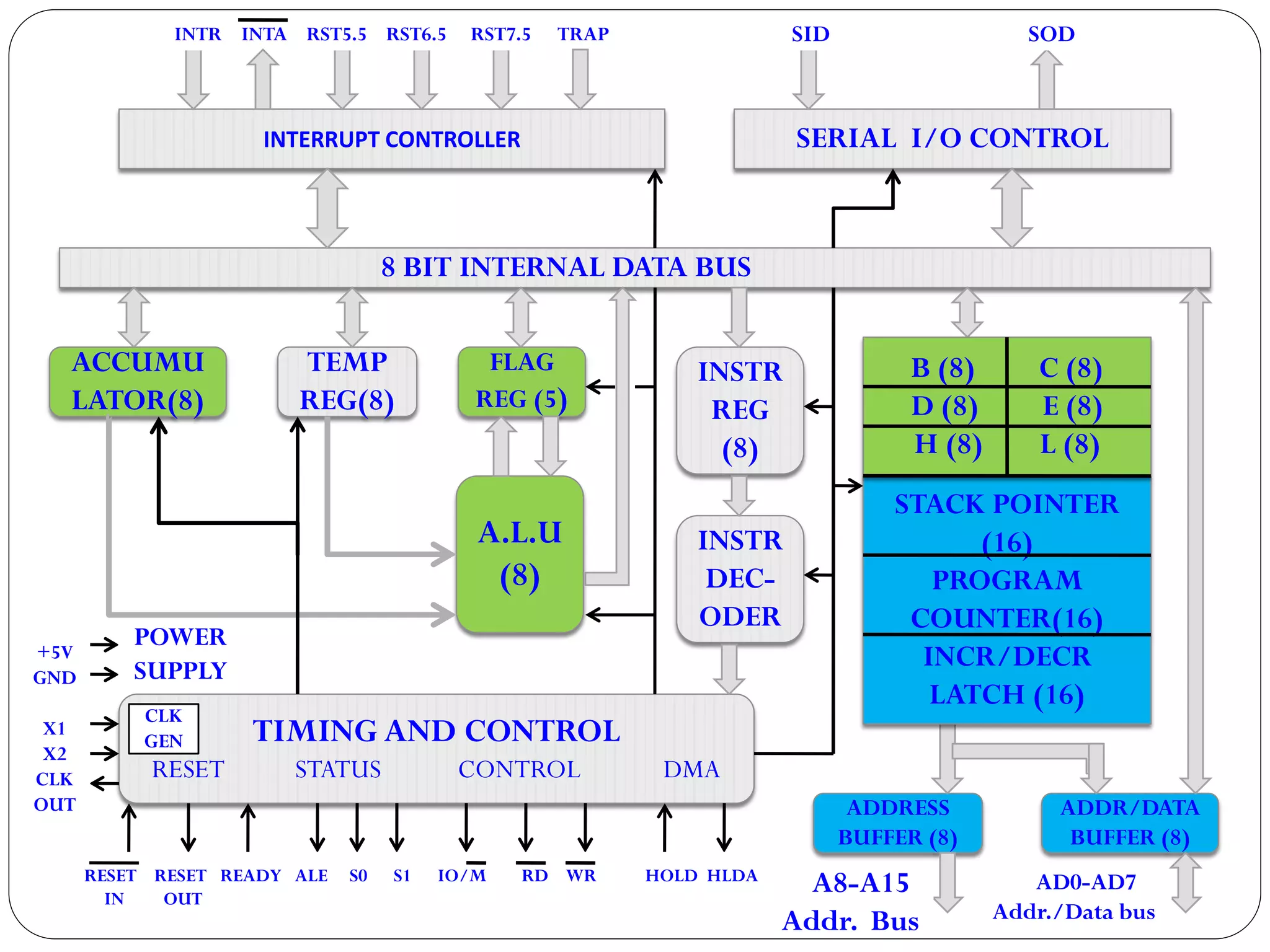
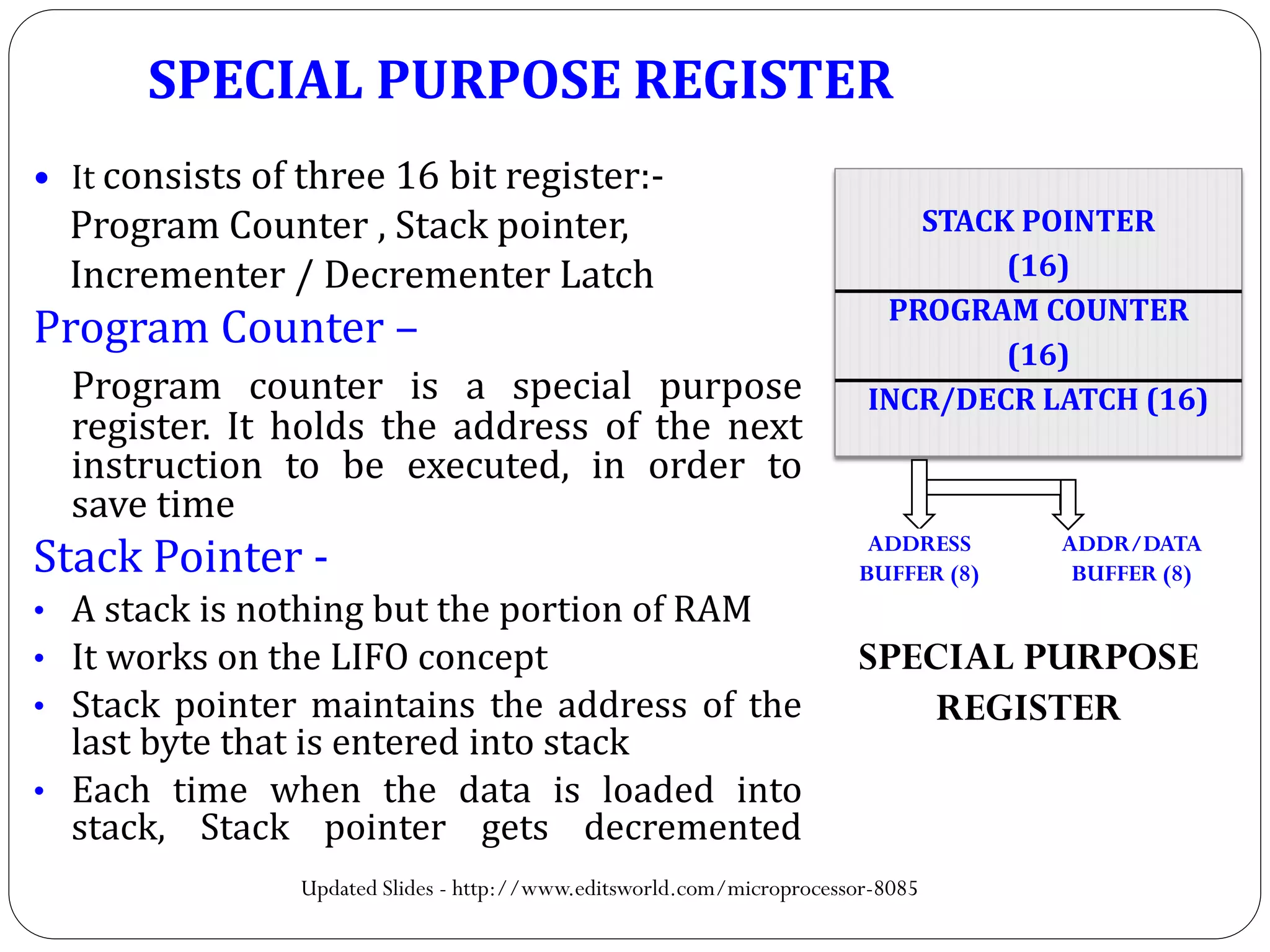
