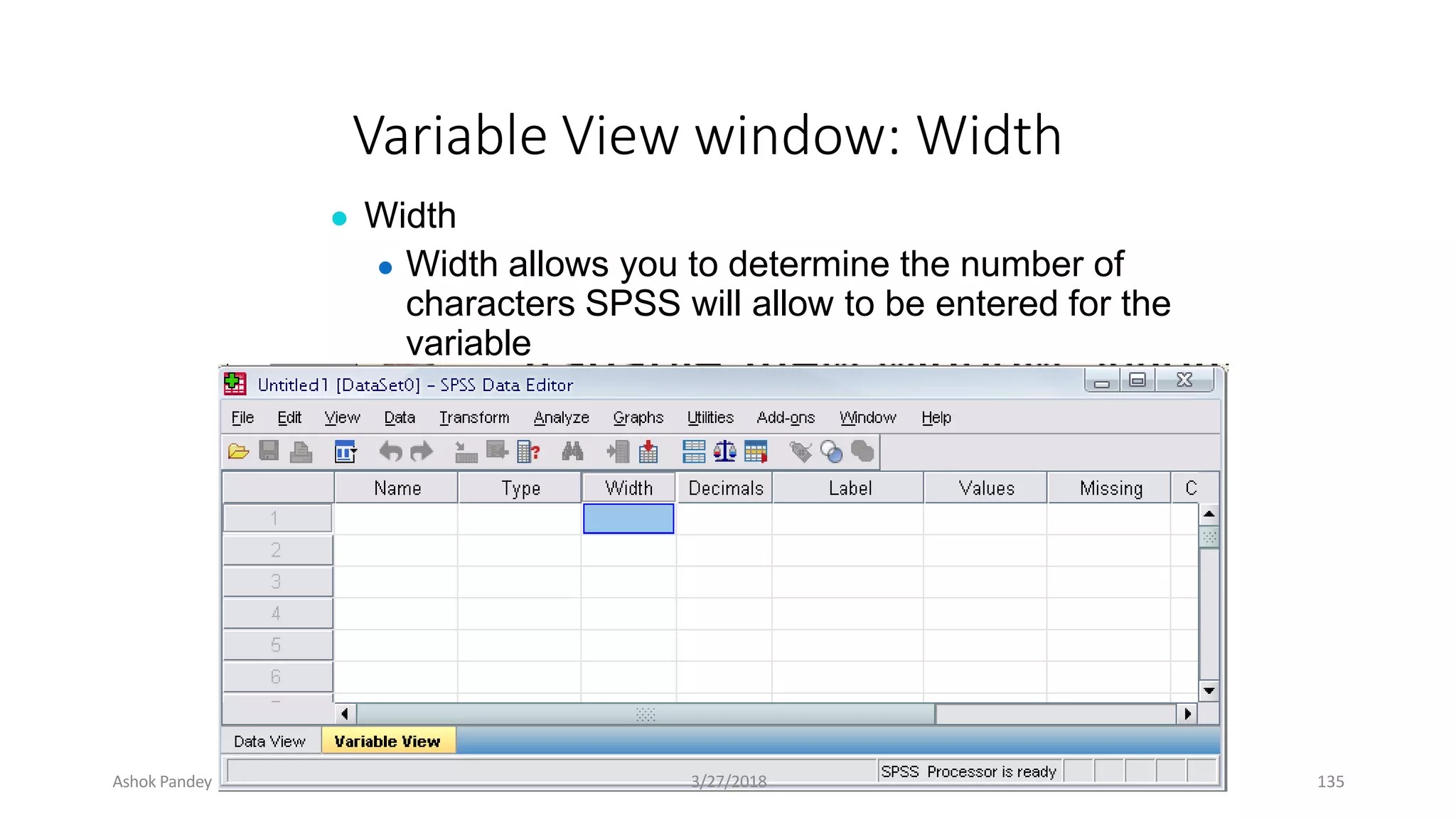
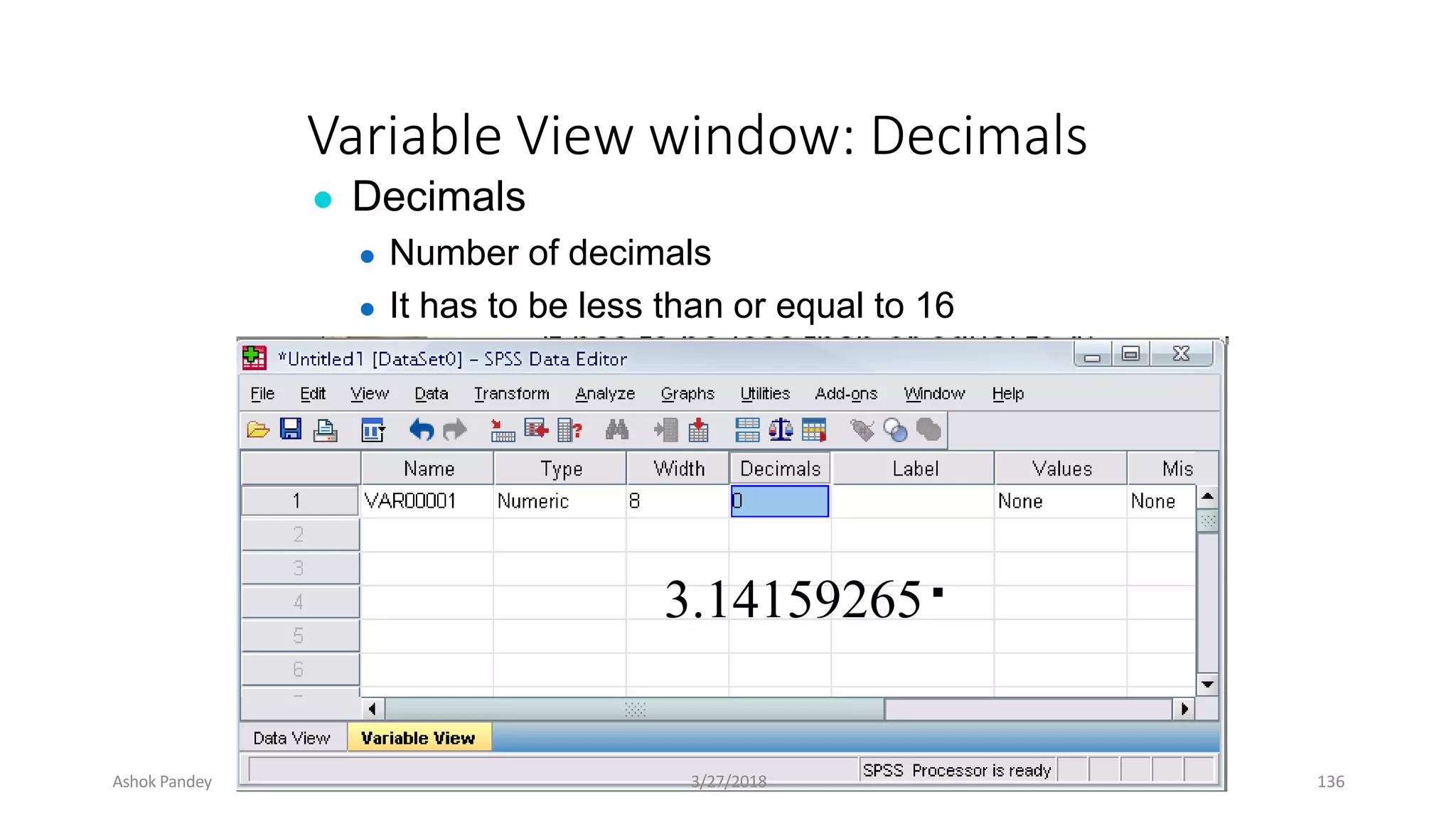
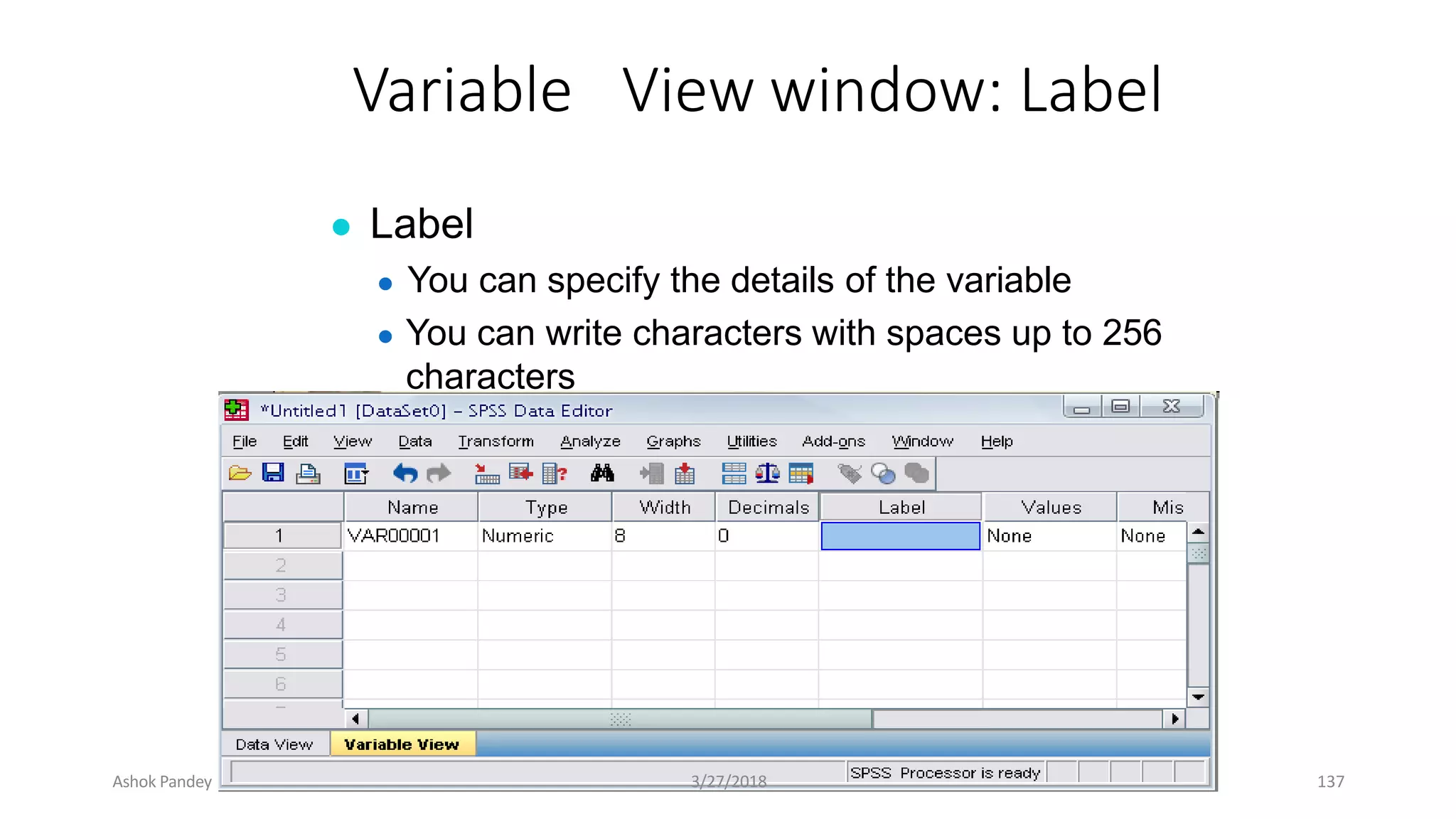
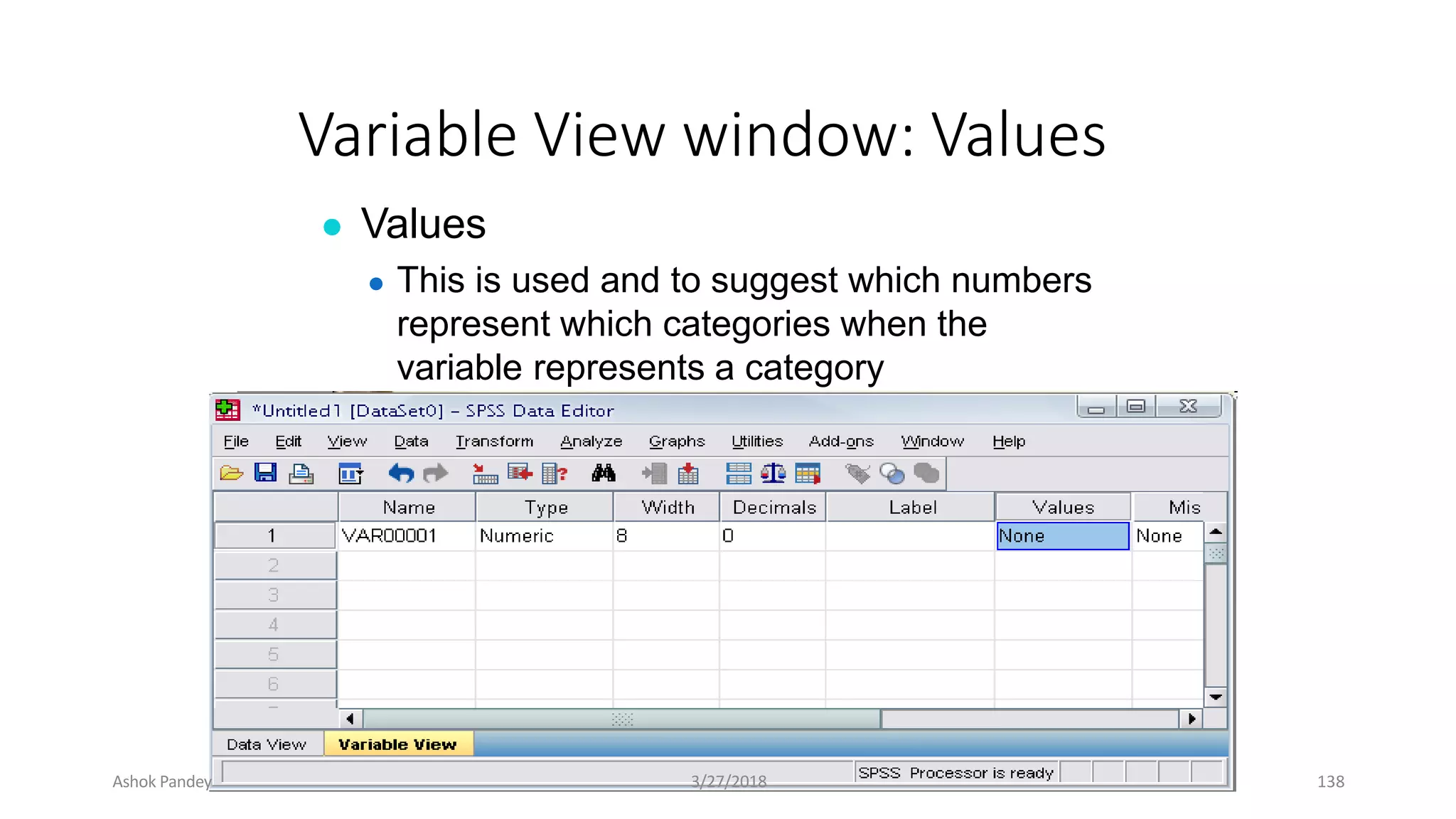
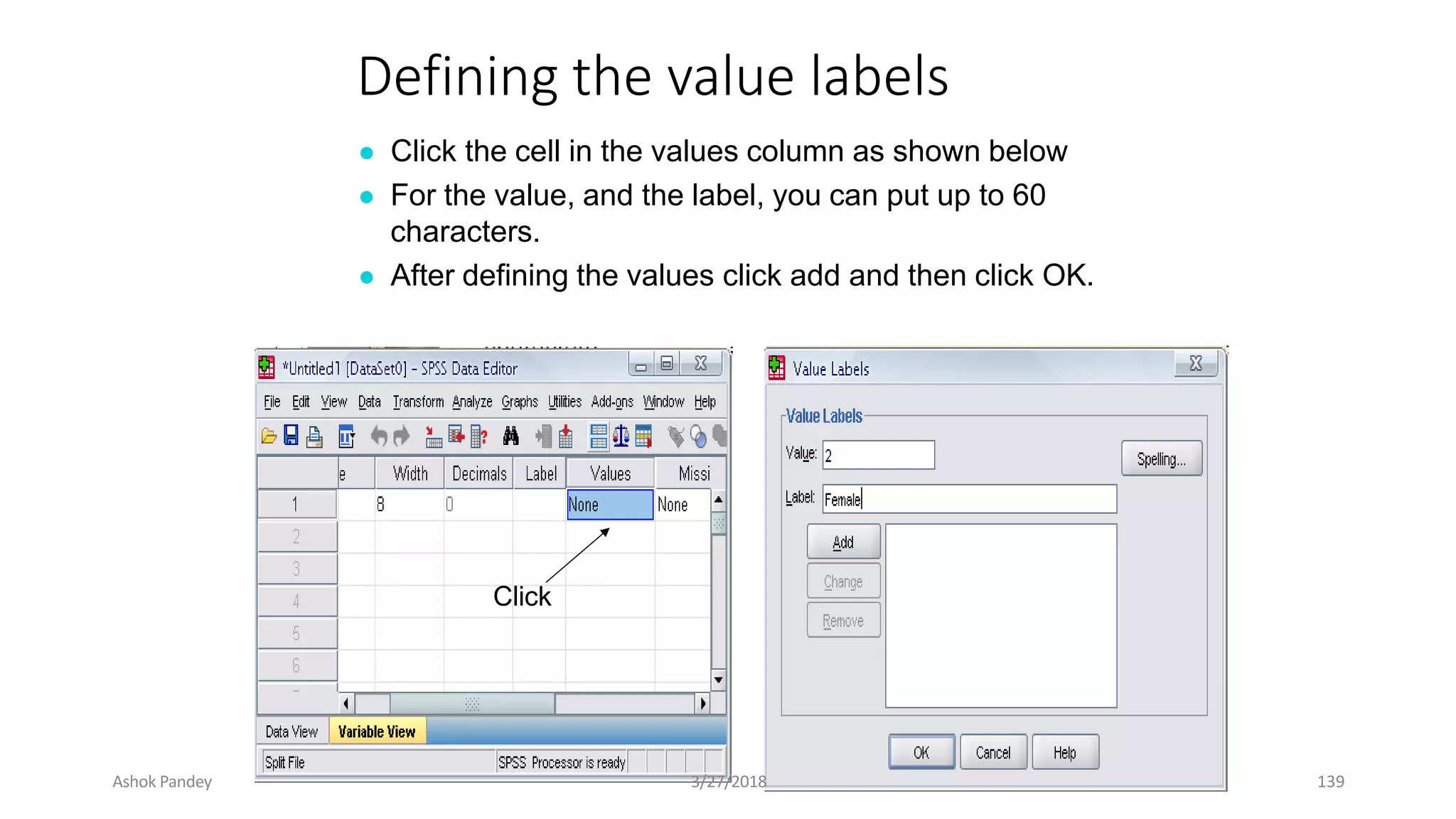
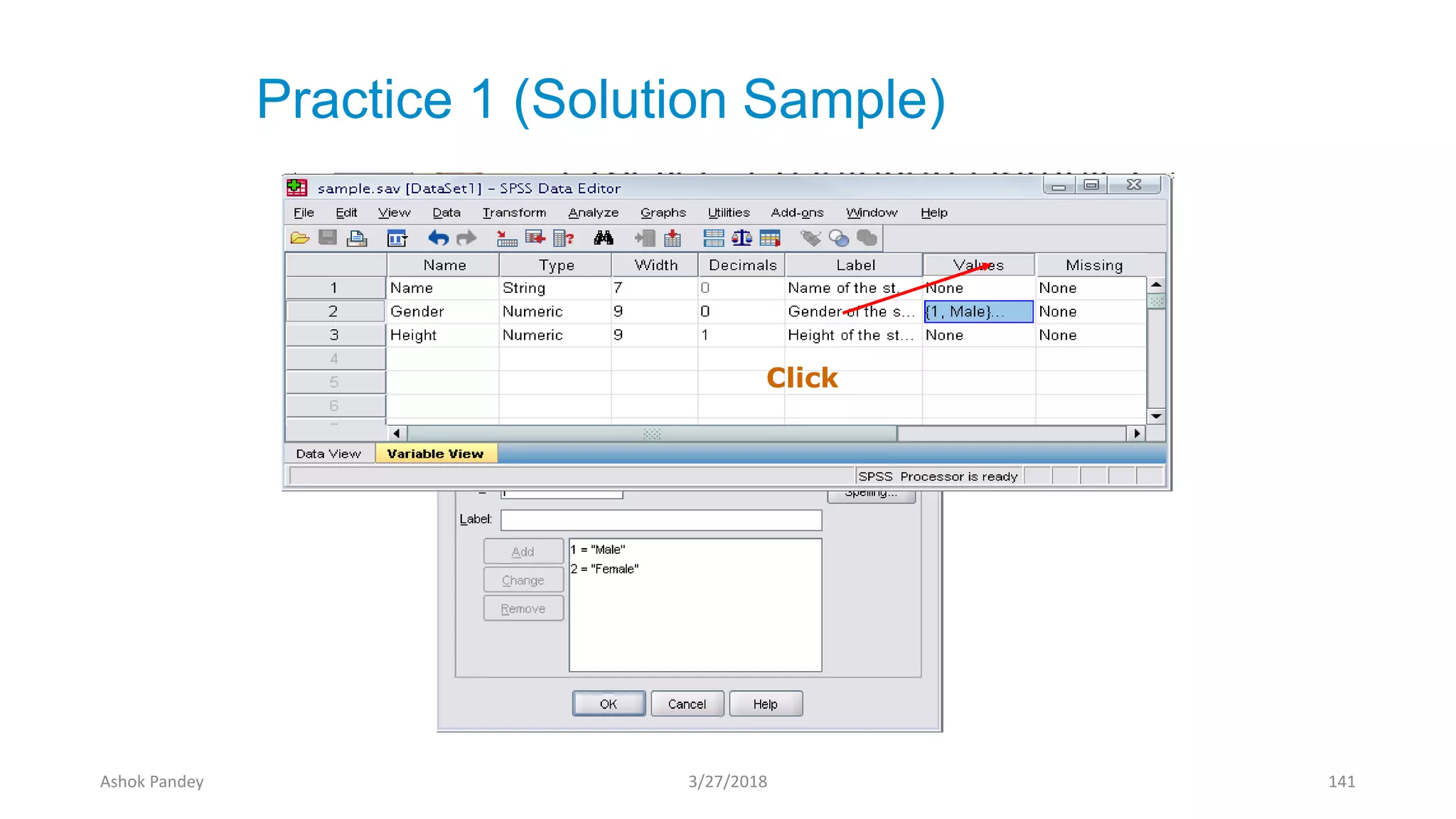
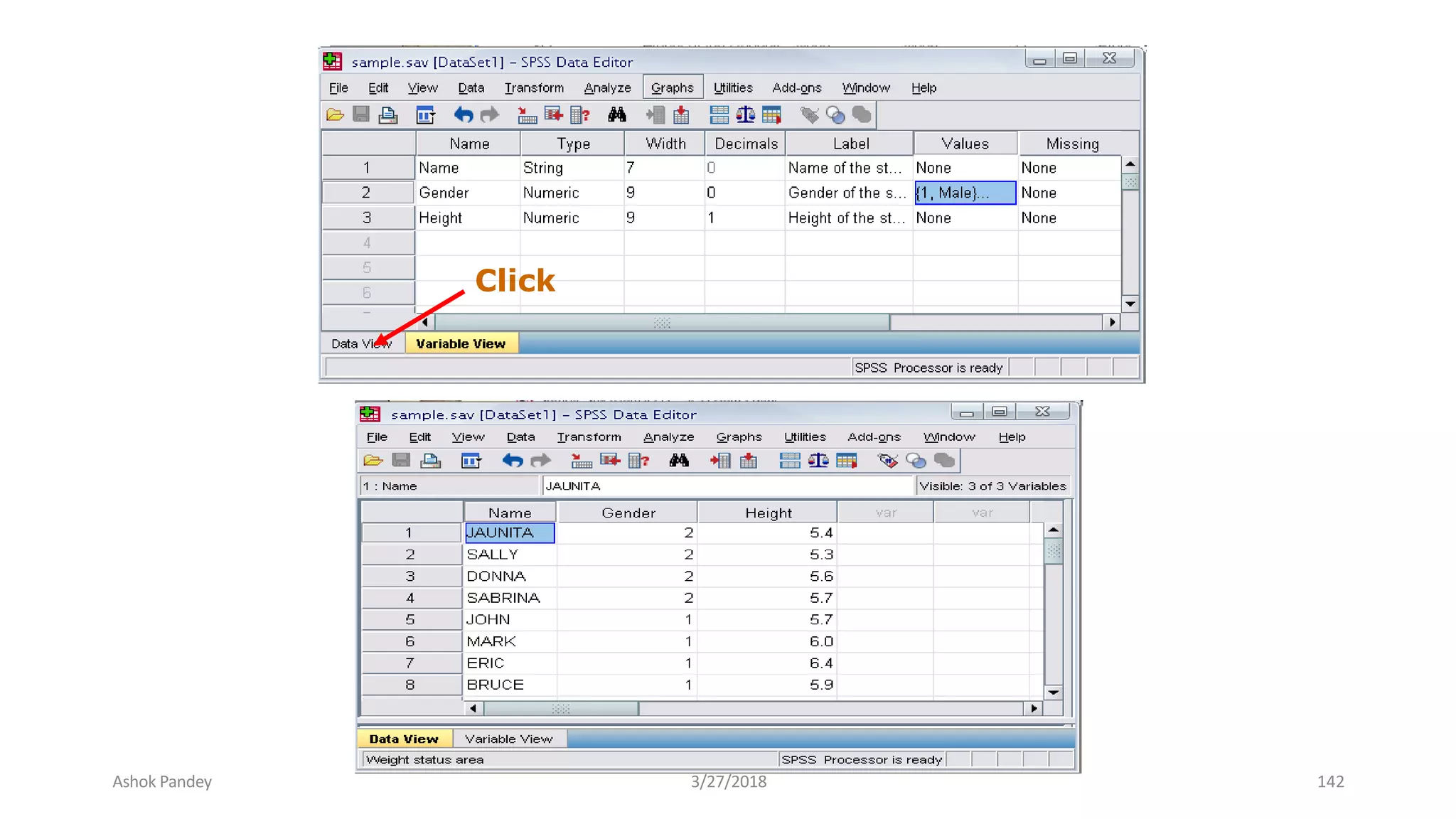
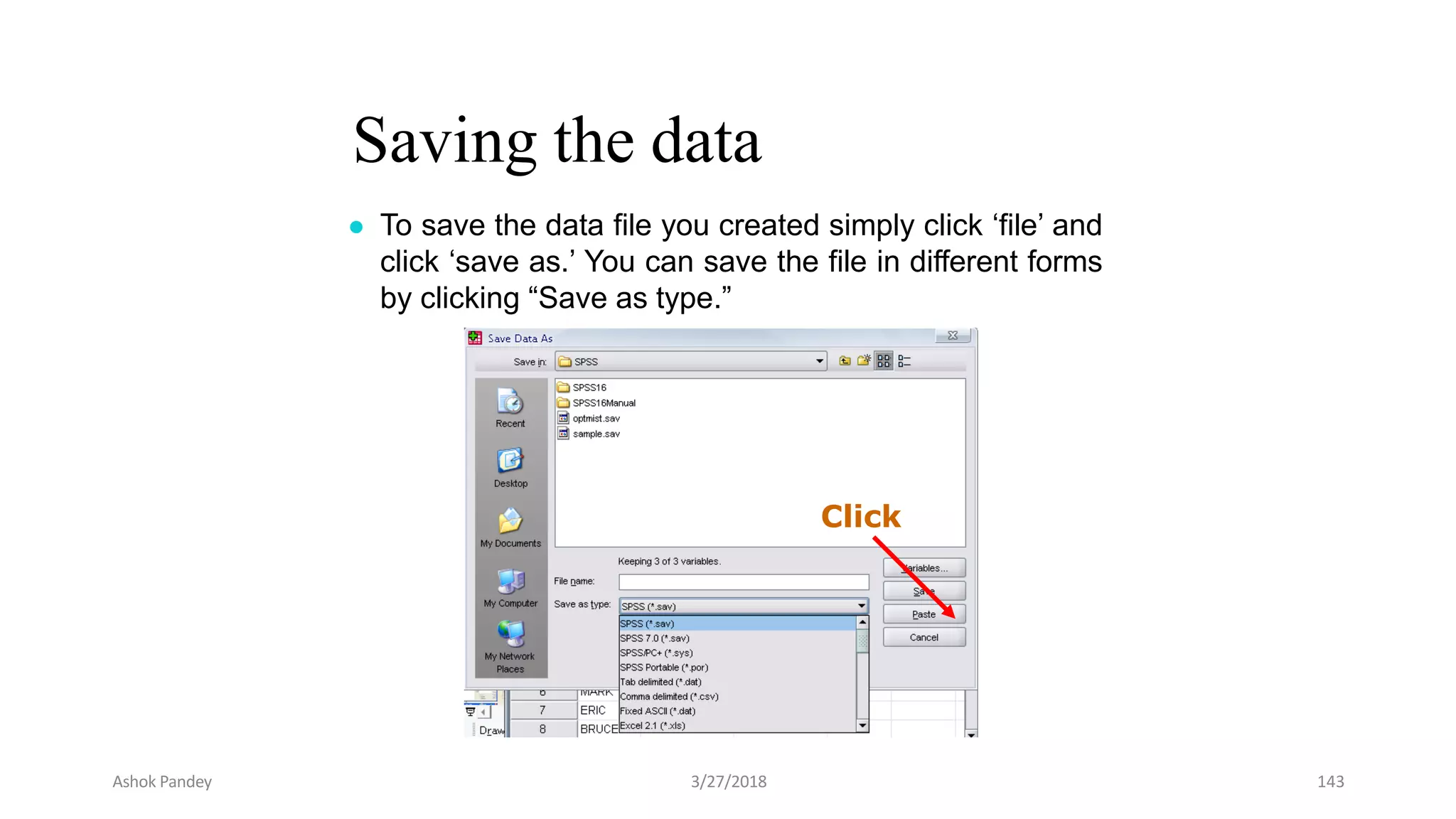
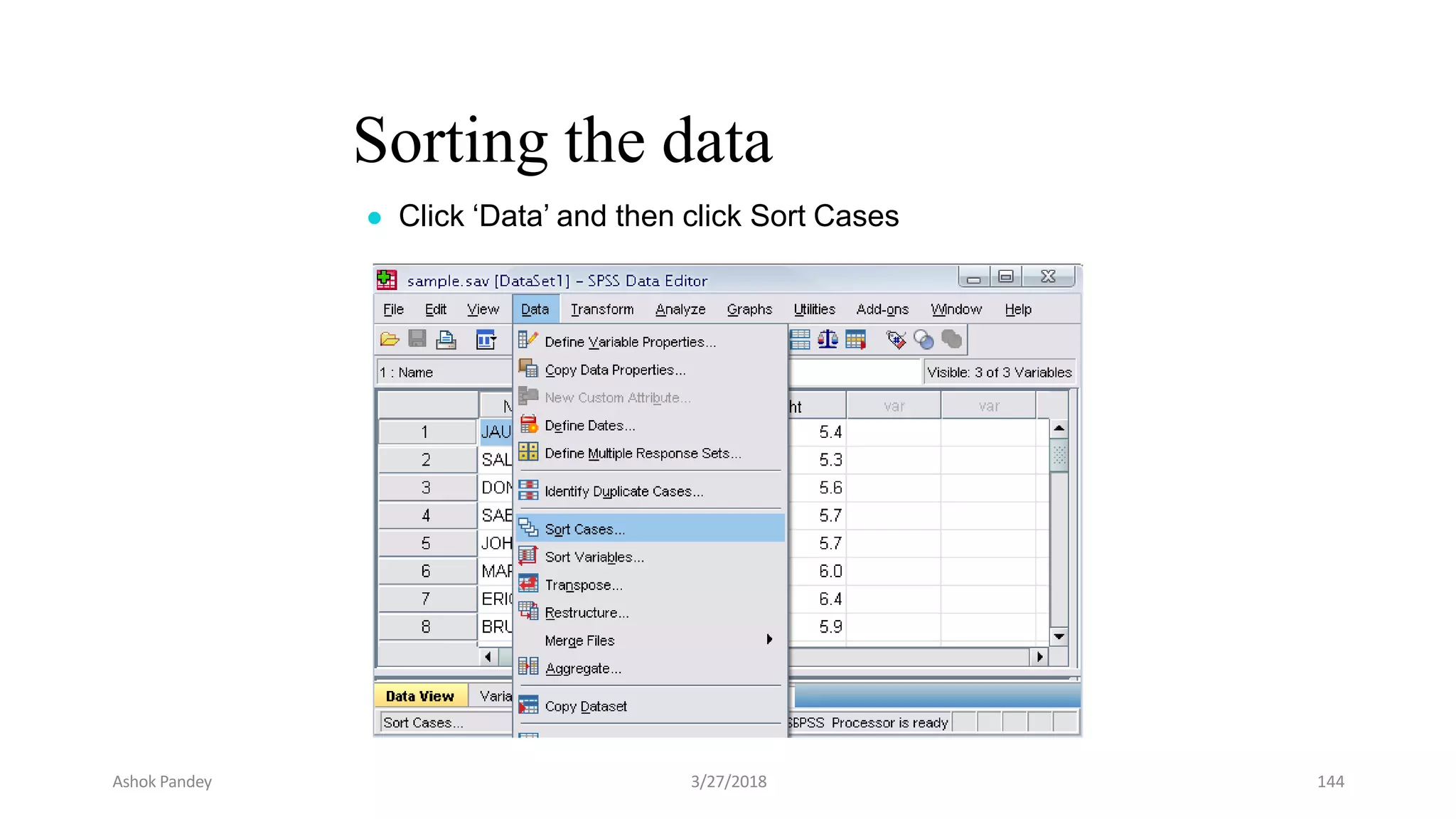
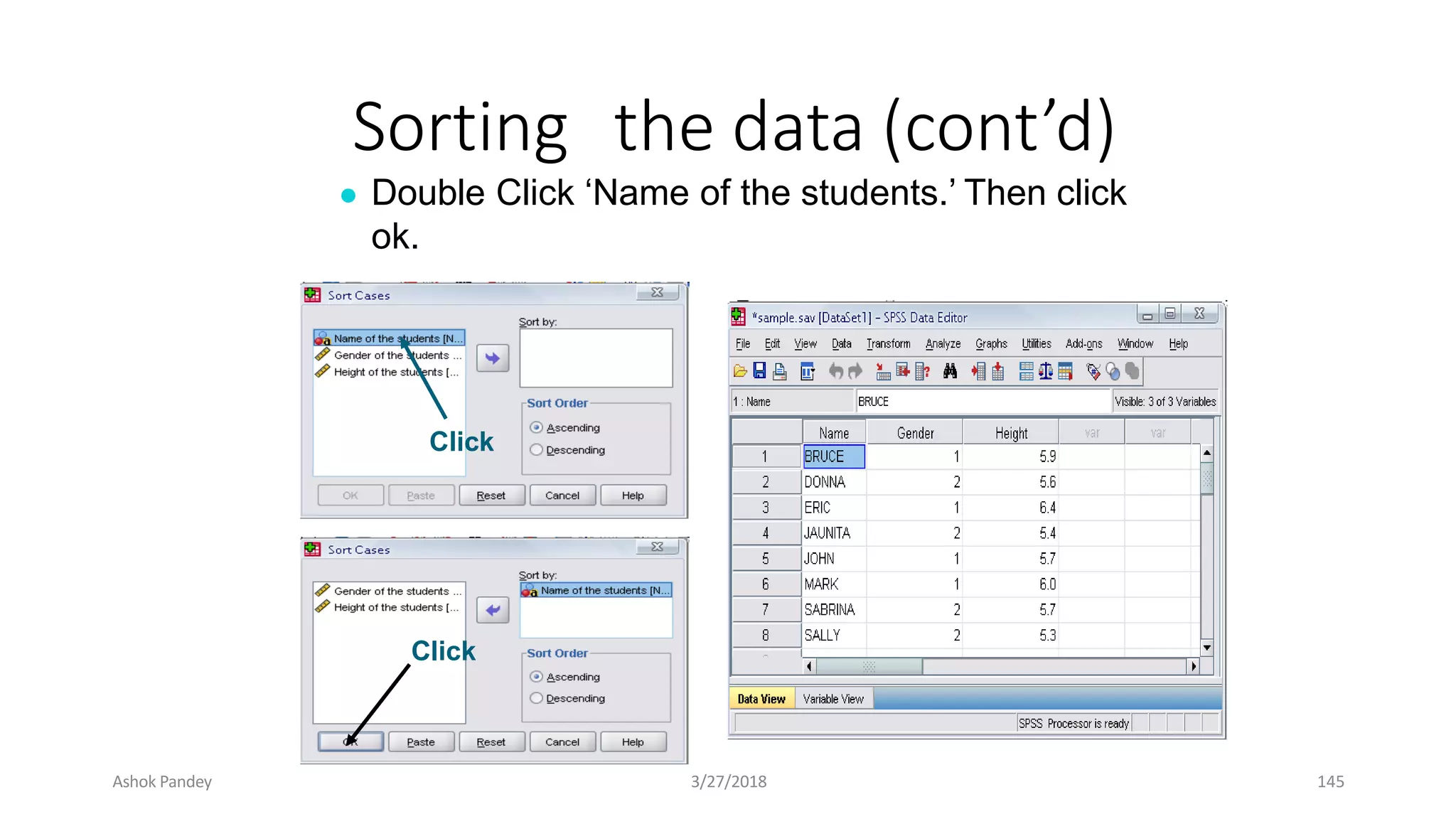
