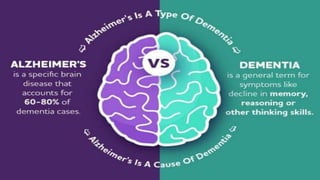
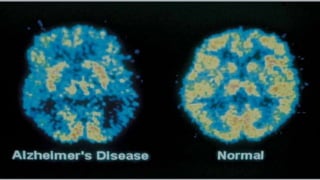
This document provides an overview of dementia, including its definition, classification, types, stages, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and nursing management. Dementia is defined as the progressive decline in cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, and reasoning due to brain damage or disease. The most common types of dementia discussed are Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia. Dementia is diagnosed based on cognitive assessments and brain imaging and progresses through early, middle, and late stages. Nursing care focuses on safety, communication, and maintaining routines and independence.