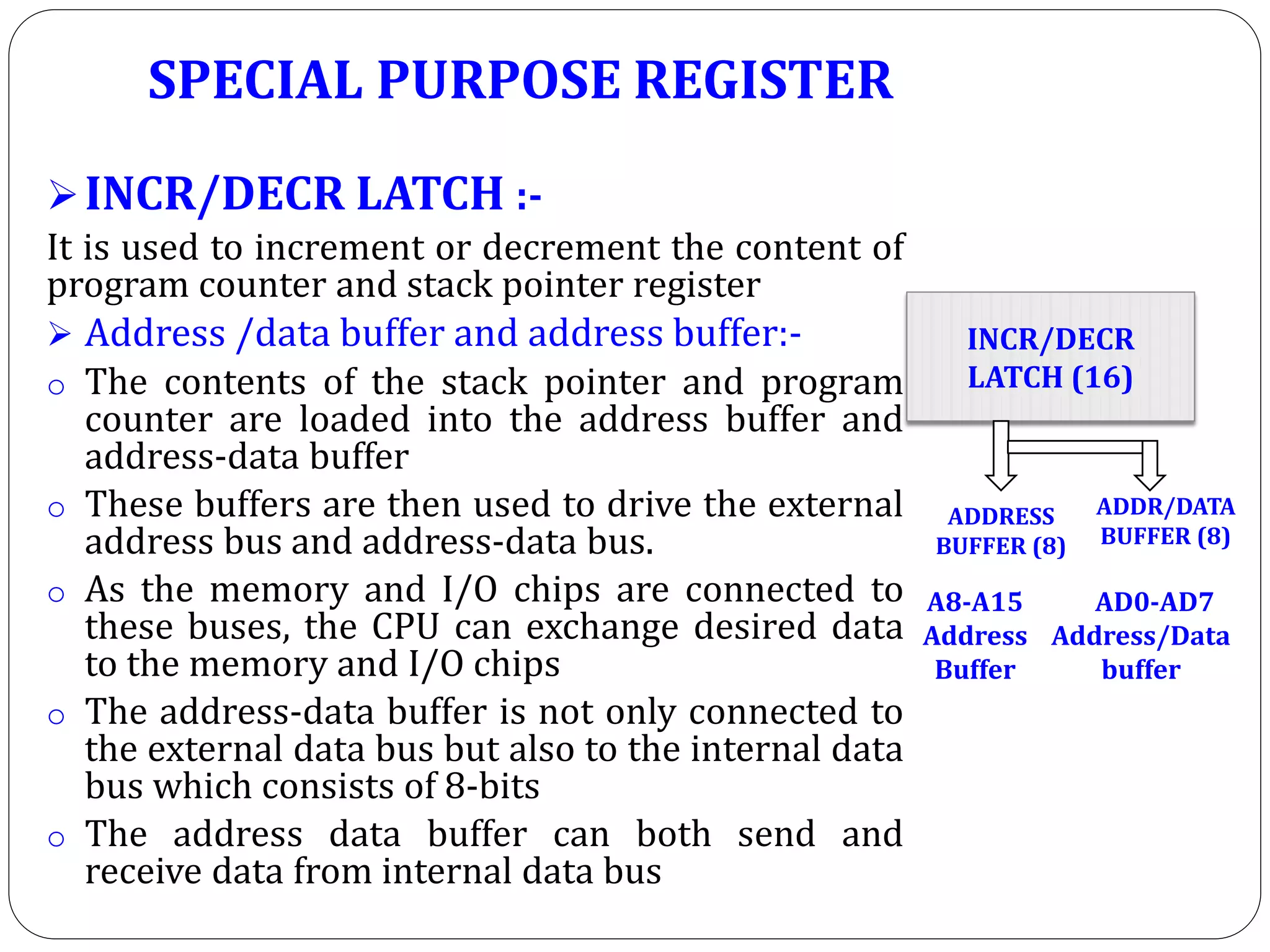
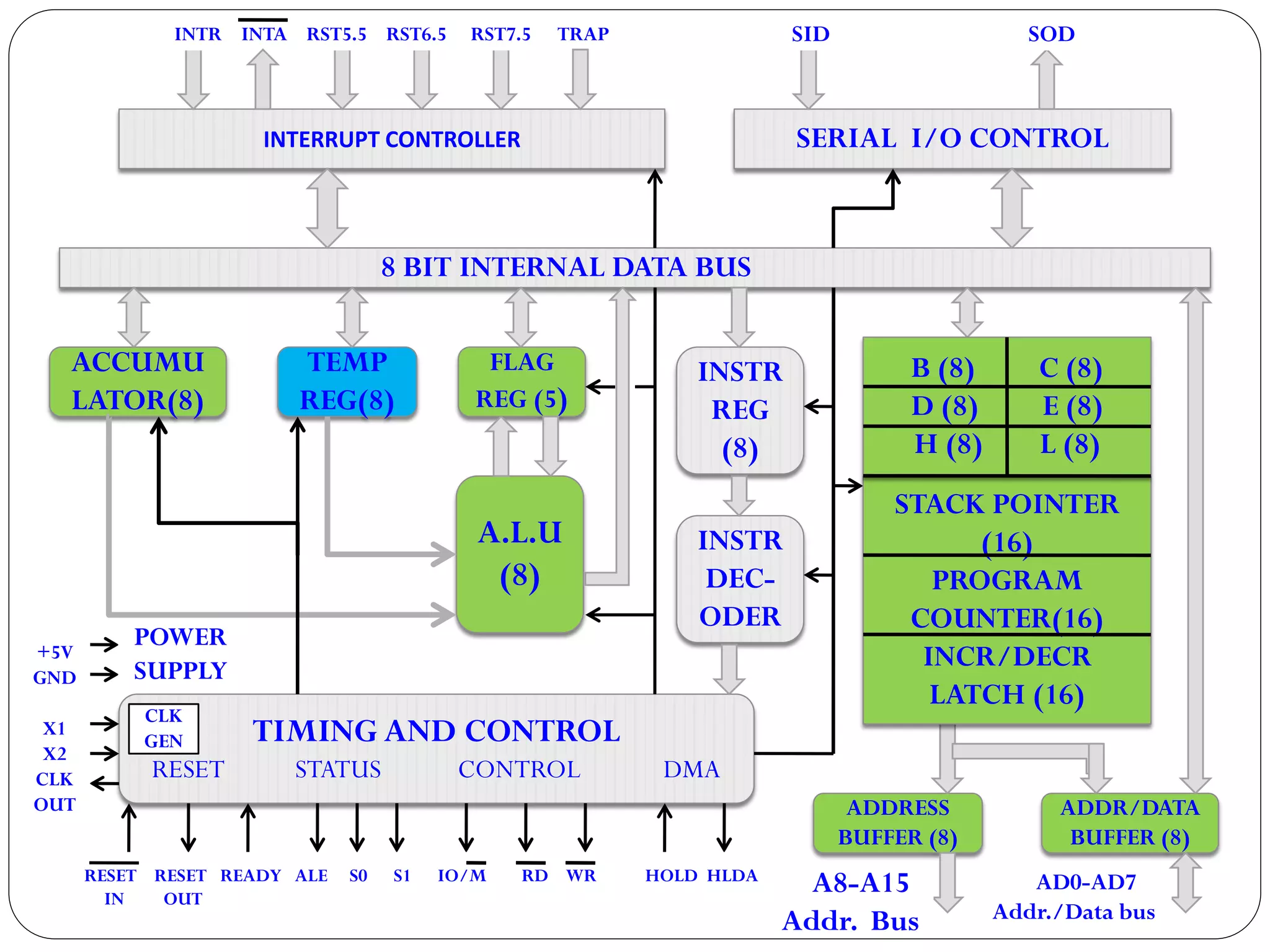
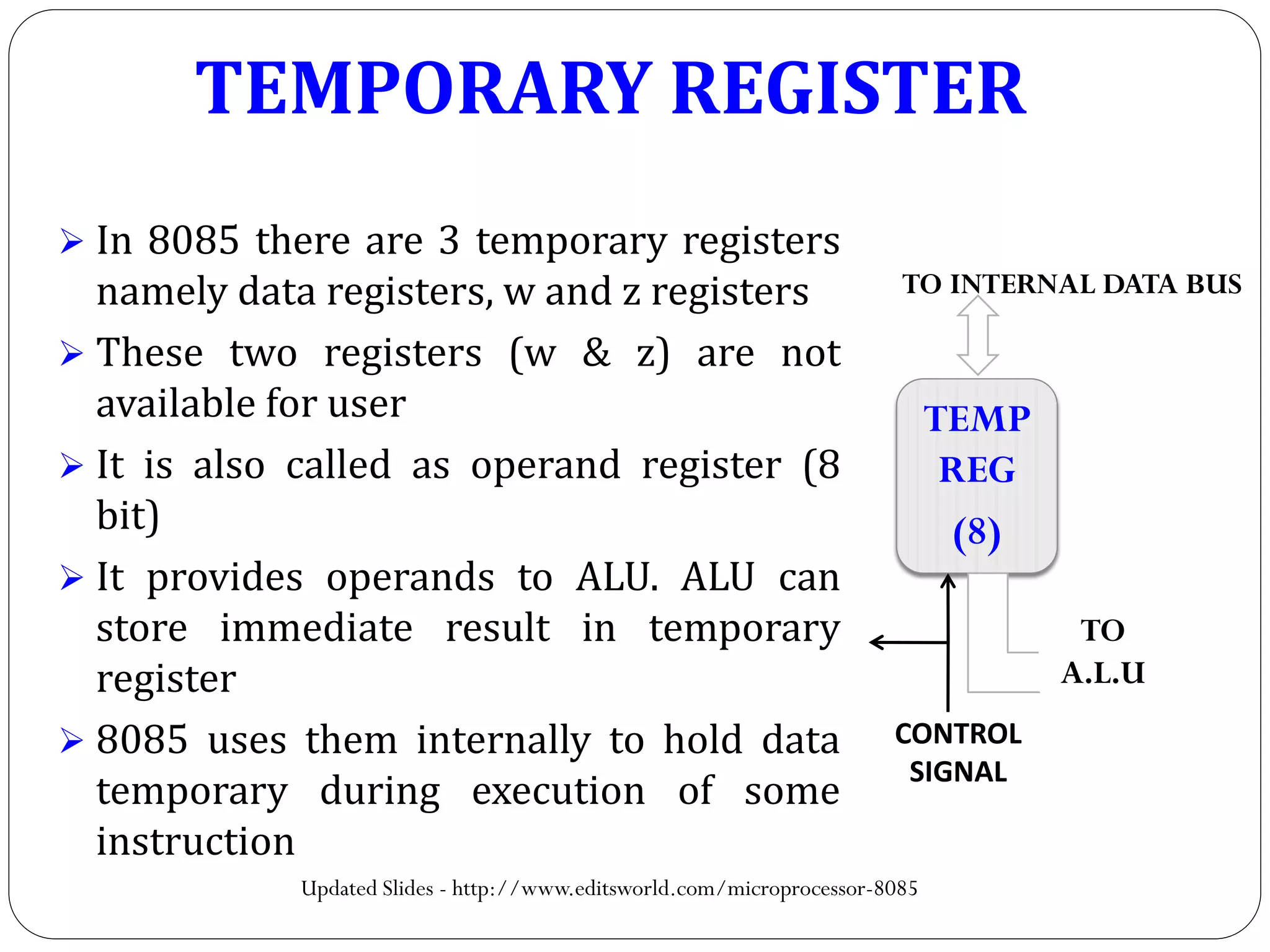
