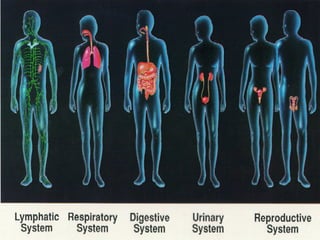
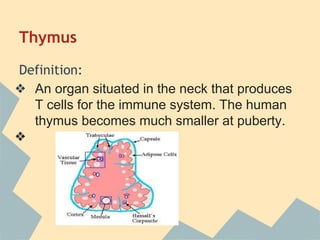
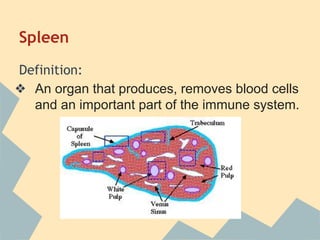
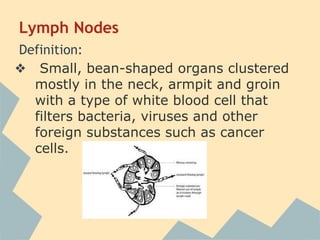
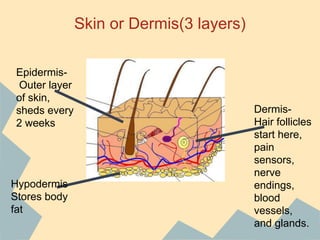
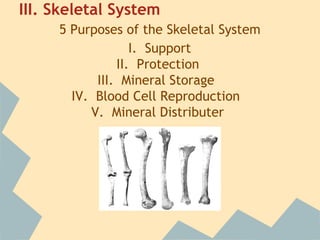
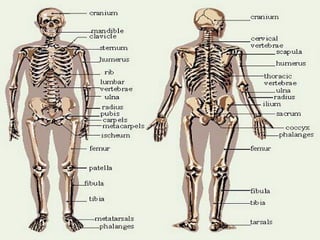
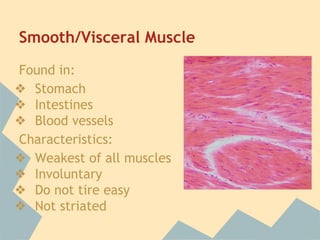
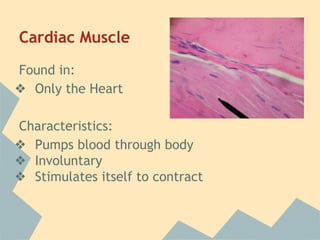
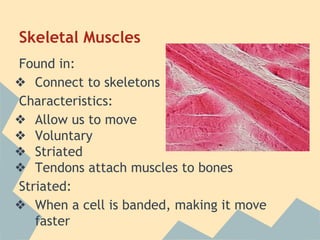
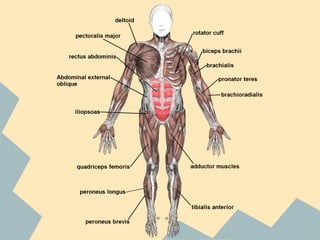
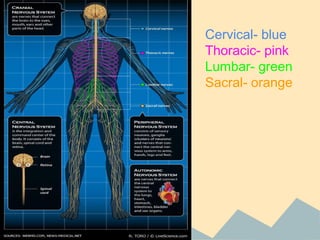
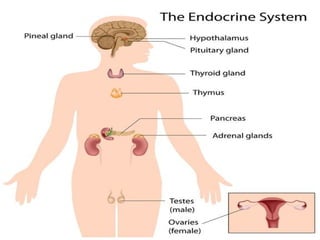
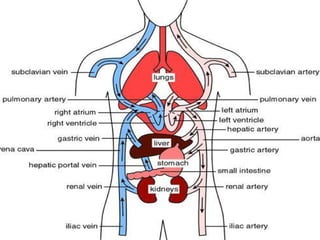
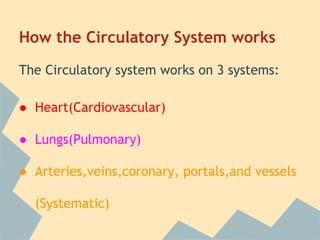
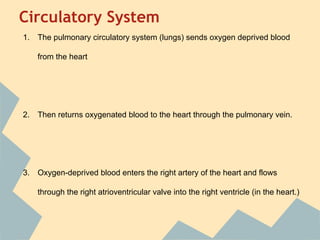
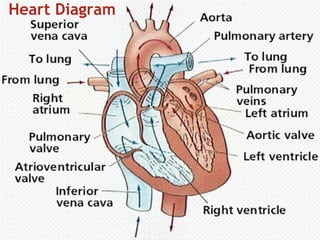
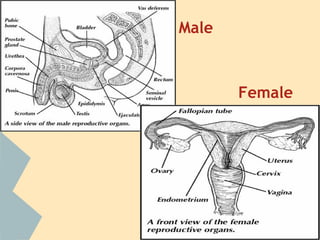
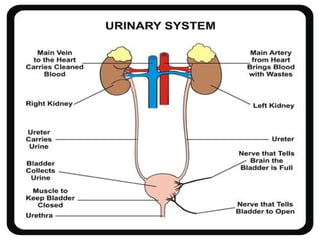
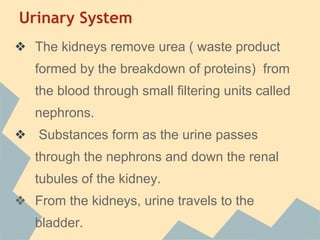
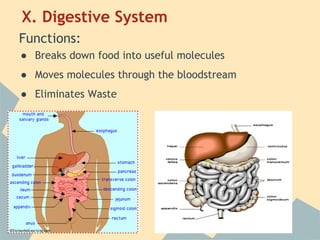
The document provides an overview of the 10 major systems that make up the human body. It discusses the immune, integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, circulatory, reproductive, urinary, and digestive systems. For each system it describes the main functions, key organs and parts, and some relevant facts. The major body systems work together to keep the human body functioning through various biological processes like protection from pathogens, support and movement, regulating internal functions, absorption of nutrients, and waste removal.