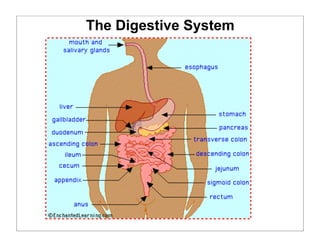
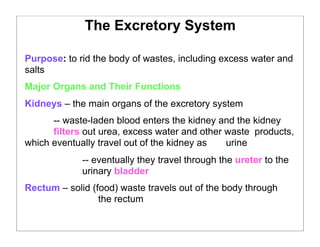
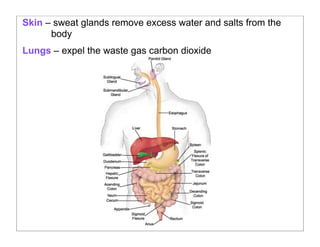
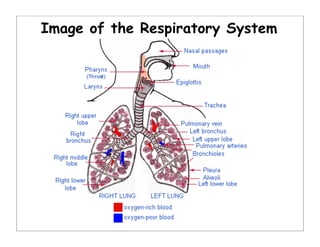
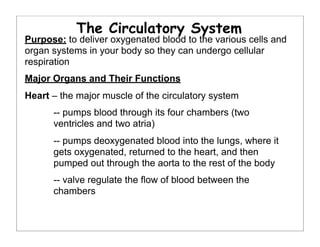
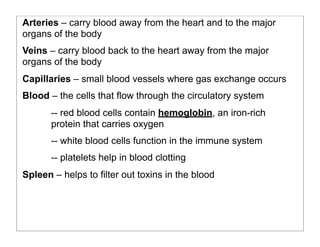
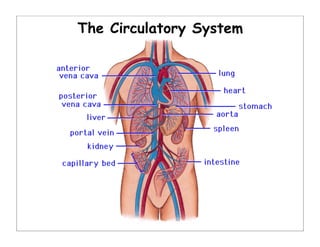
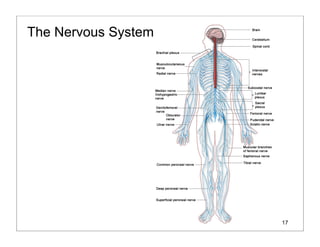
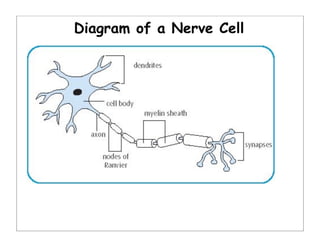
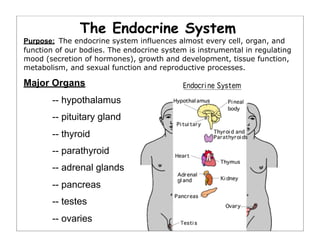
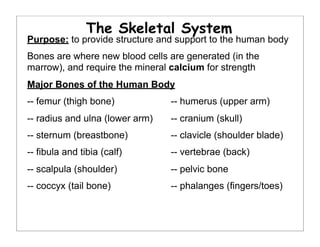
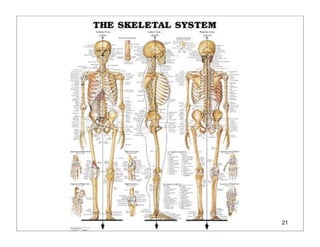
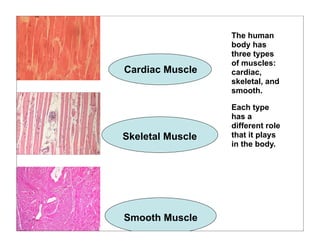
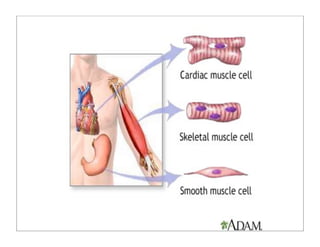
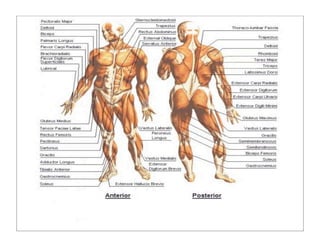
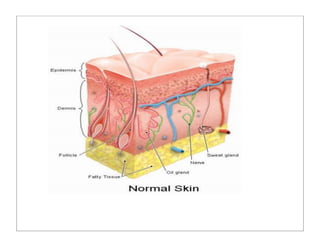
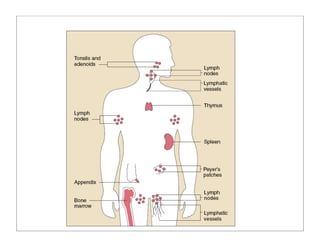
The human body is organized into 11 organ systems that work together to maintain homeostasis. The organ systems include the digestive, excretory, respiratory, circulatory, nervous, endocrine, skeletal, muscular, lymphatic, integumentary, and reproductive systems. Each system is composed of organs that work together to perform important functions for the body. Homeostasis refers to keeping the internal body environment stable despite changes outside it.