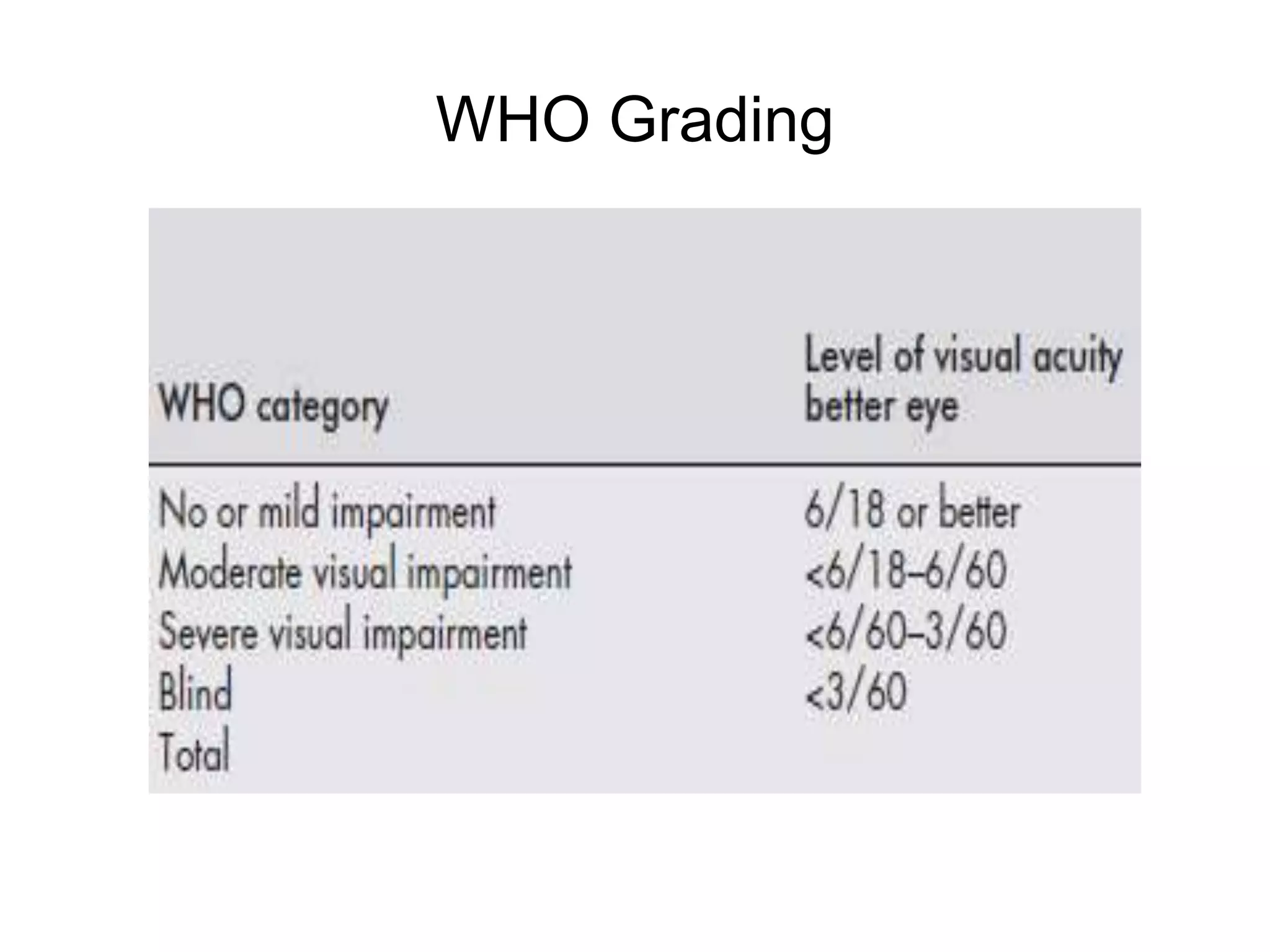
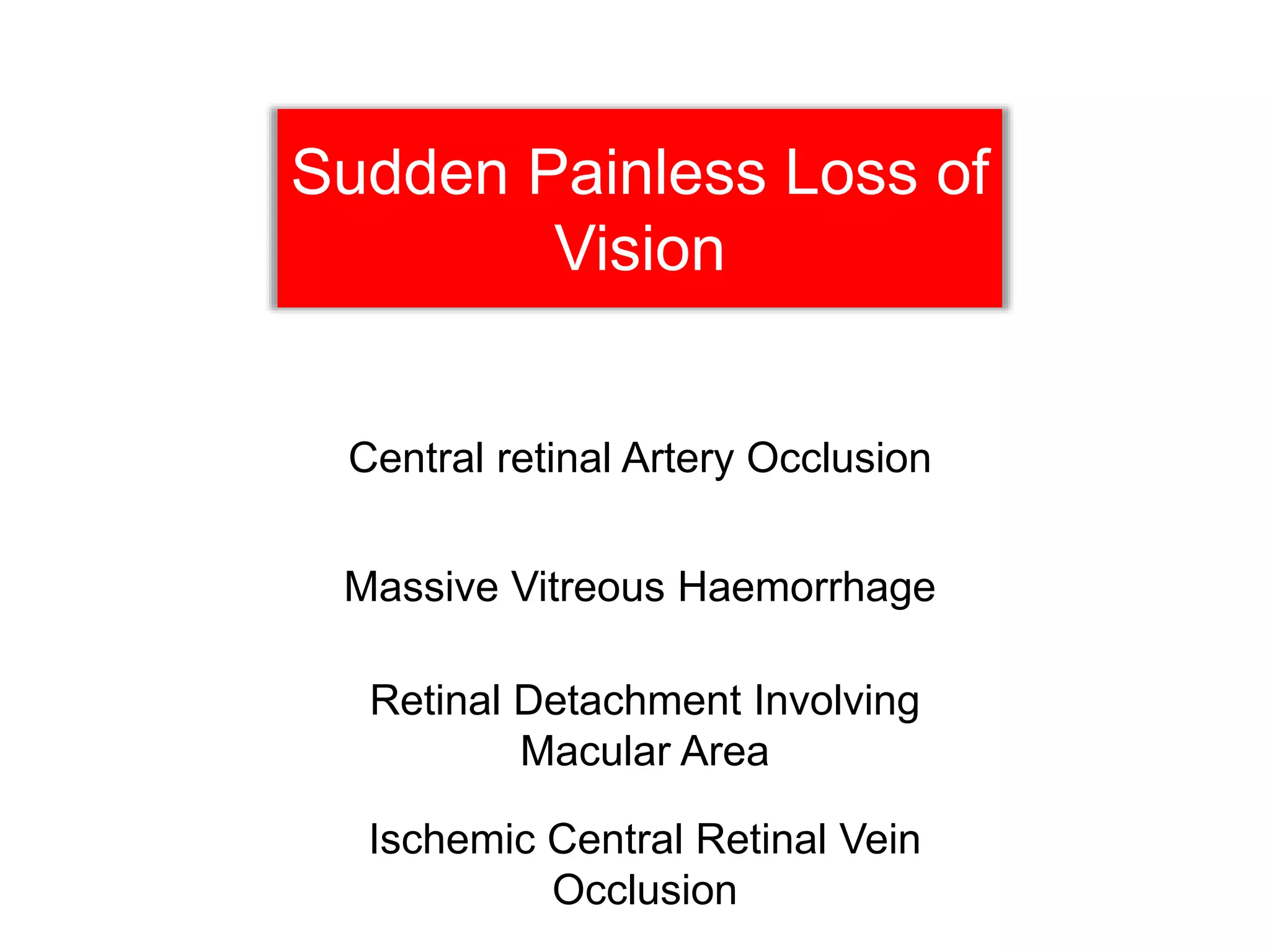
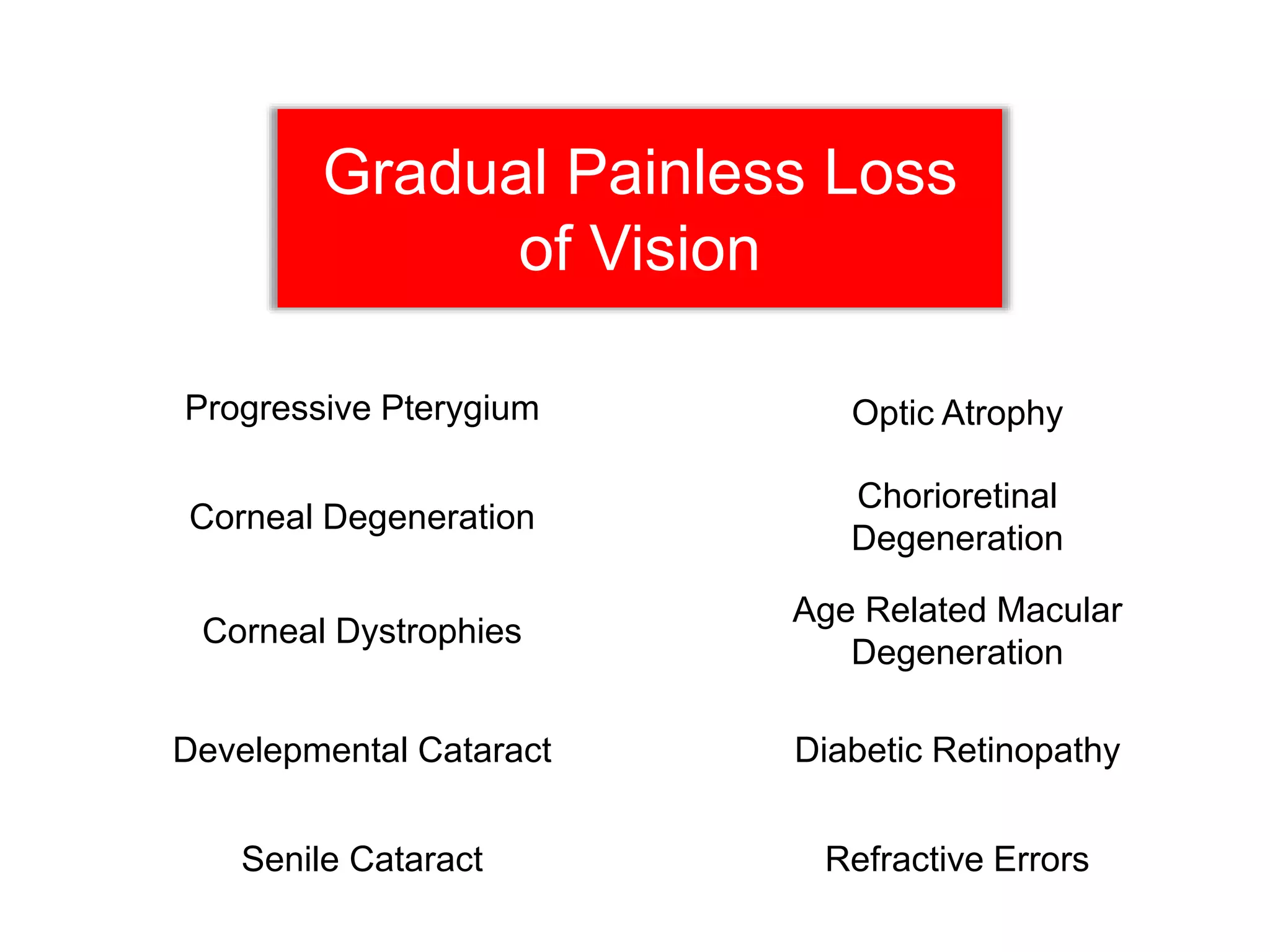
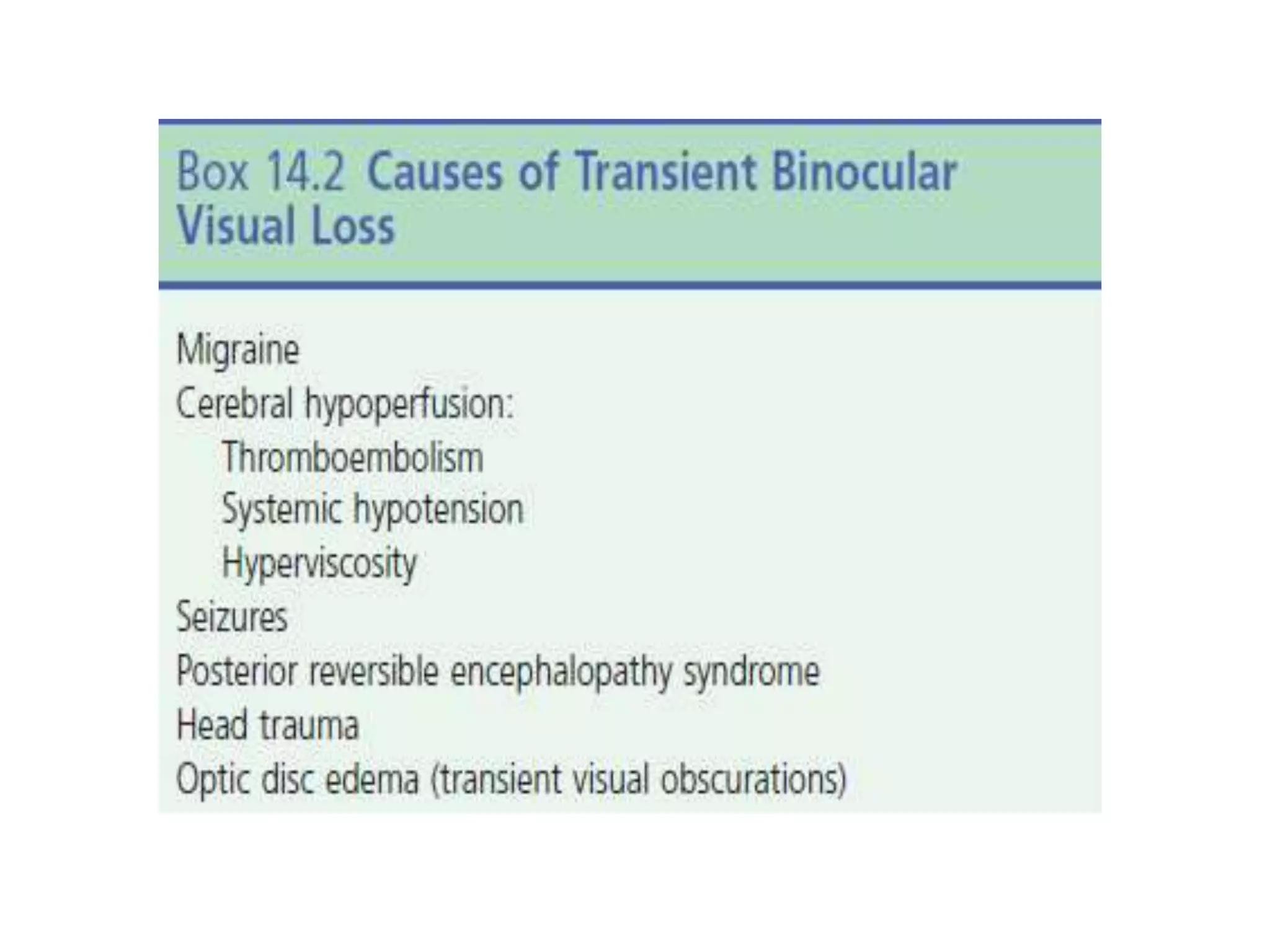