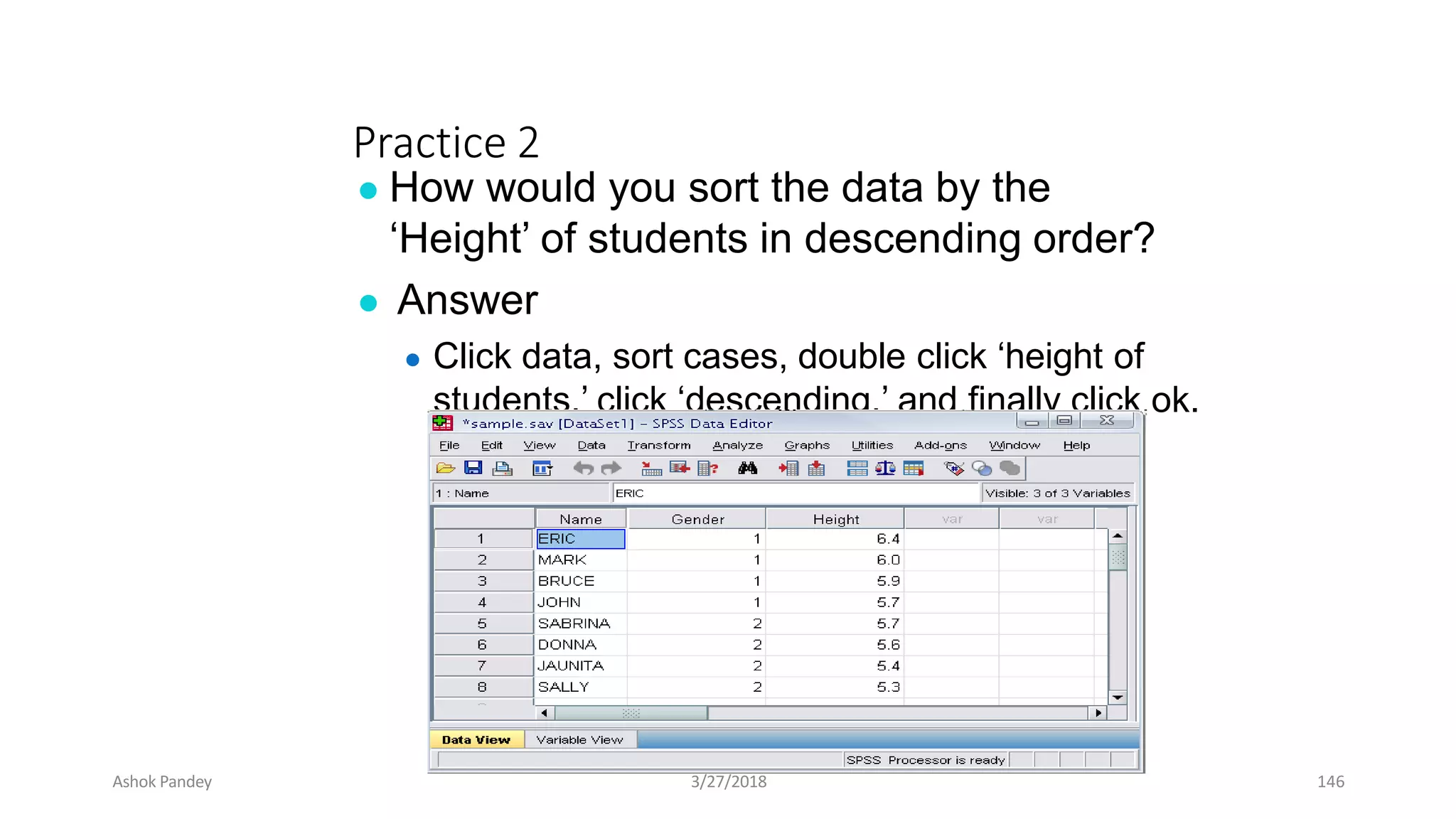
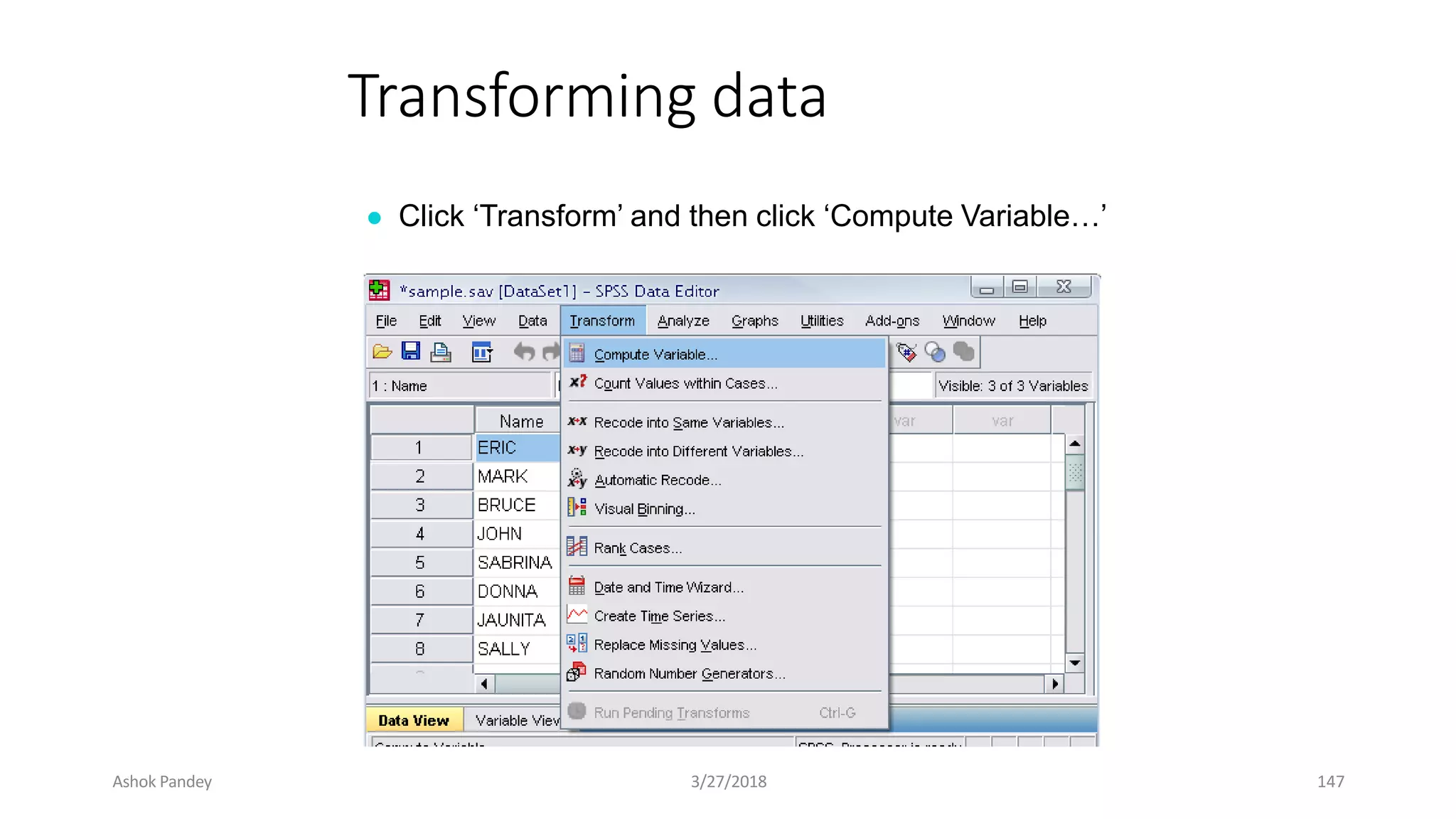
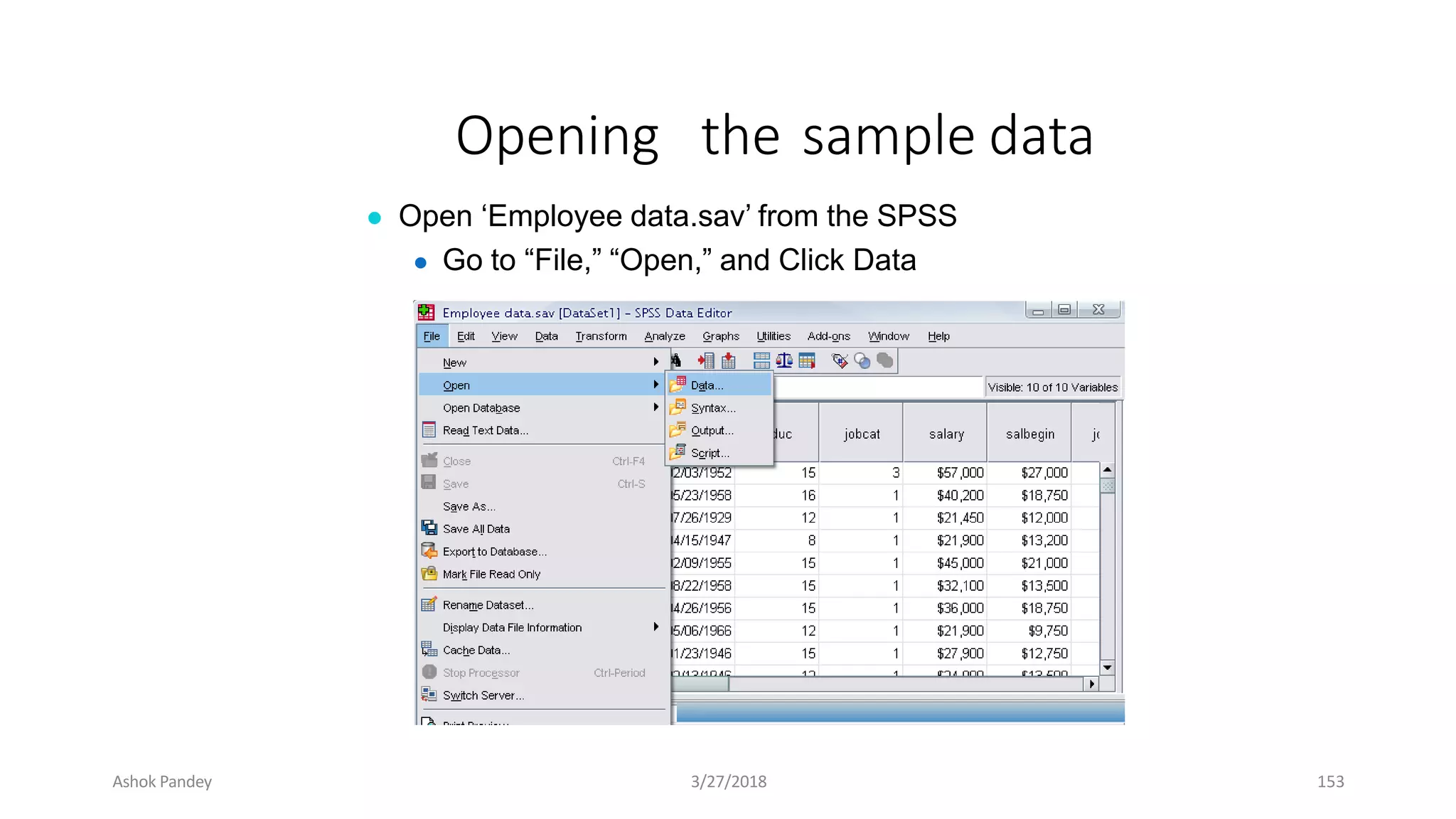
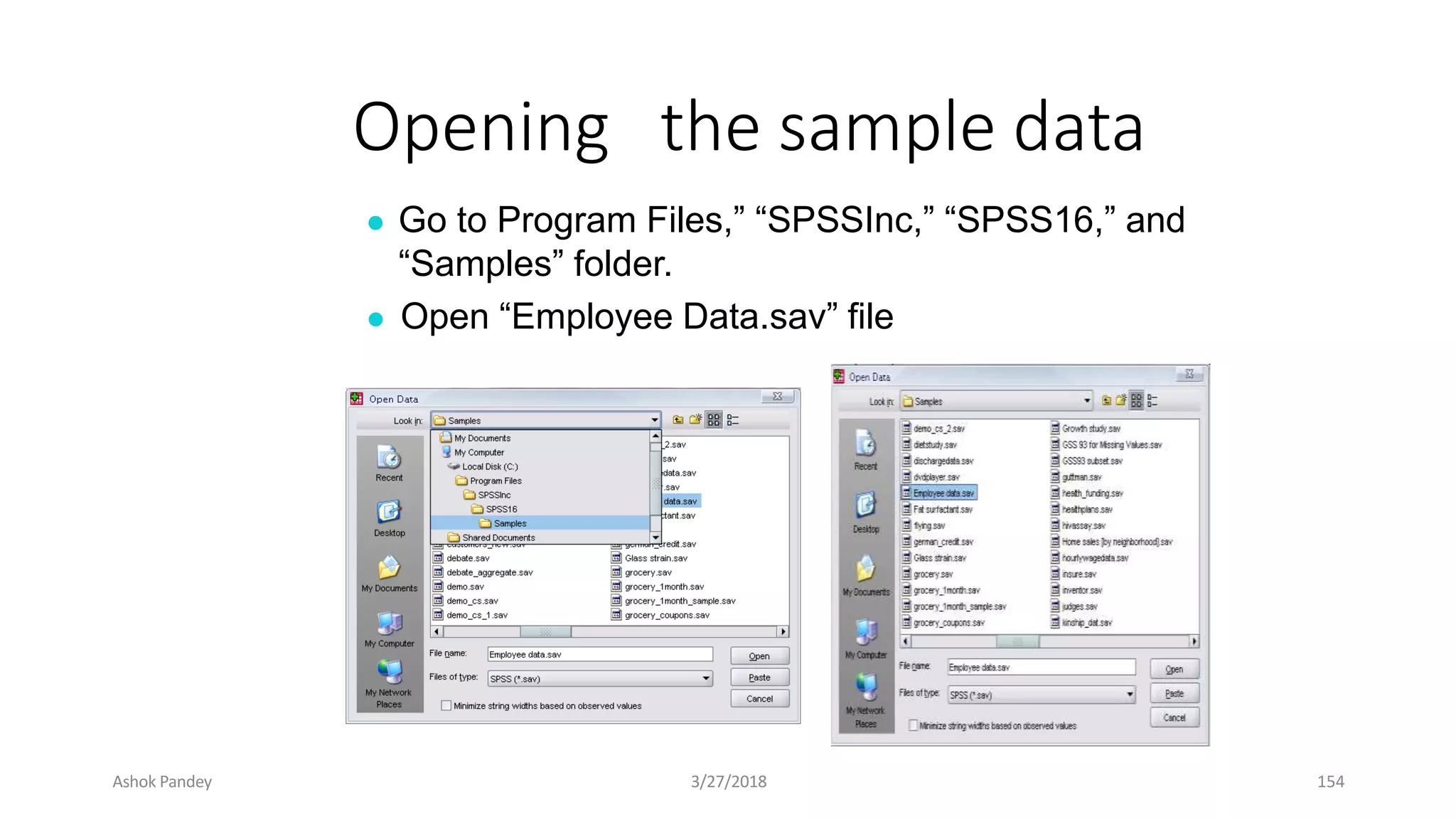
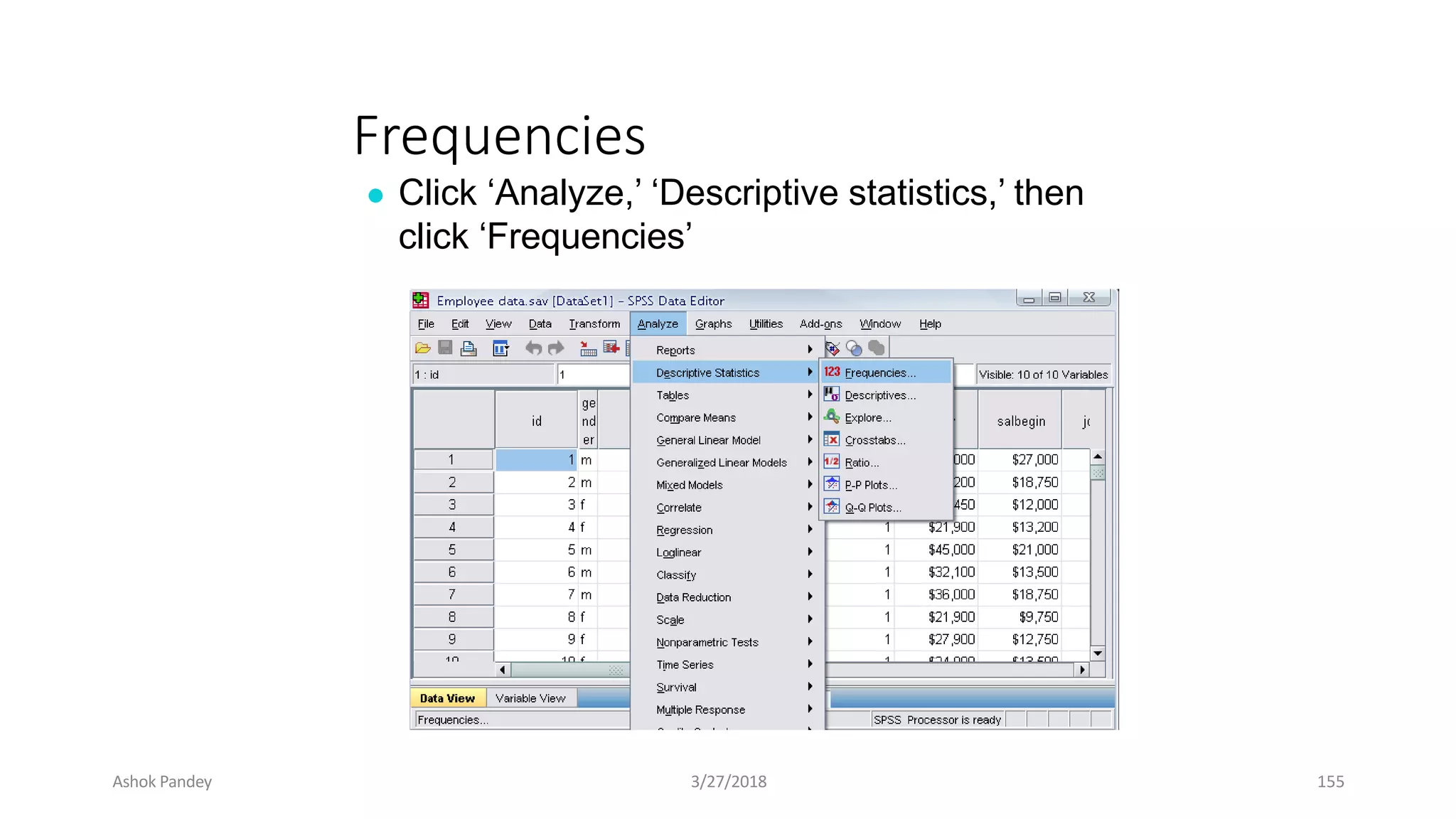
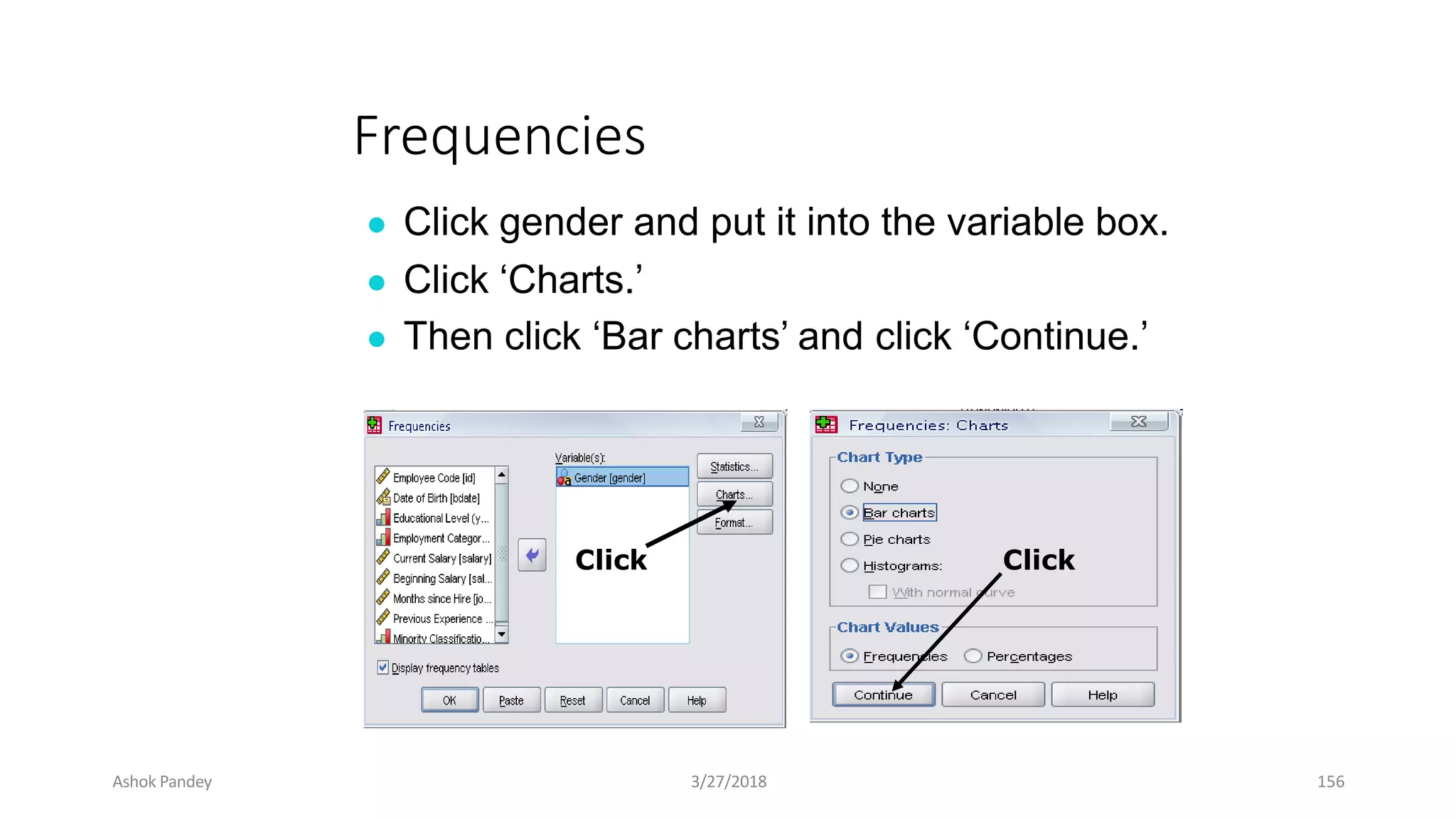
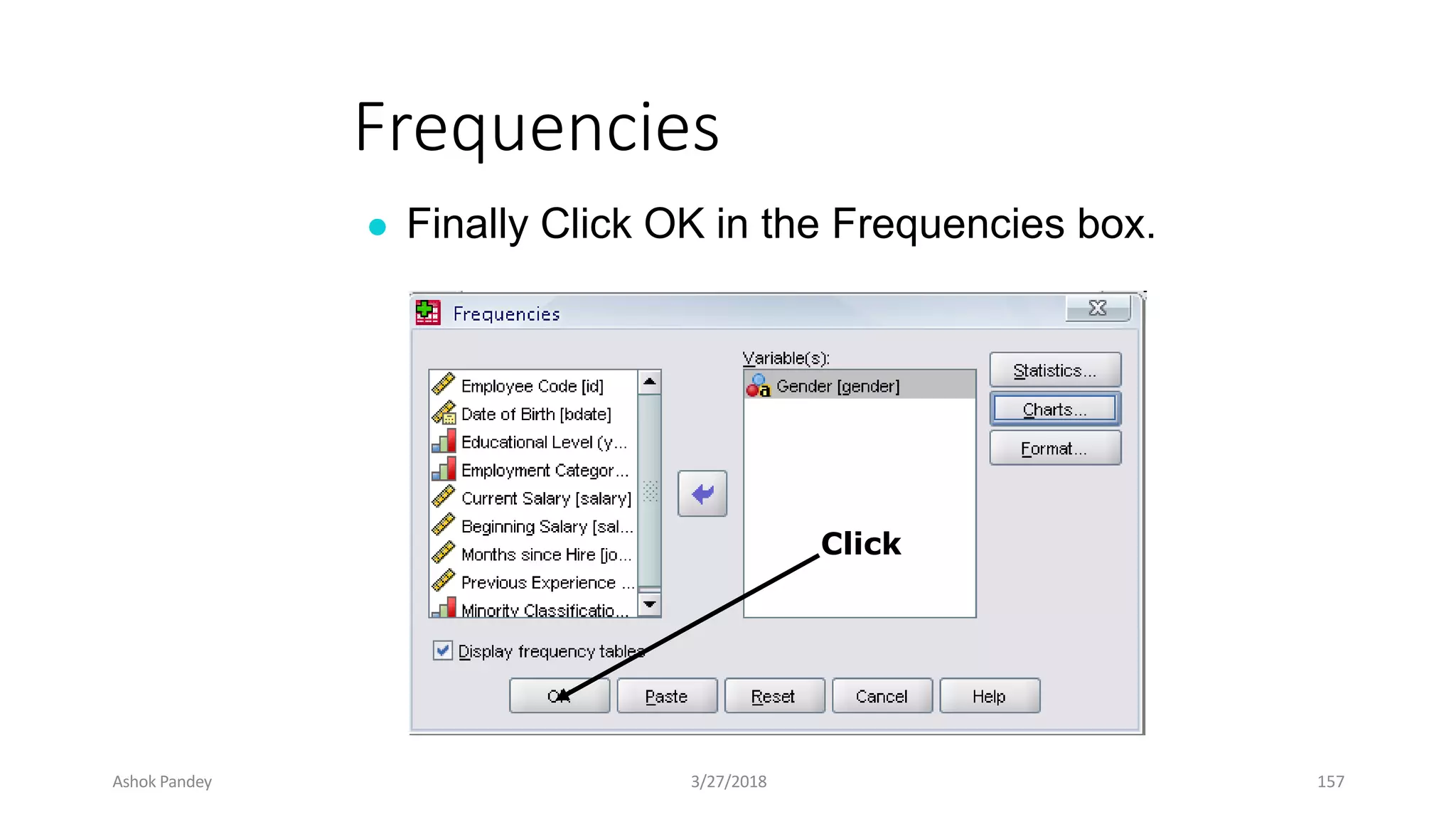
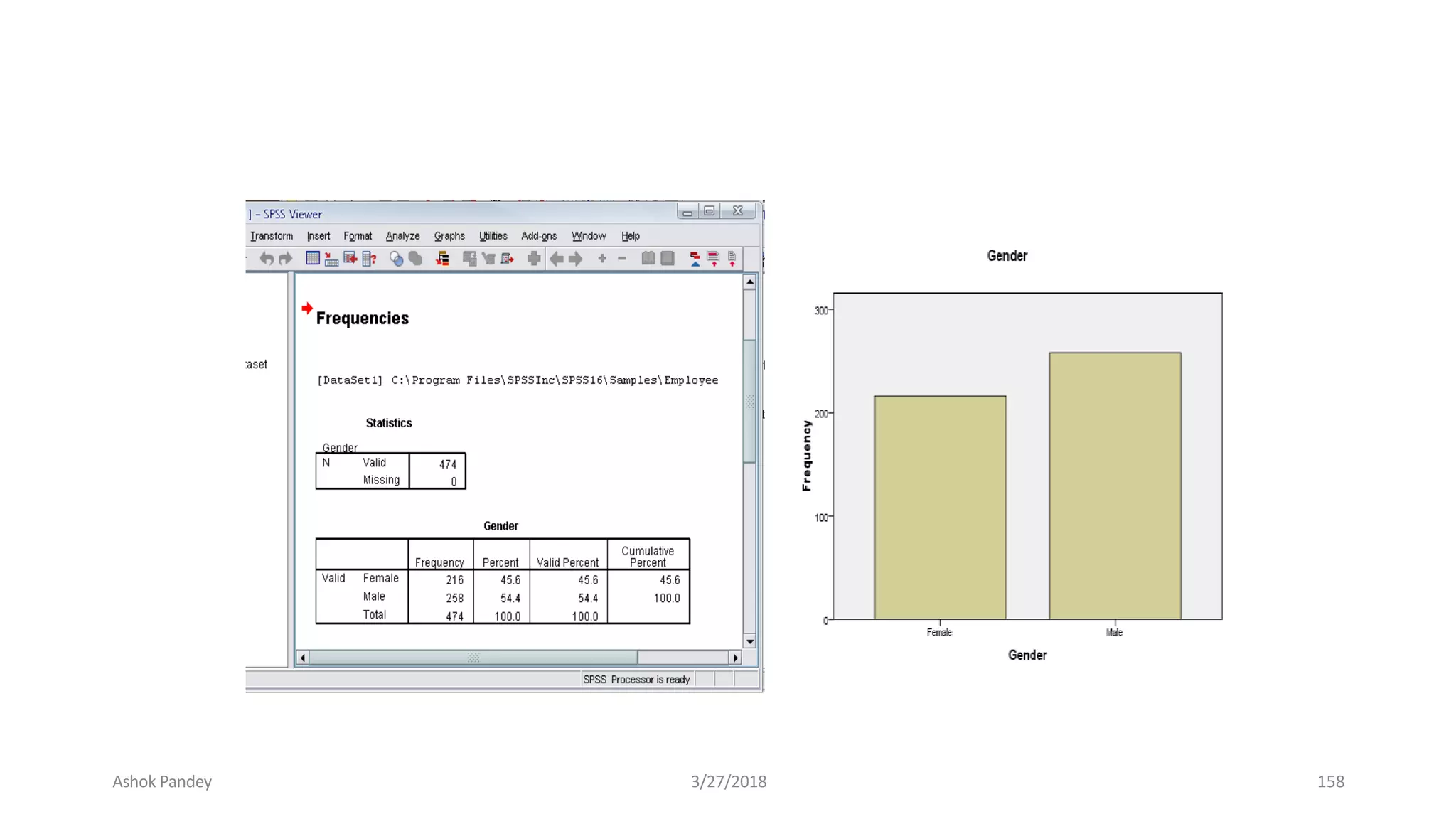
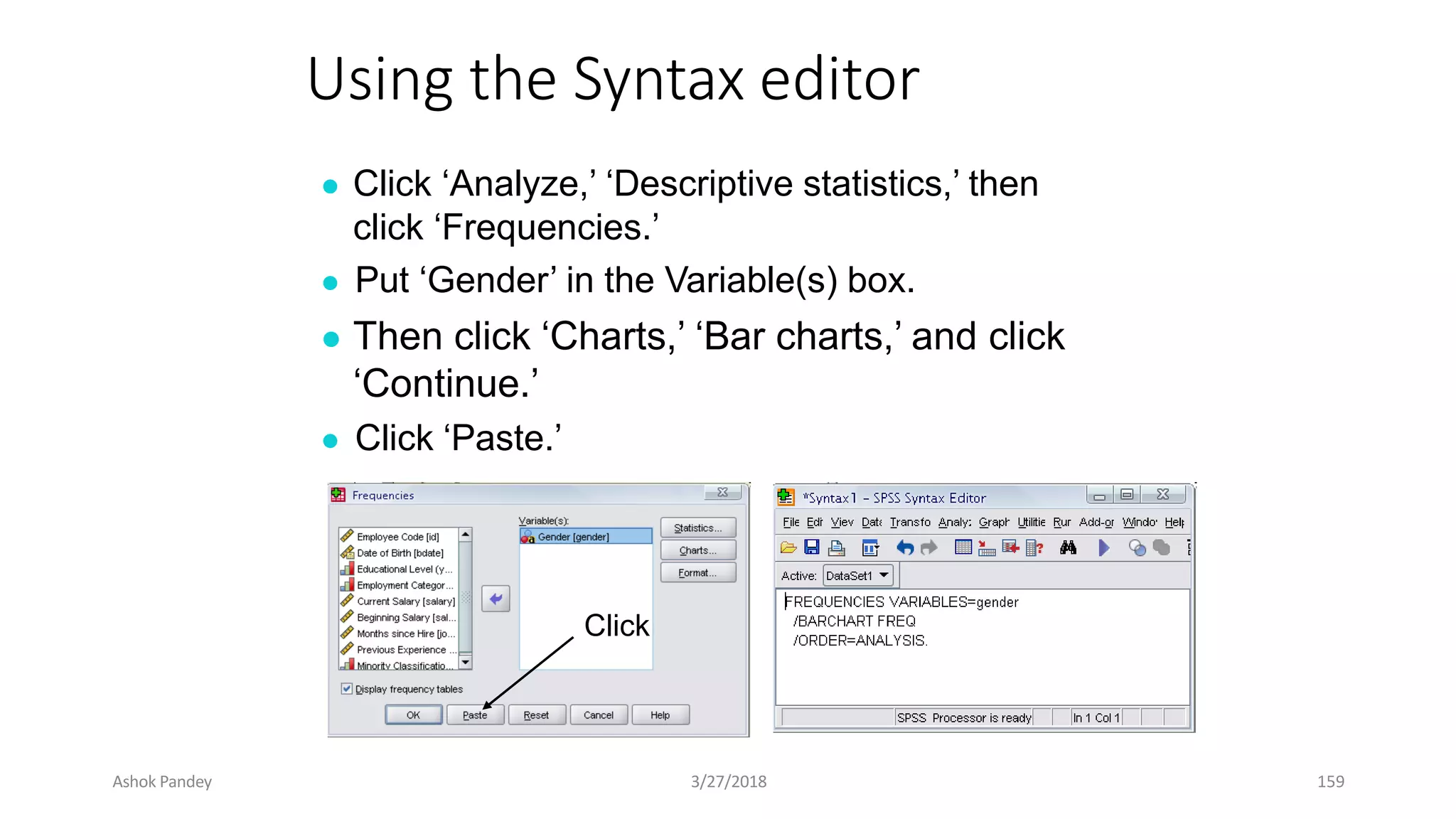
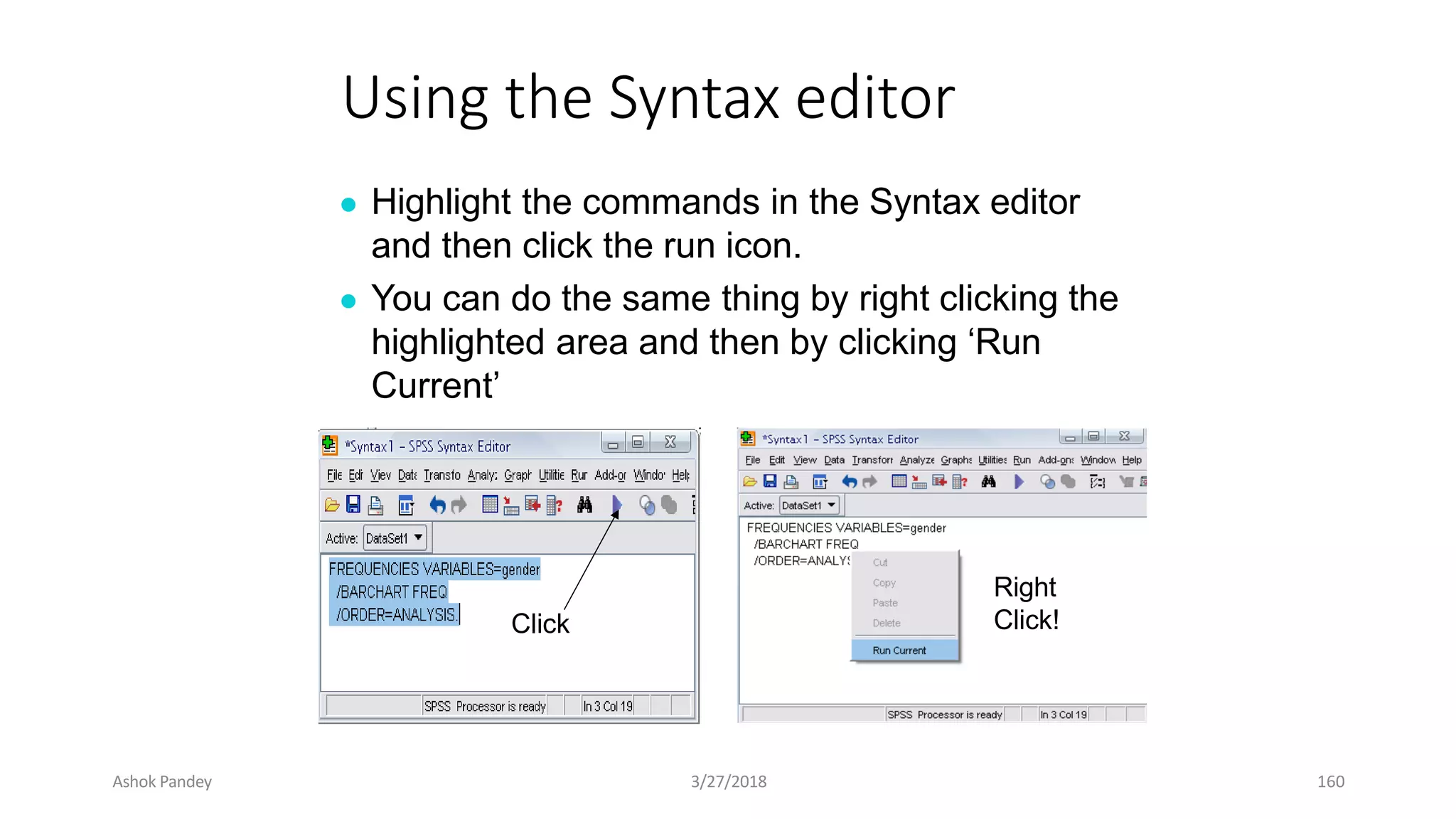