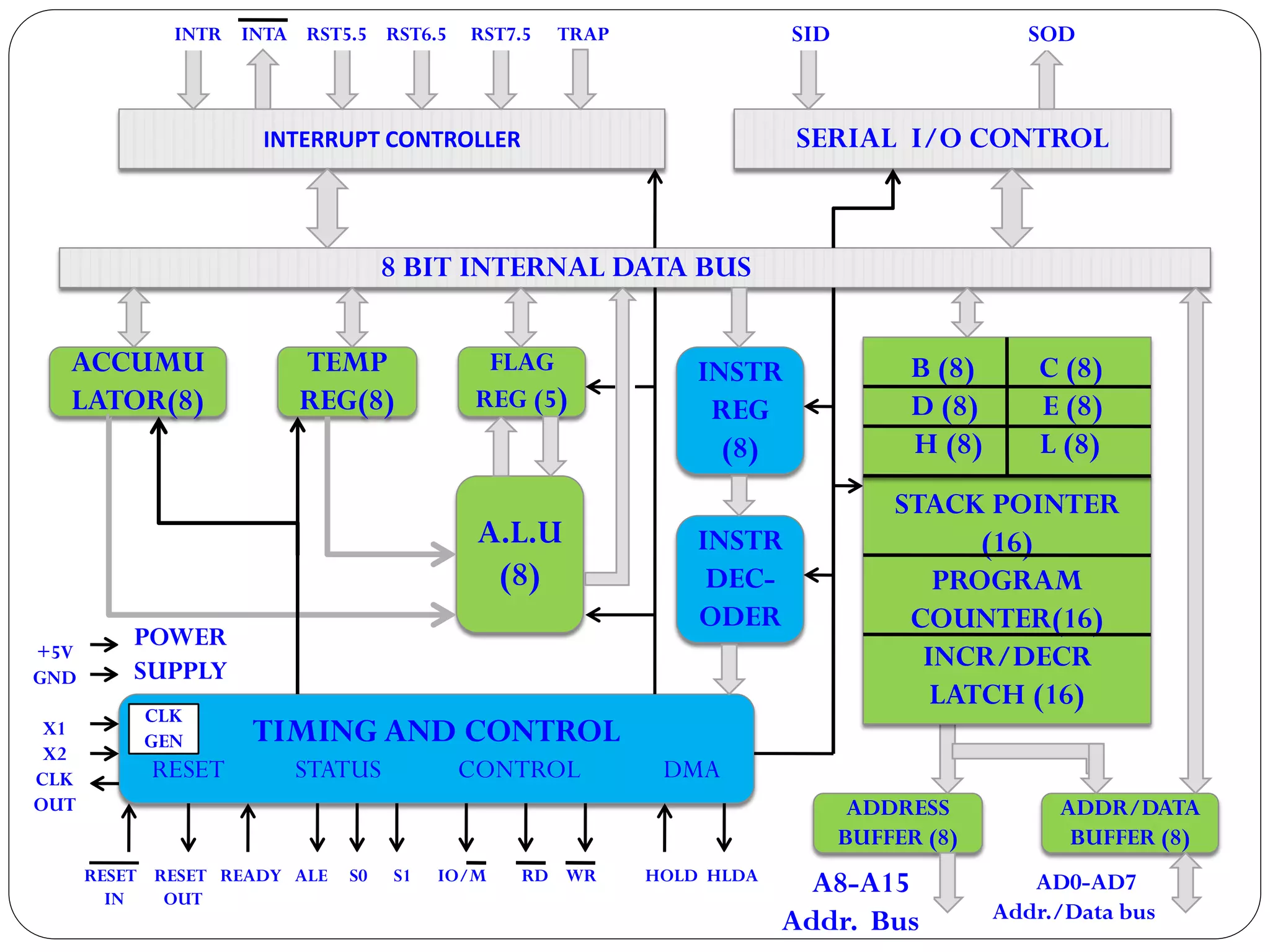
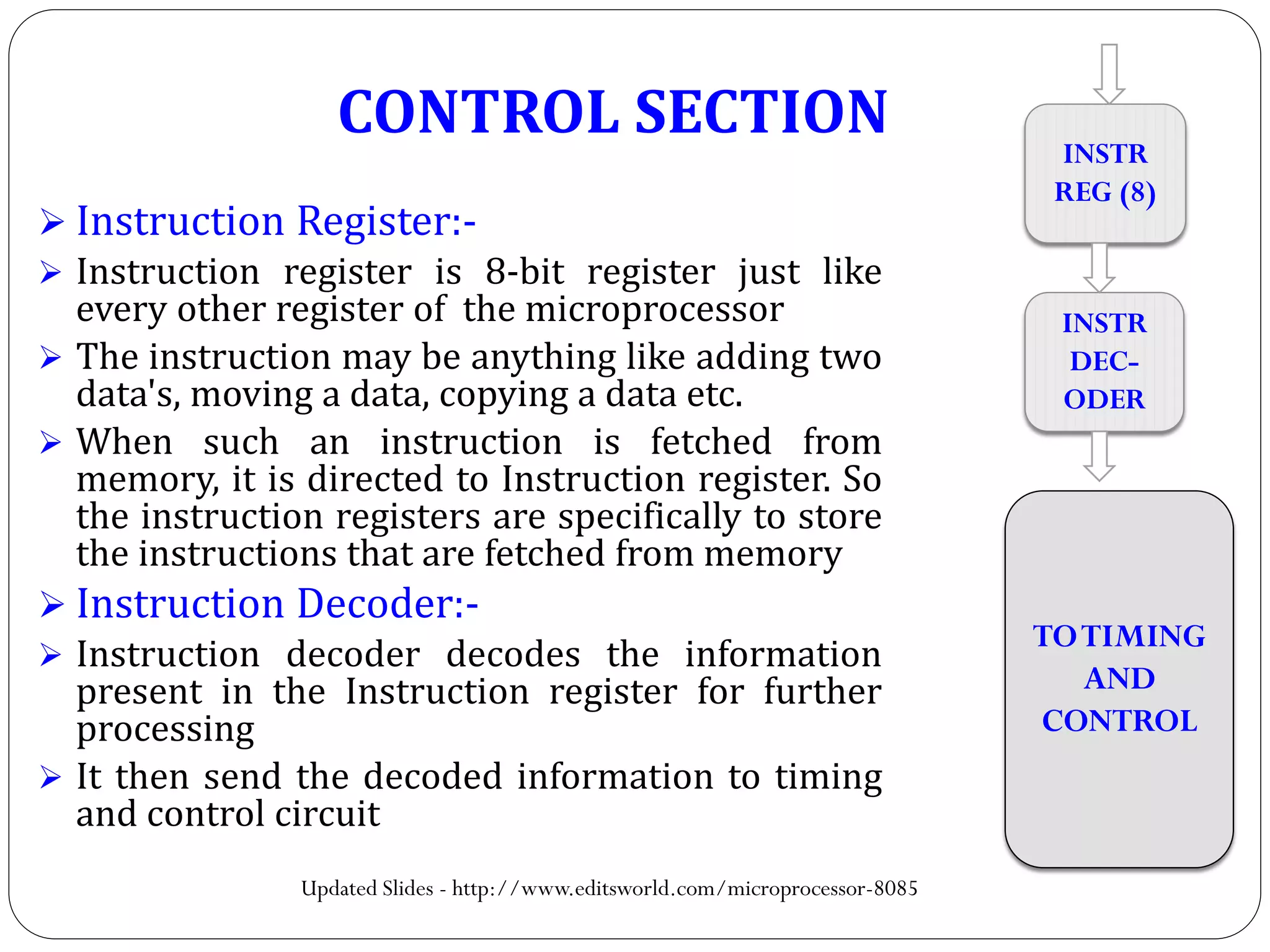
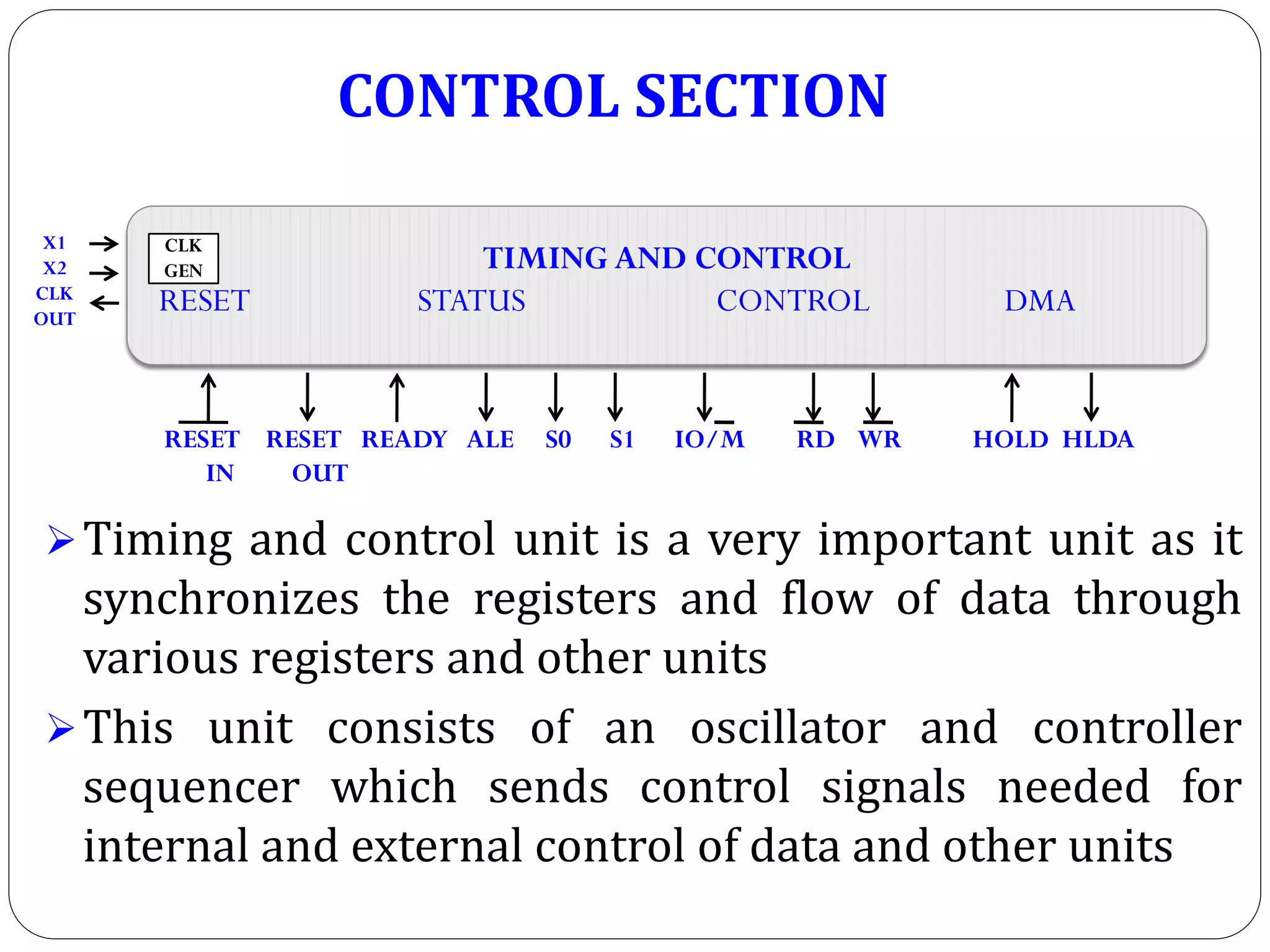