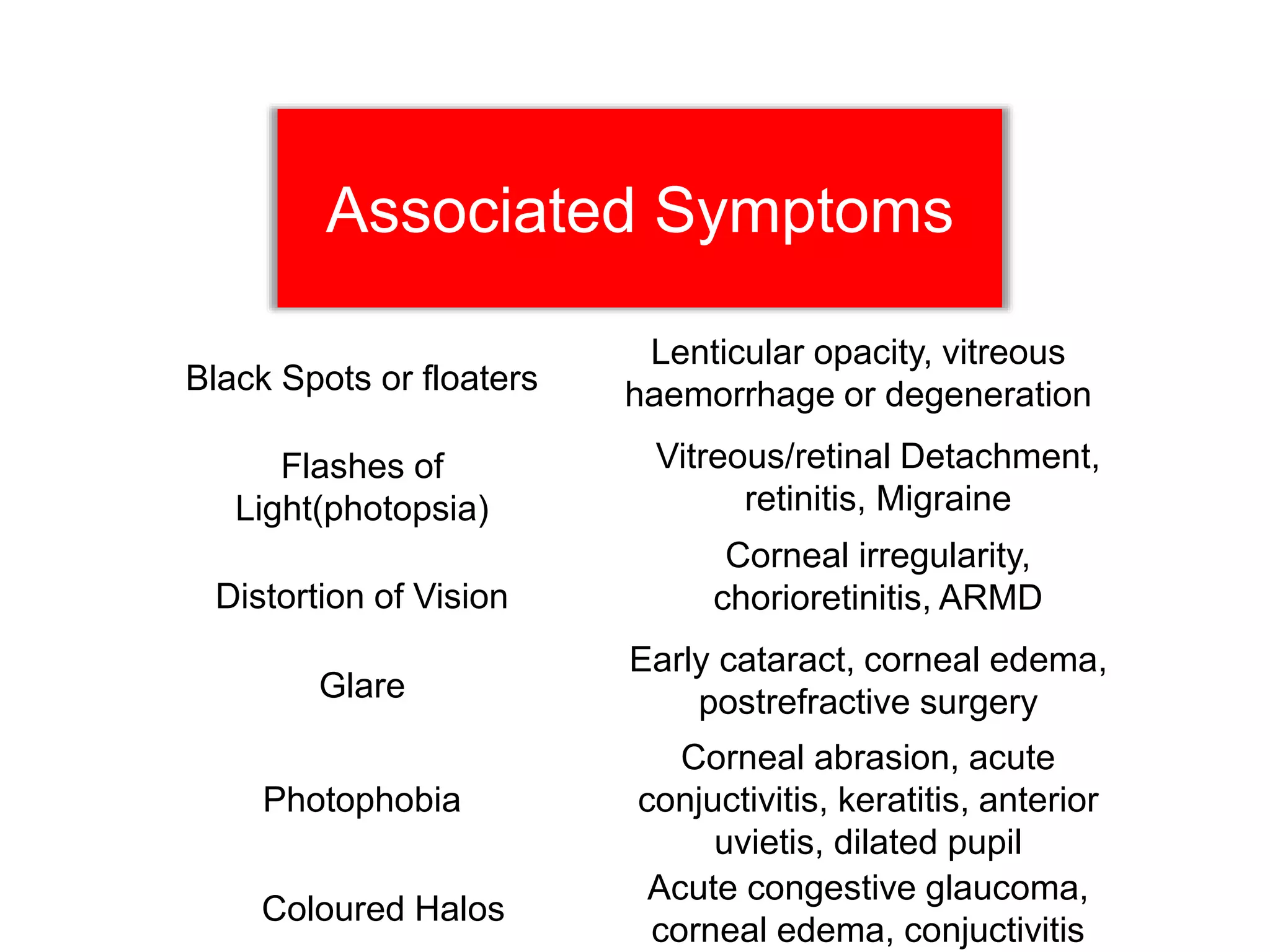
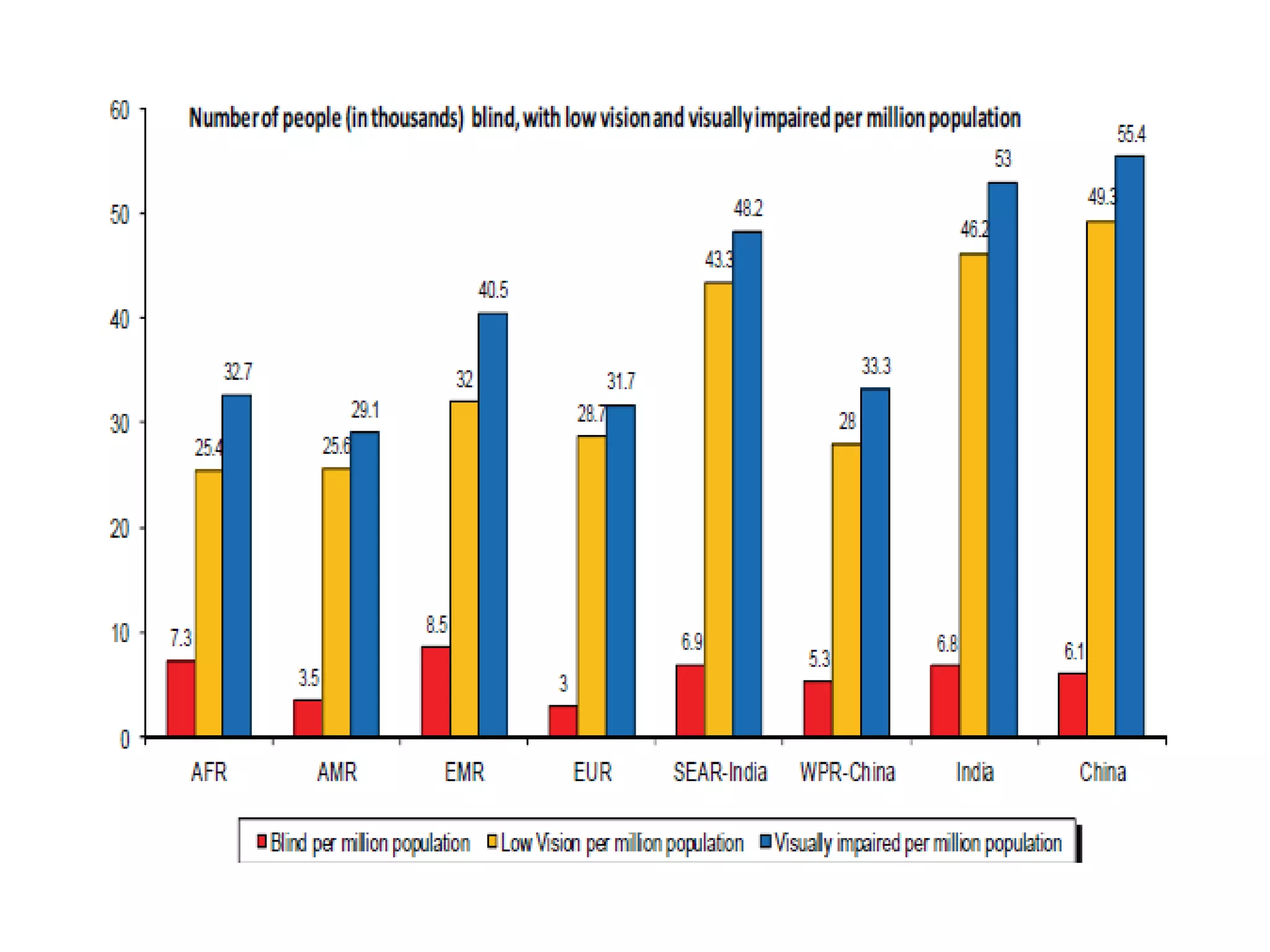
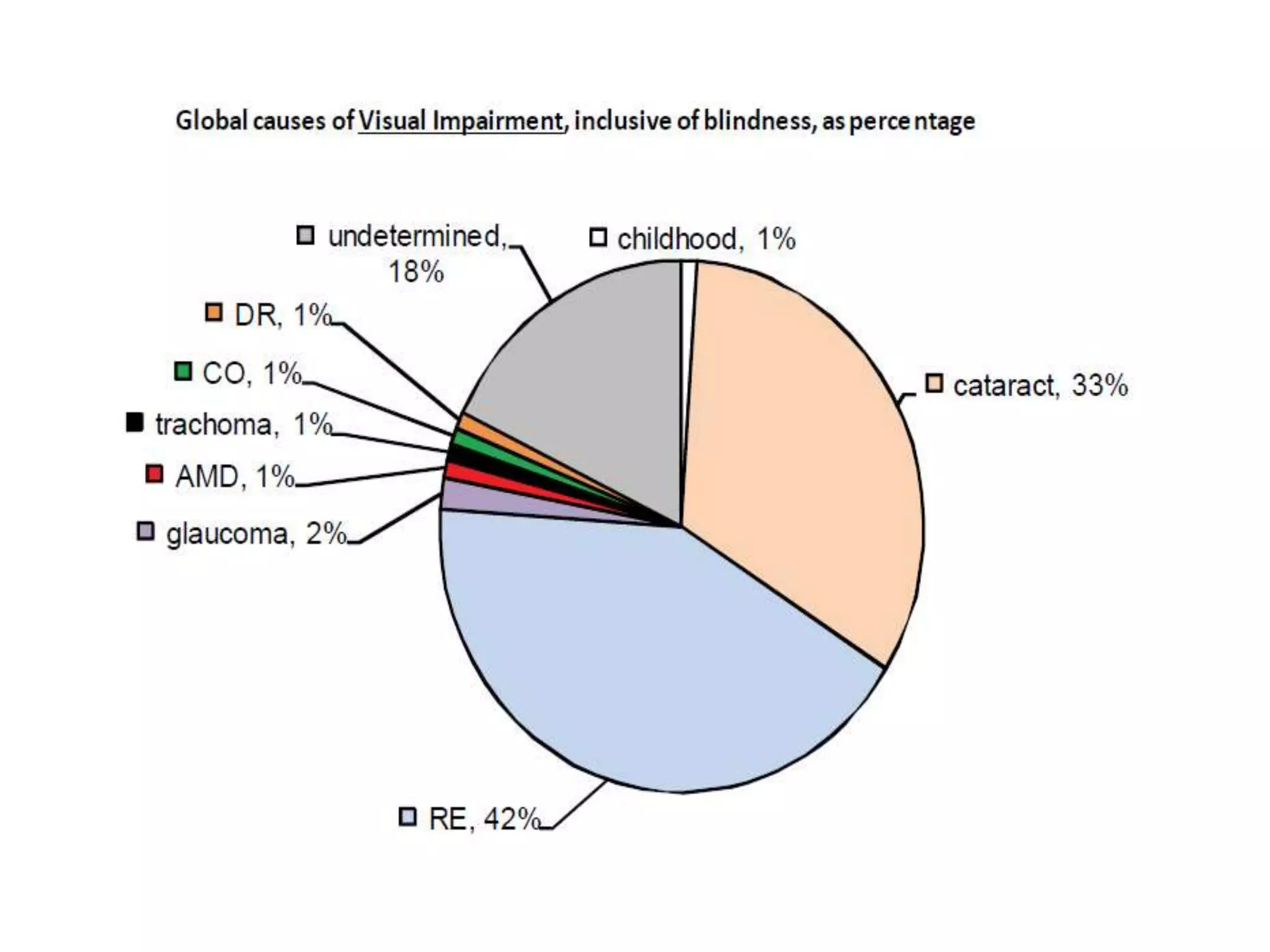
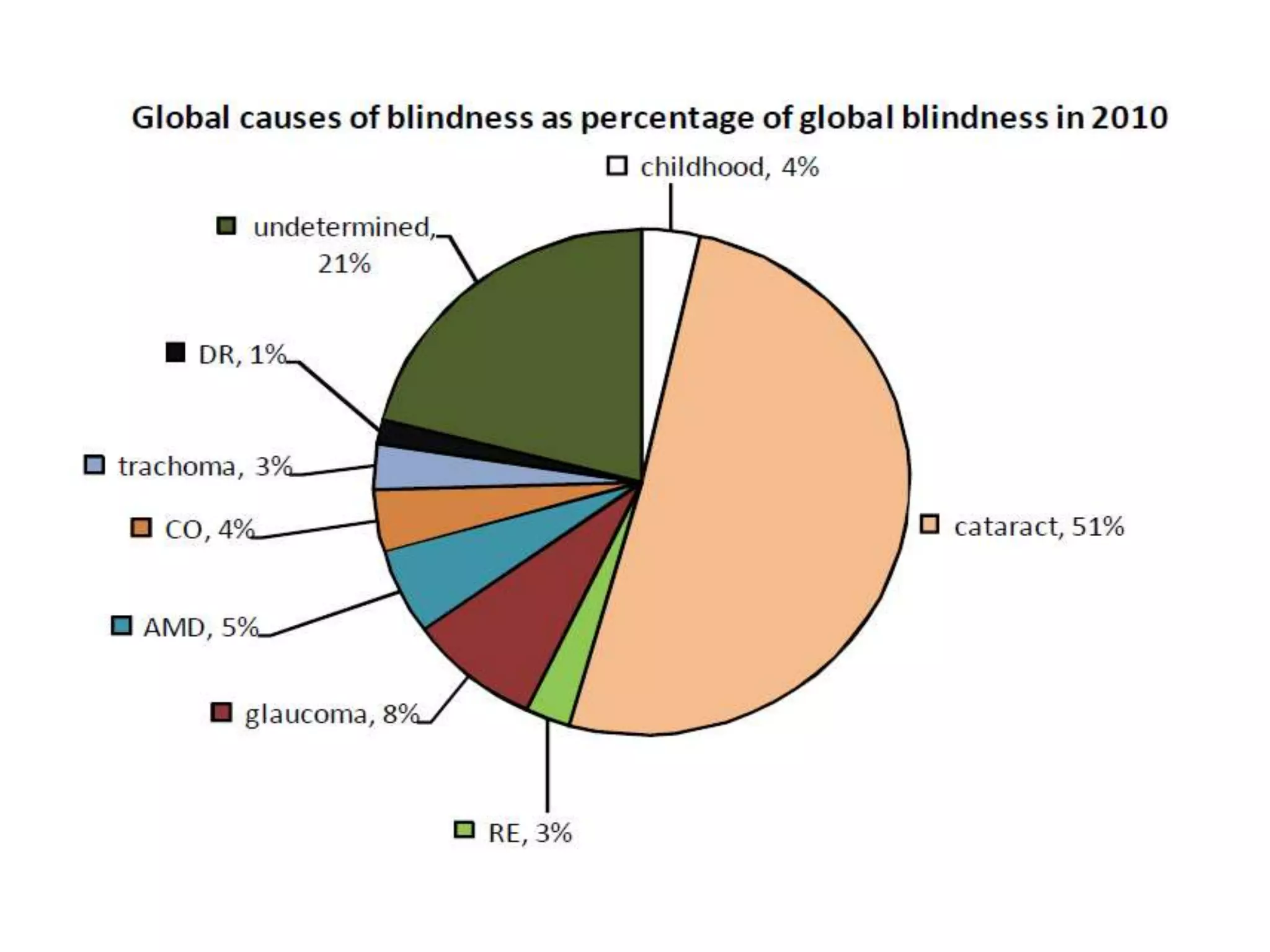
