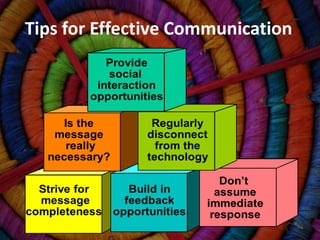
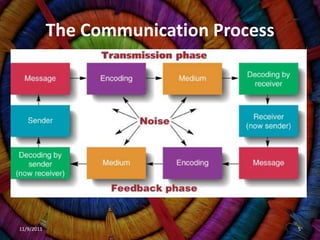
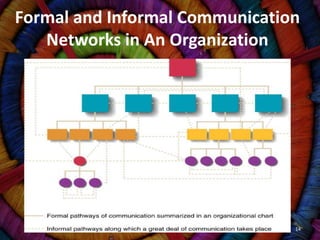
The document discusses organizational communication and behavior. It defines communication, explores the importance of good communication in organizations, and examines communication processes, issues, barriers, and networks. It also analyzes new communication technologies, how they affect behavior, and defensive versus non-defensive communication styles. Key topics covered include the definition of communication, importance of communication for efficiency, quality and innovation, verbal and nonverbal communication, formal and informal communication networks, and technological advances in organizational communication.




















![Defensive Tactics
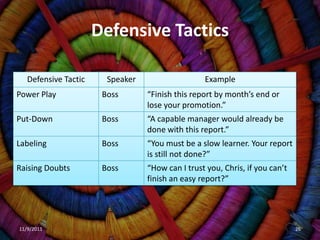
Defensive Tactic Speaker Example
Misleading Employee “Morgan has not gone over with me
Information the information I need for the report.”
[Morgan left Chris with a copy of the
report.]
Scapegoating Employee “Morgan did not give me input until
just today.”
Hostile Jokes Employee “You can’t be serious! The report isn’t
that important.”
Deception Employee “I gave it to the secretary. Did she lose
it?”
11/9/2011 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentob-111110001445-phpapp02/85/Organizational-Behavior-Communication-27-320.jpg)