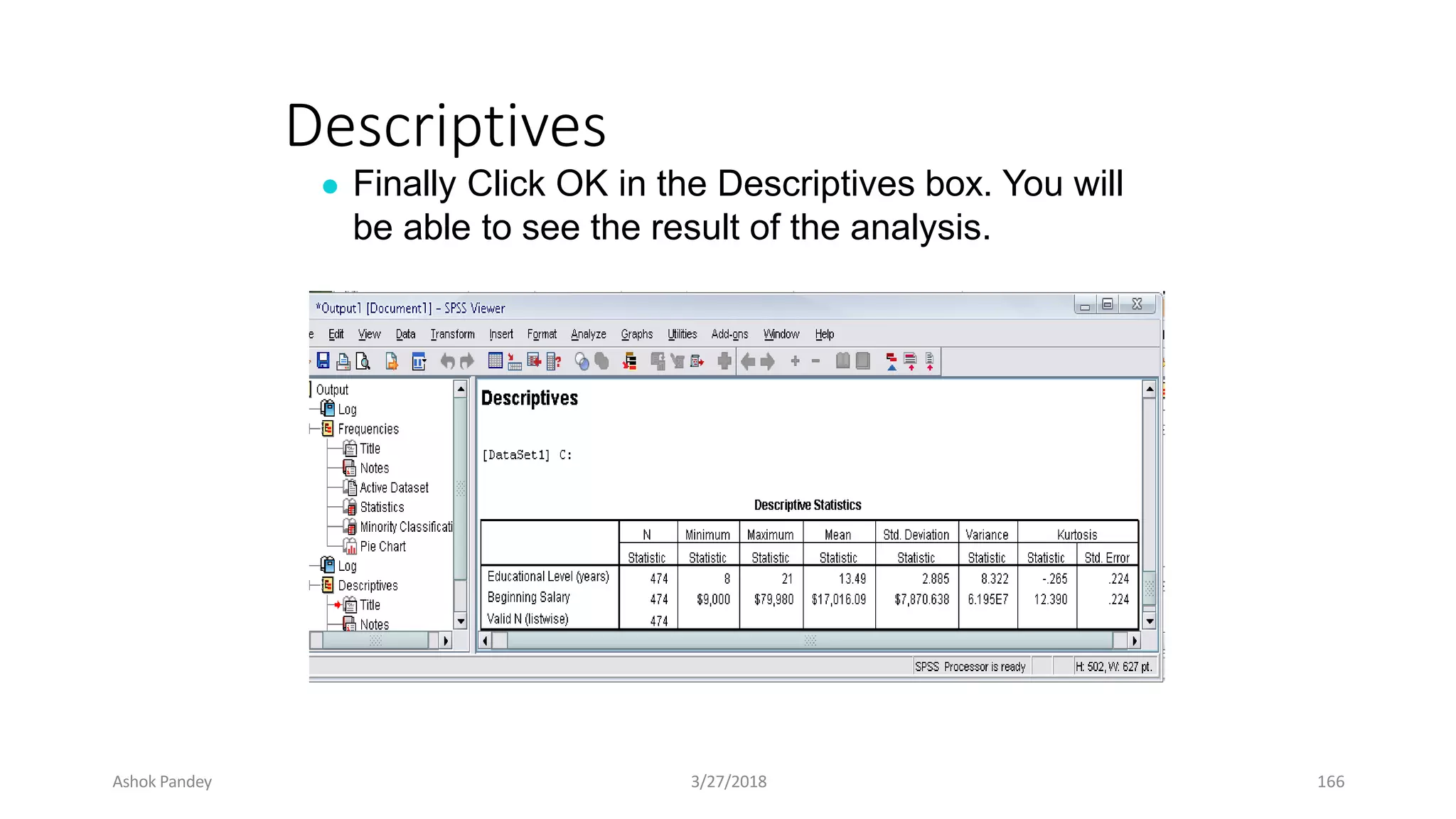
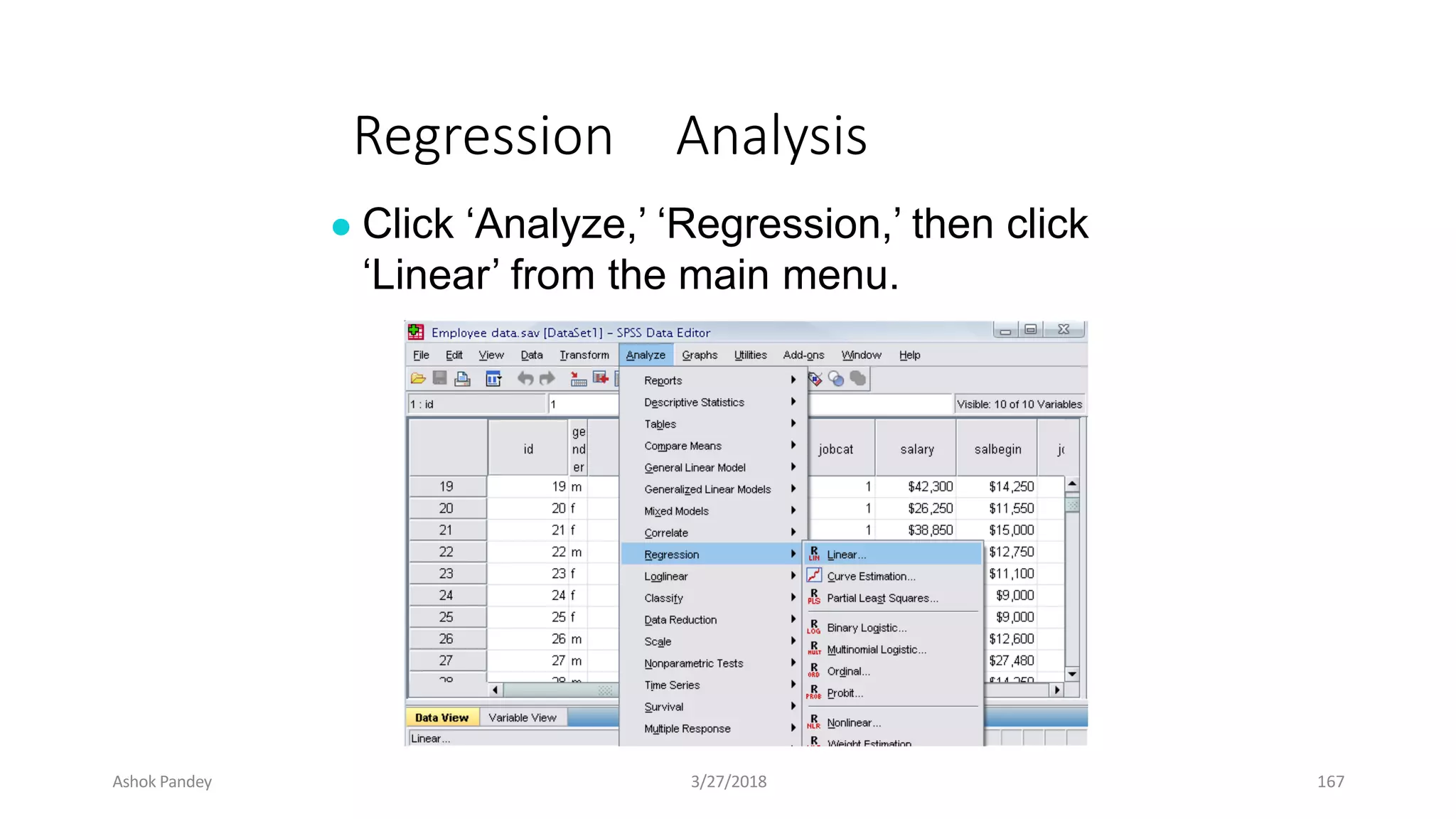
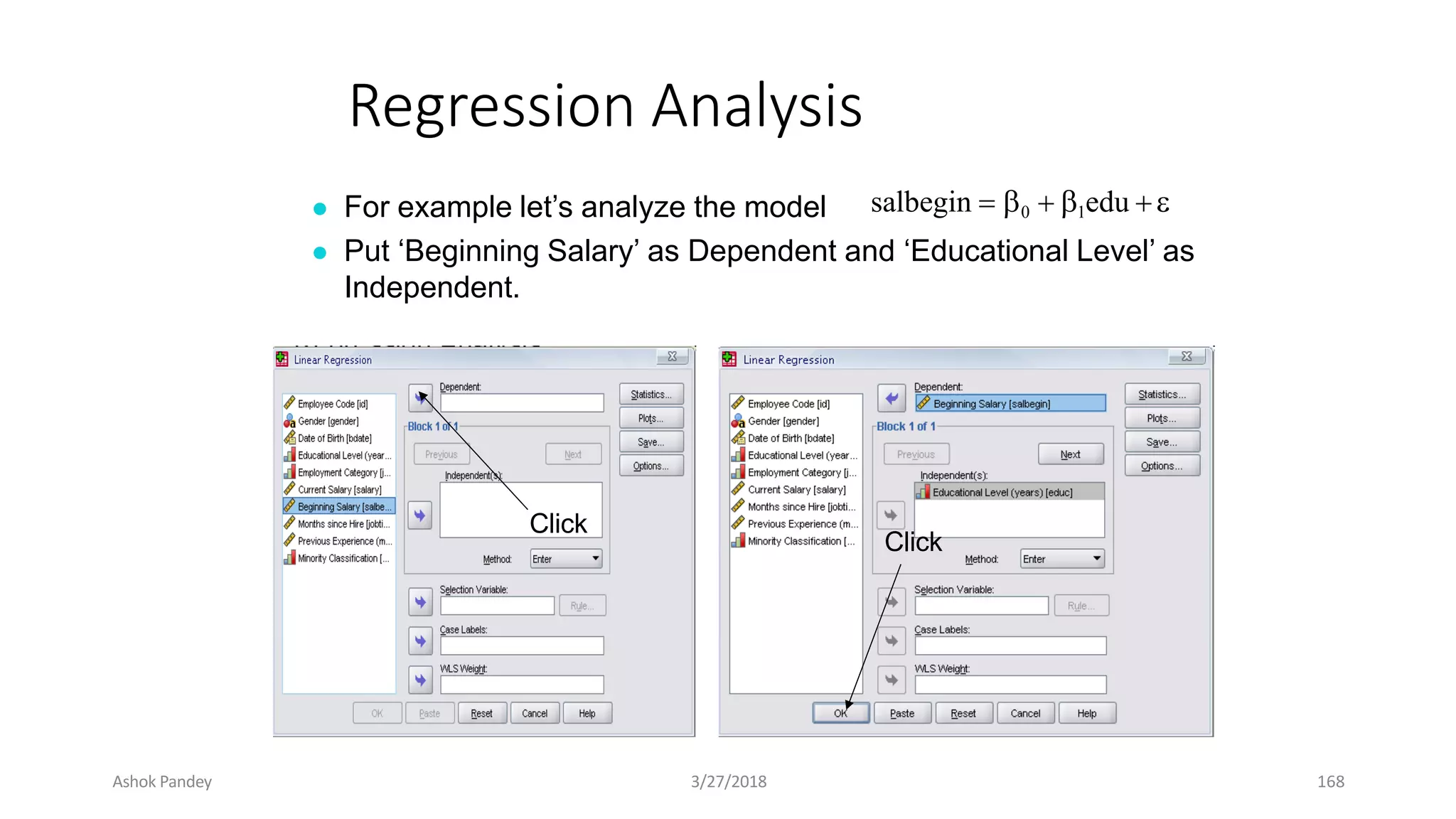
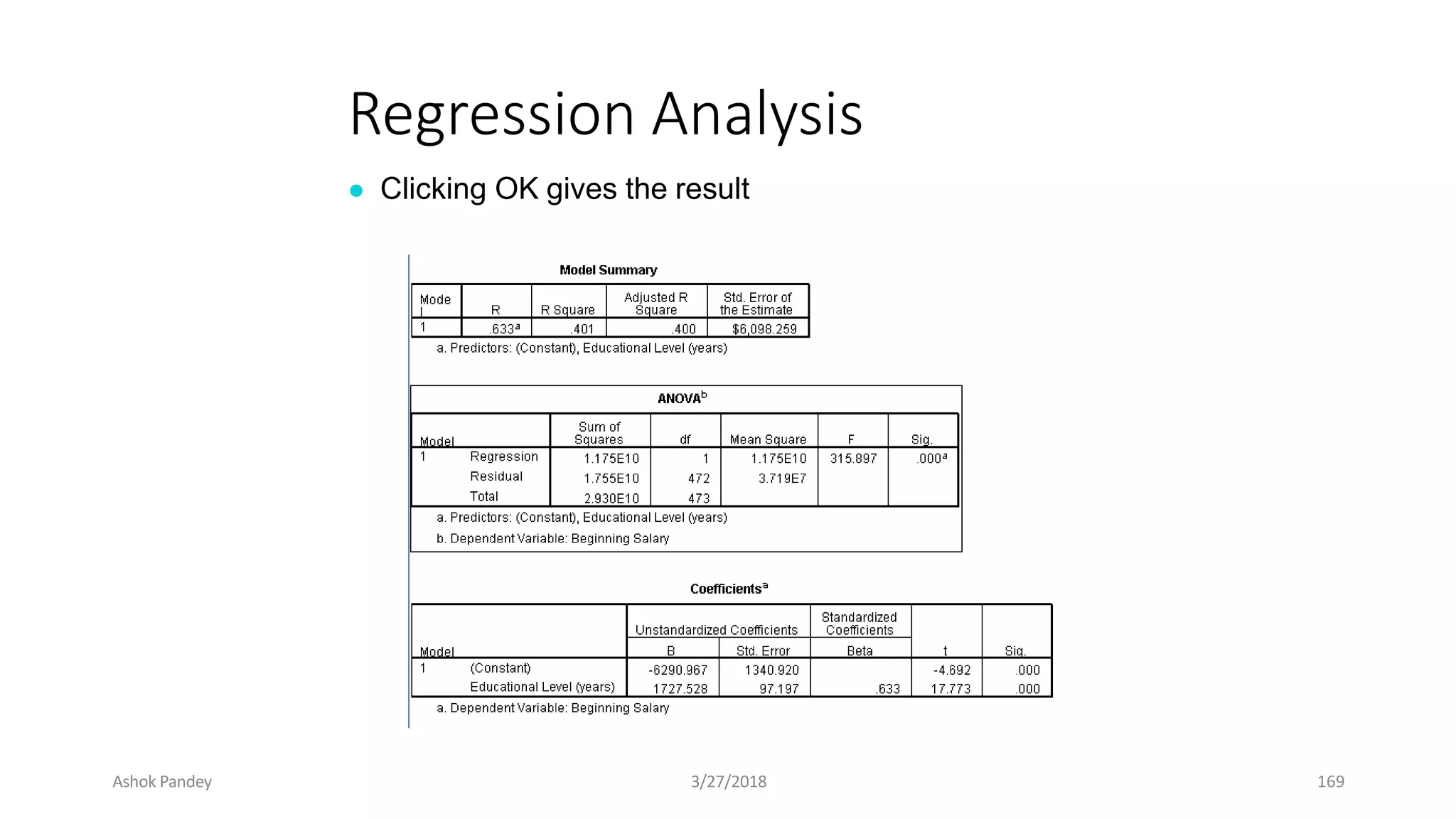
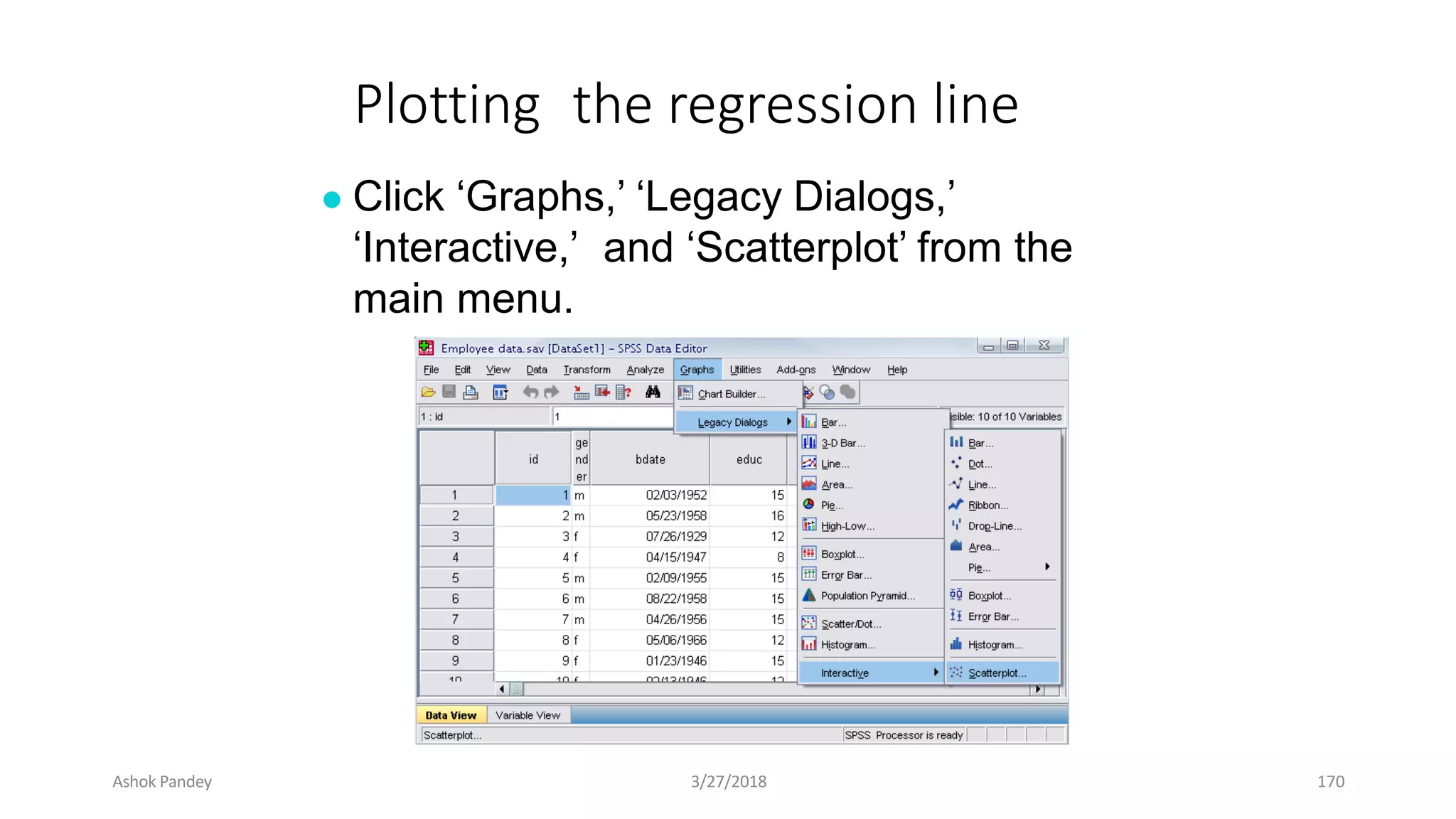
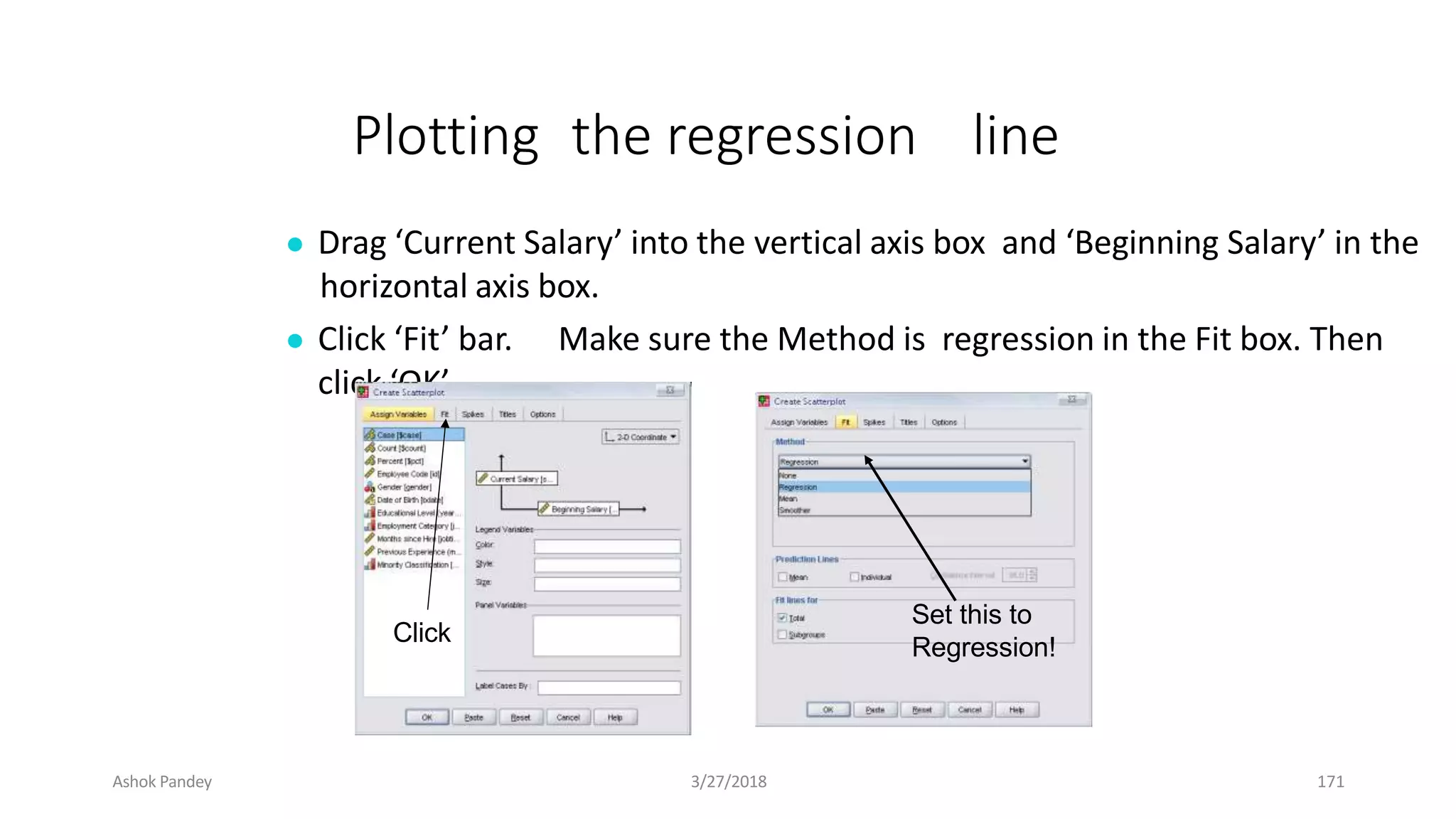
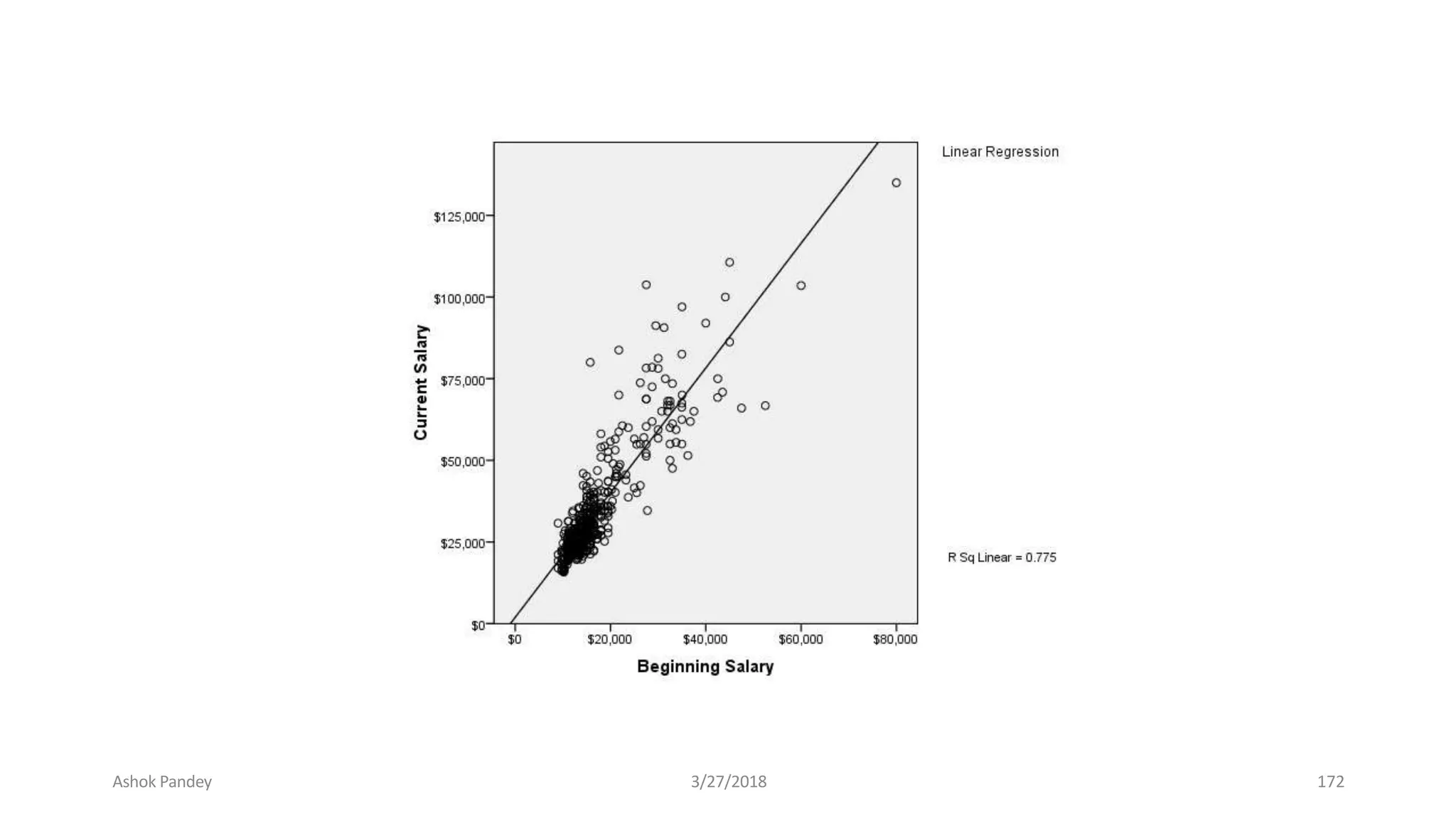
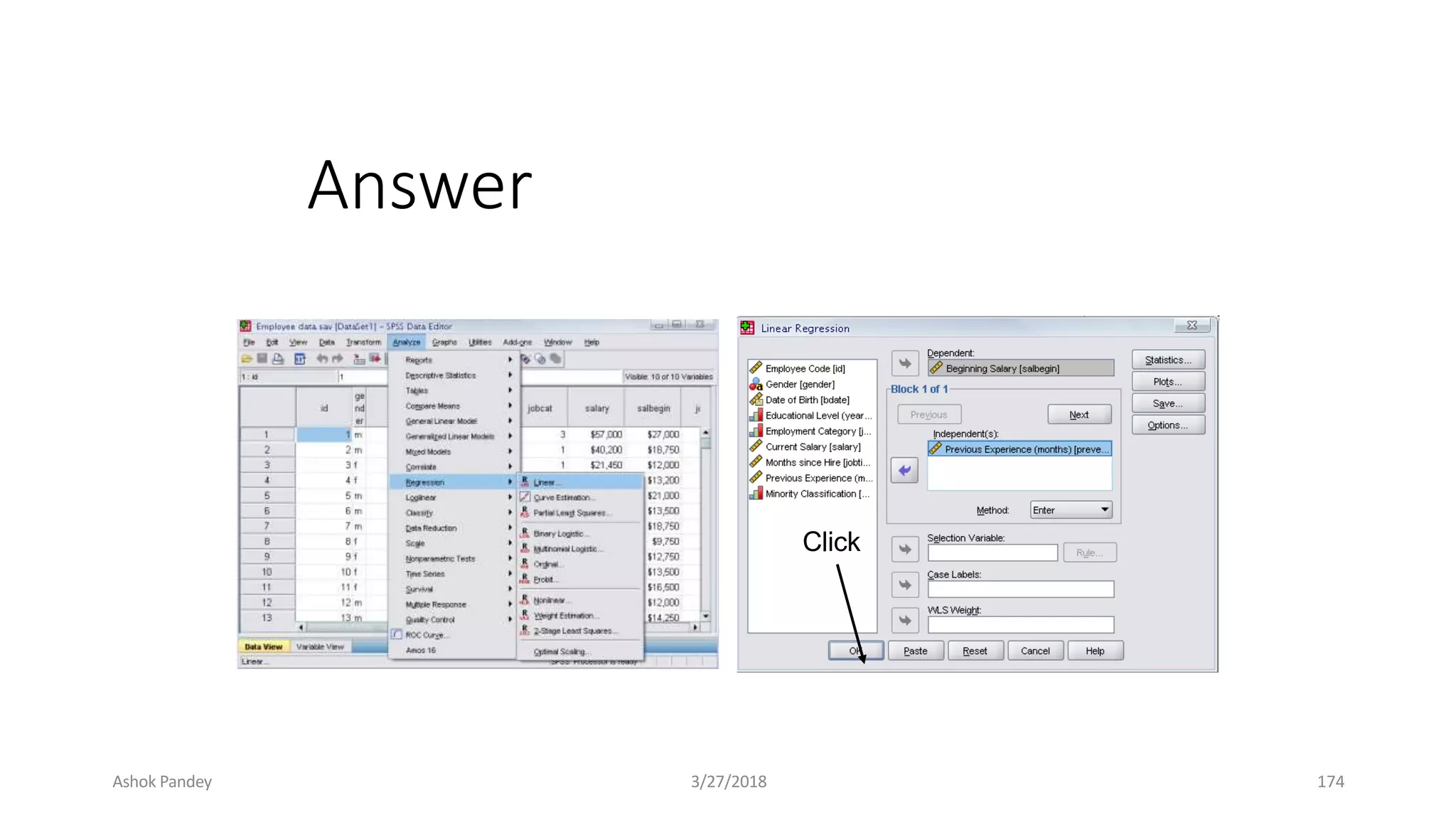
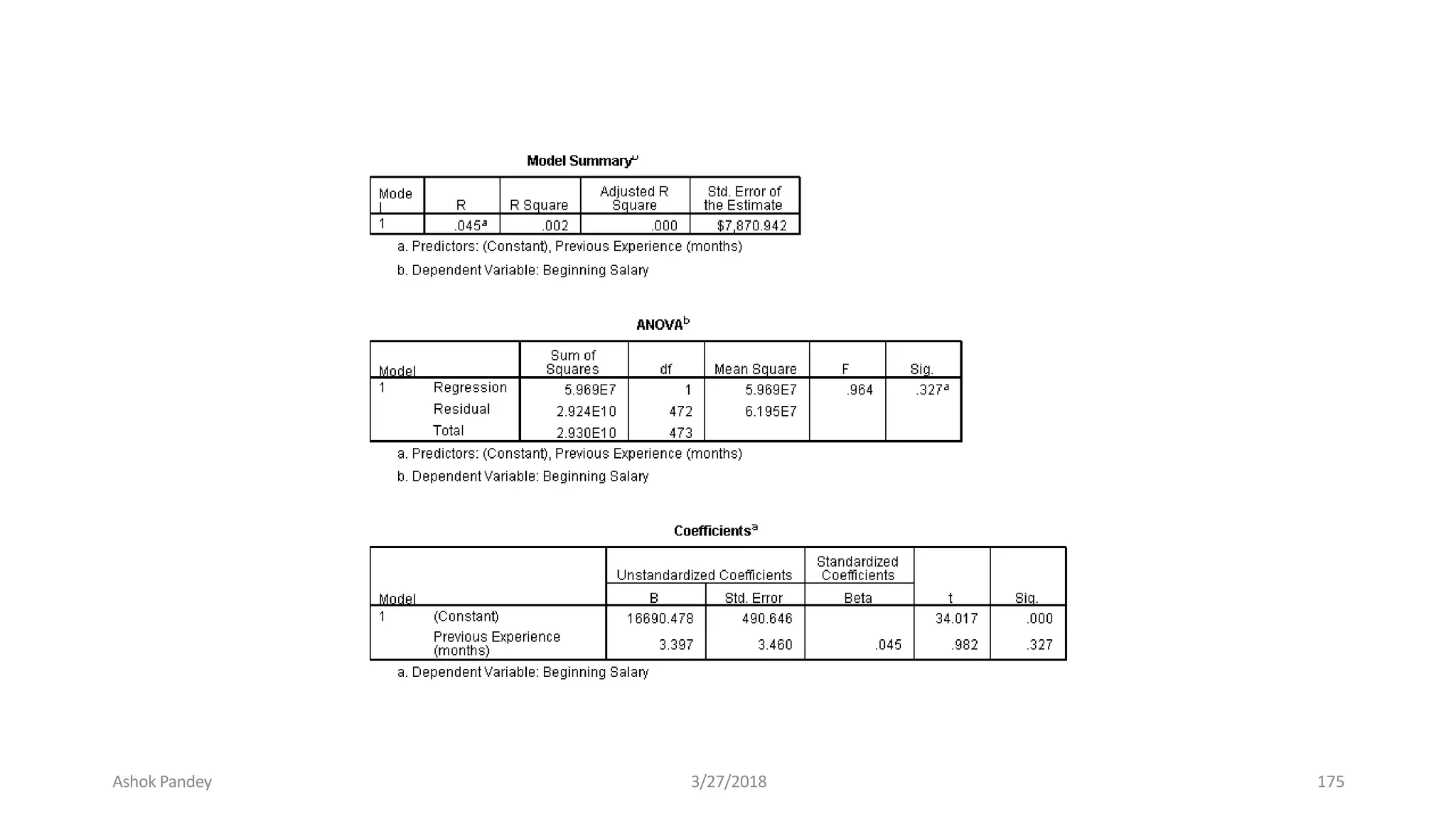
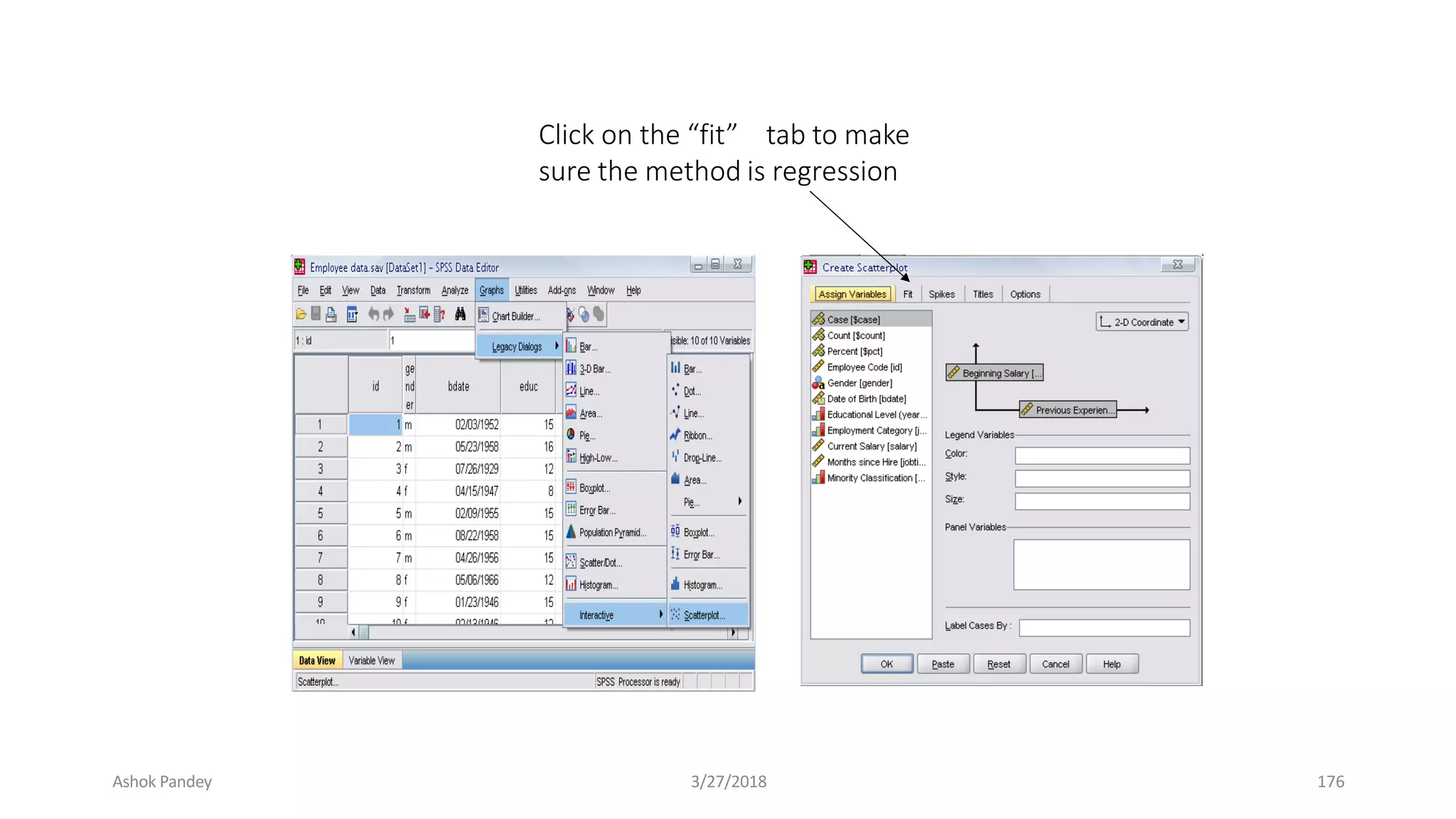