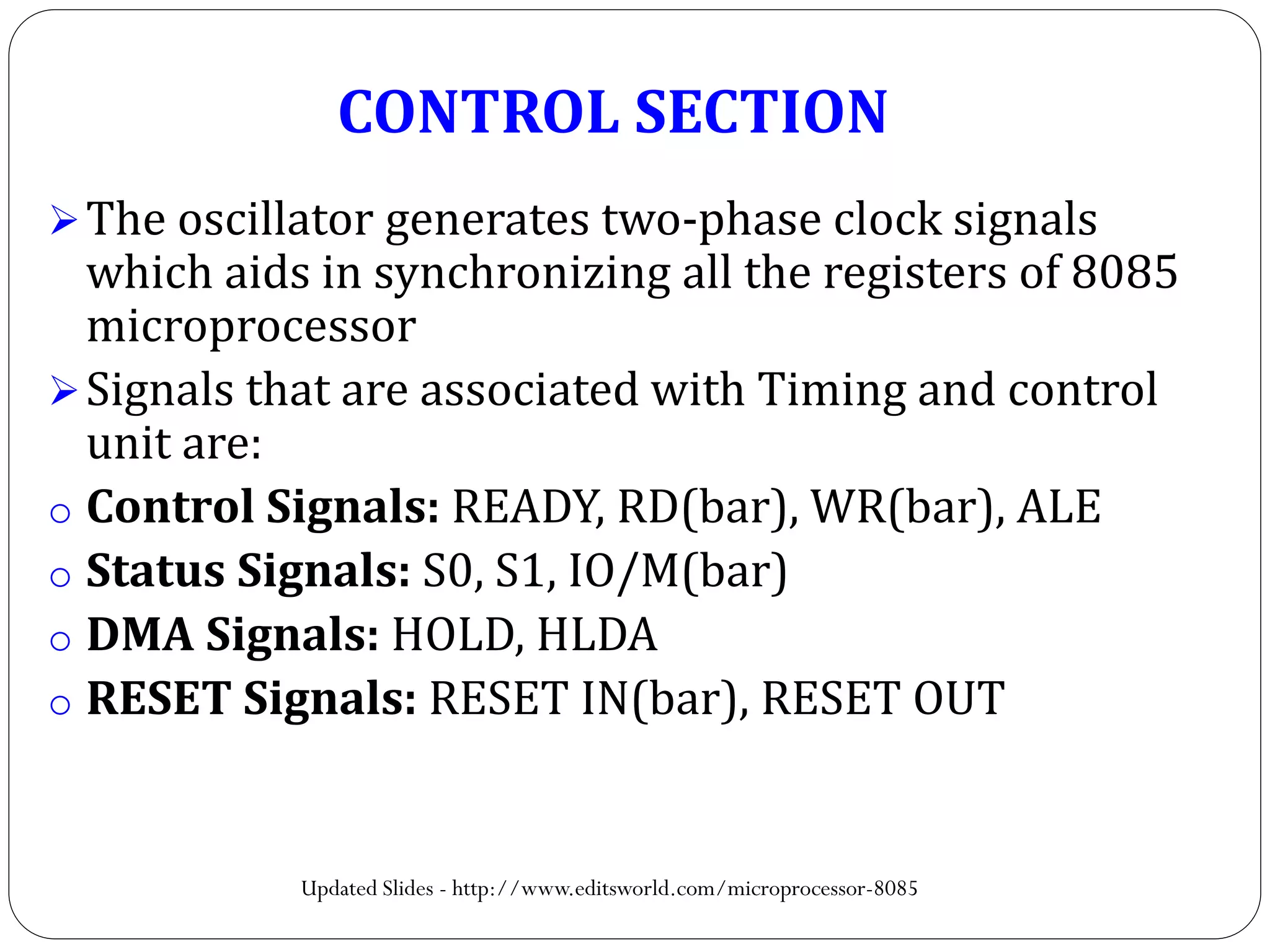
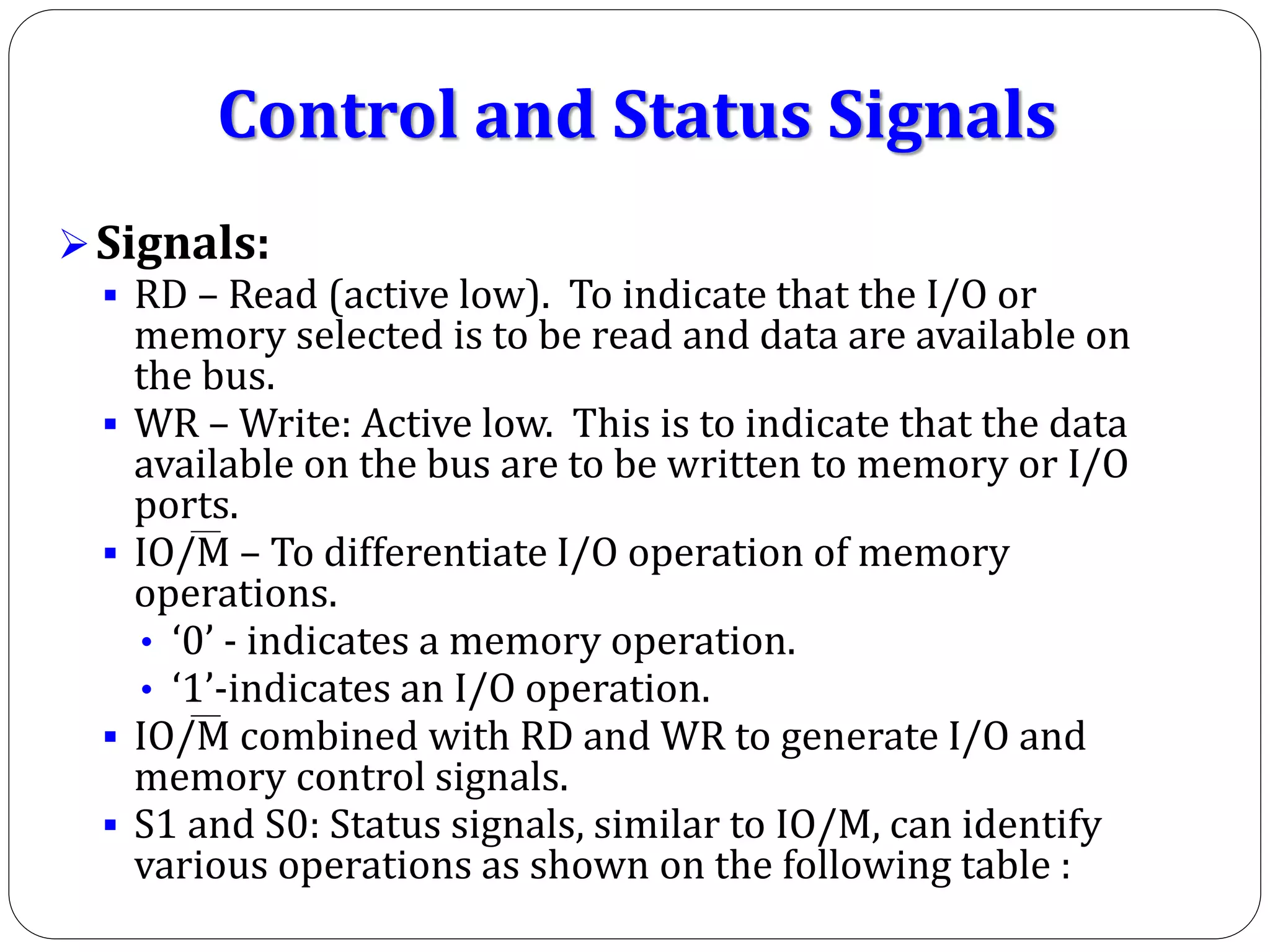
