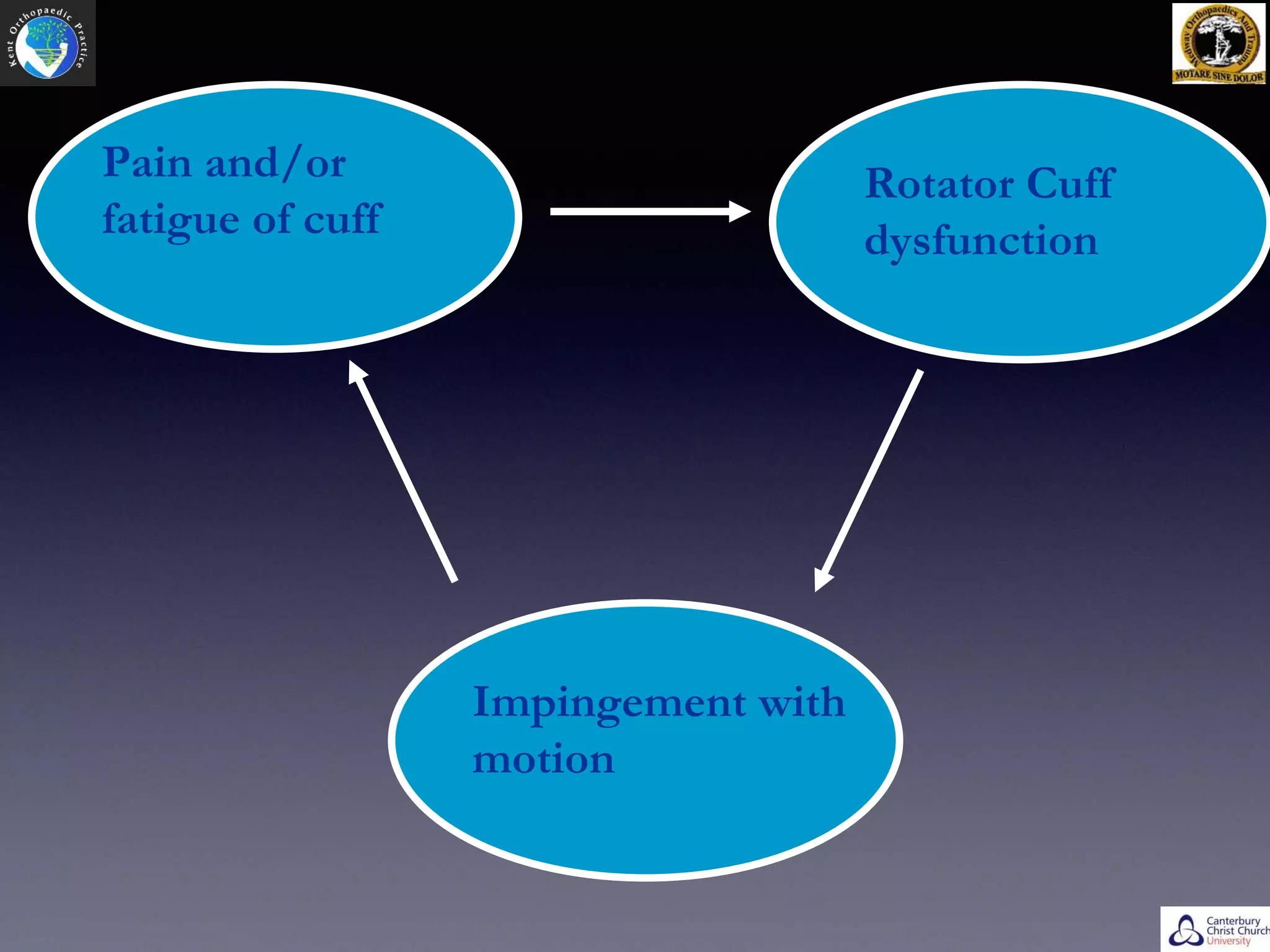
- Rotator cuff tears can be caused by extrinsic factors like repetitive use or impingement, or intrinsic factors like changes in tendon vascularity or degenerative changes.
- Physical examination involves inspection, palpation, range of motion testing and muscle strength testing. Investigations include ultrasound and MRI.
- Symptomatic rotator cuff tears tend to increase in size over time if left untreated, especially in younger patients under 60 years old.
- Surgery is indicated for failed conservative treatment, significant weakness, or acute tears in young active patients.
- Arthroscopic repair has advantages over open repair like less pain and blood loss, but requires special instruments and equipment.
-