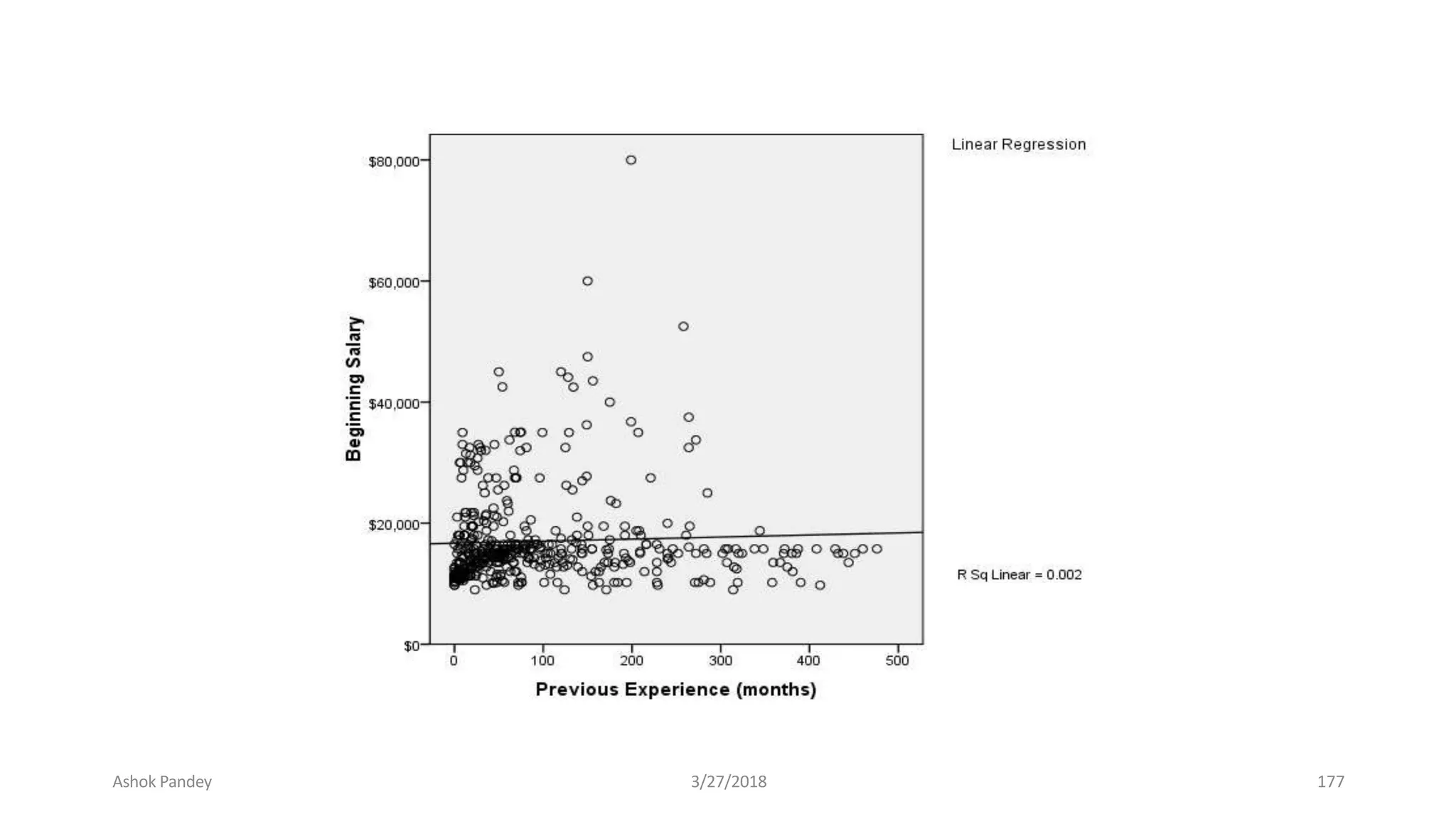
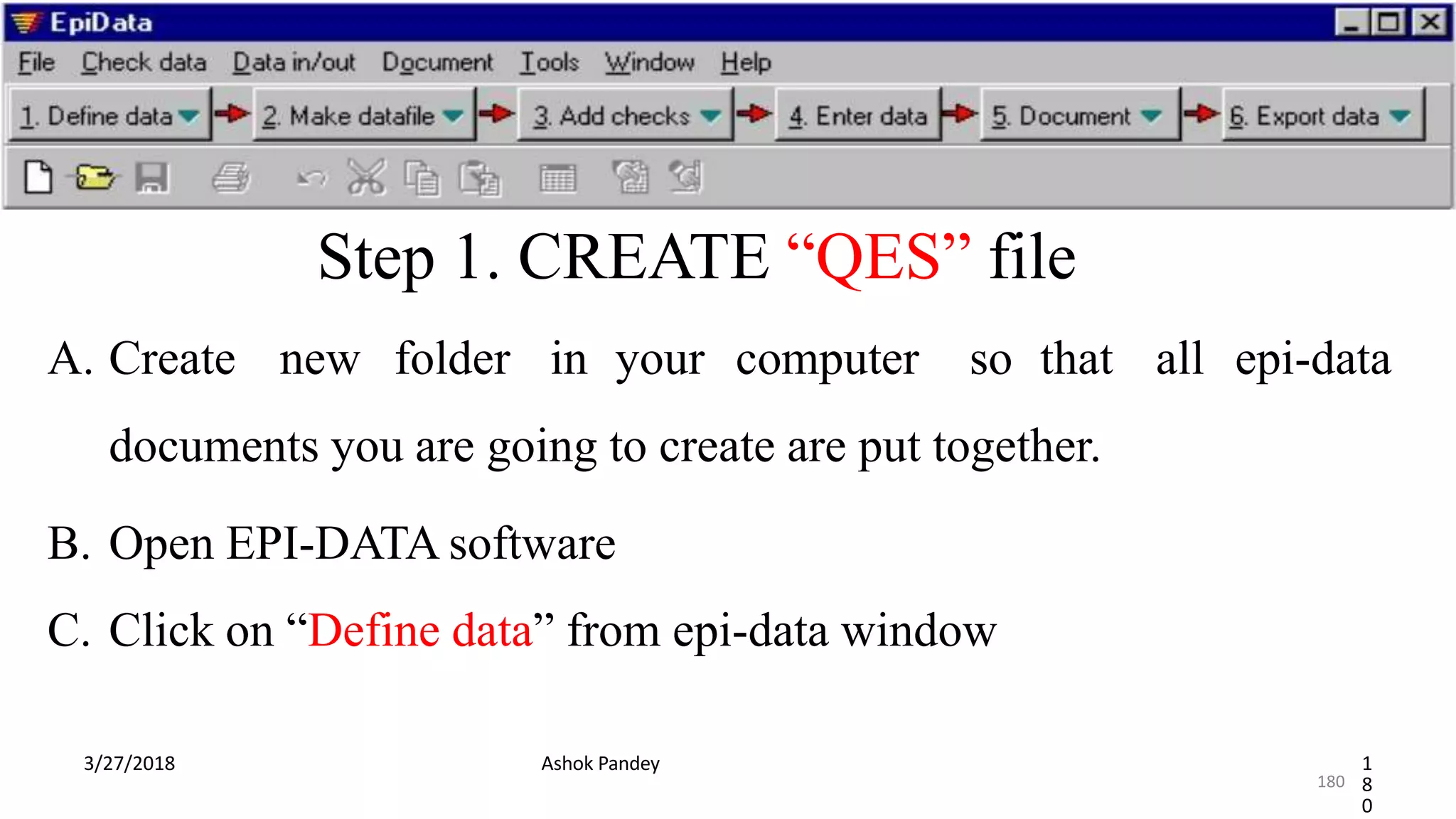
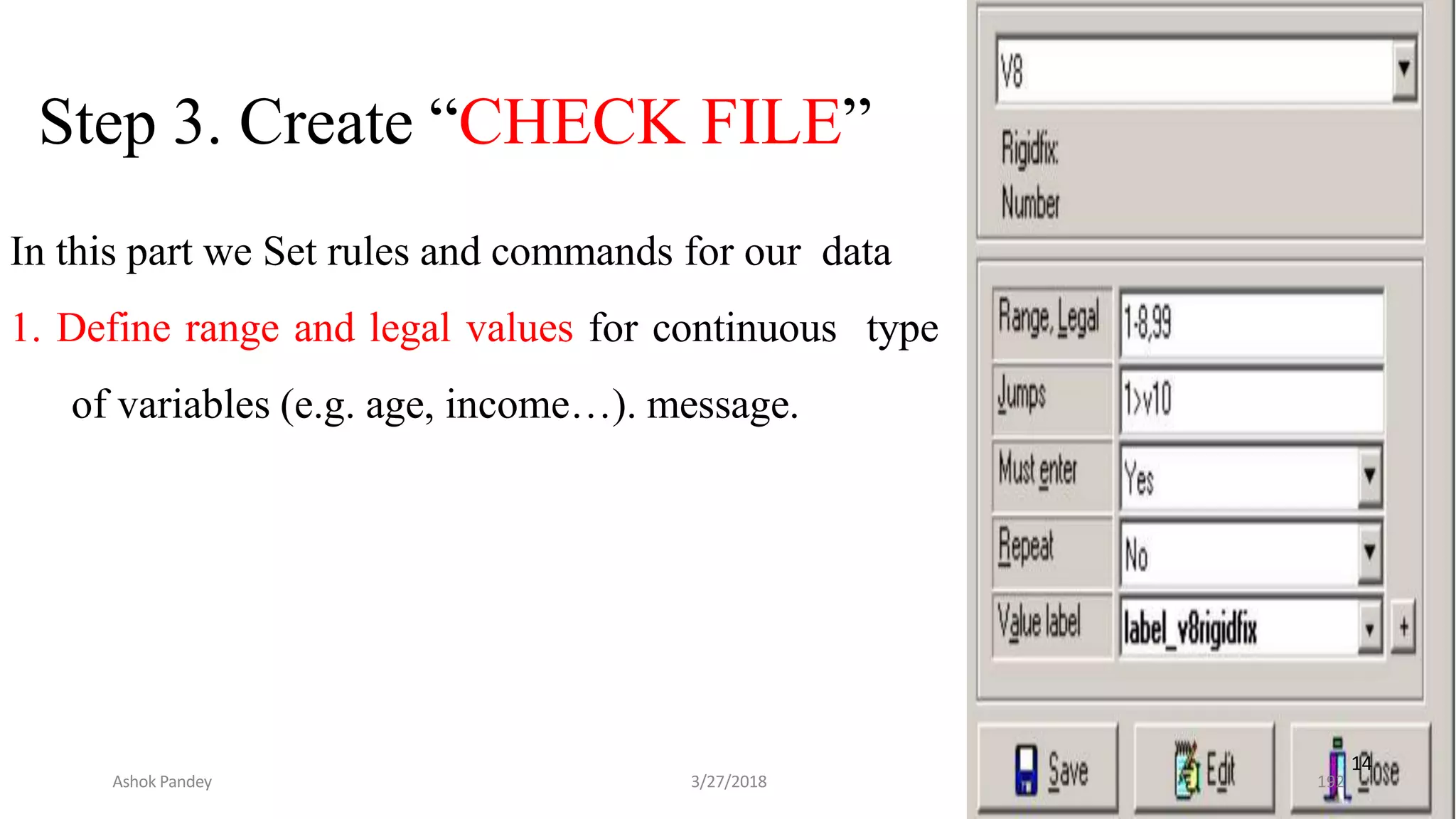
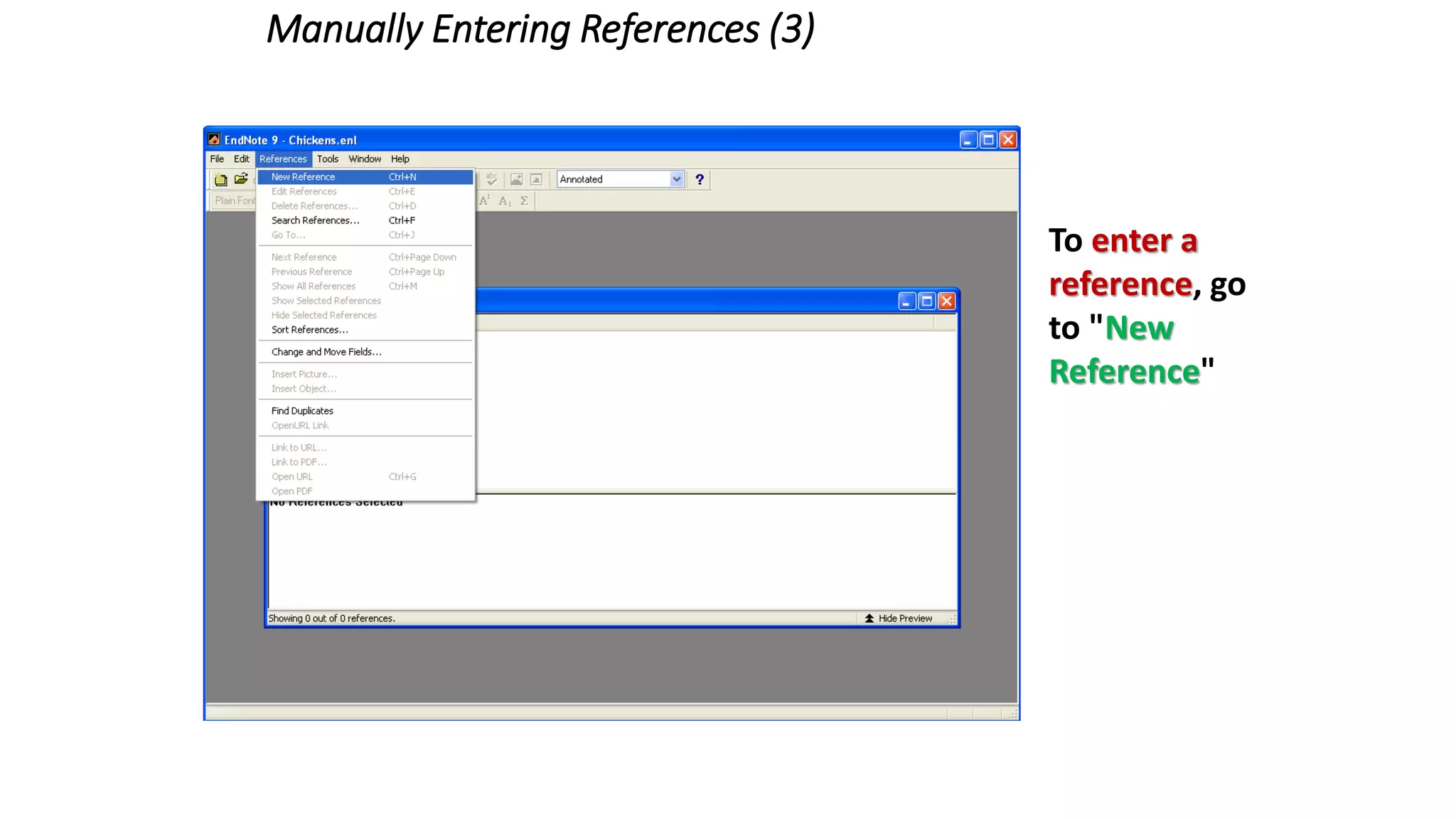
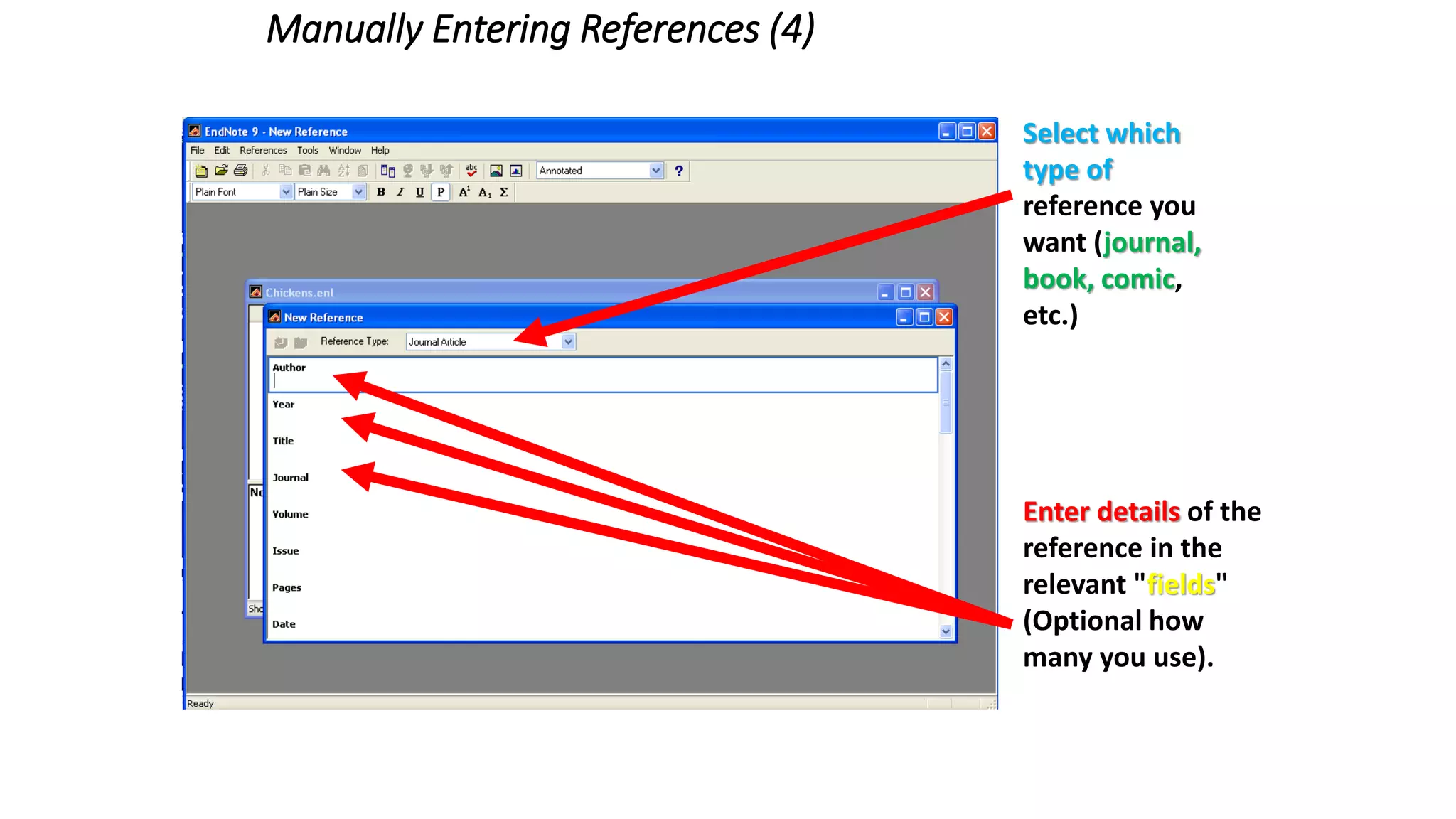
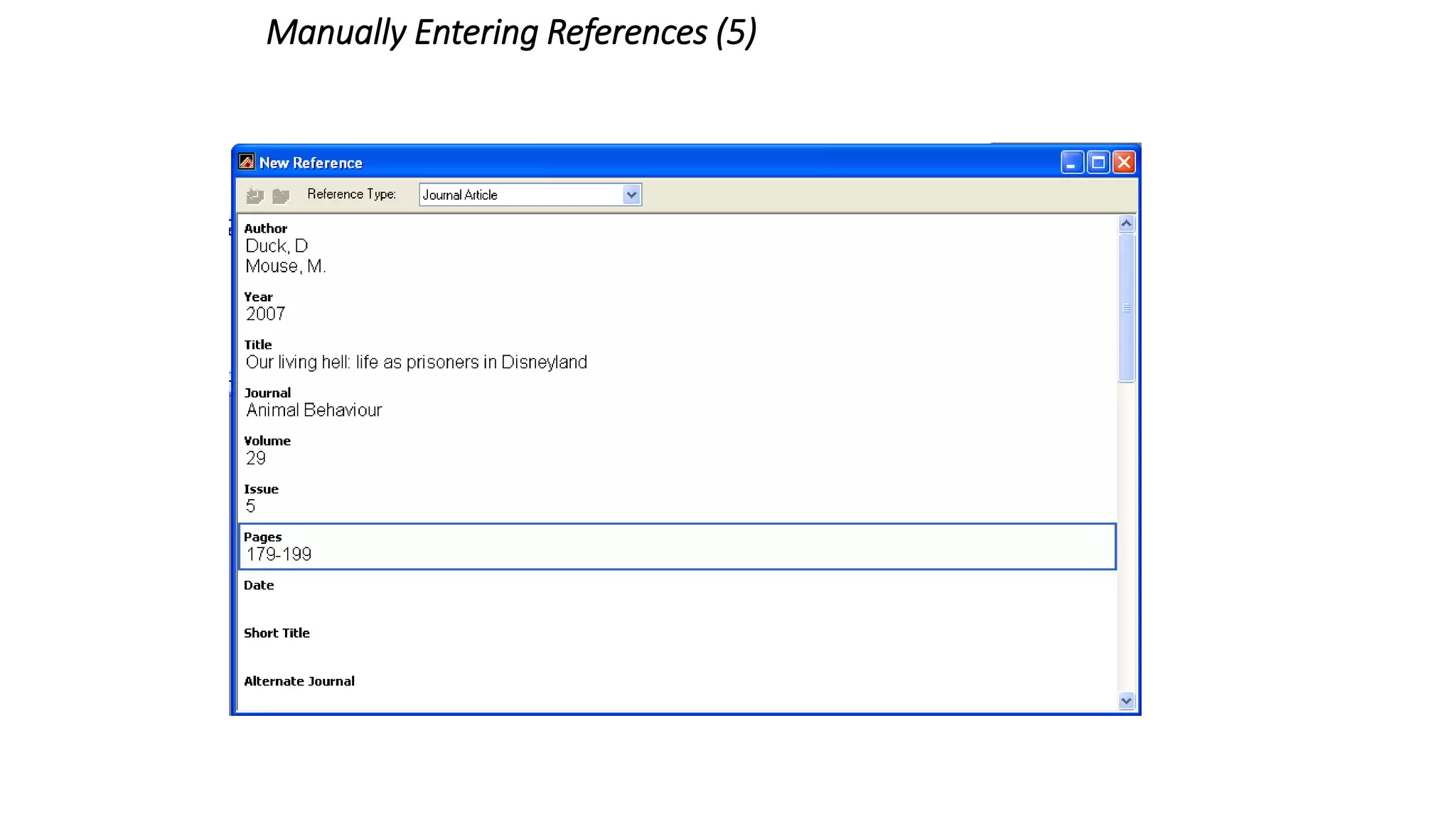
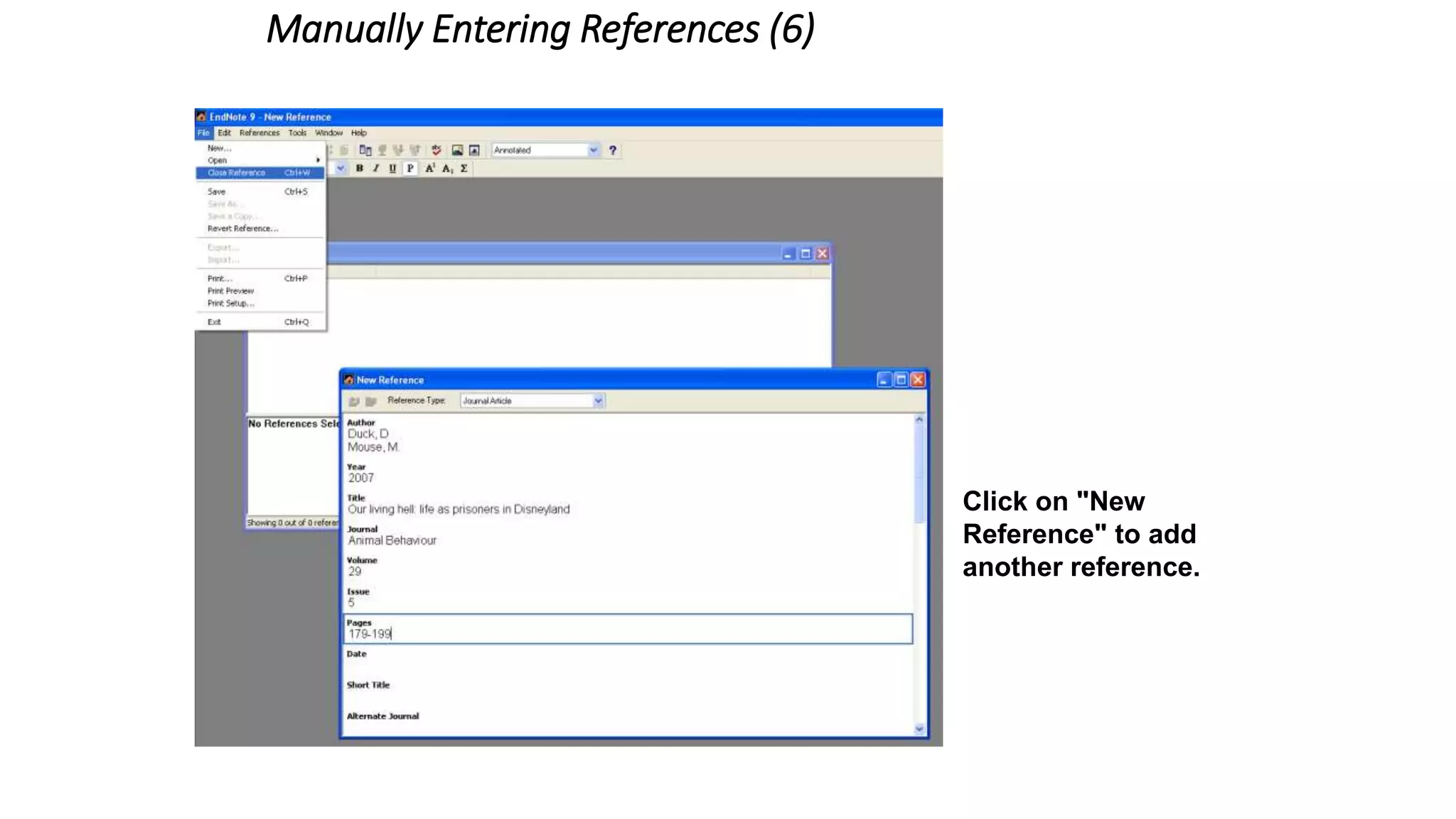
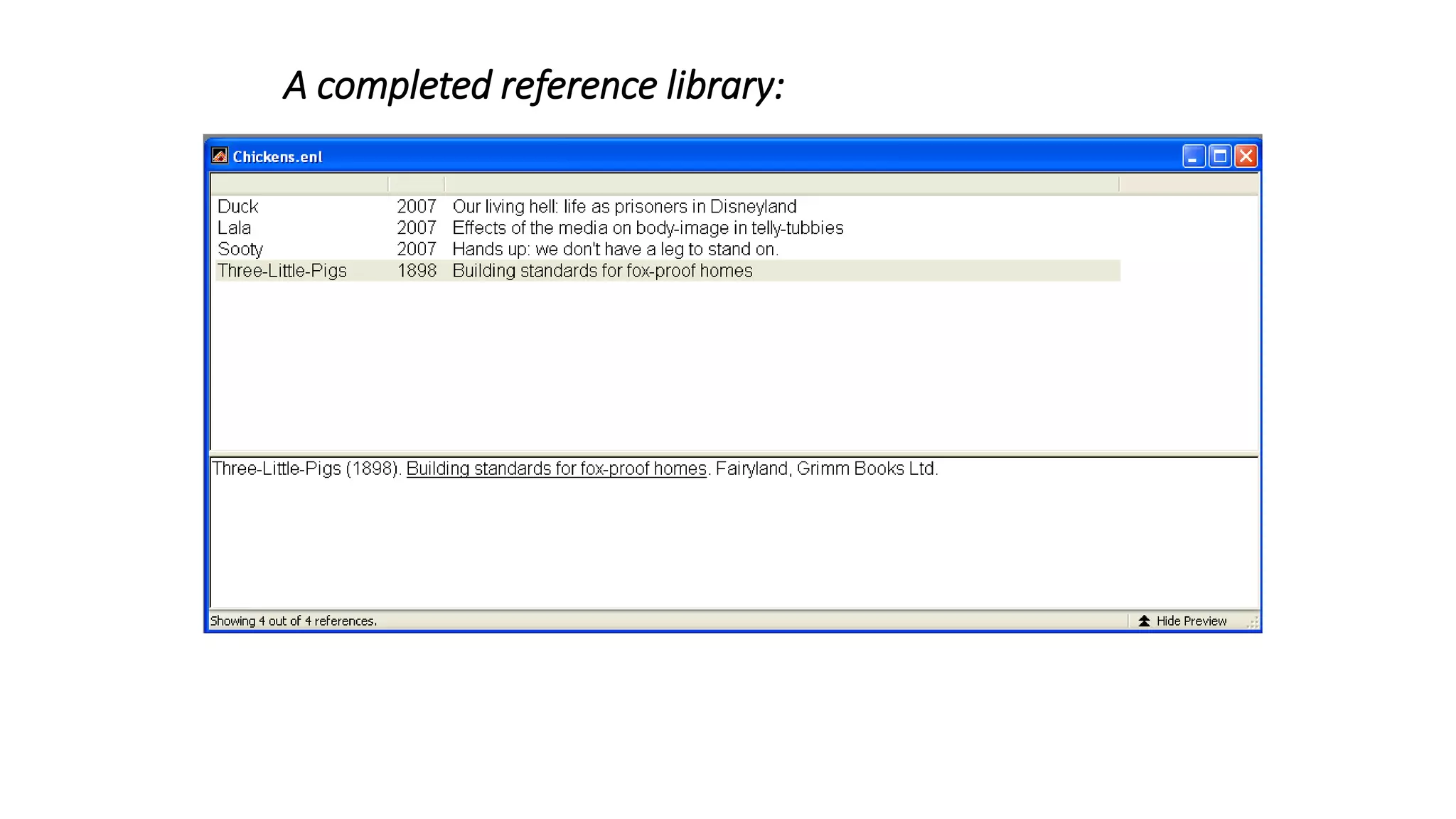
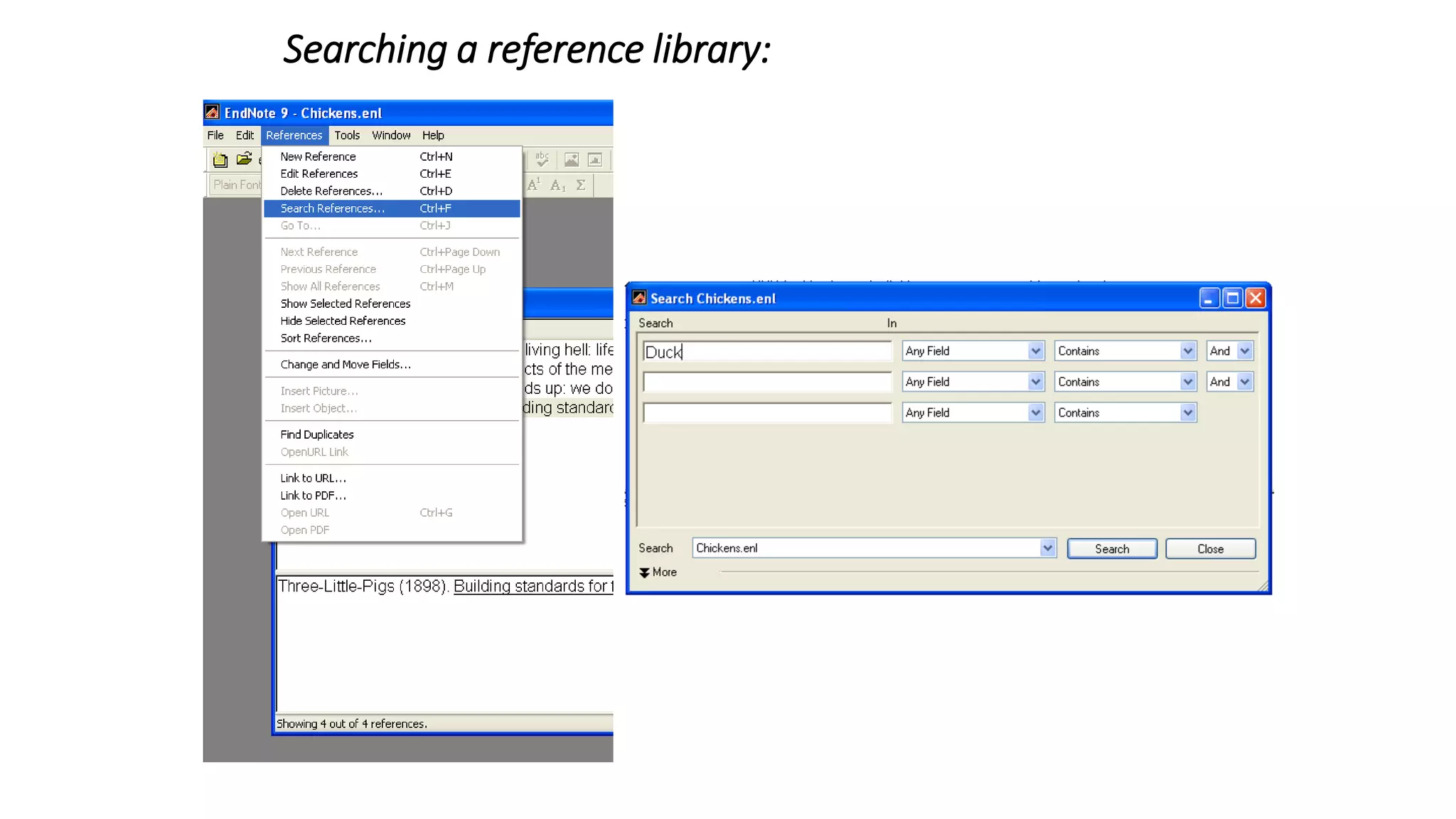
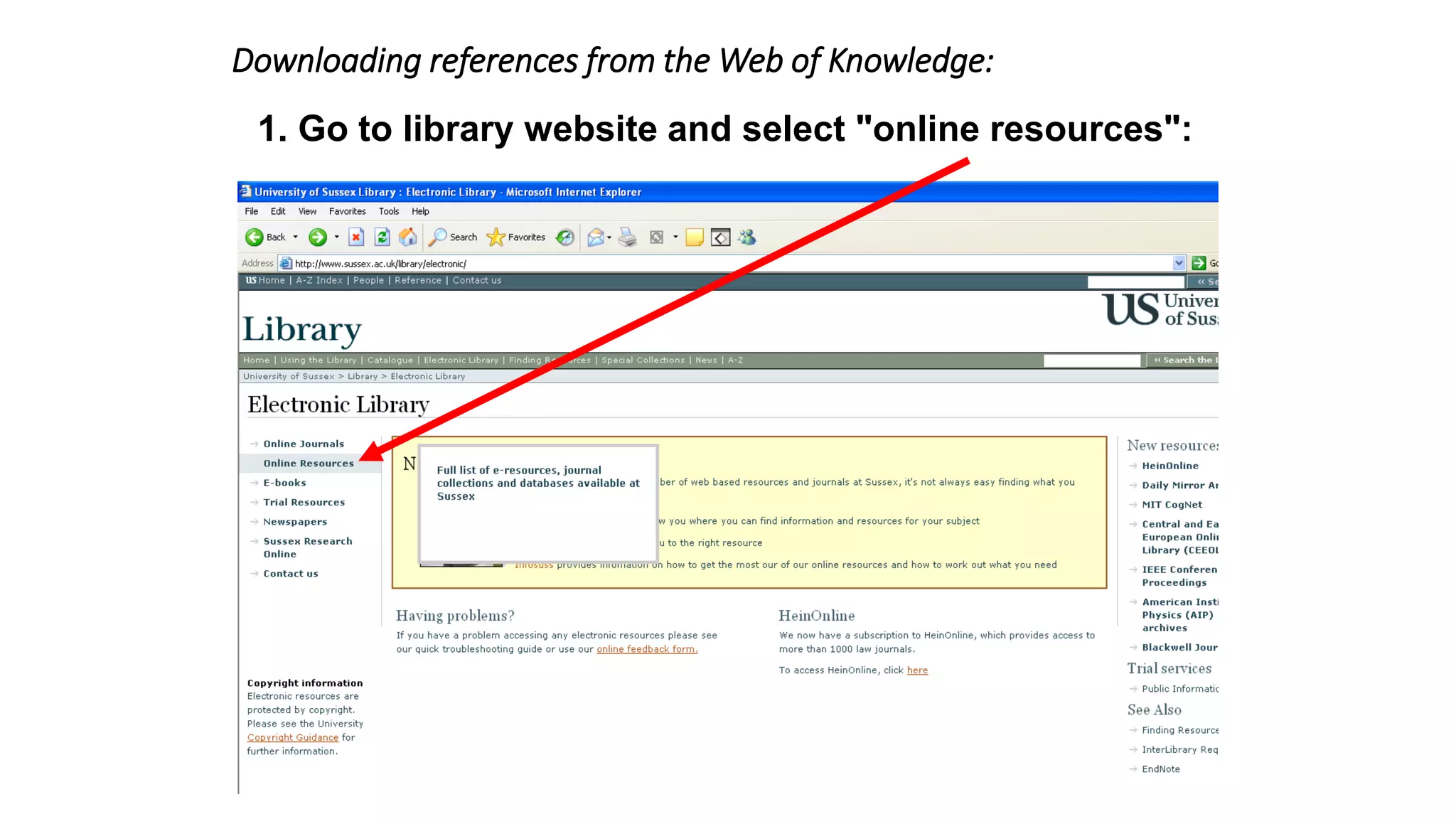
