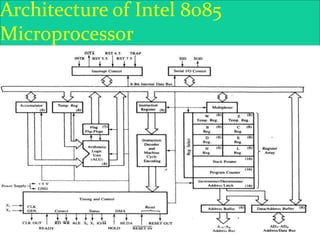
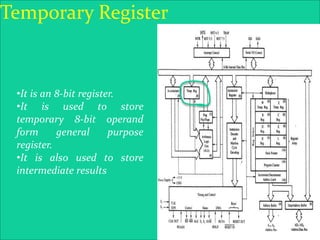
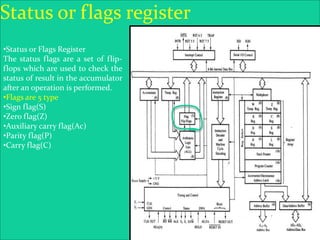
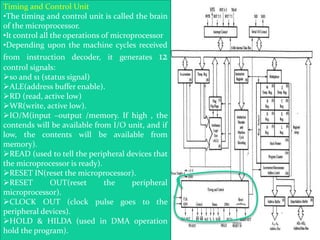
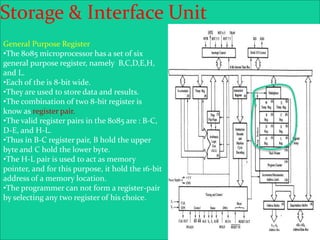
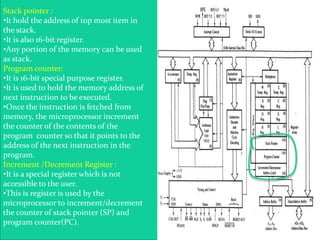
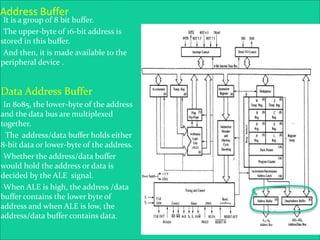
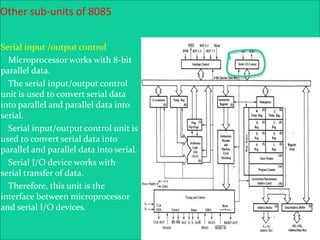
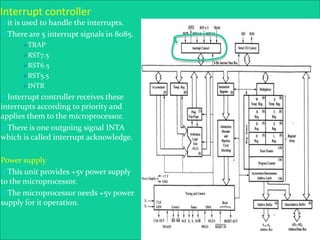
The 8085 microprocessor is an 8-bit processor with 6,200 transistors. It has 74 instructions and can address 64KB of memory. The 8085 has an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations on data from the accumulator and registers. It also has a control unit, registers, and interfaces to external memory and I/O devices. The 8085's architecture includes components like the accumulator, flags register, and general purpose registers that help it process instructions.