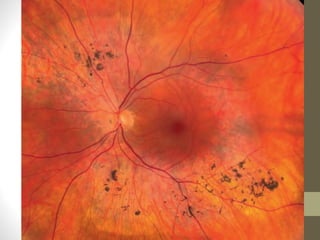
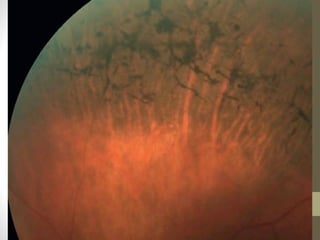
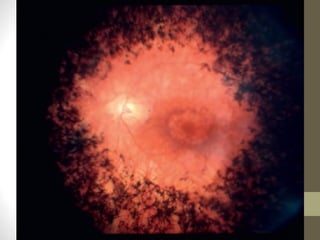
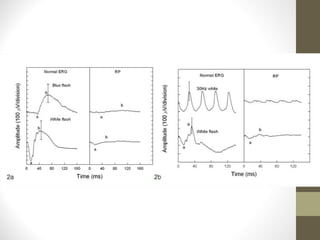
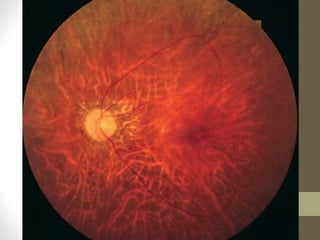
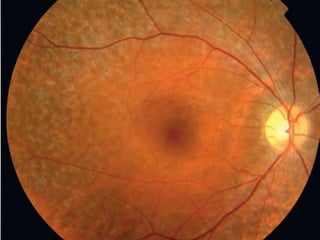
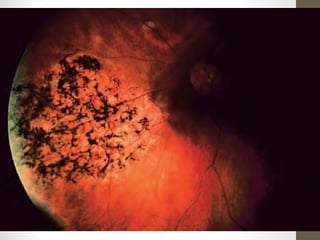
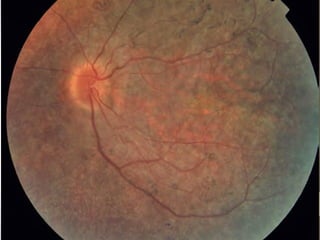
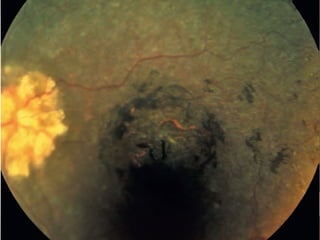
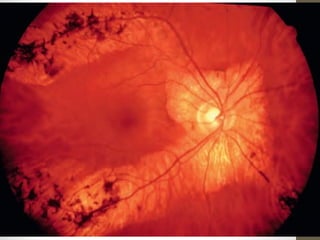
Retinitis pigmentosa is a group of inherited retinal diseases characterized by progressive degeneration of the photoreceptors. It initially affects rods, resulting in night blindness and peripheral vision loss, and later involves cones leading to tunnel vision. Symptoms include nyctalopia and peripheral field defects. Signs include bone spicule pigmentation, arteriolar attenuation, and disc pallor. It can be inherited in autosomal dominant, recessive or X-linked patterns. Investigations include electroretinography to detect photoreceptor dysfunction and optical coherence tomography. There is currently no cure or treatment to stop progression.