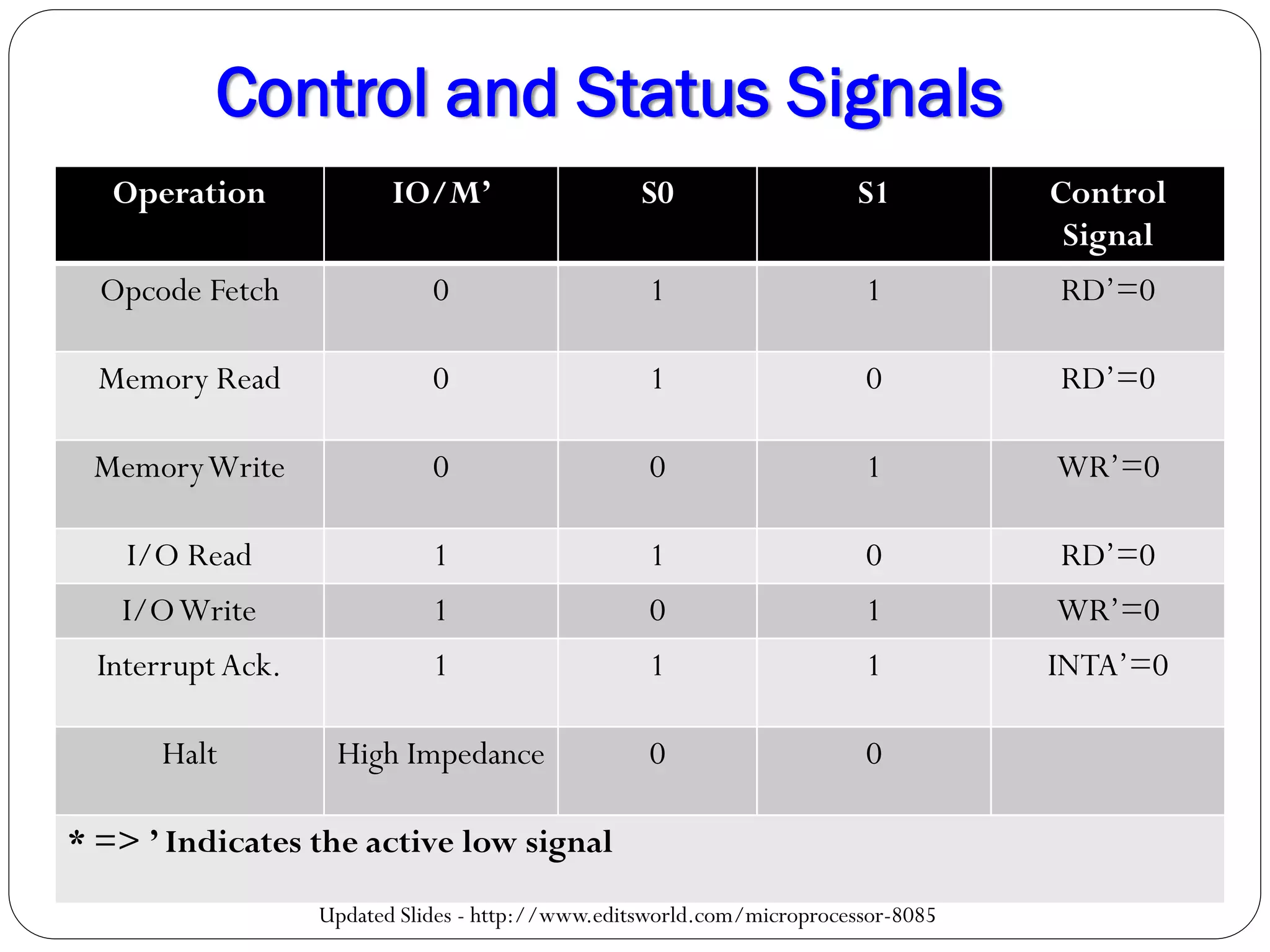
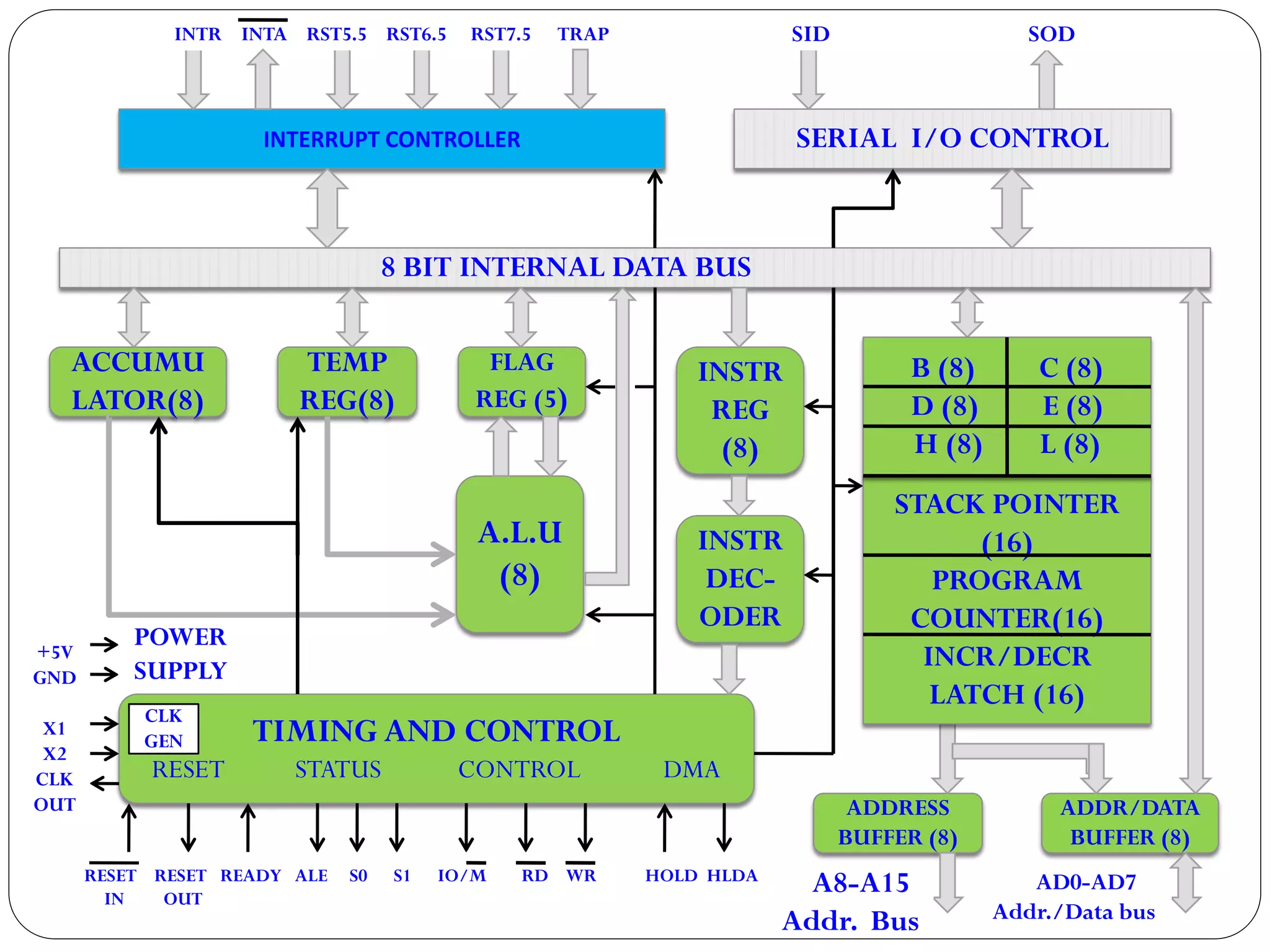