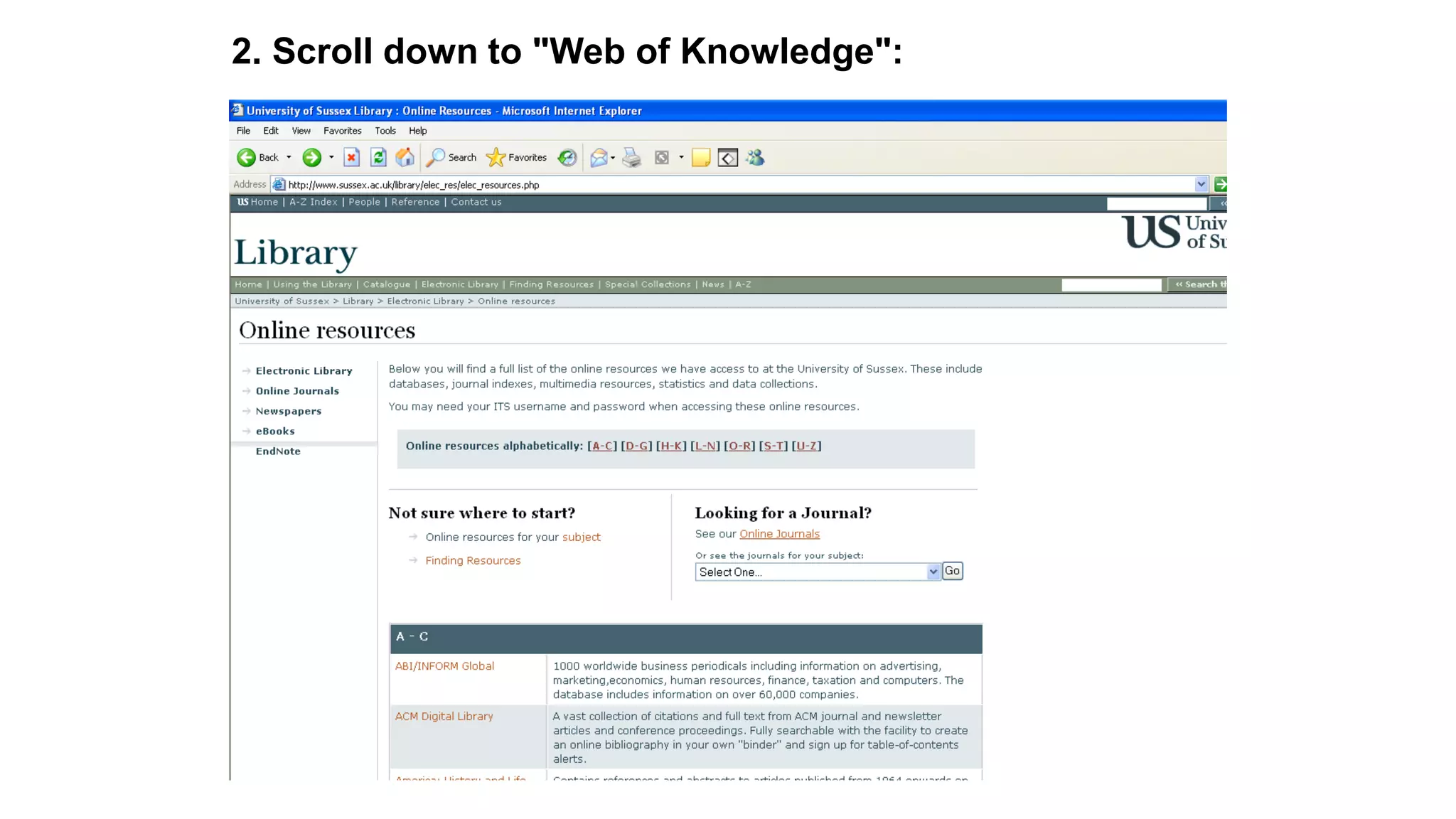
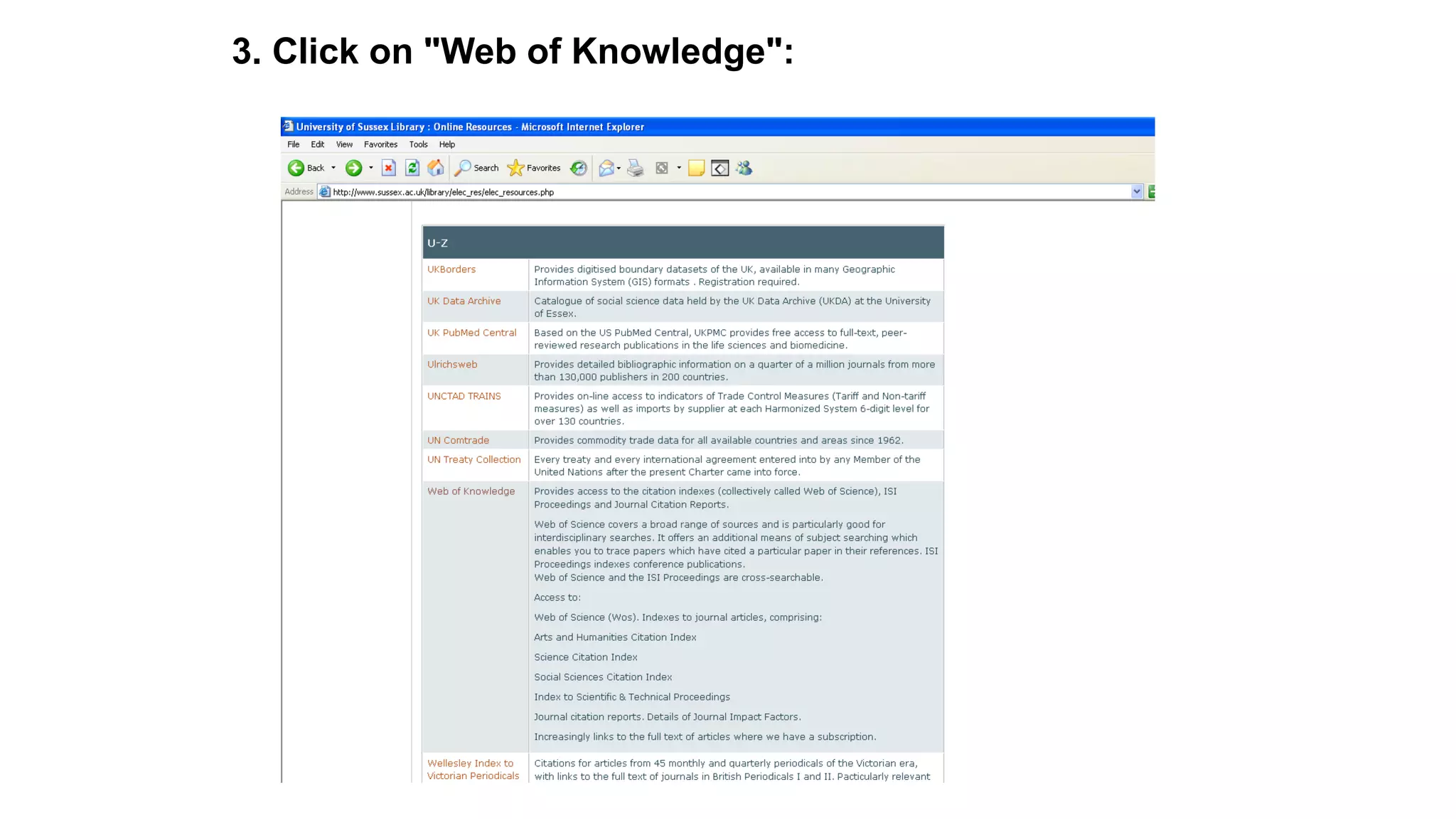
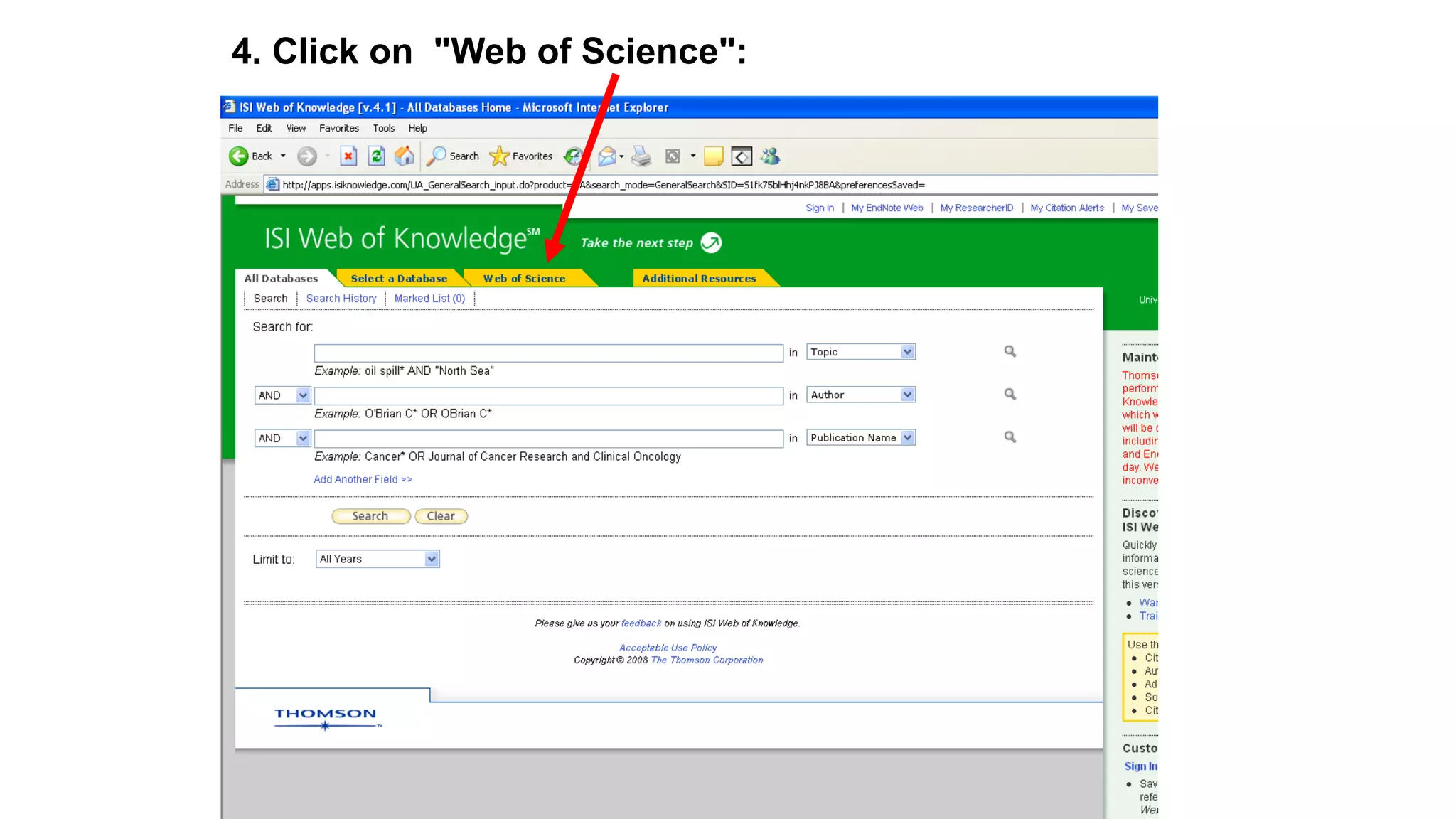
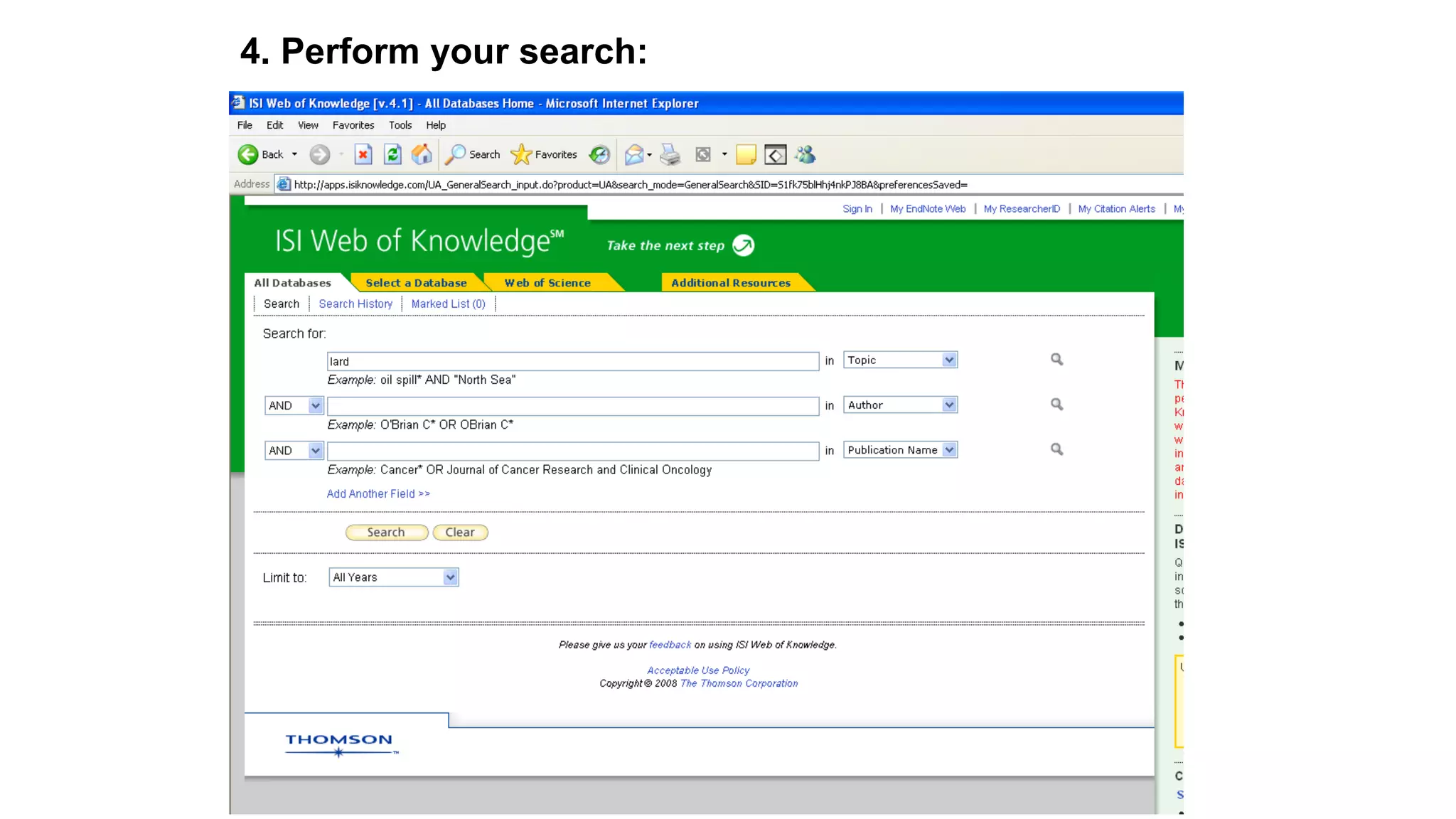
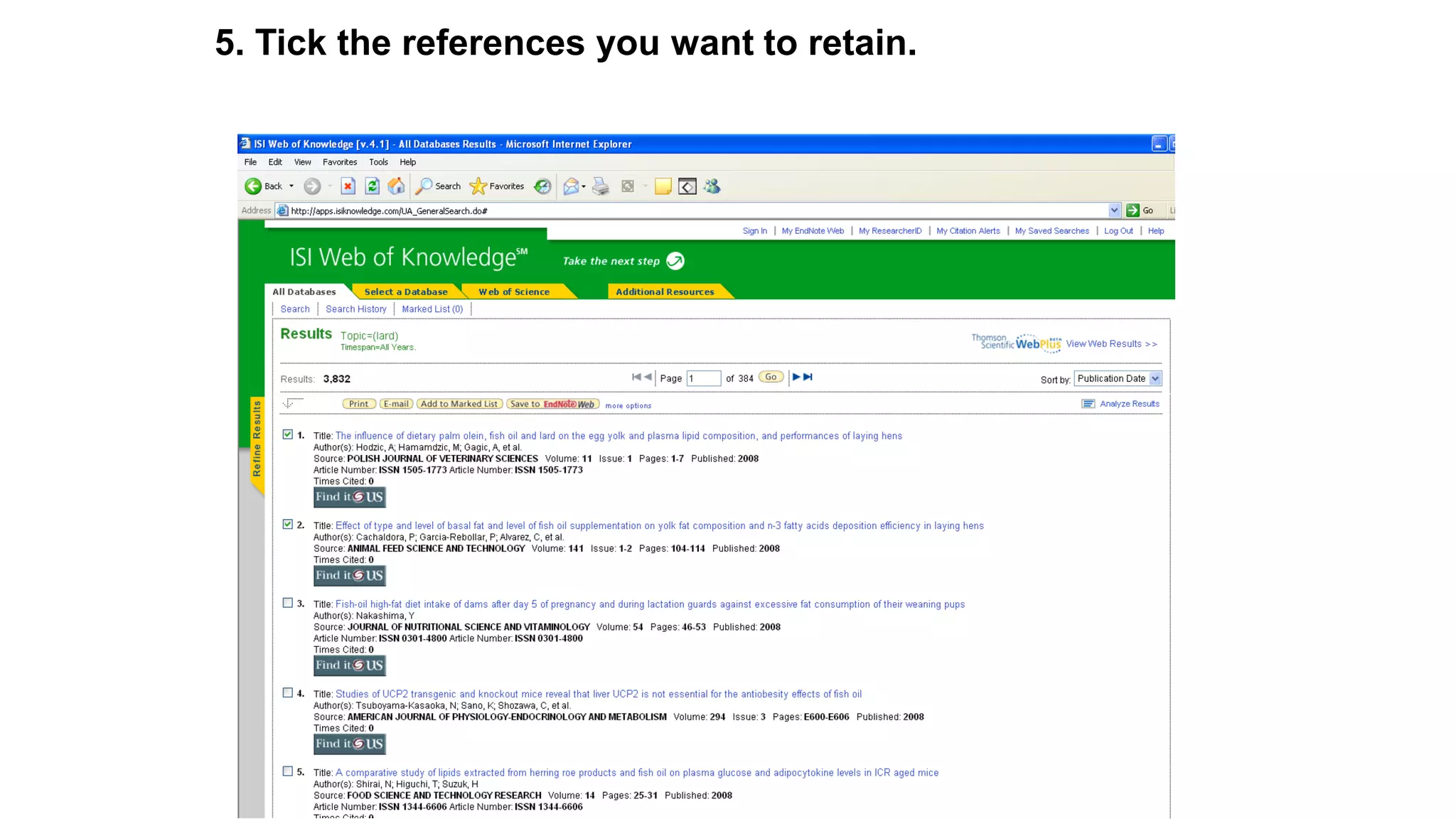
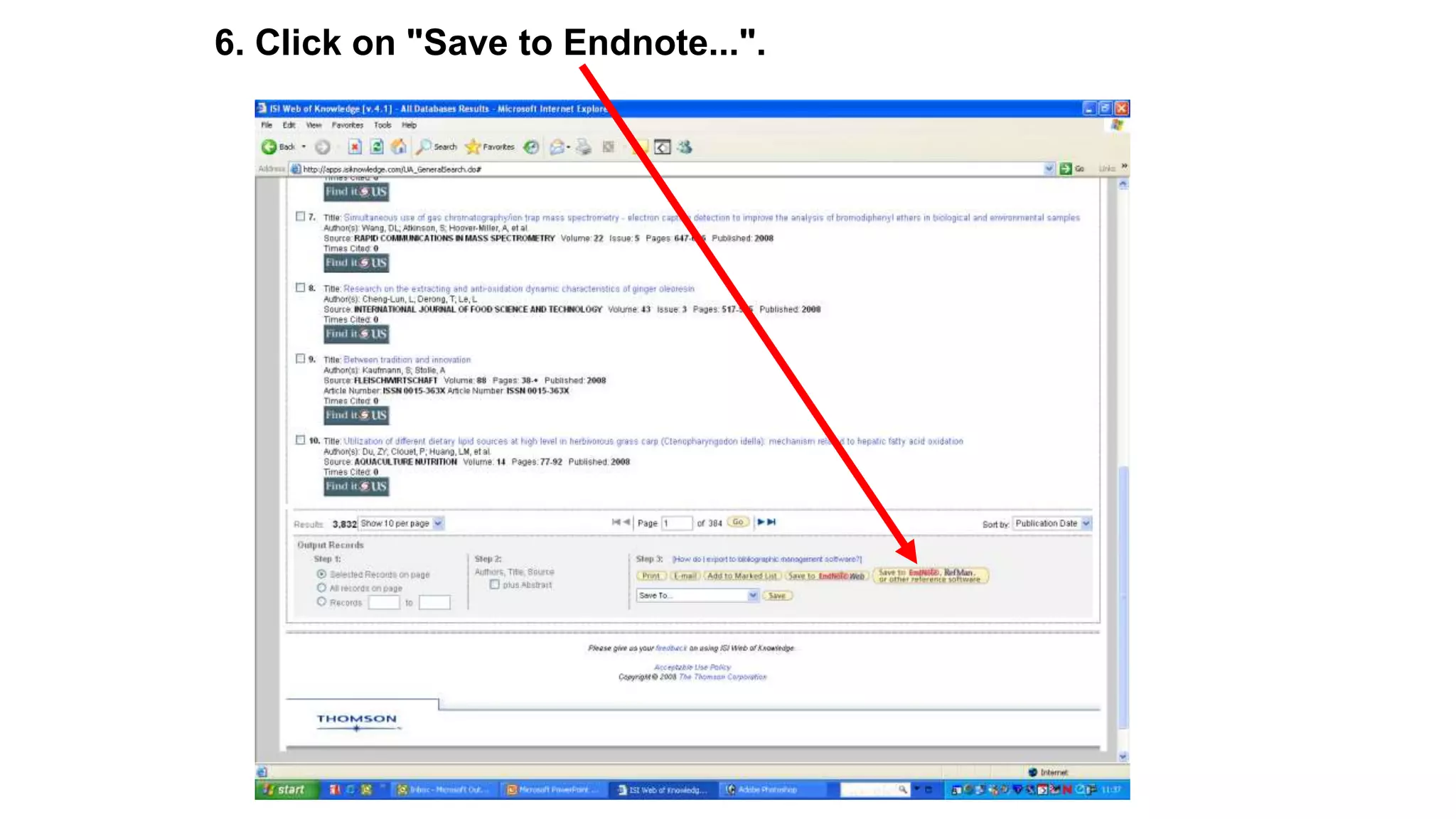
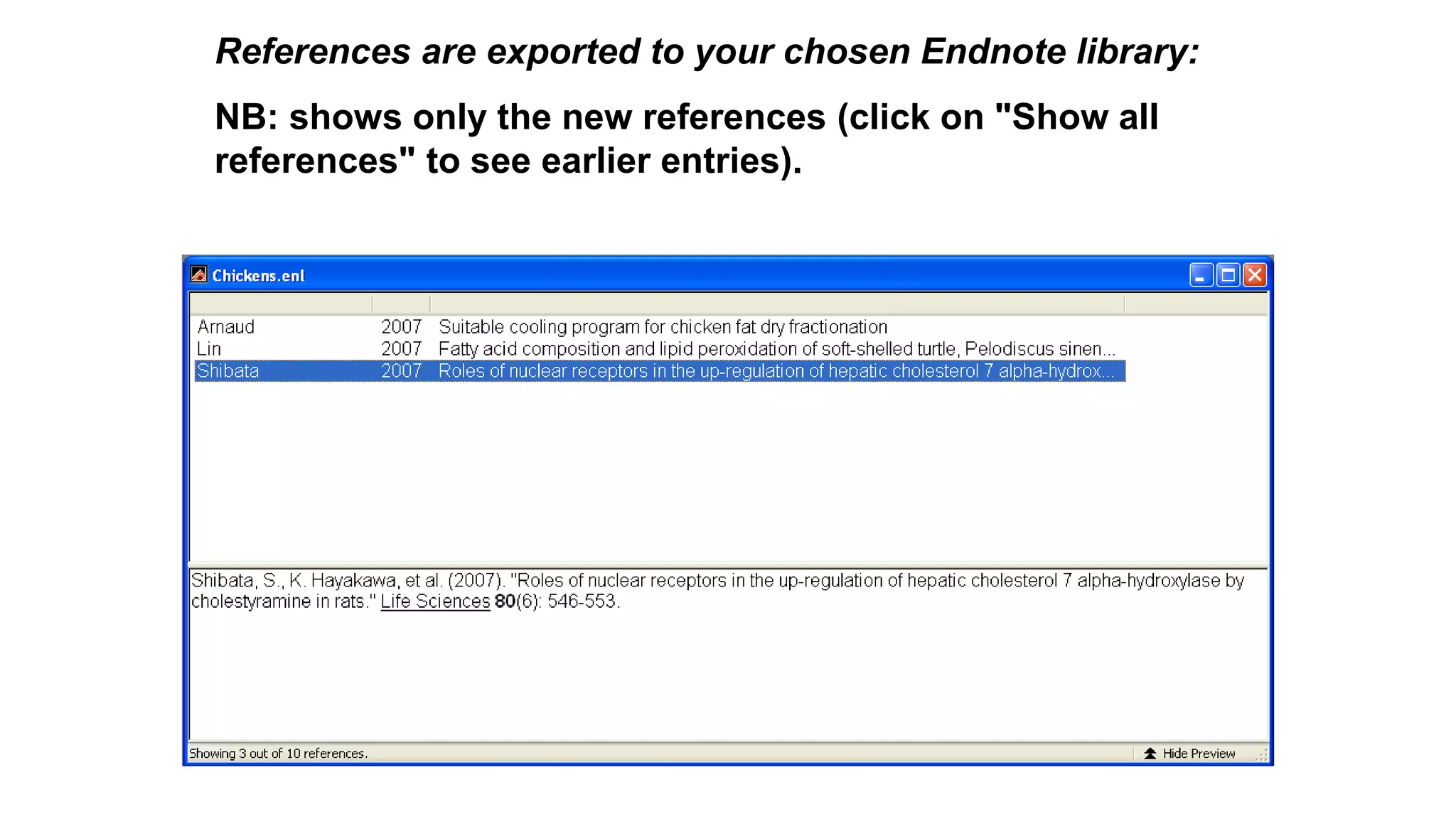
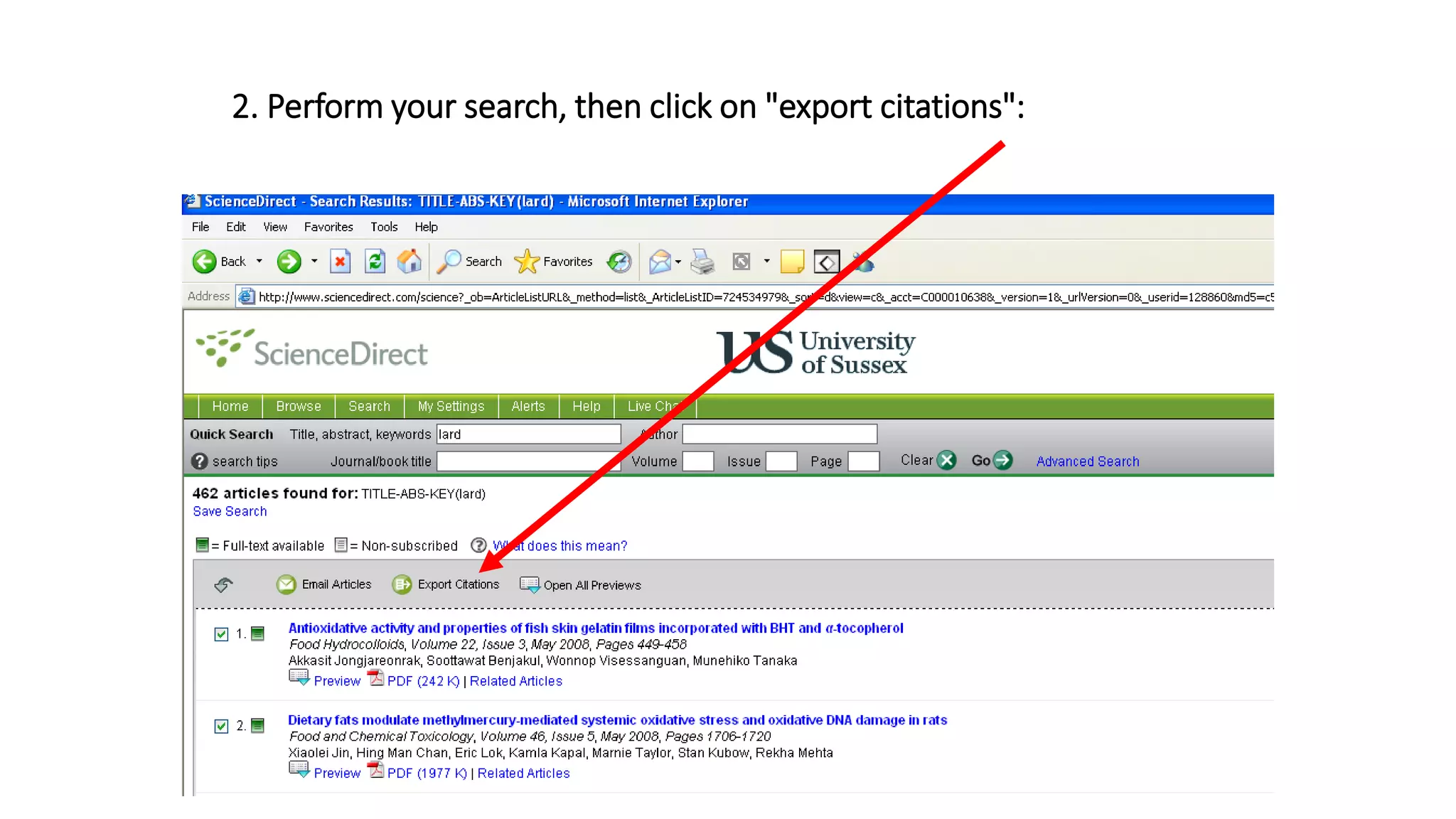
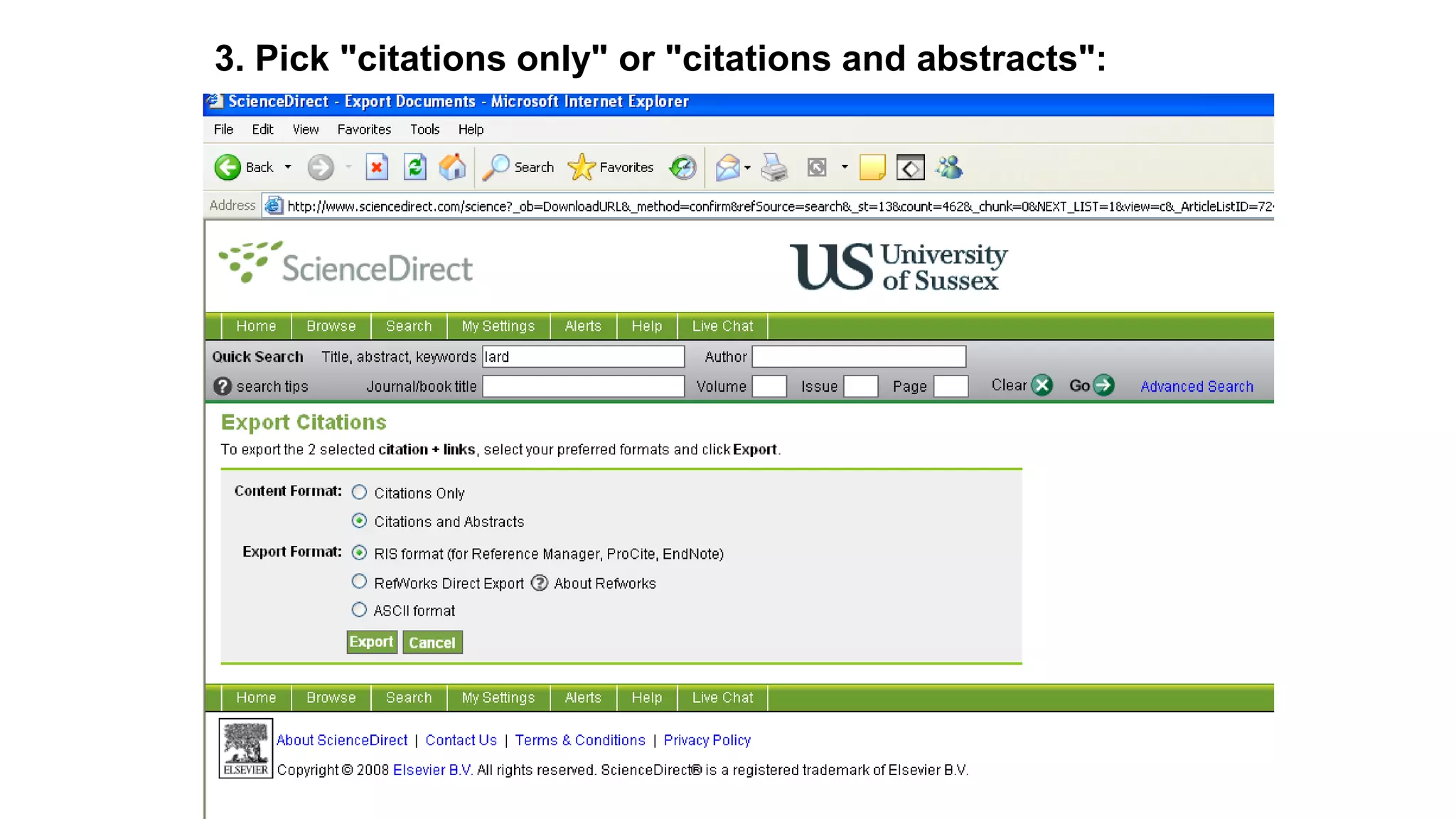
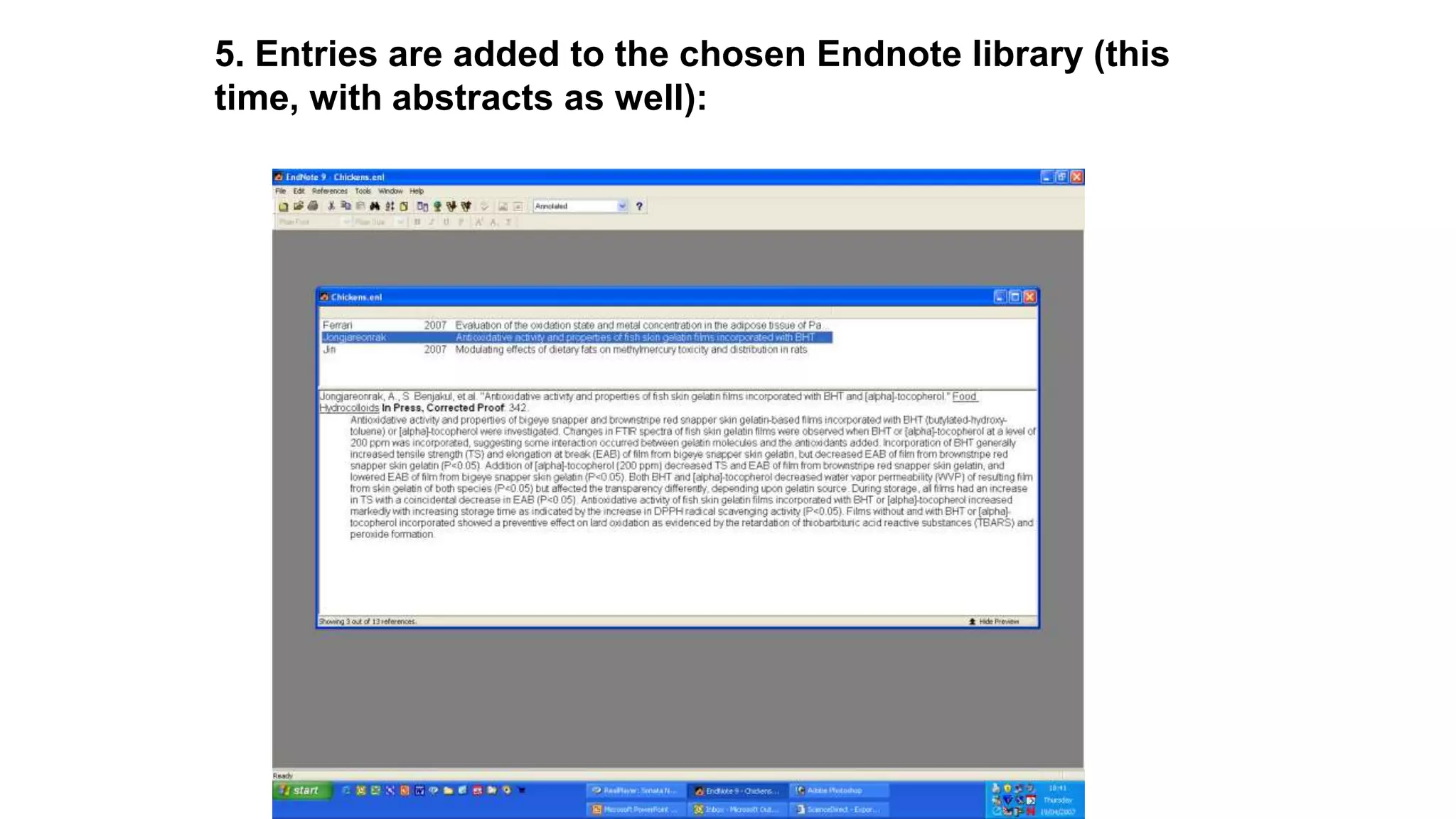
