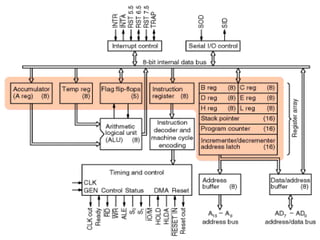
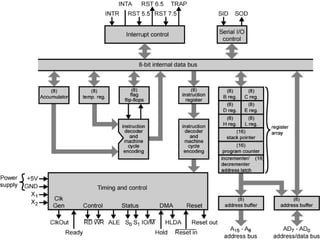
The 8085 architecture contains several functional blocks including registers, an ALU, instruction decoder, address buffer, and timing/control circuitry. It has general purpose registers, temporary registers, and special purpose registers like the program counter, stack pointer, and flags register. The flags register tracks the sign, zero, auxiliary carry, parity, and carry flags. The ALU performs arithmetic and logic operations on data in the accumulator and temporary register. The address and data buses use time-shared address/data lines to transfer instructions and data. Instructions are fetched from memory by the program counter and executed by decoding and performing the operation.