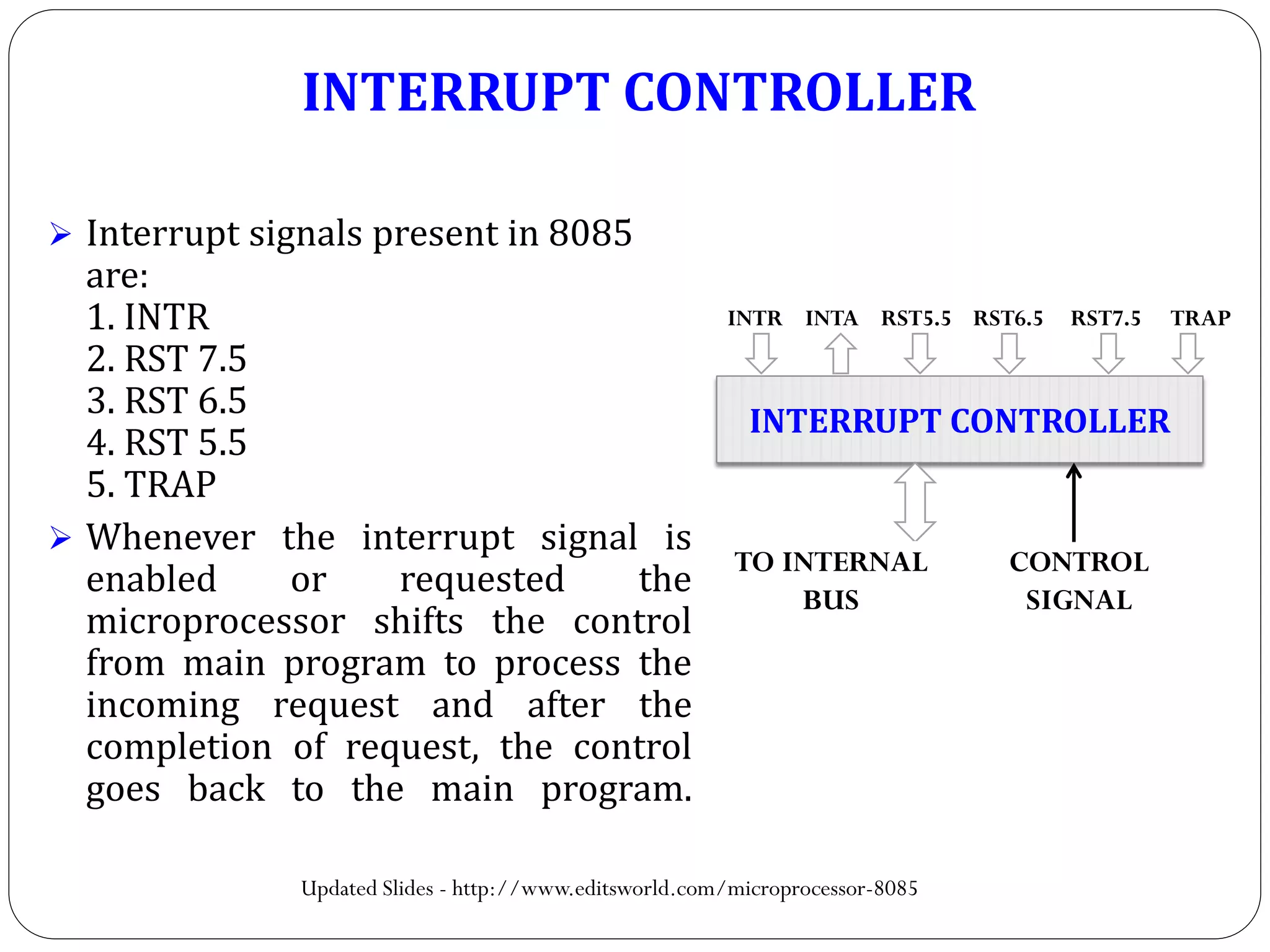
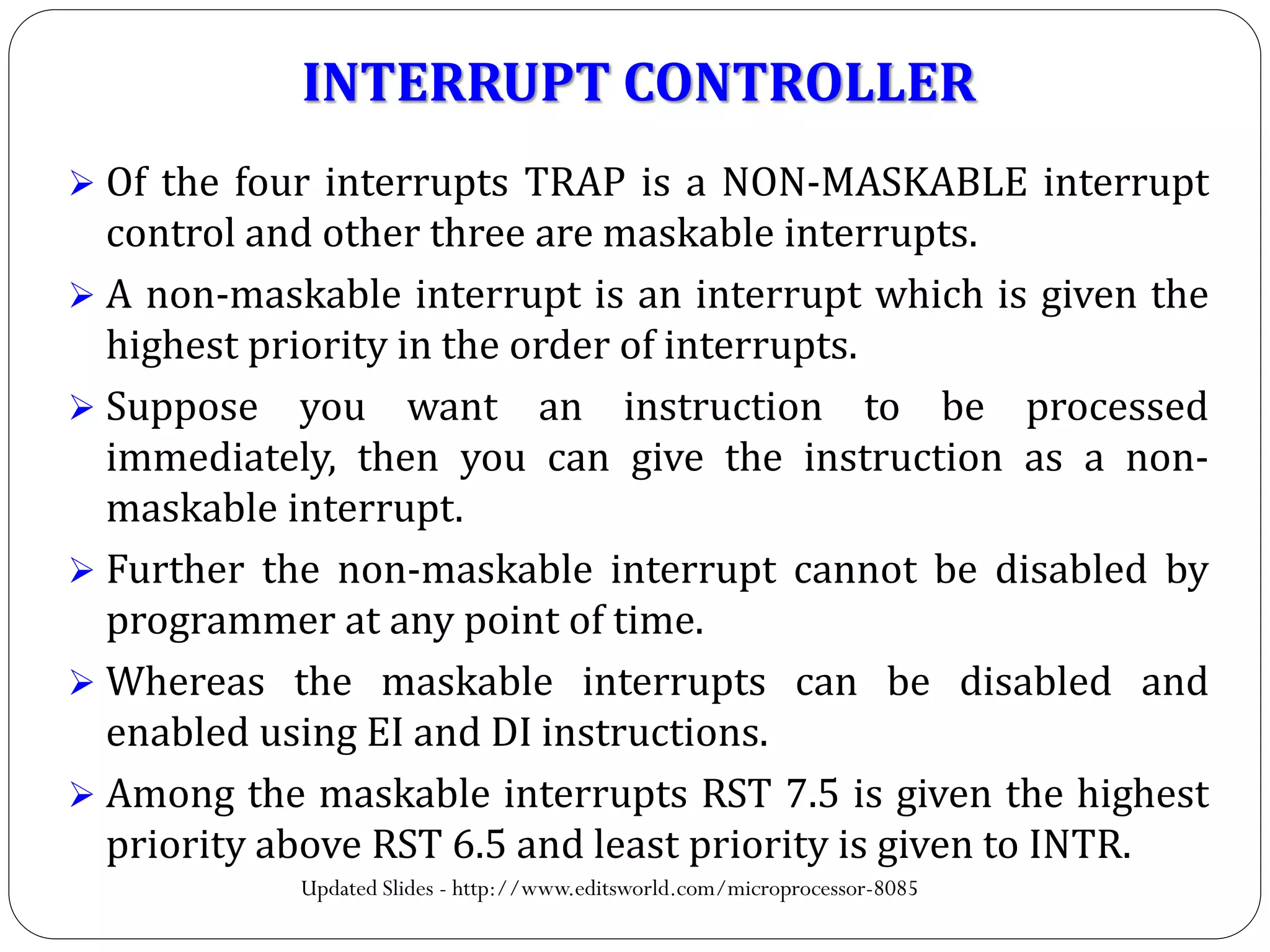
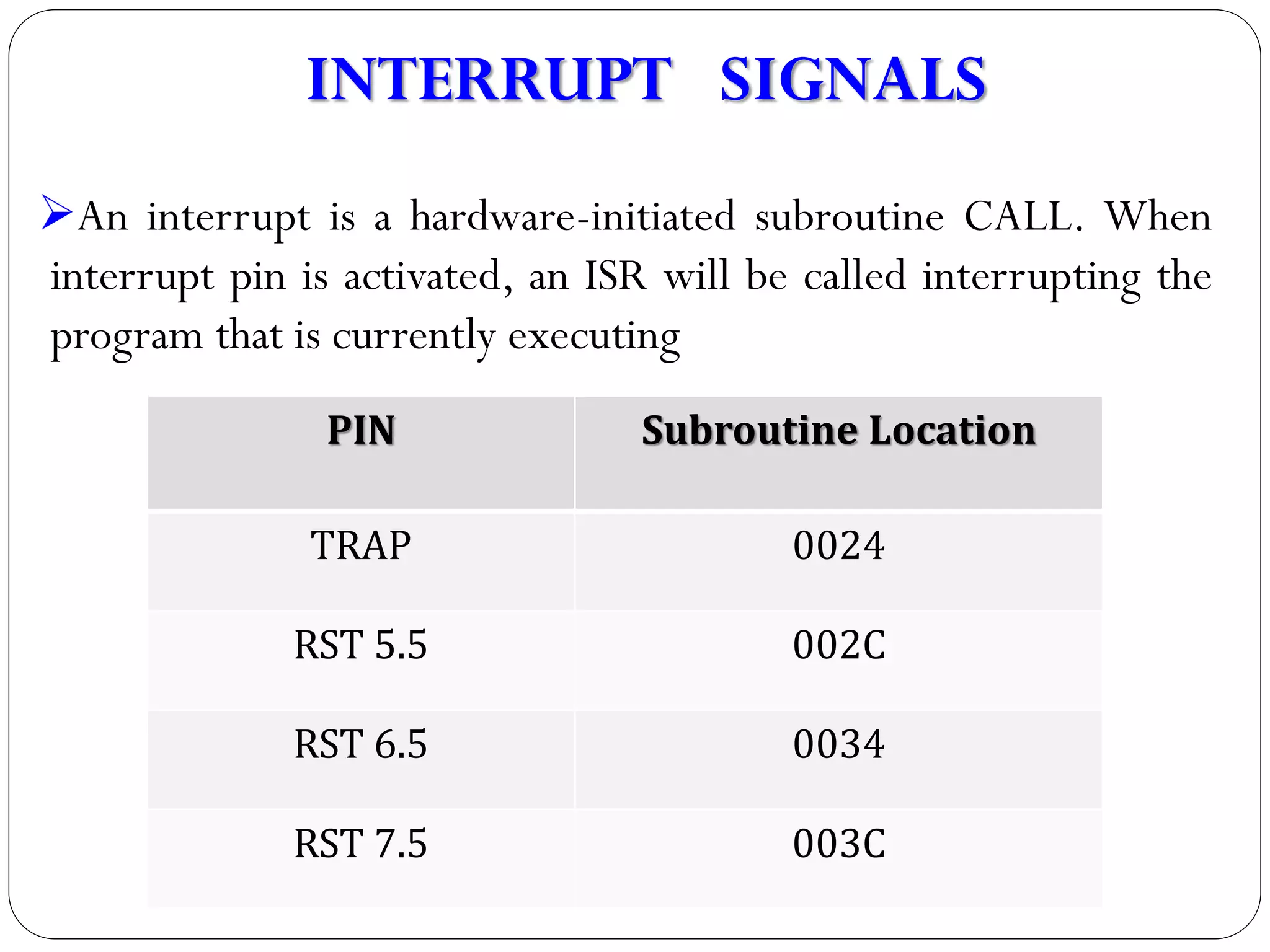
