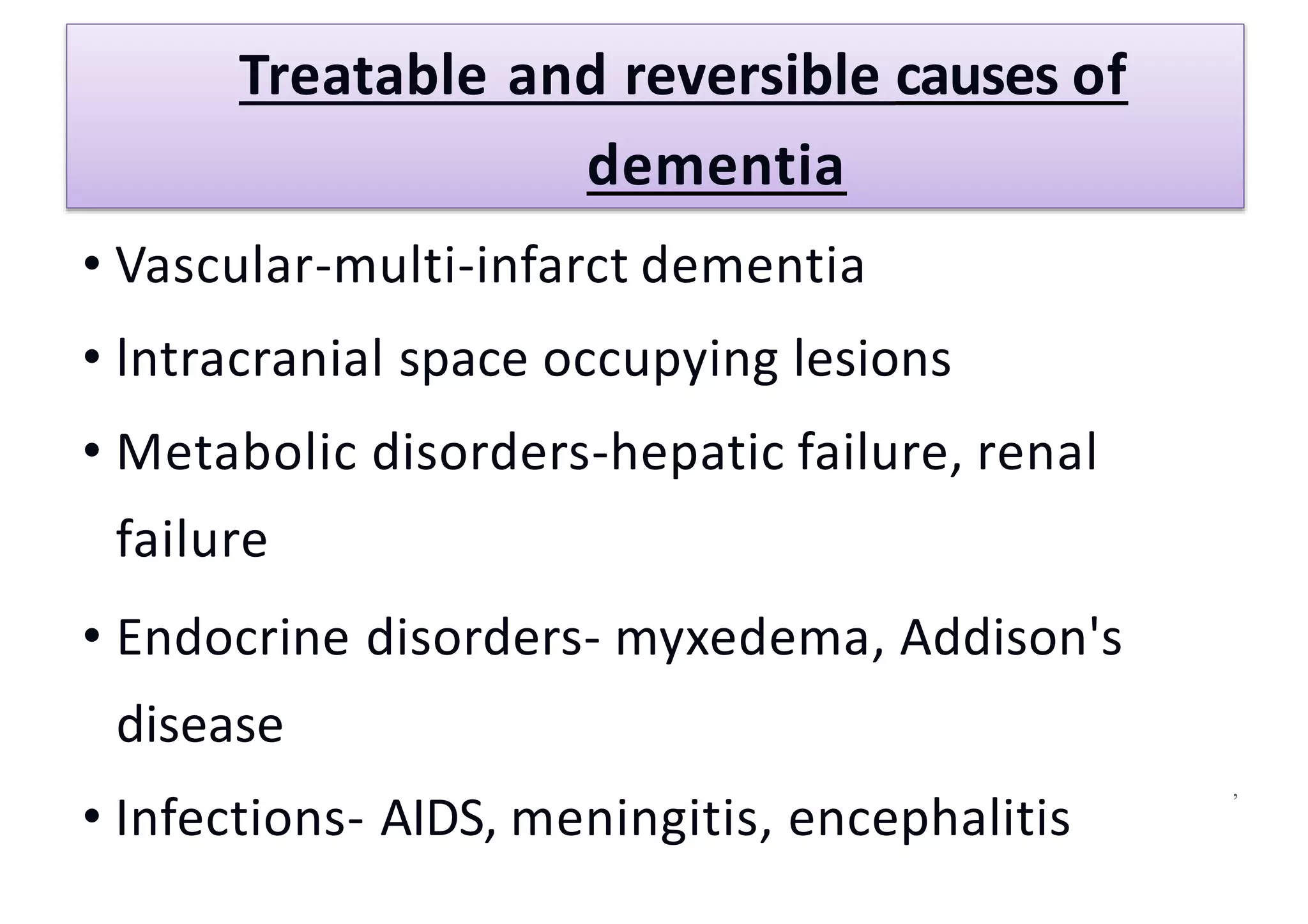
The document is a comprehensive presentation on dementia, covering its definition as a cognitive impairment primarily affecting memory and intellect without loss of consciousness. It discusses various types, causes, stages, warning signs, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, emphasizing the importance of nursing management and caregiver support. The conclusion highlights the prevalence of dementia in the elderly and the necessity for awareness and education about the condition.