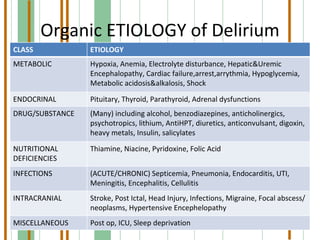
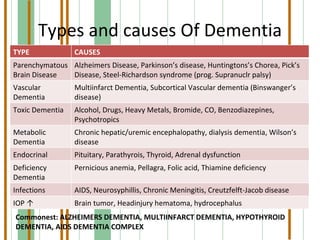
This document summarizes various organic mental disorders including delirium, dementia, organic amnestic syndrome, and other organic mental disorders. It describes the key features and causes of delirium including acute onset, confusion, and underlying medical conditions. Dementia is defined as a chronic mental disorder characterized by intellectual impairment and memory loss over 6 months. Alzheimer's disease and multi-infarct dementia are described as the most common causes. Organic amnestic syndrome is characterized primarily by memory impairment due to thiamine deficiency in alcoholics. Other organic mental disorders include organic hallucinosis, catatonia, delusions, and mood/anxiety disorders caused by underlying medical conditions.