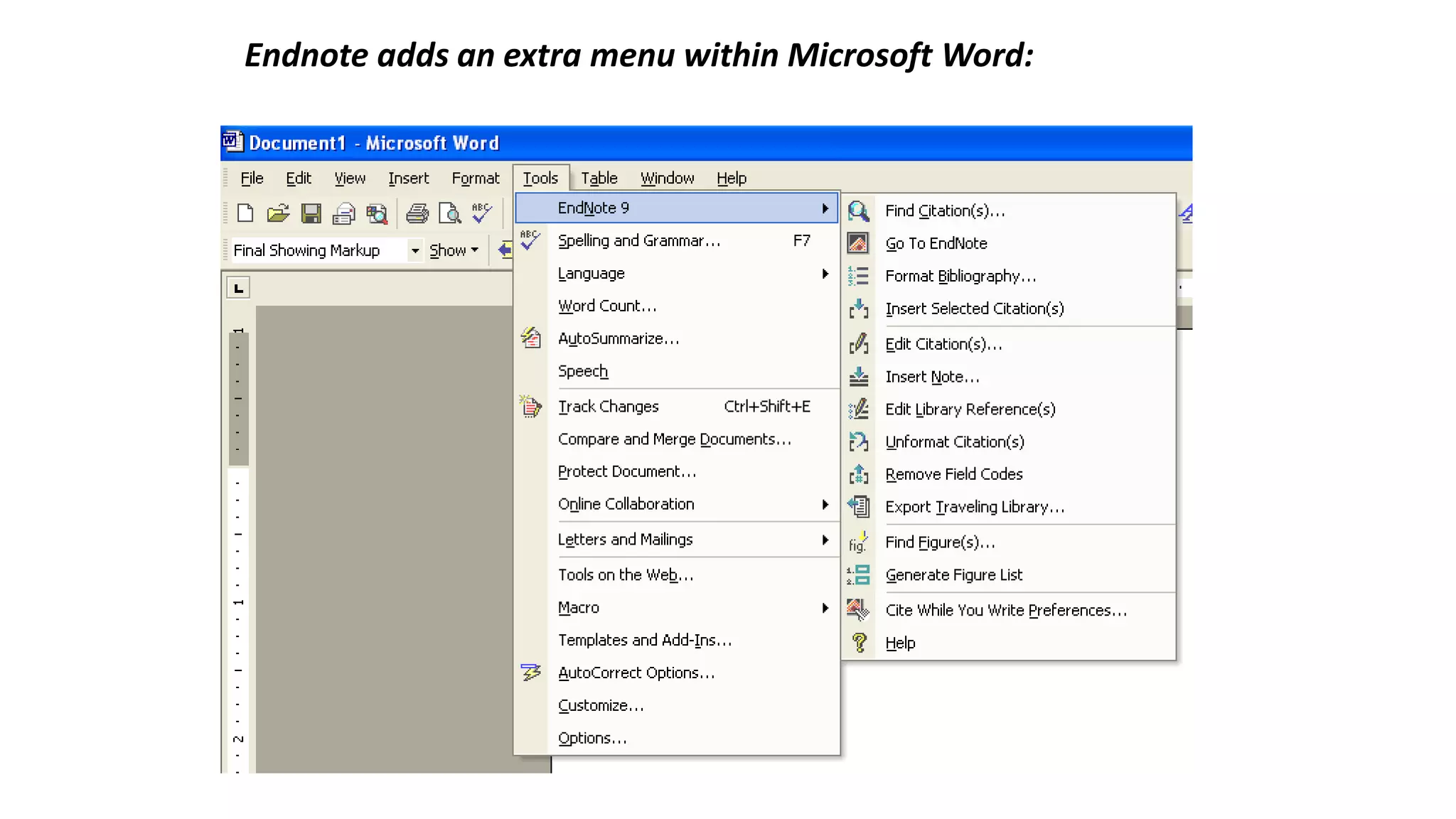
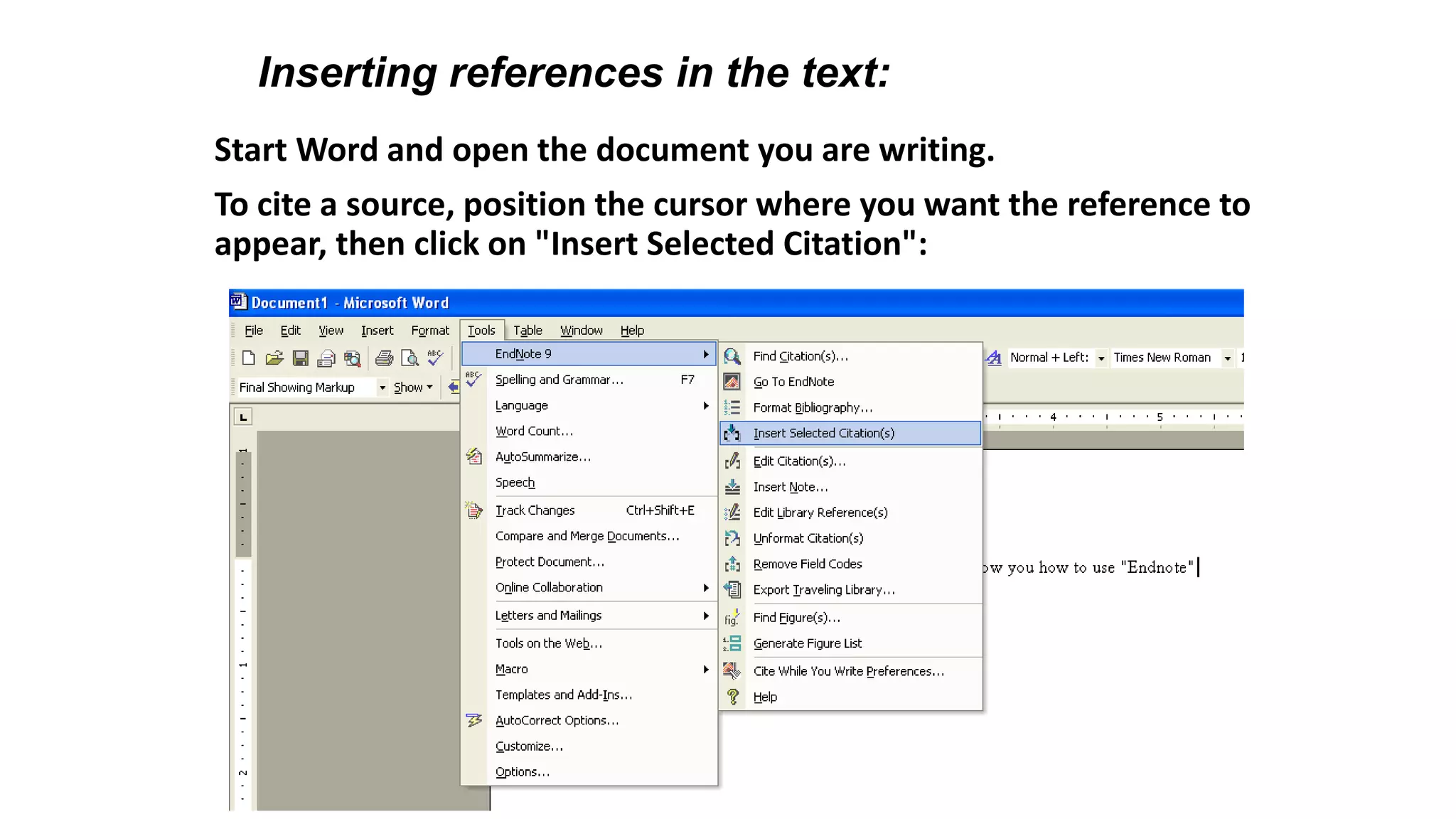
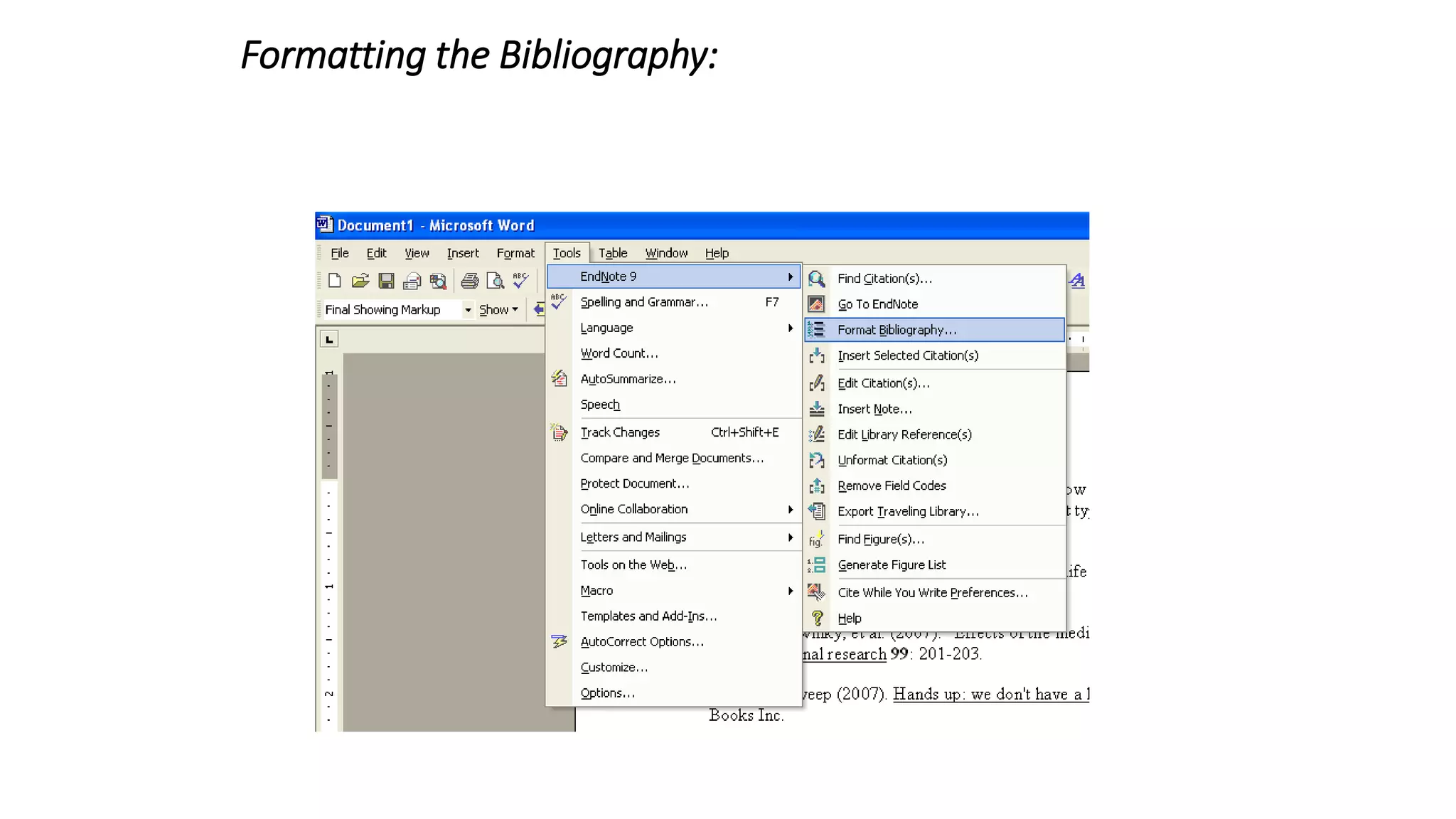
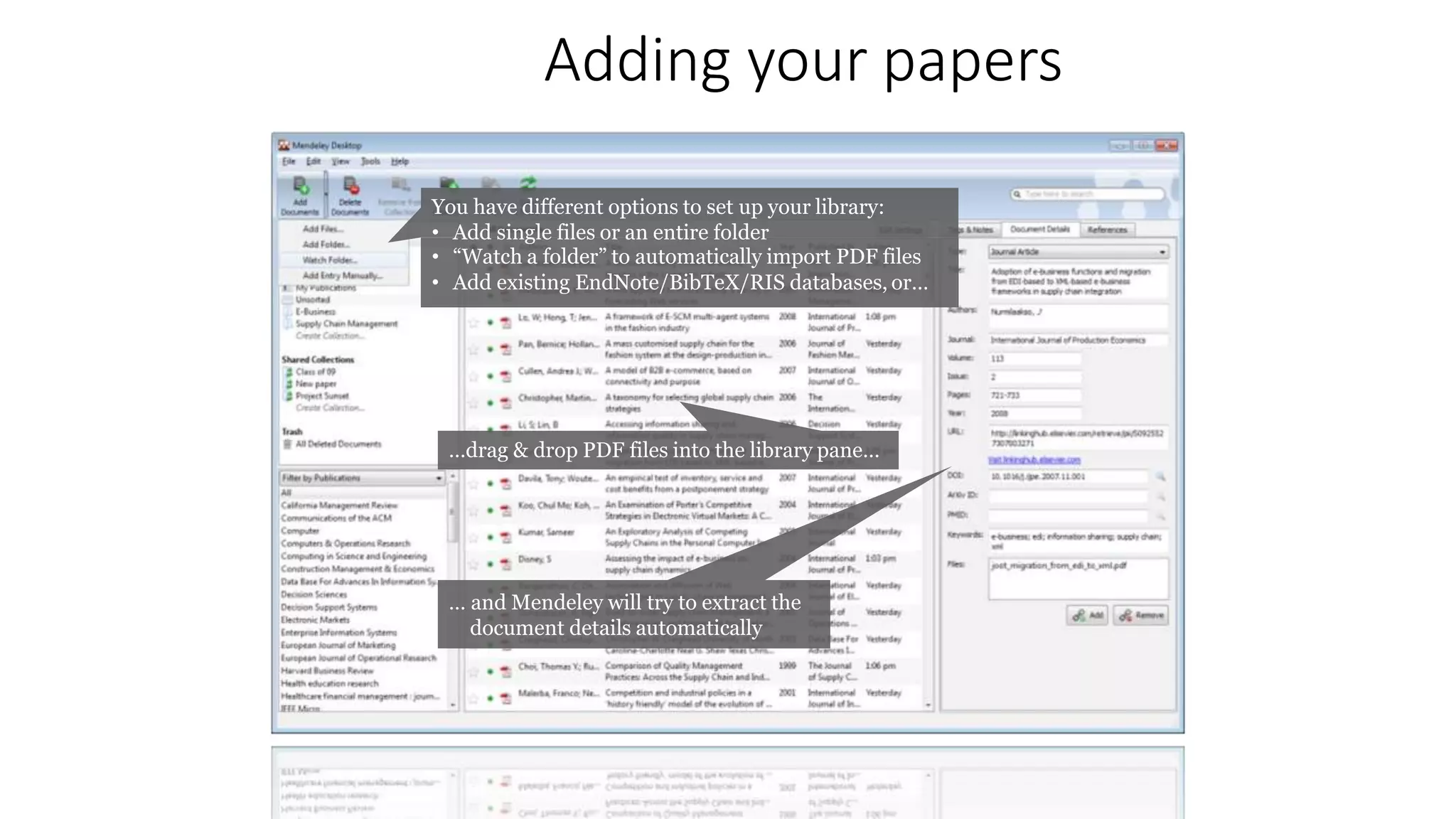
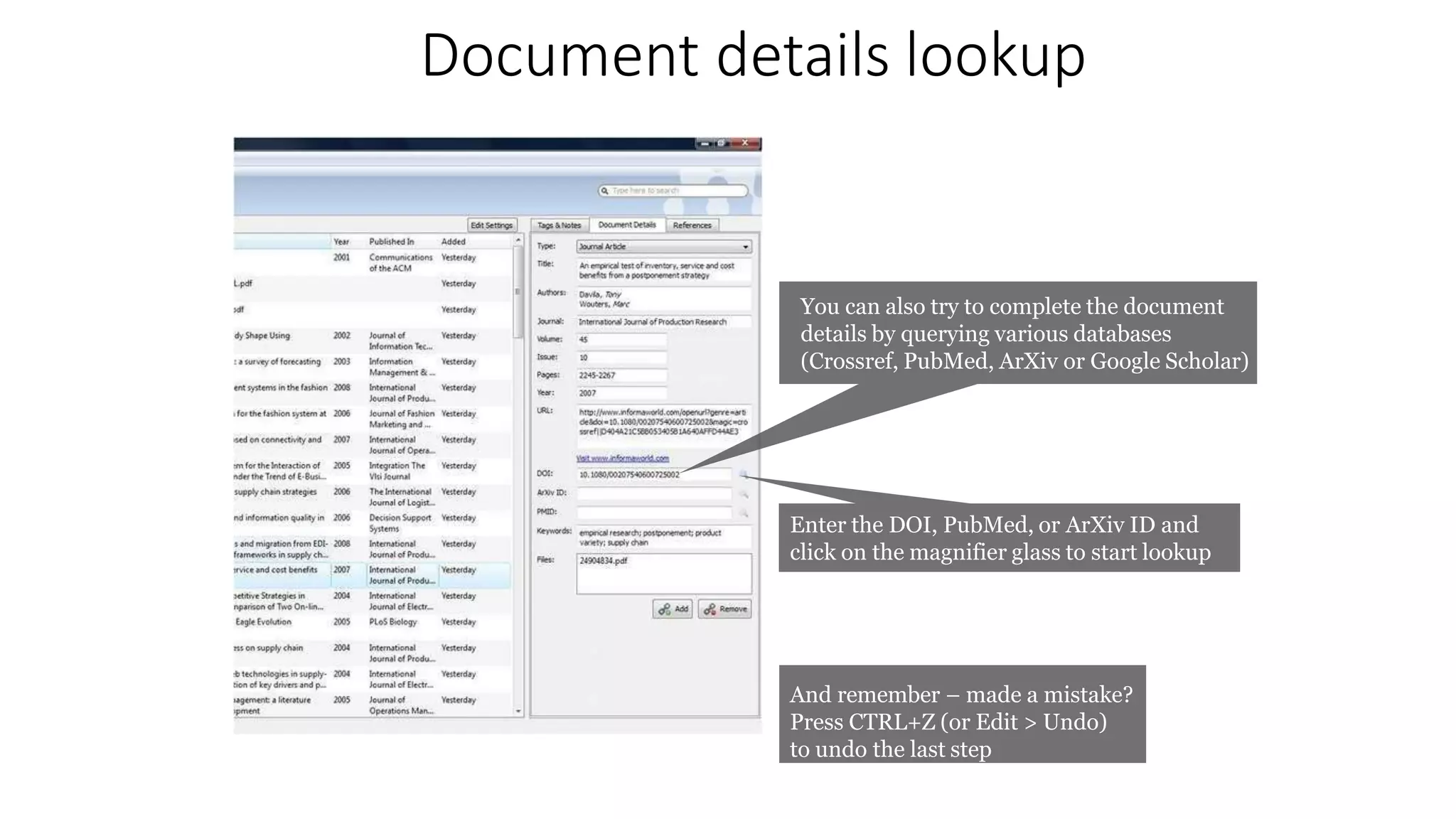
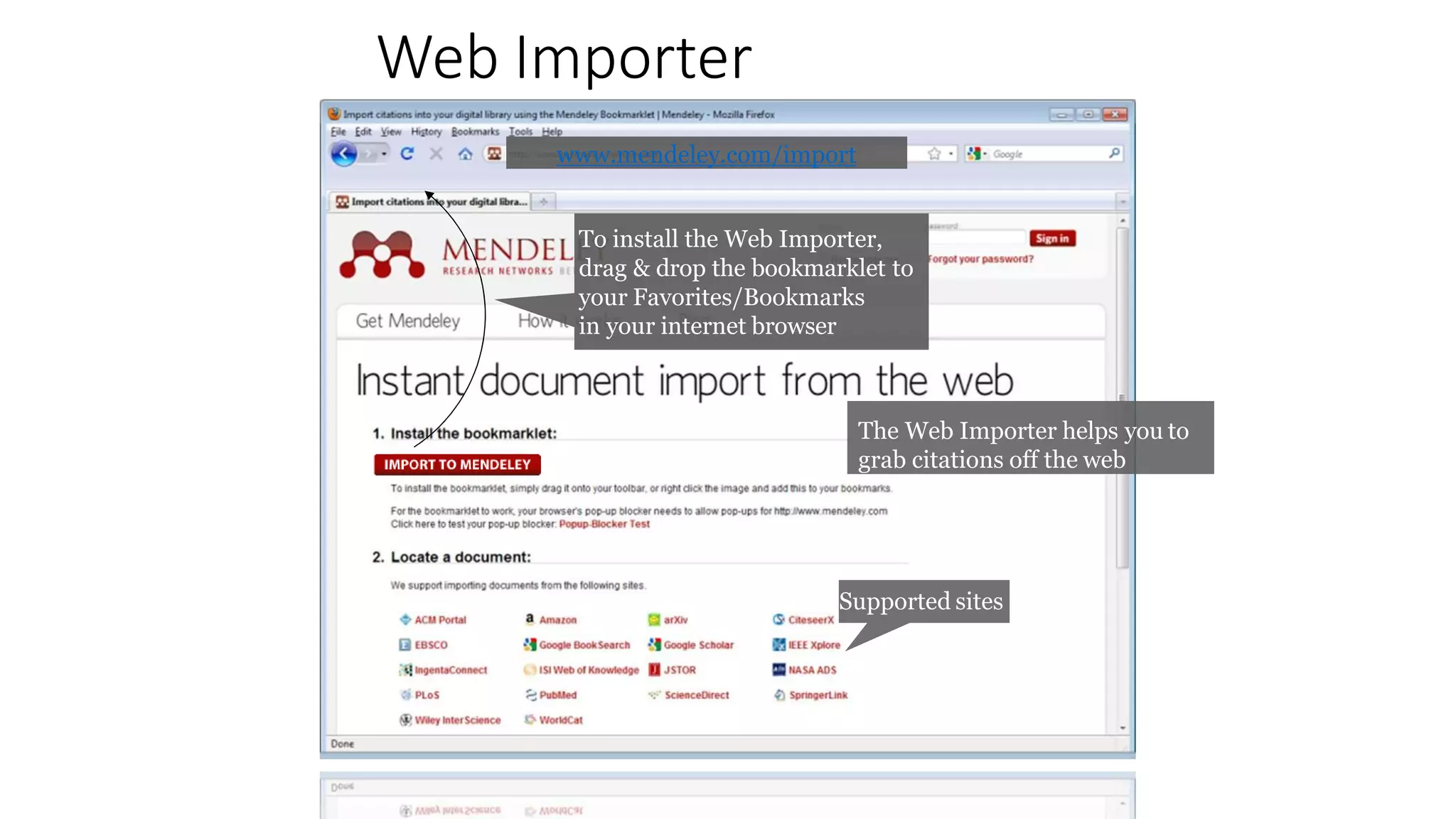
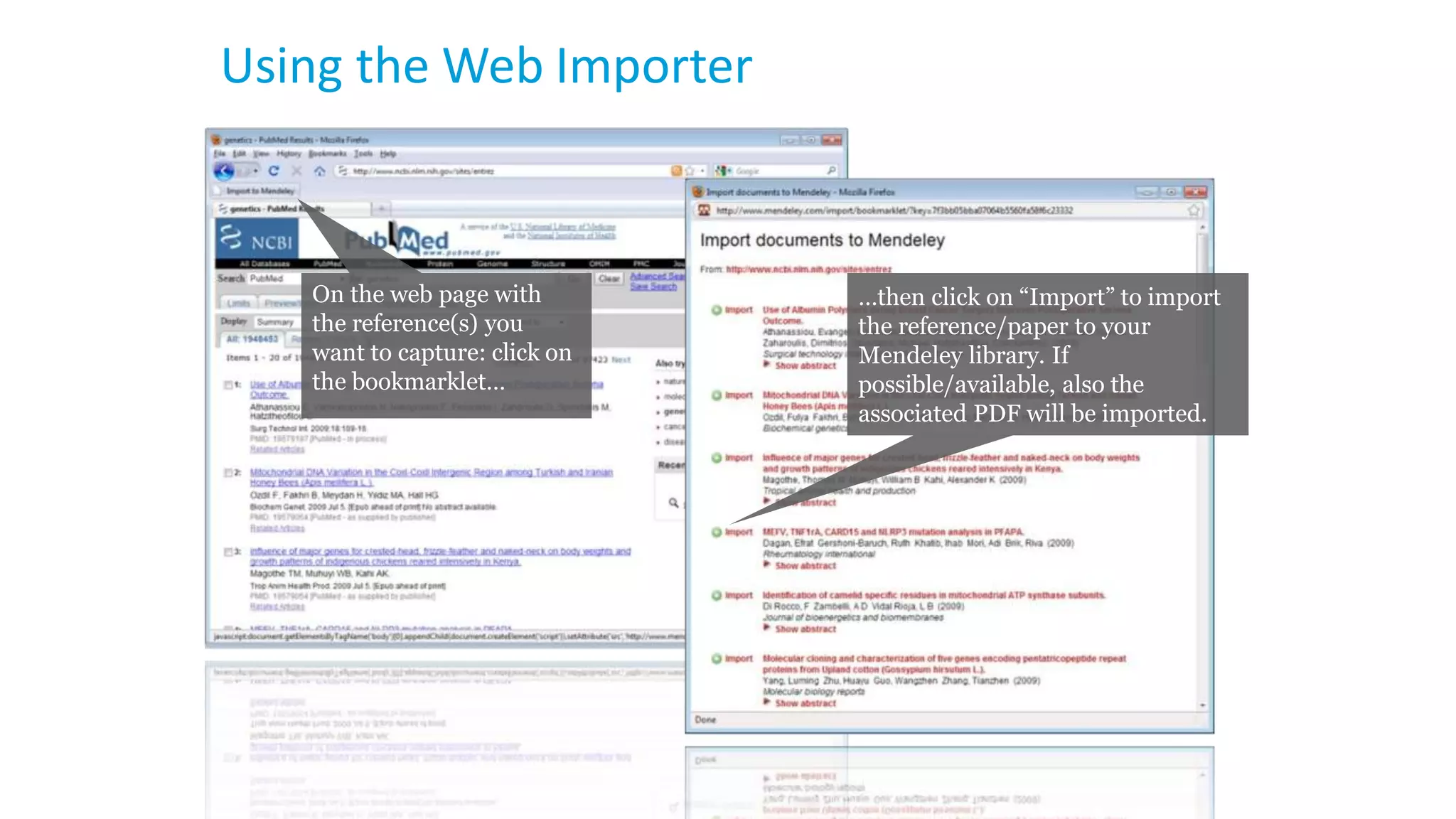
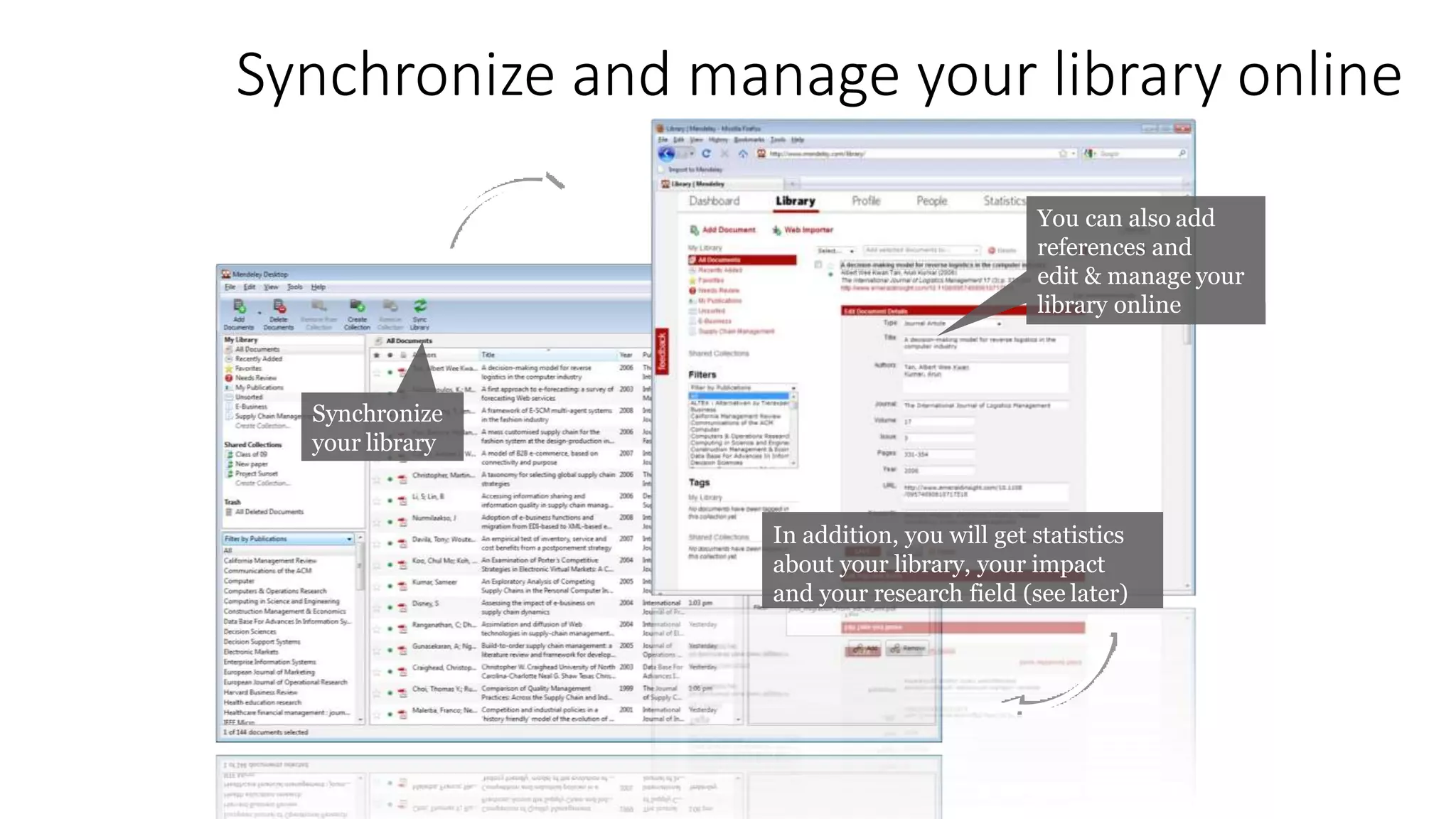
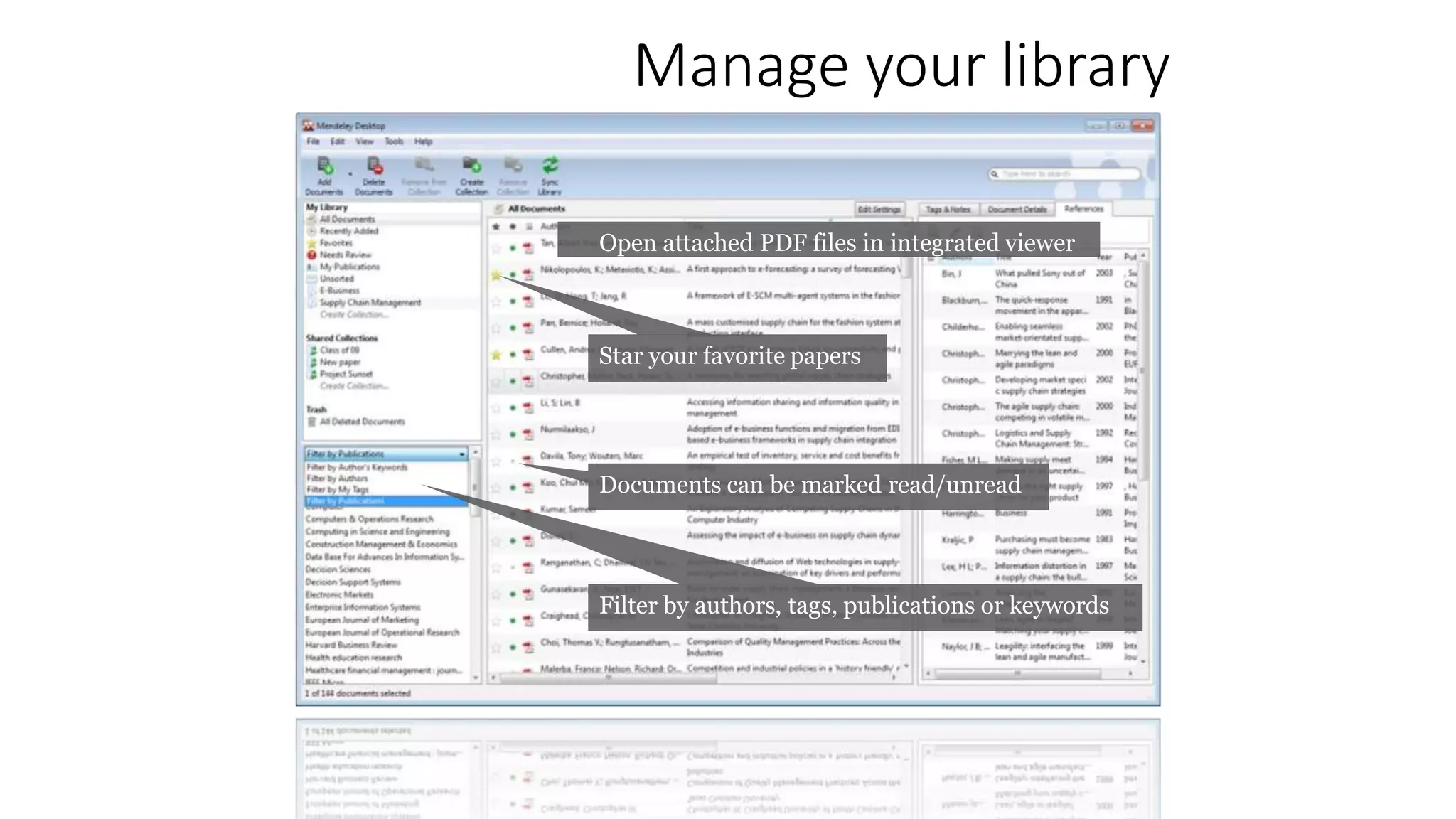
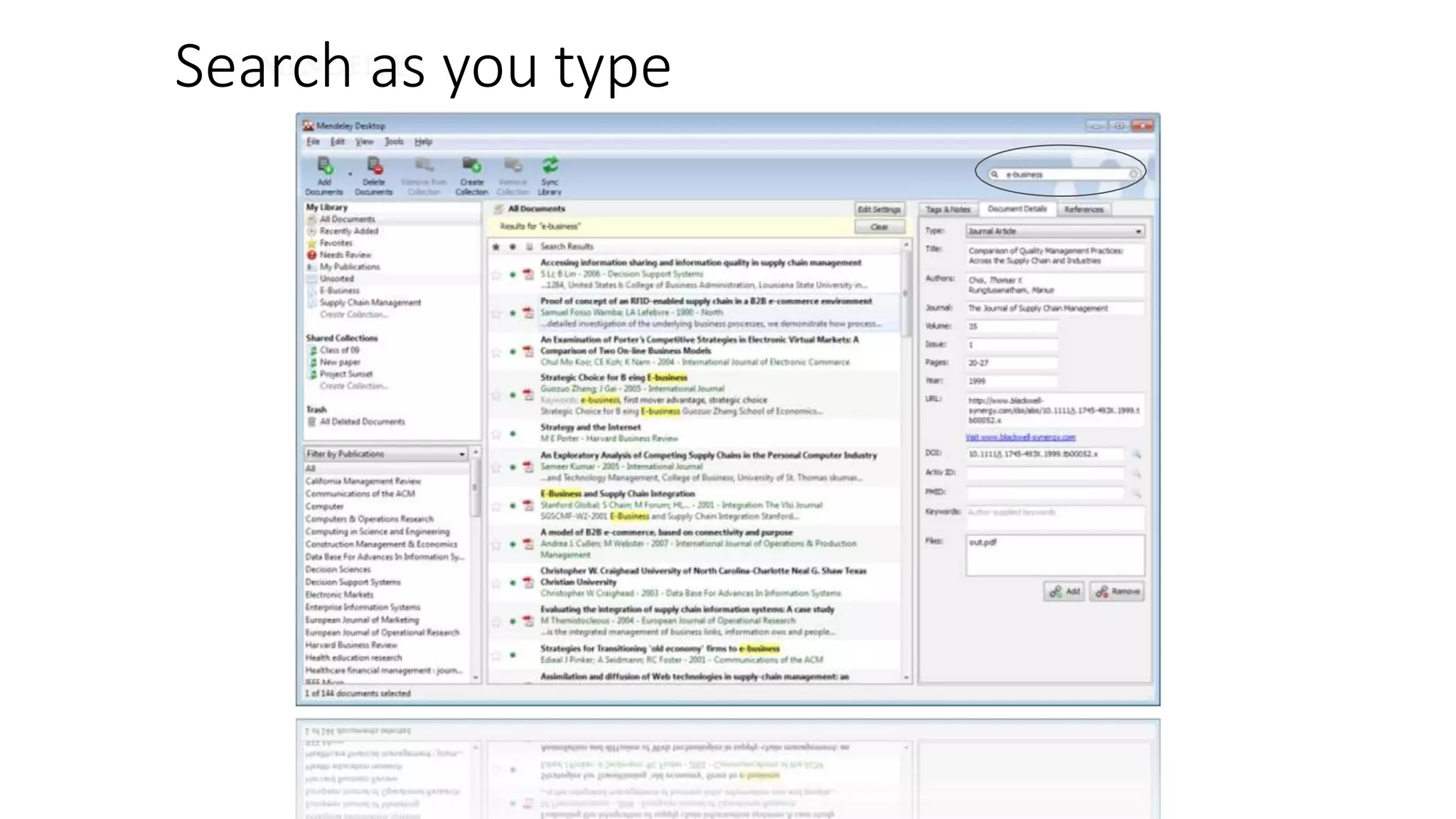