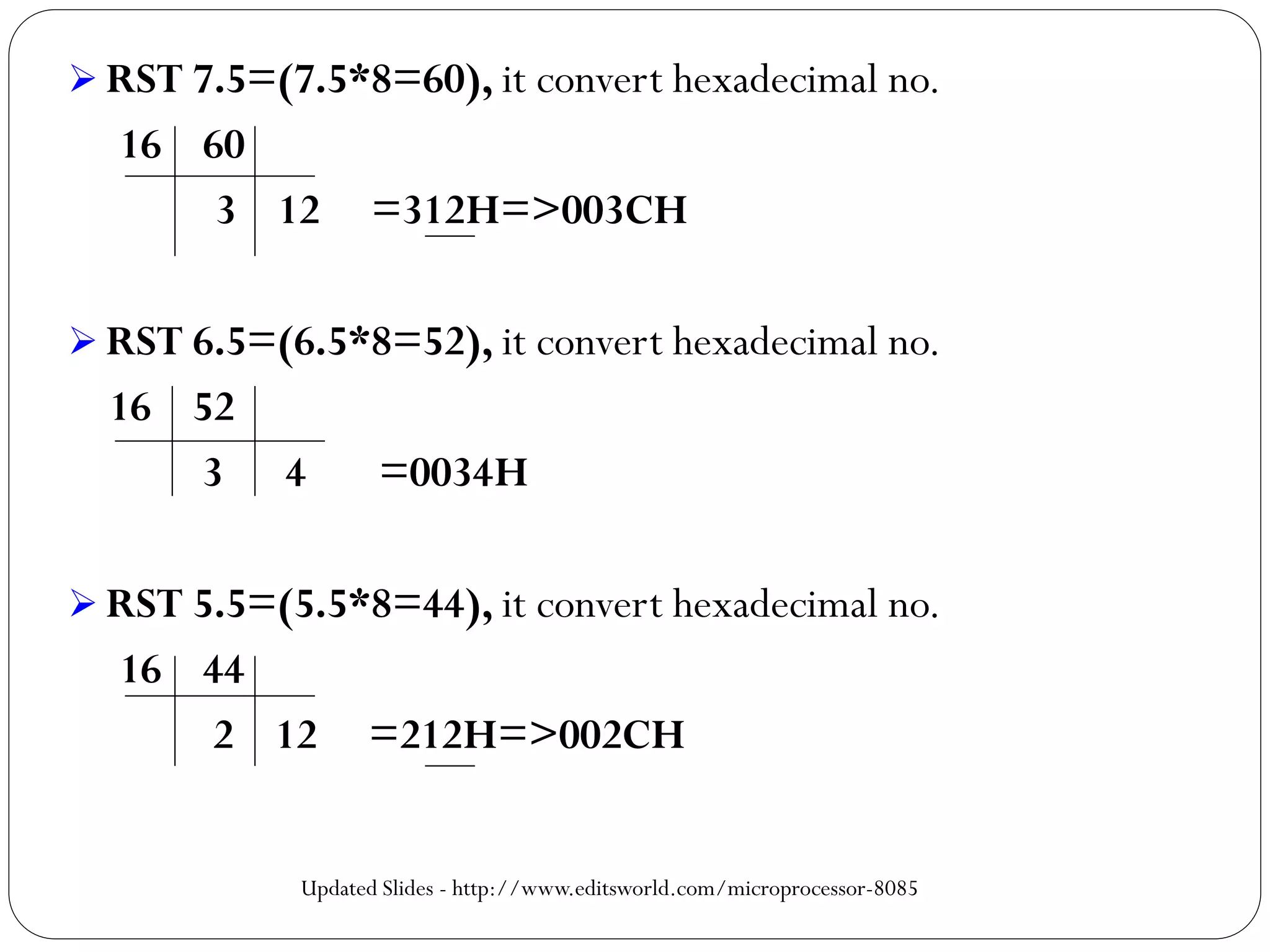
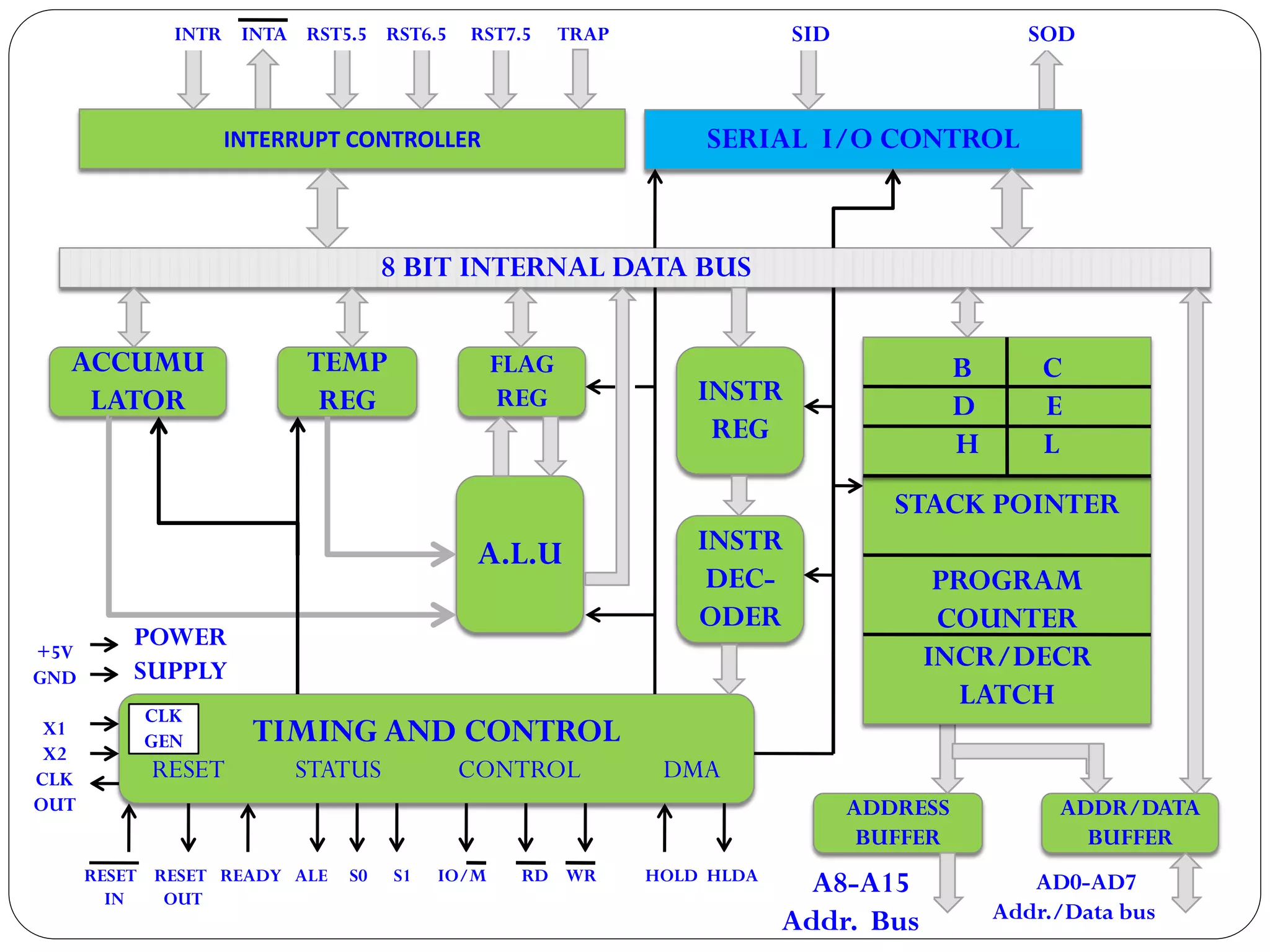
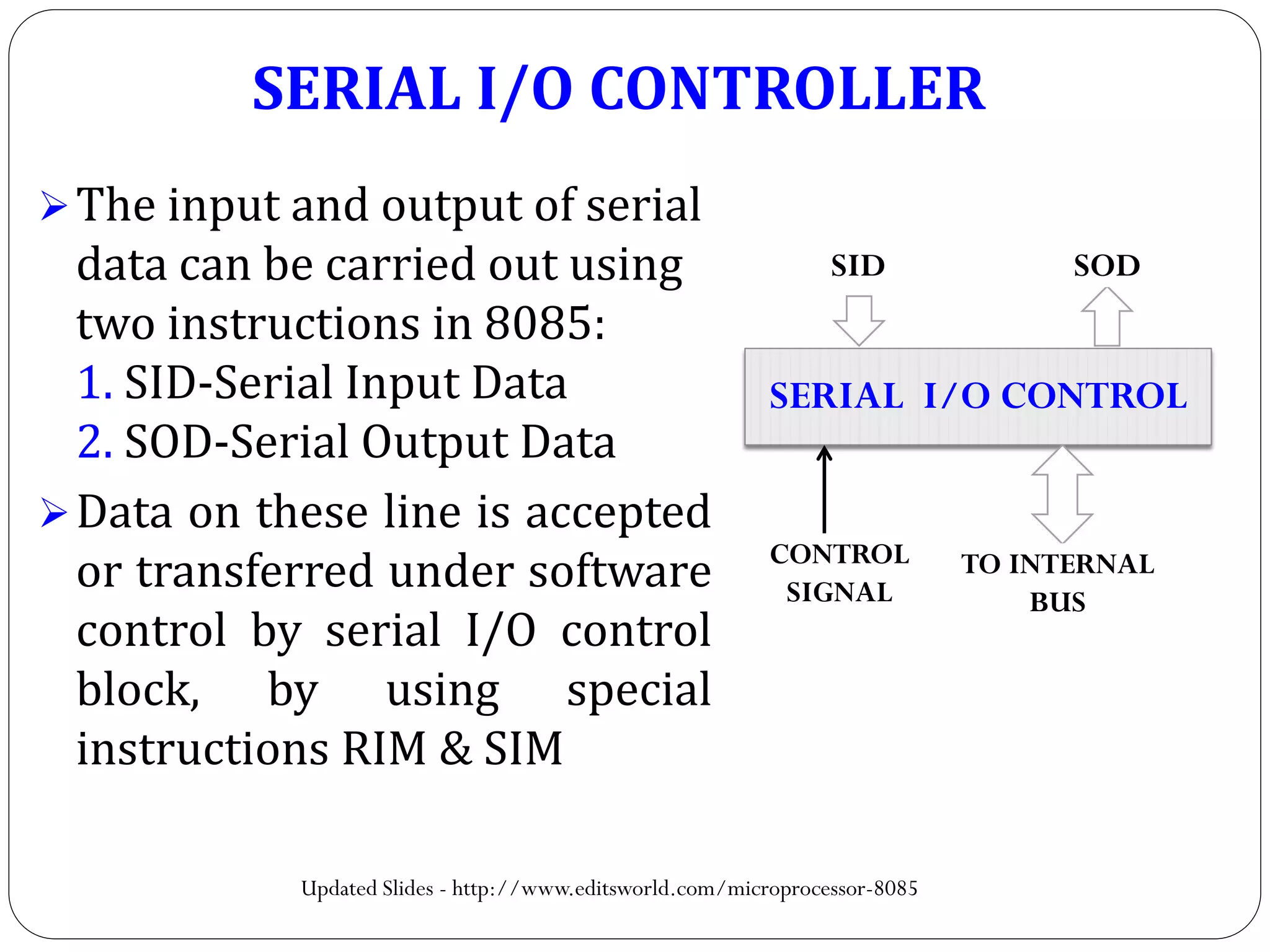
