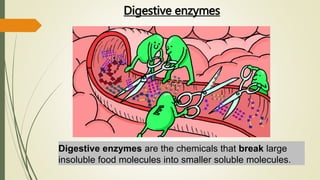
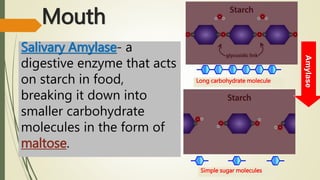
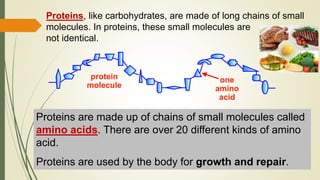
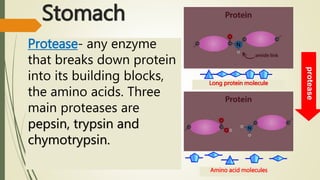
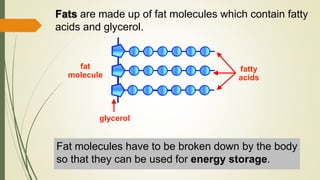
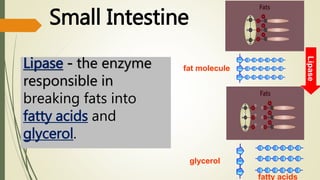
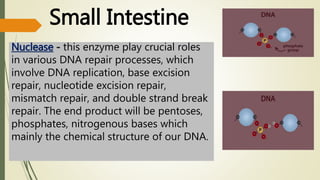
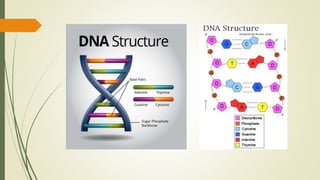
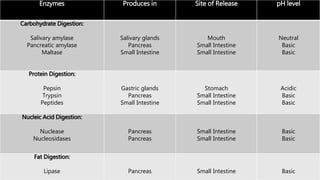
The document explains the process of chemical digestion, detailing the main nutrients needed by the body, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as the enzymes responsible for breaking them down. It outlines the roles of specific digestive enzymes such as amylase, protease, and lipase, and highlights the importance of these enzymes in converting large food molecules into smaller, usable forms. Additionally, it describes the stages of fat digestion, including the role of bile in emulsification.