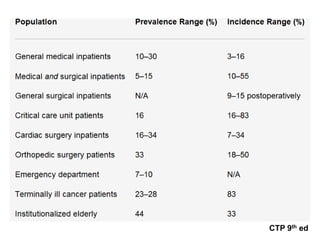
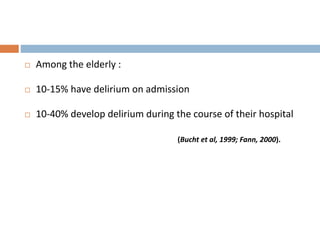
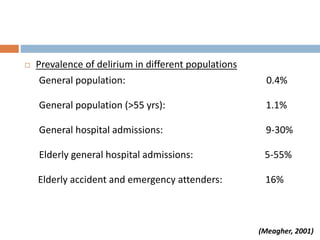
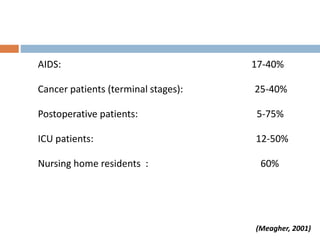
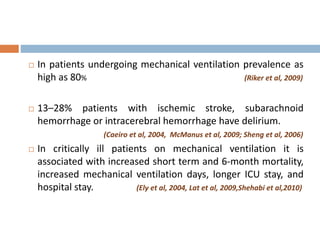
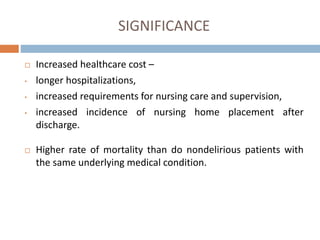
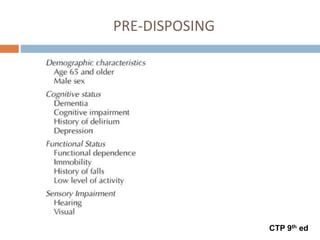
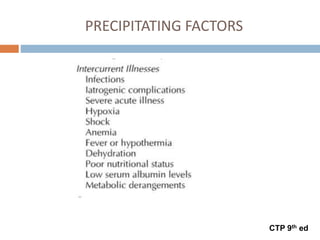
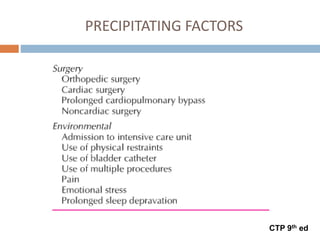
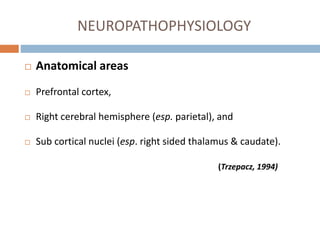
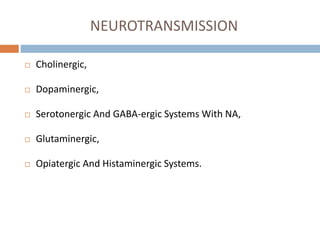
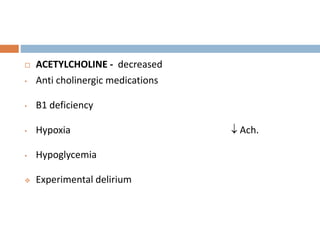
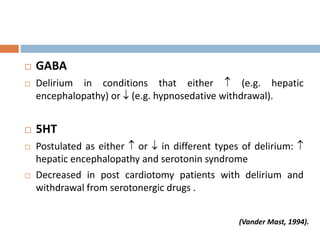
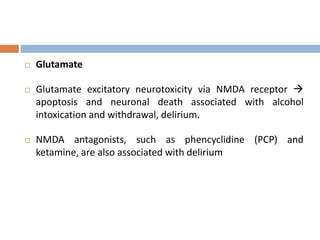
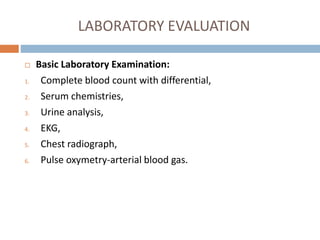
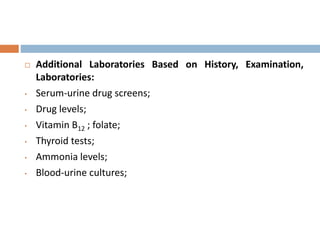
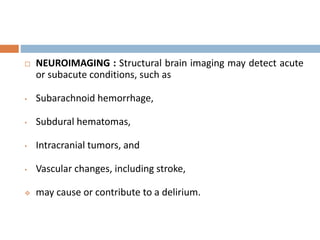
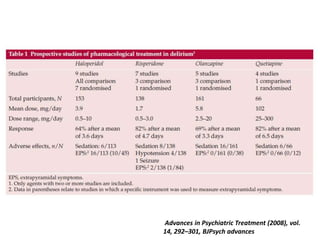
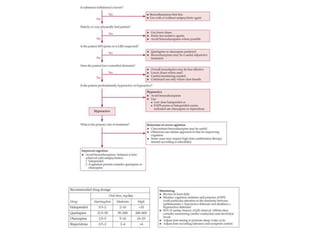
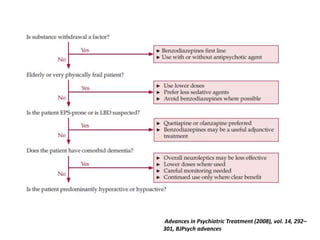
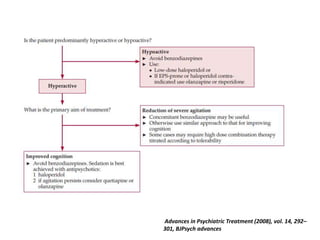
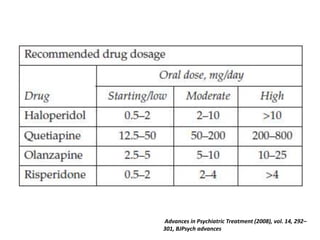
This document provides an overview of delirium, including its introduction, history, epidemiology, etiology, neuropathology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, course, prevention and management. Delirium is characterized by an acute change in mental status and cognition that fluctuates over the course of a day. It has a prevalence of 5-55% among elderly hospitalized patients and is associated with increased mortality, longer hospital stays and higher healthcare costs. The pathophysiology involves multiple neurotransmitter systems and risk factors include predisposing patient factors and precipitating insults like infection, medication side effects or metabolic disturbances. Prevention focuses on reducing risk factors and early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.