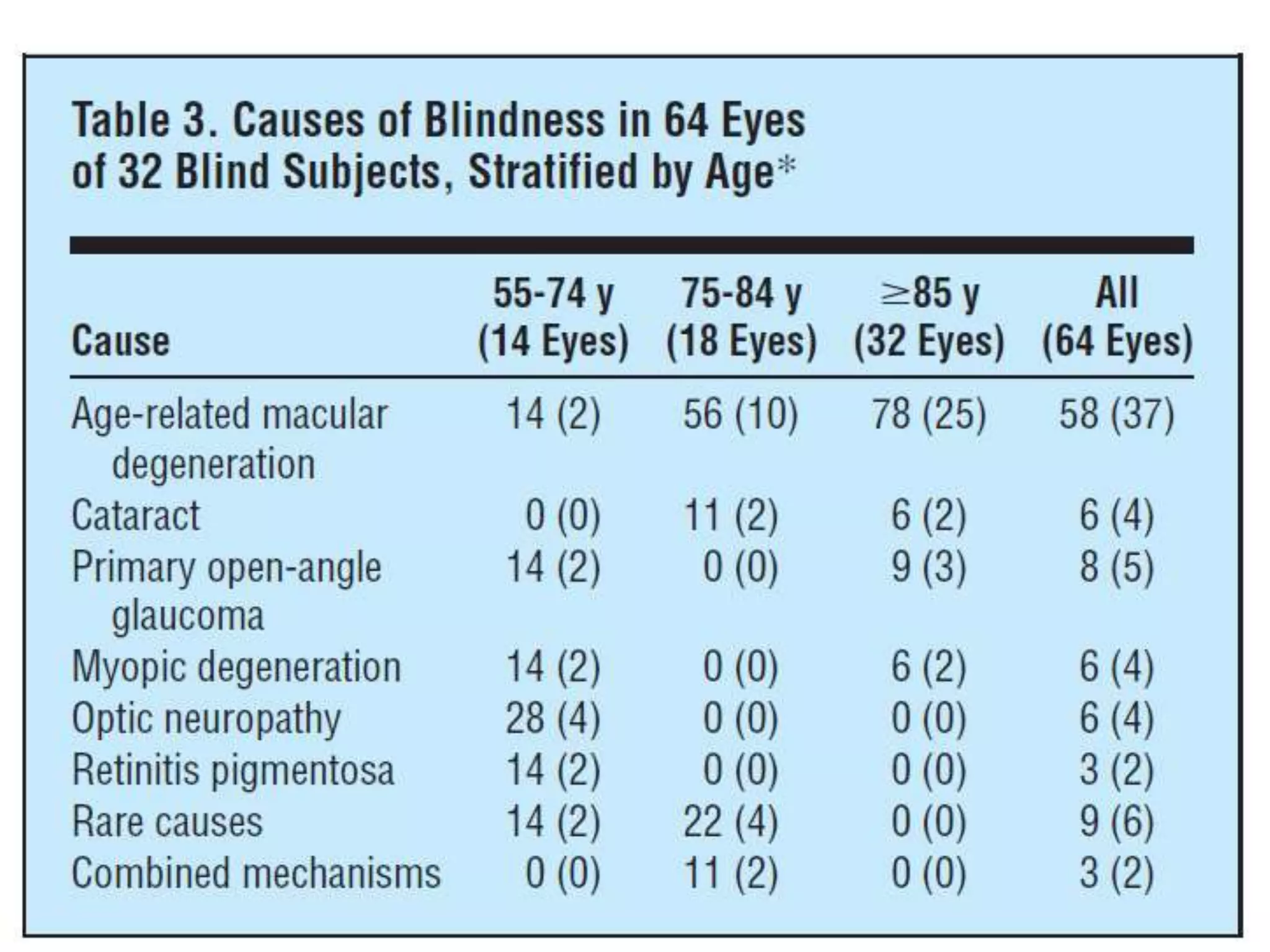
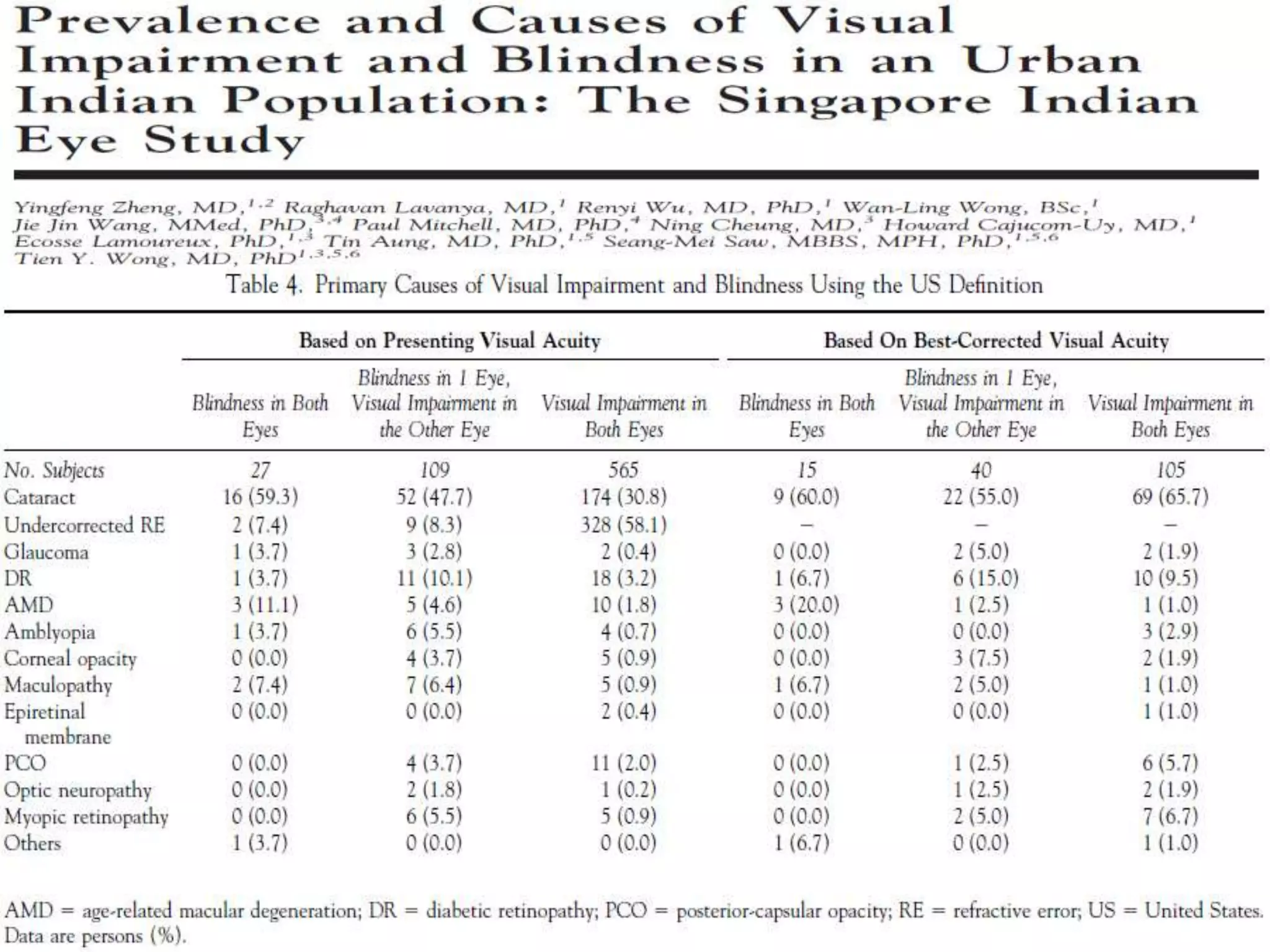
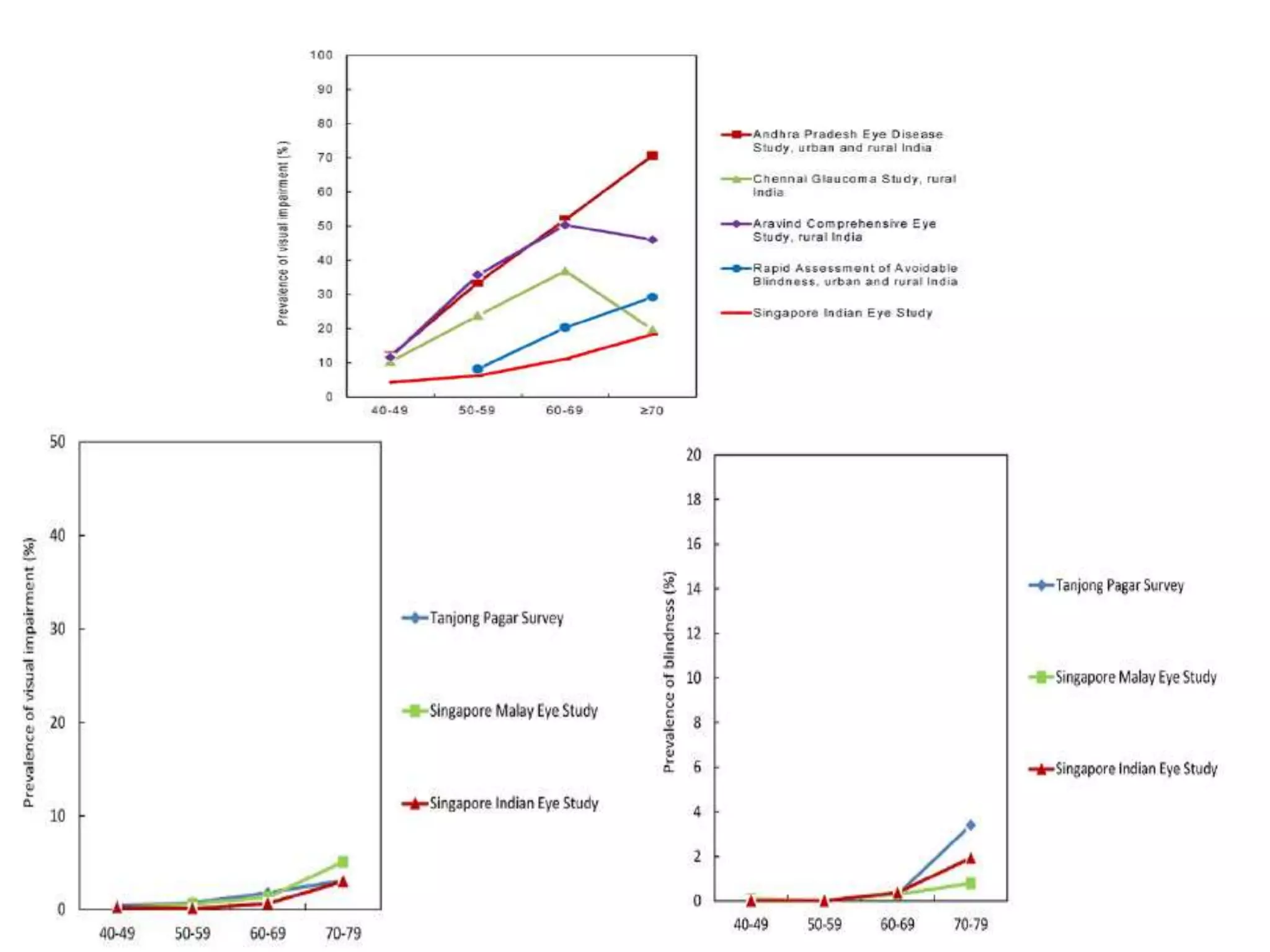
