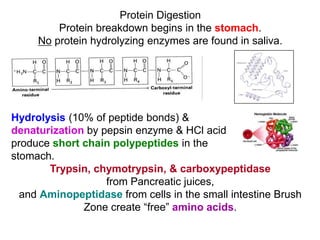
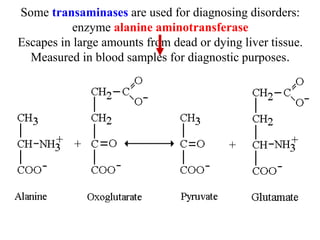
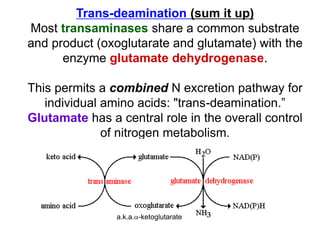
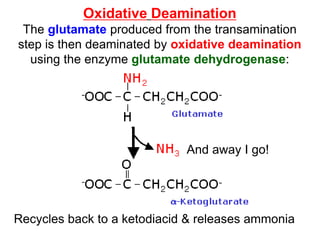
Protein digestion begins in the stomach through the action of pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which break proteins into smaller polypeptides. In the small intestine, proteases like trypsin and chymotrypsin further break polypeptides into amino acids. Amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells. Within cells, amino acids undergo transamination, where their amino groups are transferred to alpha-ketoglutarate to form glutamate, and oxidative deamination, where the amino groups are removed as ammonia by glutamate dehydrogenase. Ammonia is toxic, so the liver converts it into urea through the urea cycle, which is then excreted in urine.





![Glutamate dehydrogenase [GluDH]
will reversibly convert
glutamate to -ketoglutarate
and -ketoglutarate to glutamate.
Deamination
reaction
uses NAD+
reverse reaction
uses NADPH
Uses both NAD+ and NADPH – how to regulate it?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinmetabolism-221130121358-5623a9fc/85/Protein-Metabolism-ppt-11-320.jpg)

























