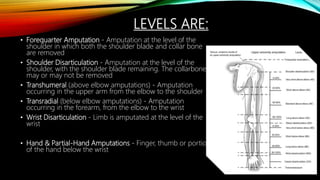
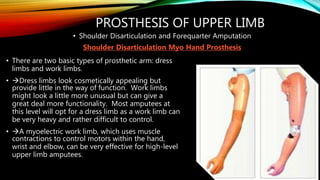
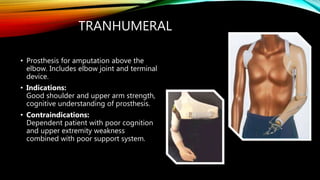
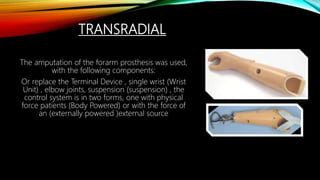
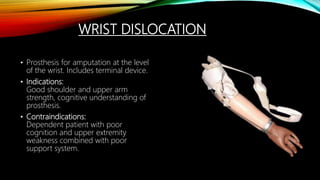
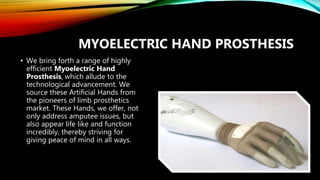
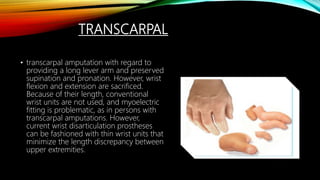
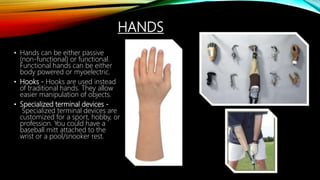
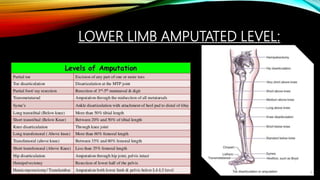
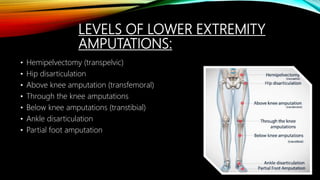
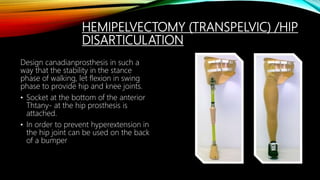
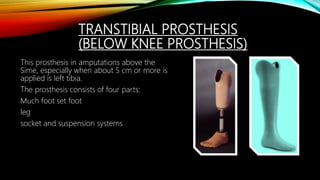
The document summarizes different levels of upper and lower limb prosthetics. It describes the components and indications for various prosthesis types including shoulder disarticulation, above elbow, below elbow, wrist disarticulation, and hand prosthetics. It also discusses prosthetics for levels such as hip disarticulation, above knee, below knee, ankle disarticulation, and partial foot amputations. The document provides details on prosthesis design considerations and components for different amputation levels.