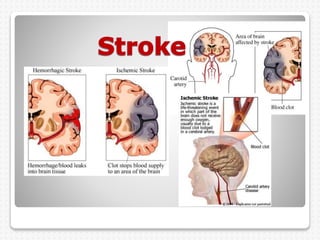
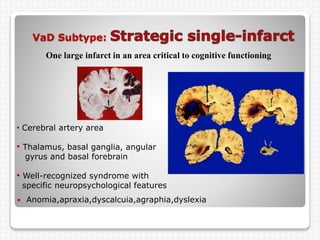
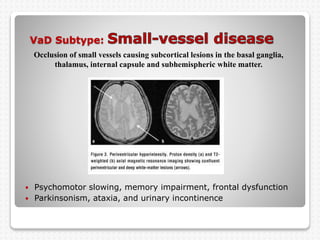
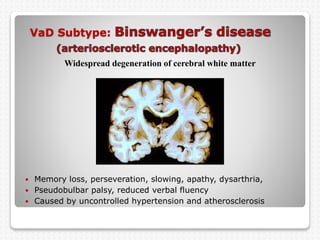
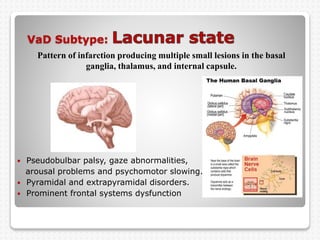
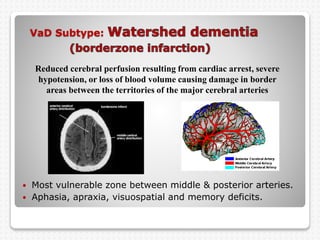
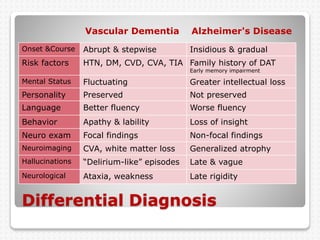
Vascular dementia is caused by brain damage from cerebrovascular disease and impaired blood flow to the brain. It has several subtypes depending on the location and size of lesions in the brain. Risk factors include uncontrolled hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, and history of stroke. Symptoms vary depending on the subtype but can include memory loss, slowed processing speed, mood changes like depression or anxiety, and problems with motor skills. Evaluation involves assessing cognitive abilities, neurological exam, and brain imaging to identify areas of damaged tissue. Treatment focuses on managing underlying risk factors to prevent further damage and addressing behavioral and psychological symptoms.