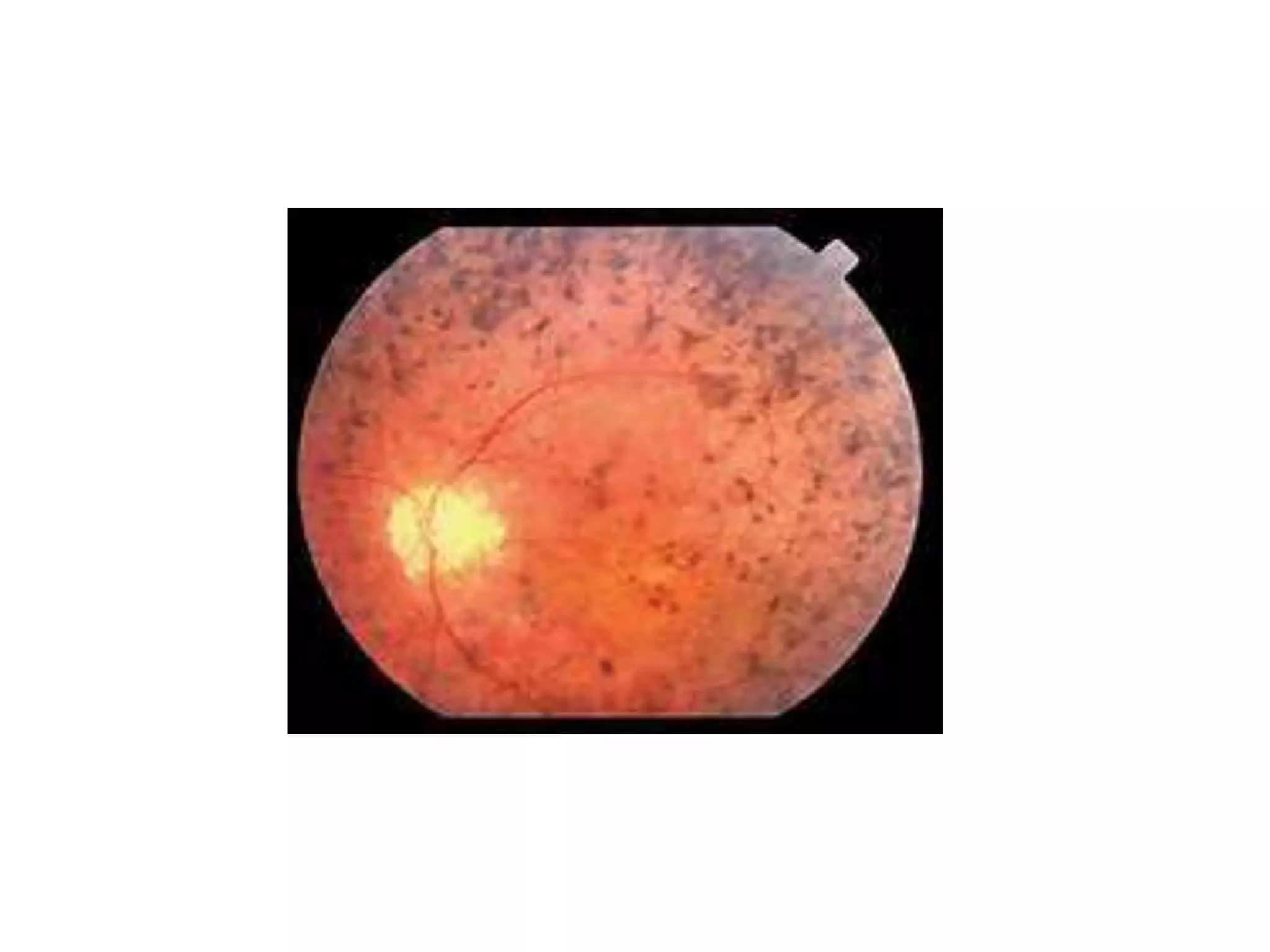
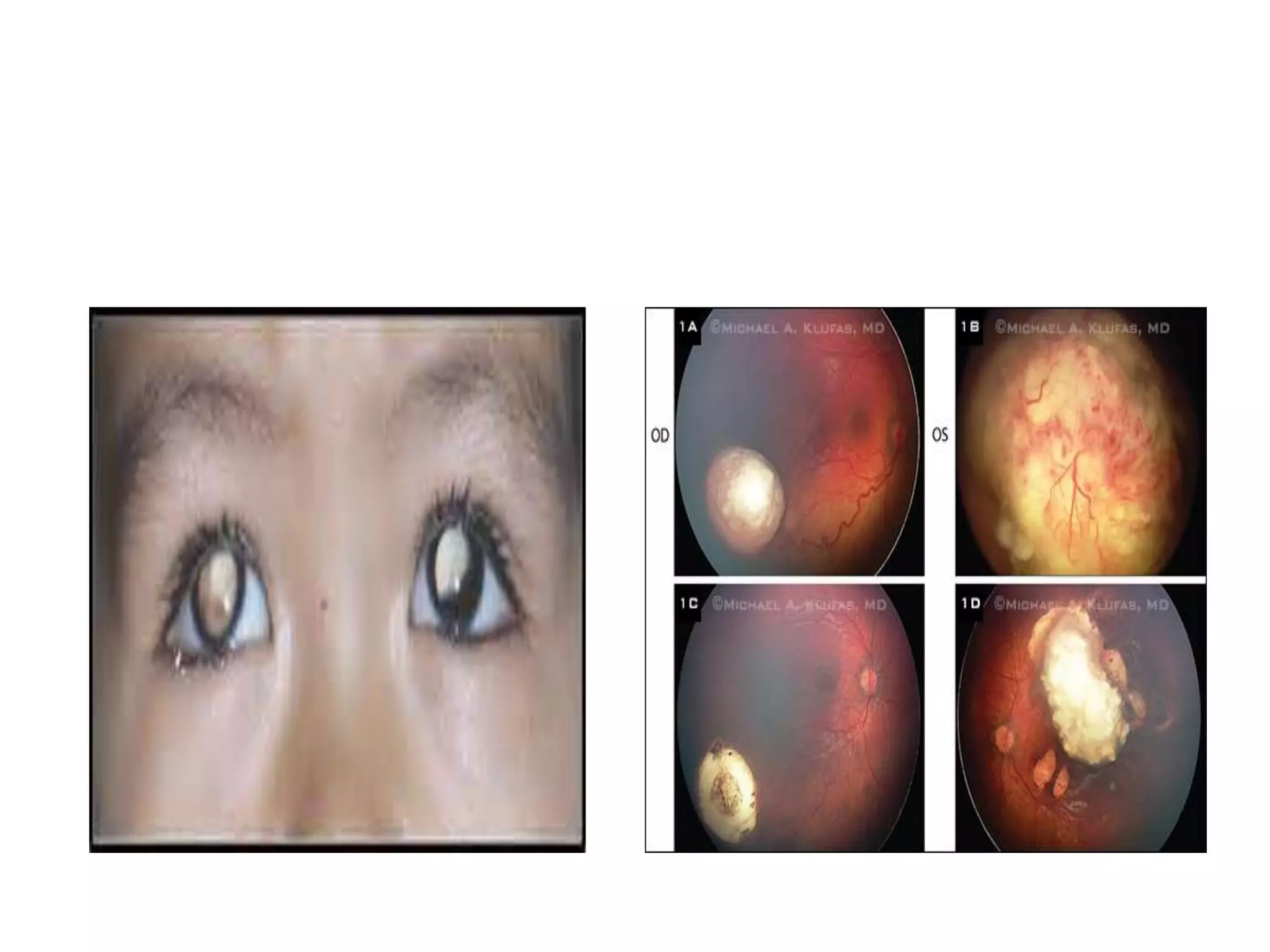
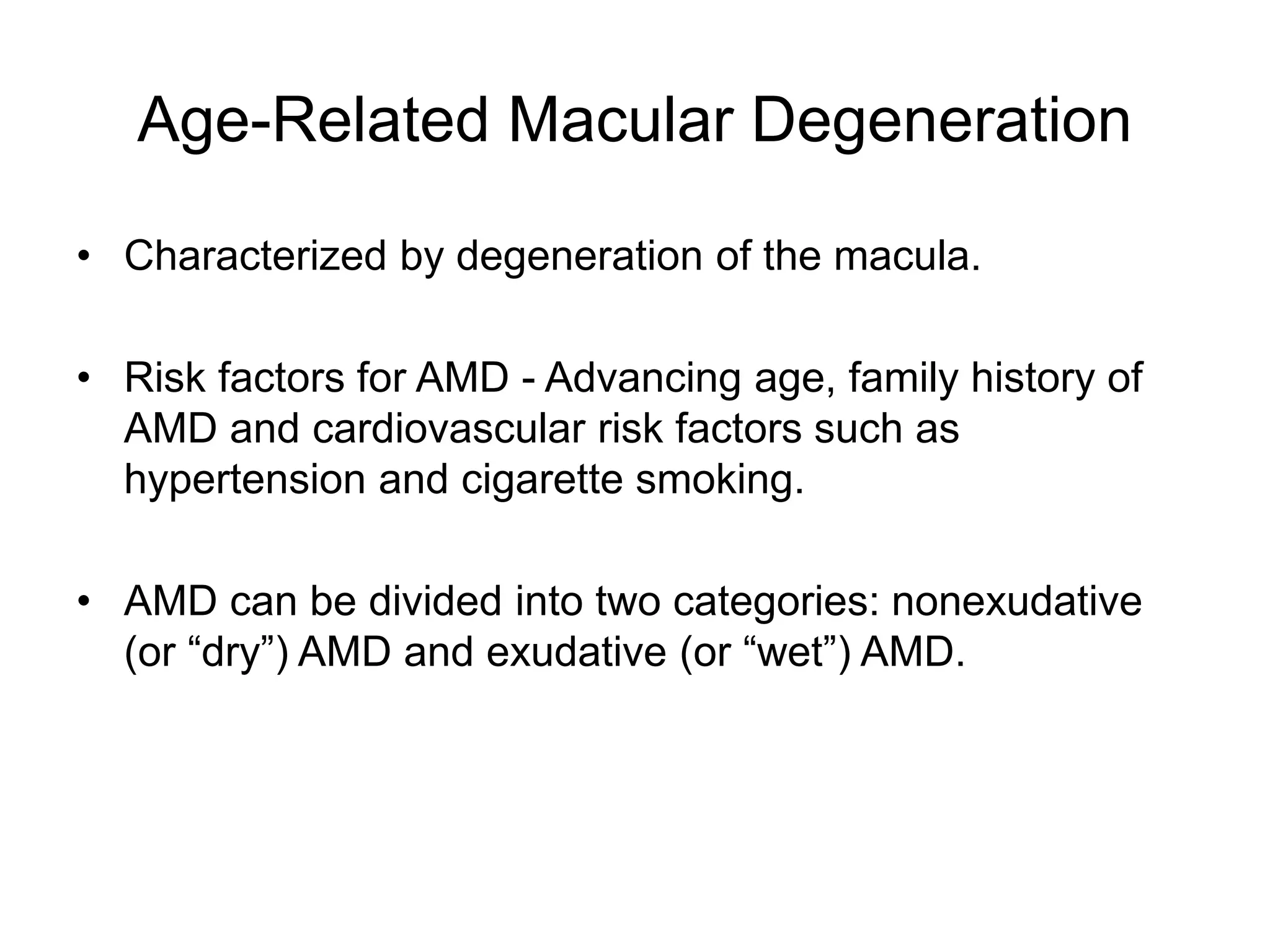
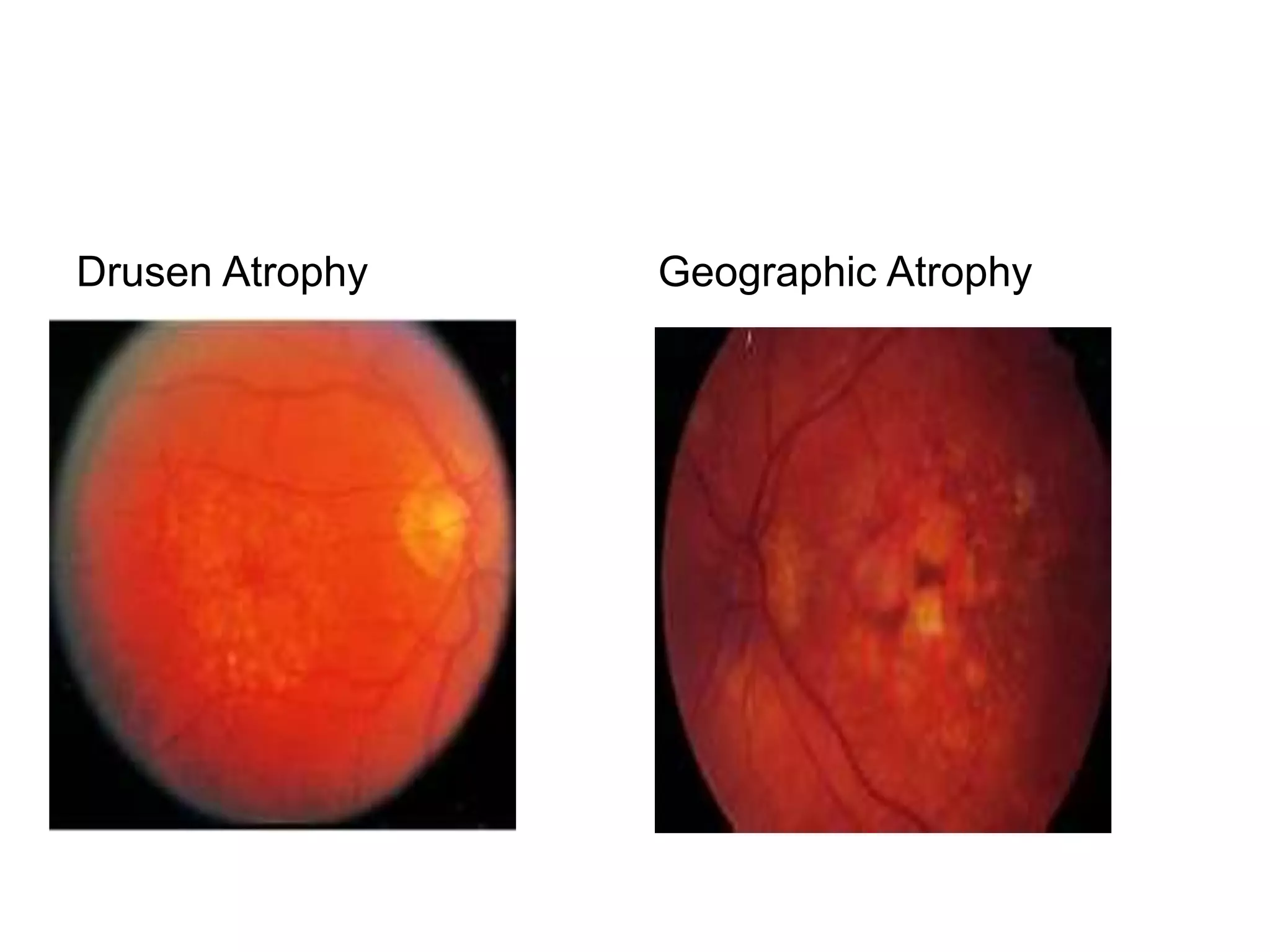