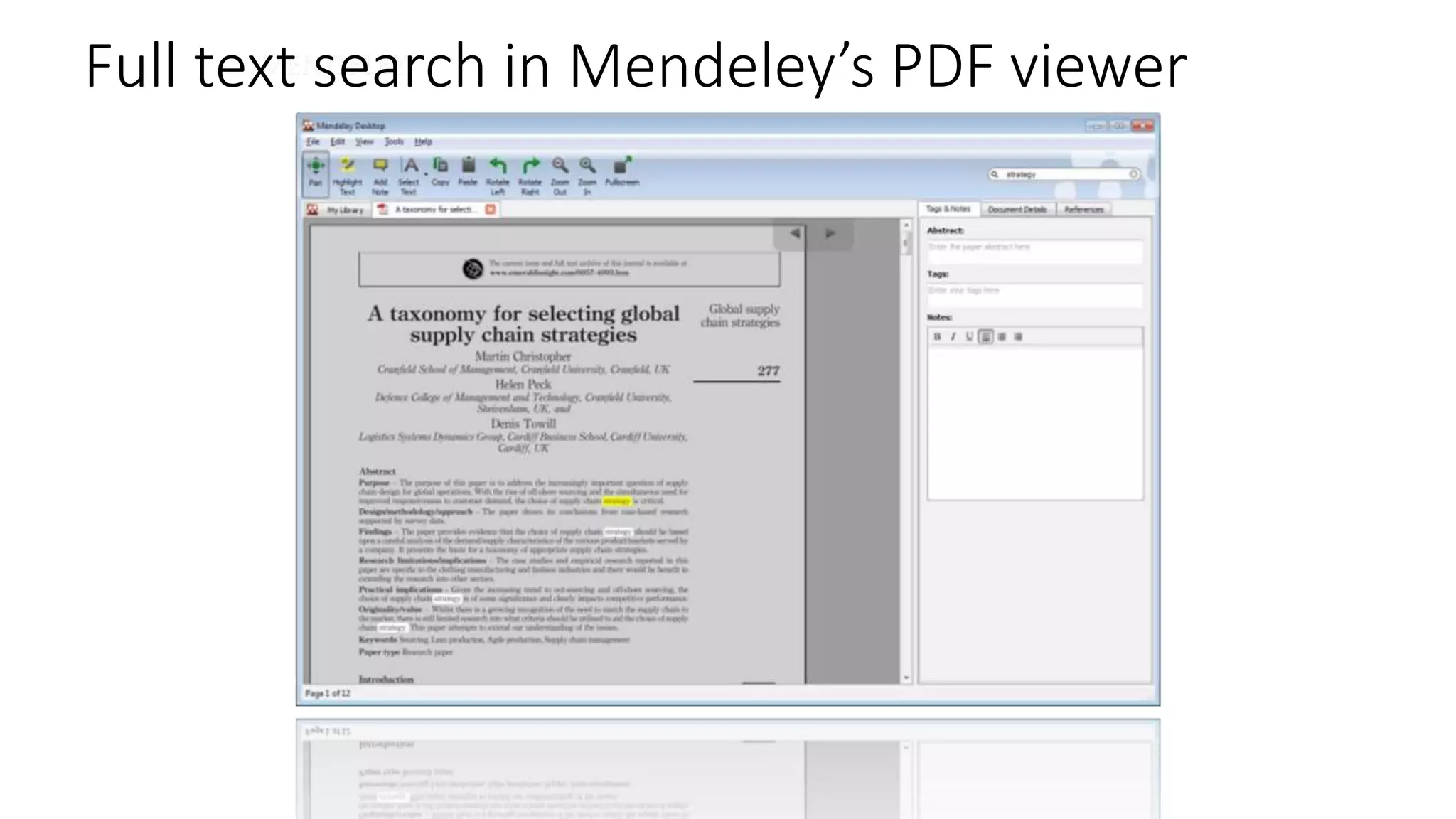
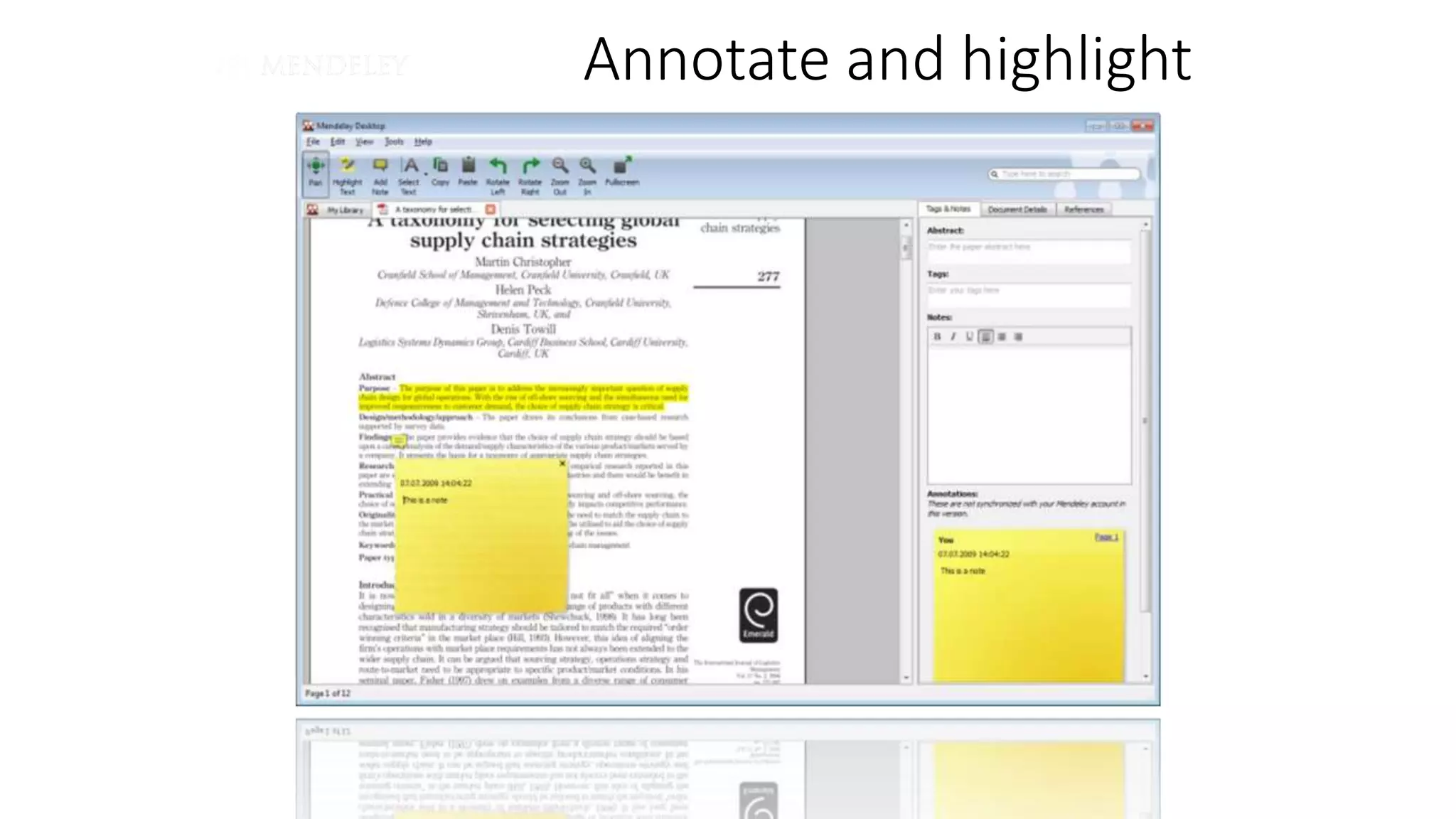
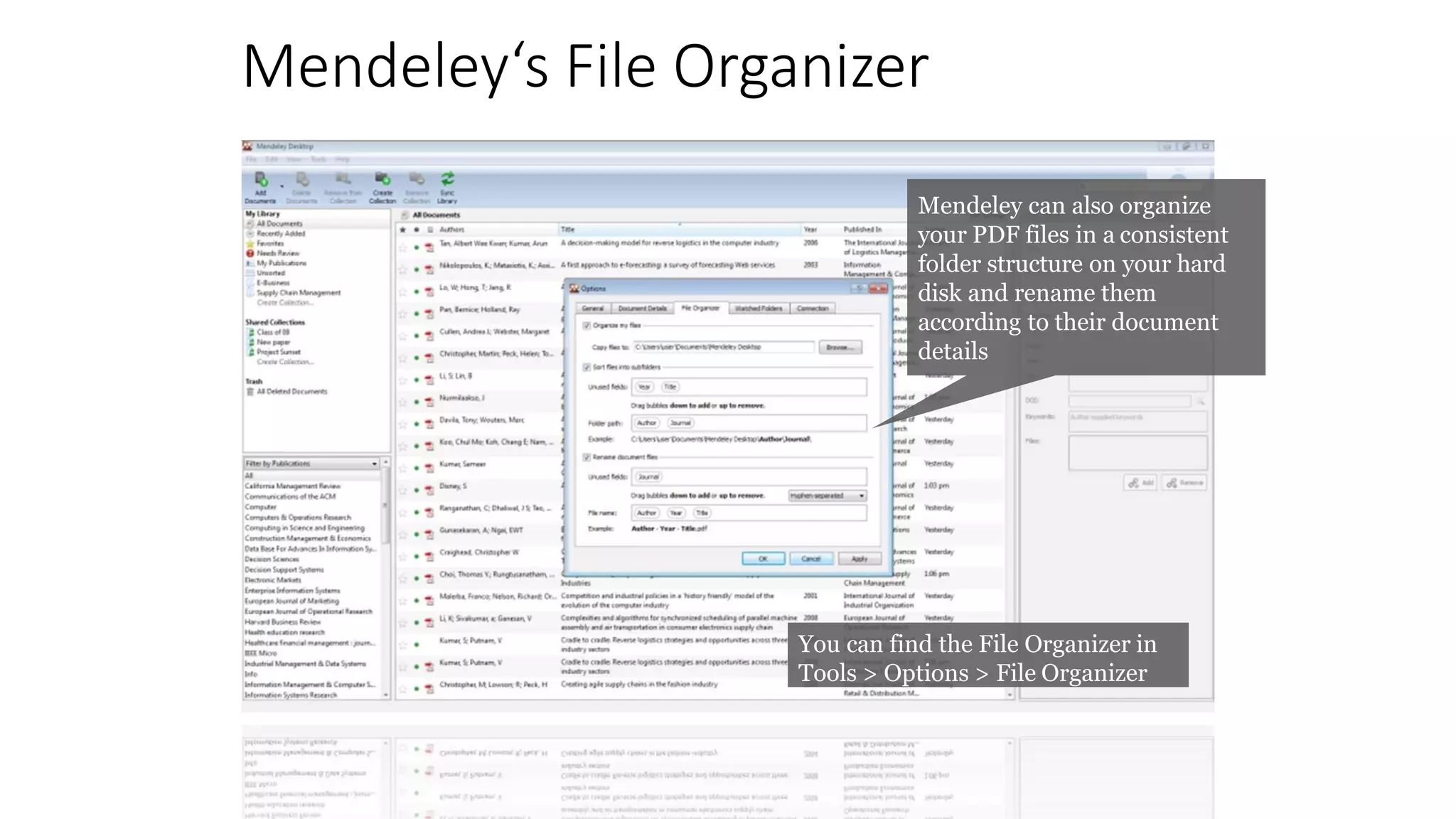
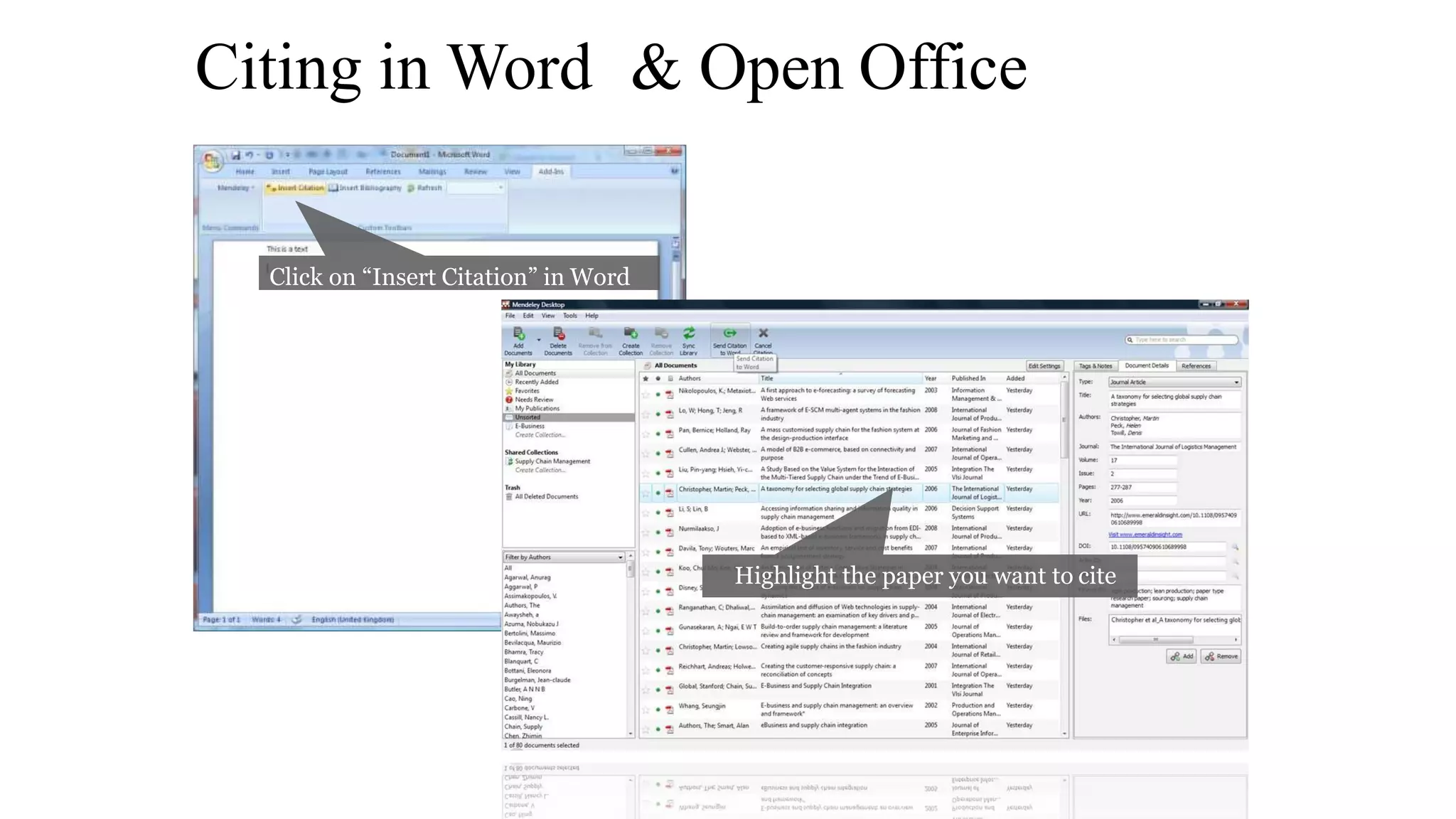
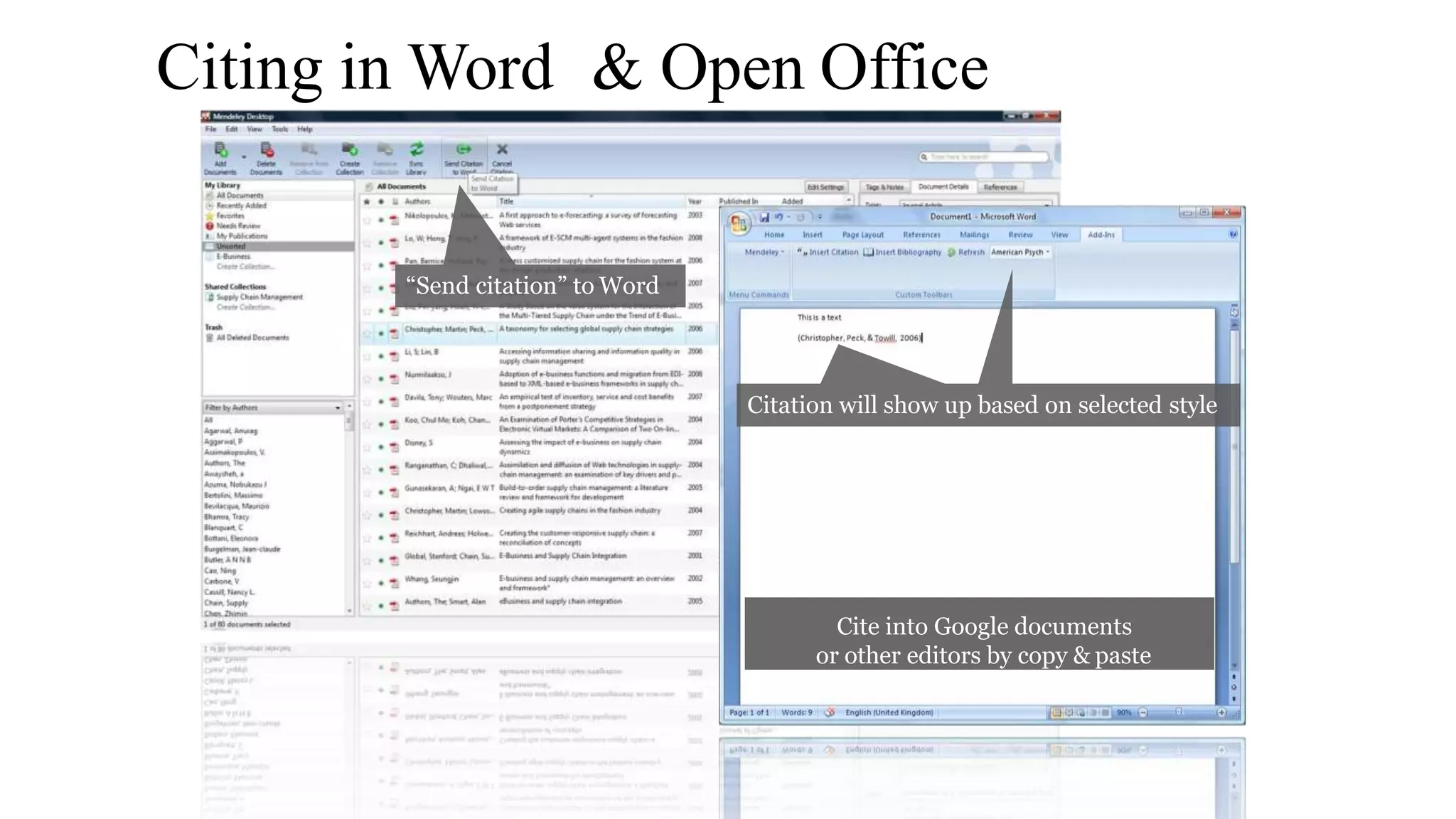
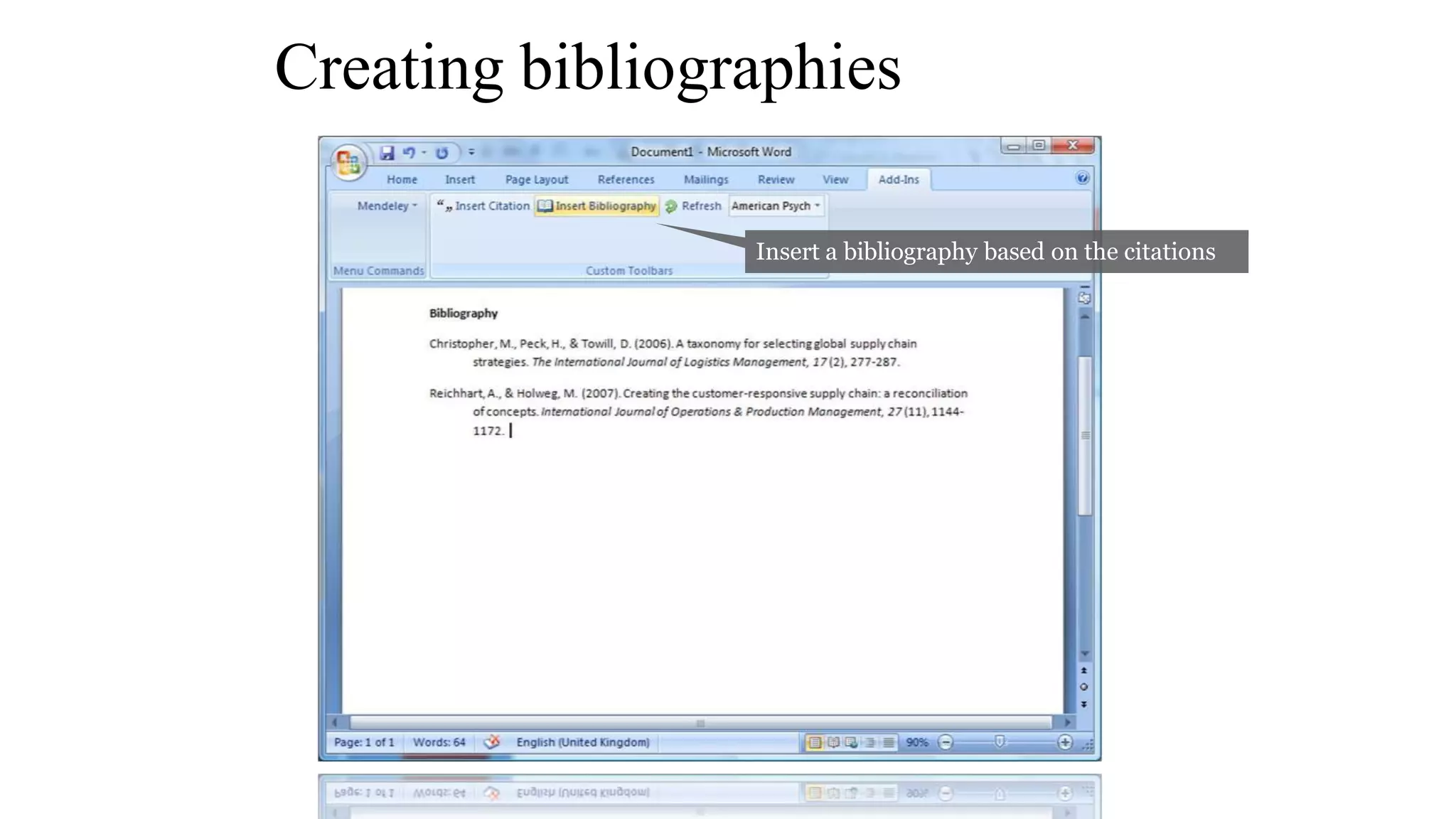
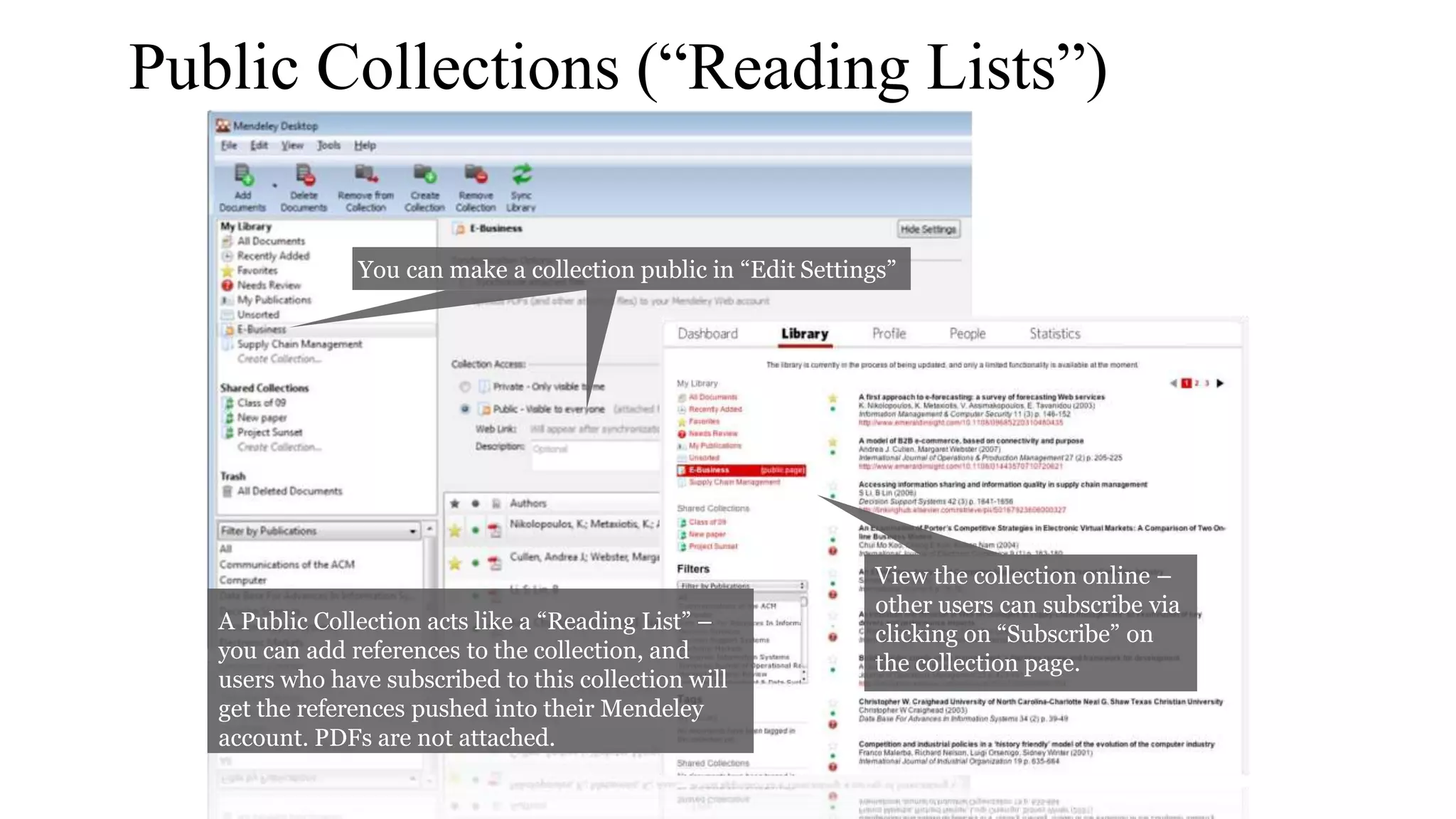
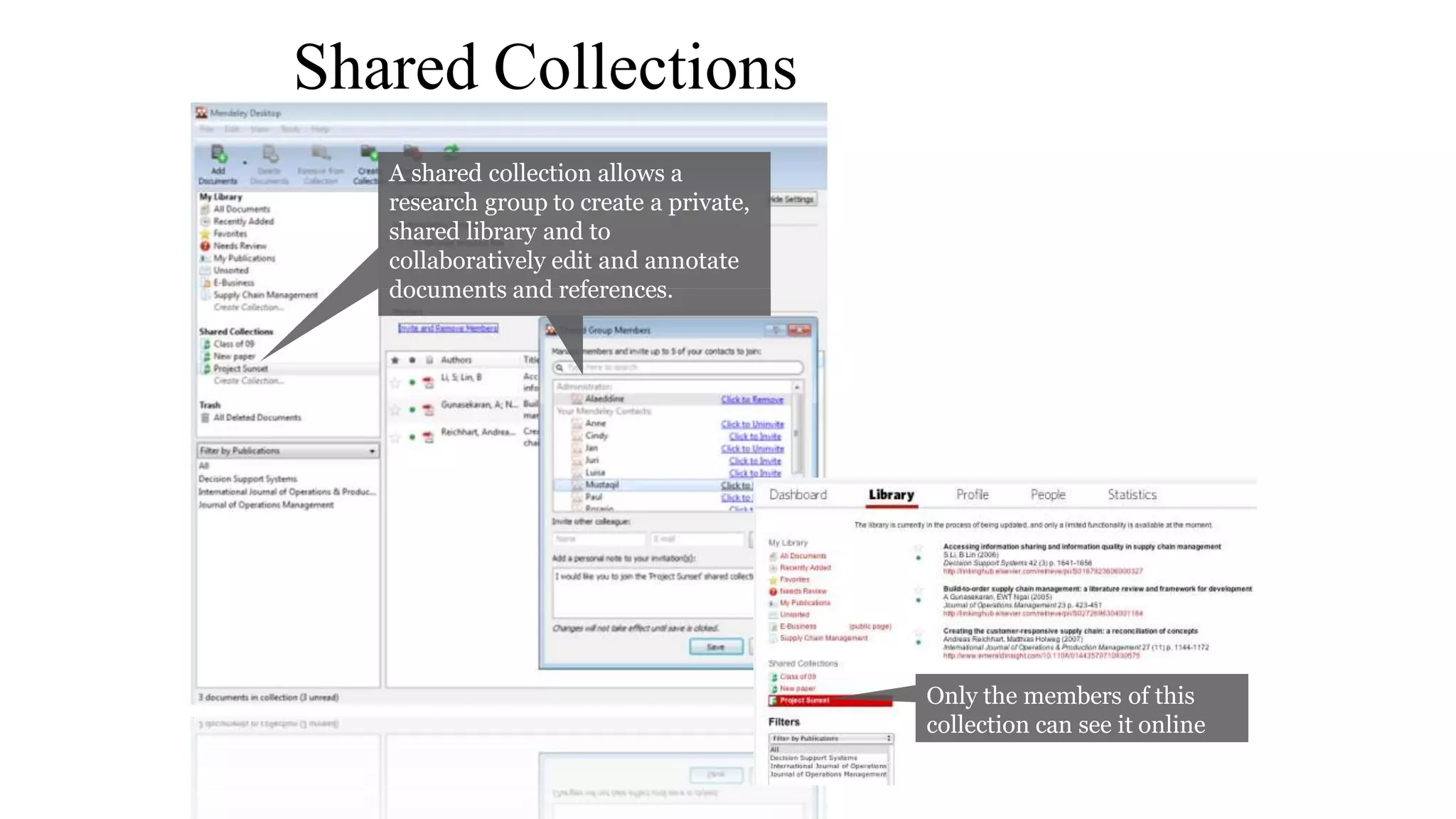
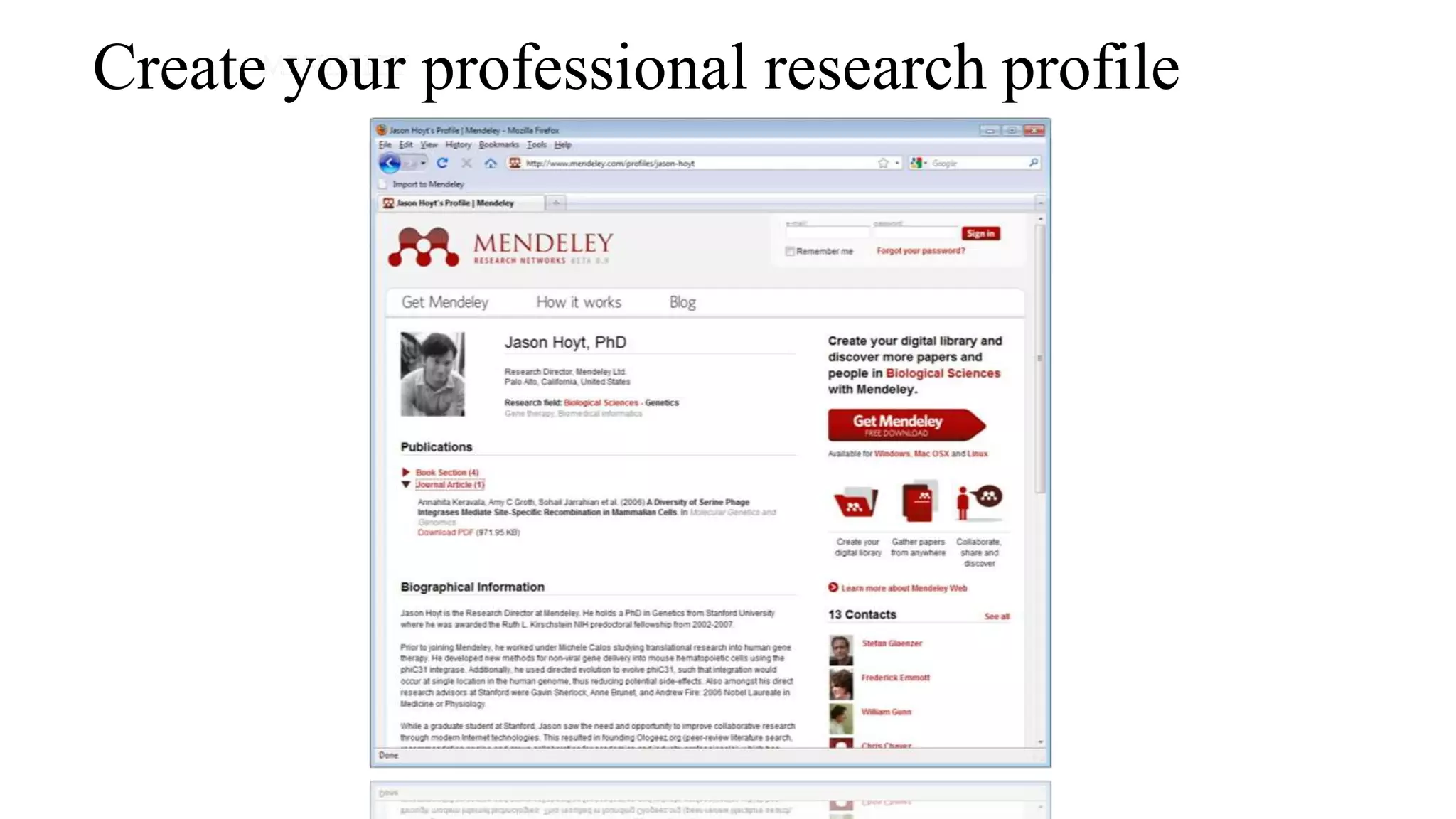
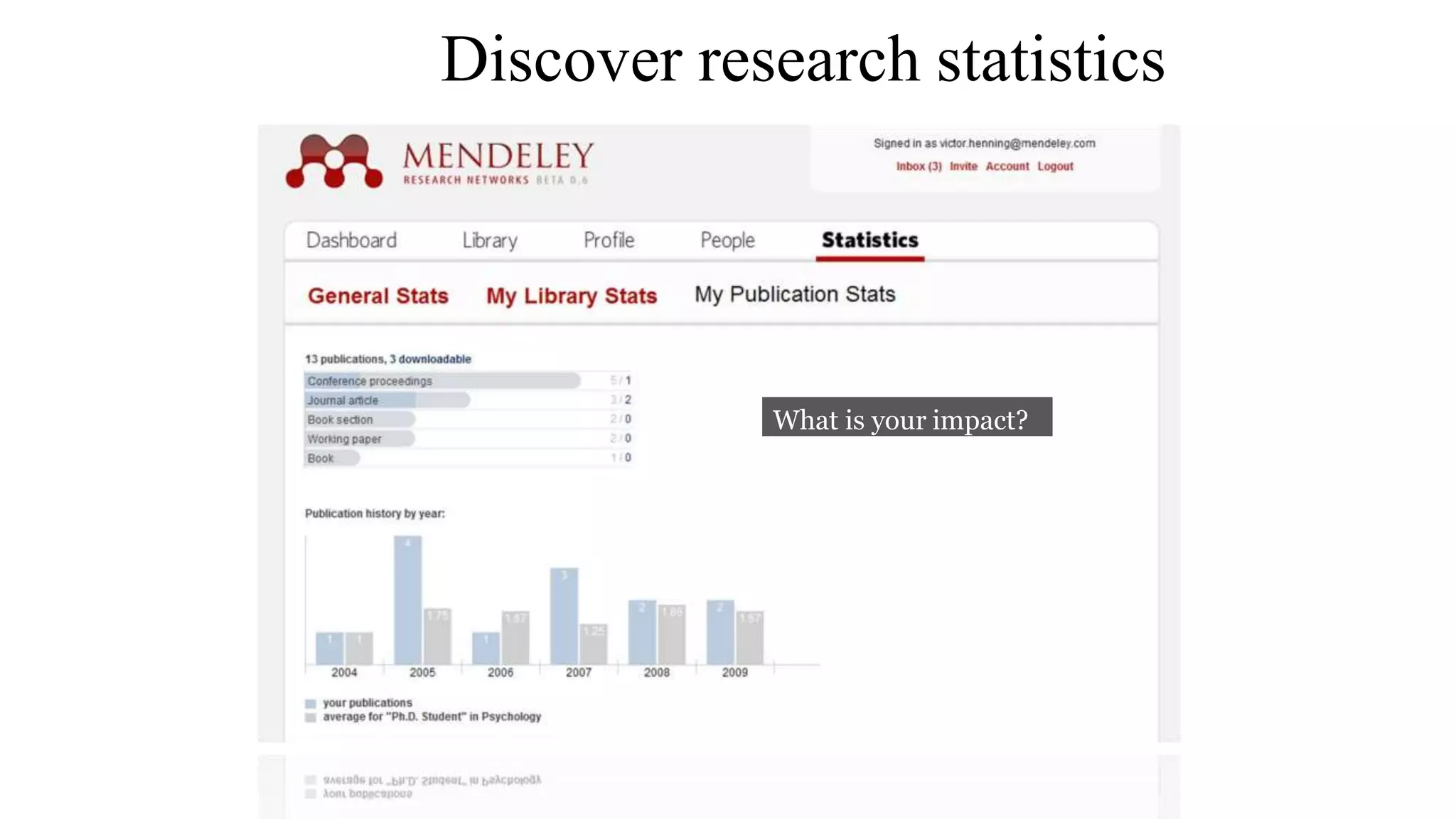
Statistics is the study of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data. It was introduced in 1791 in English by Sir John Sinclair when he published the first volume of a statistical account of Scotland. SPSS is a widely used software package for statistical analysis and data management. It allows users to easily enter and manage data, conduct statistical analyses, and display results in graphs and tables.