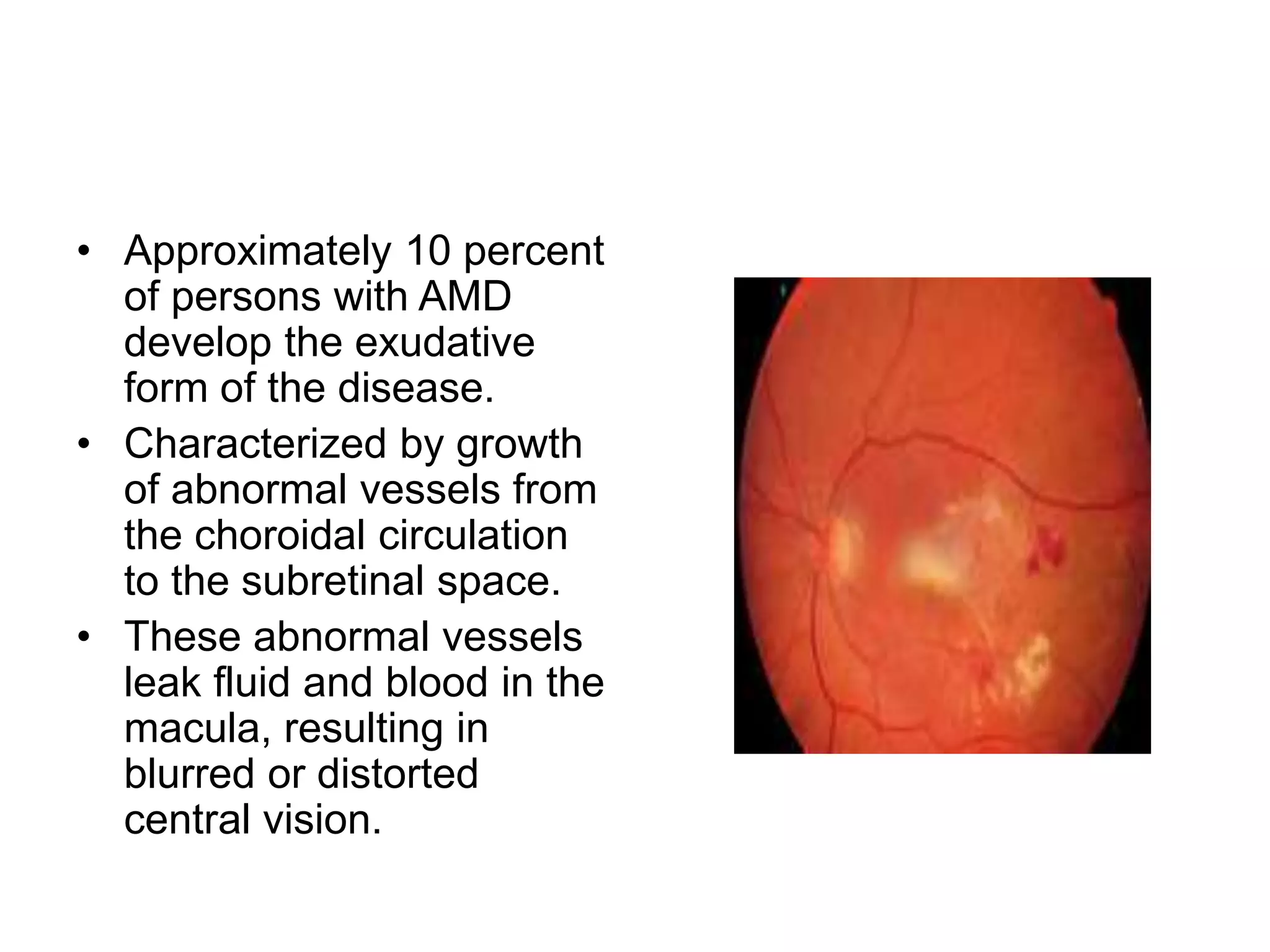
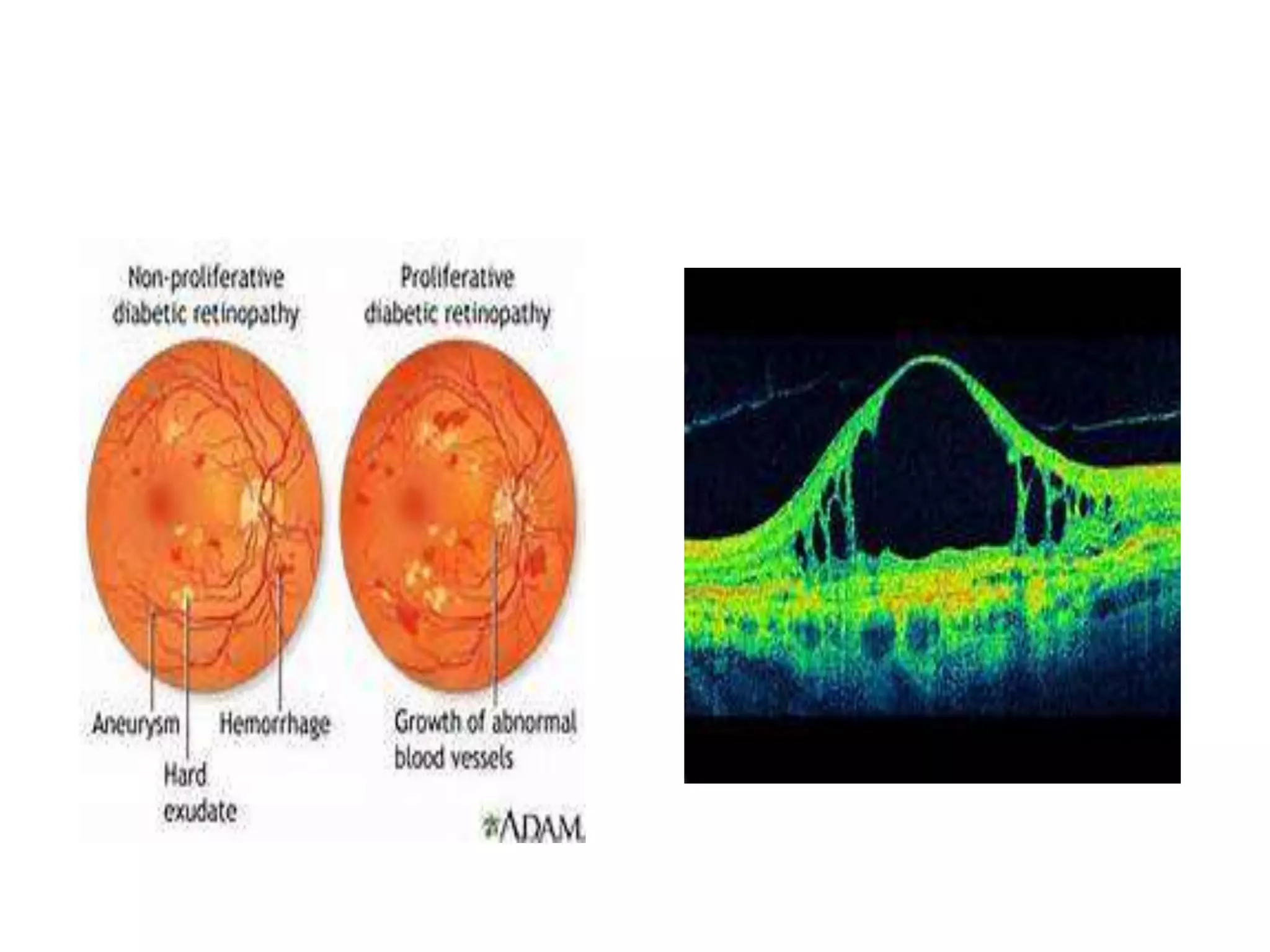
Ophthalmologic causes of visual impairment include retinal issues like retinal artery occlusion, retinal detachment, and macular degeneration as well as optic nerve problems like glaucoma. Cataracts, refractive errors, and diabetic retinopathy are also common causes of visual loss. Visual impairment can be gradual and painless from conditions like cataracts and macular degeneration or sudden from retinal detachments or artery occlusions. Treatment depends on the underlying problem but may include eyeglasses, surgery, laser treatment, or medication.