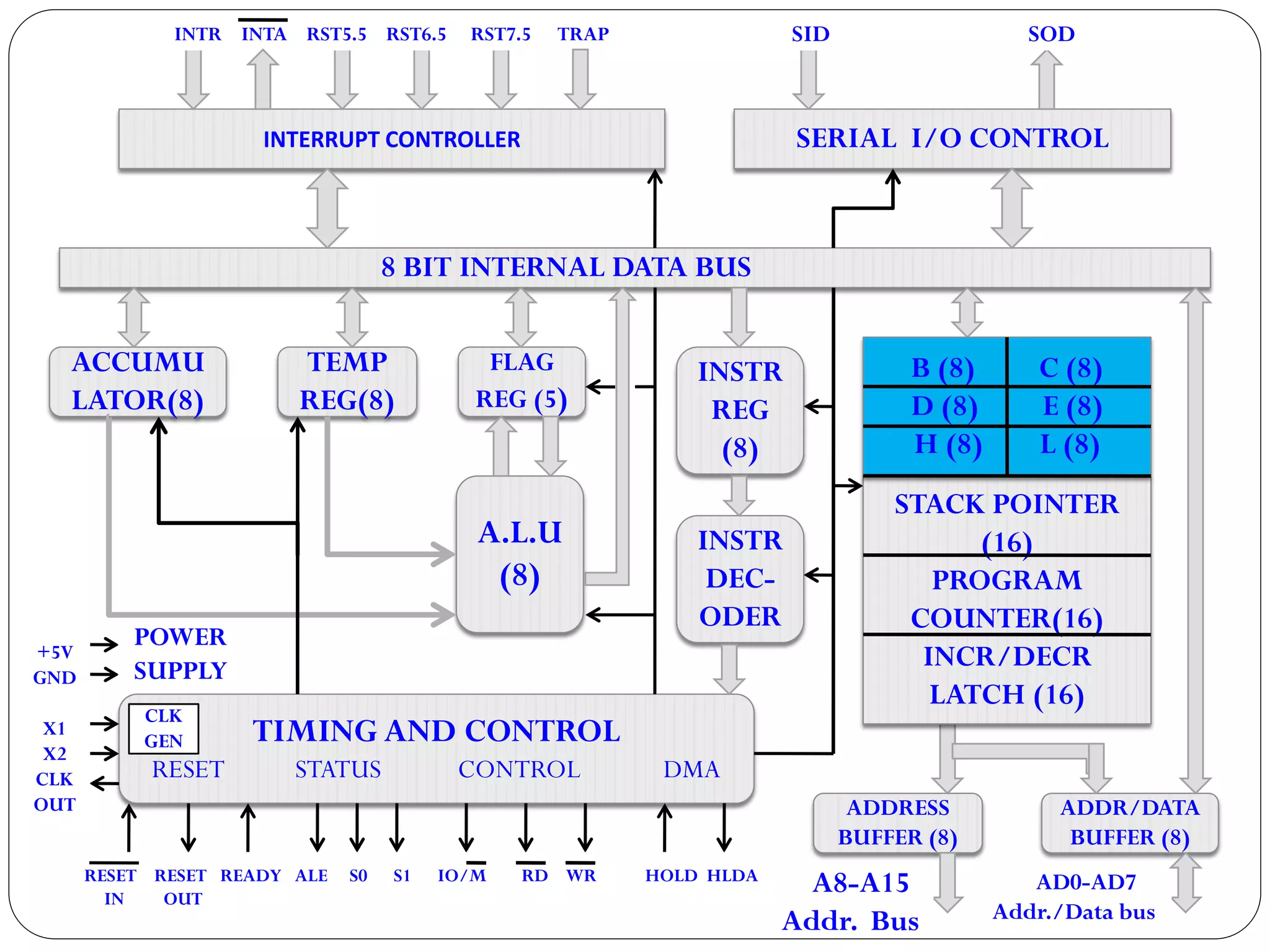
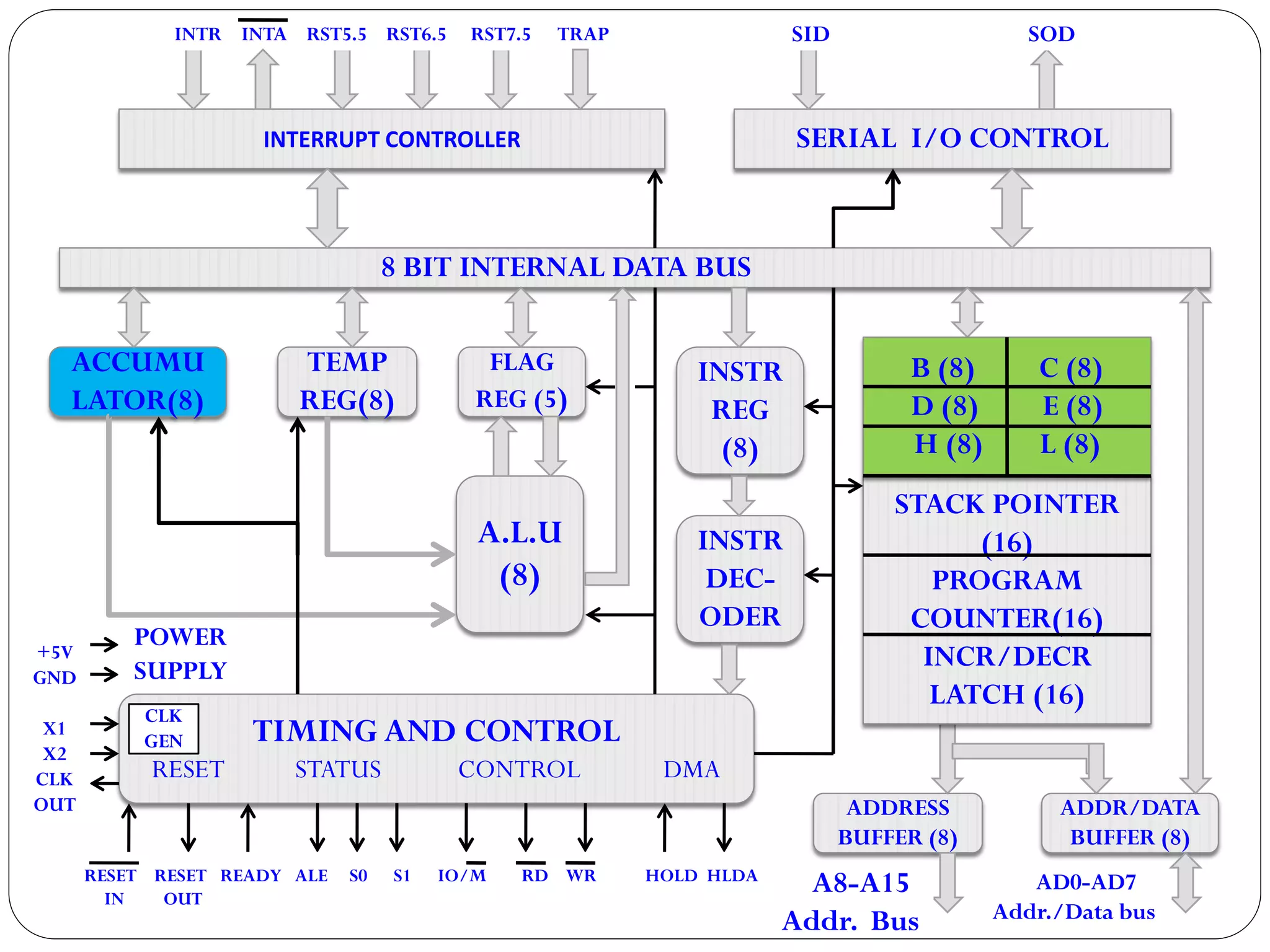
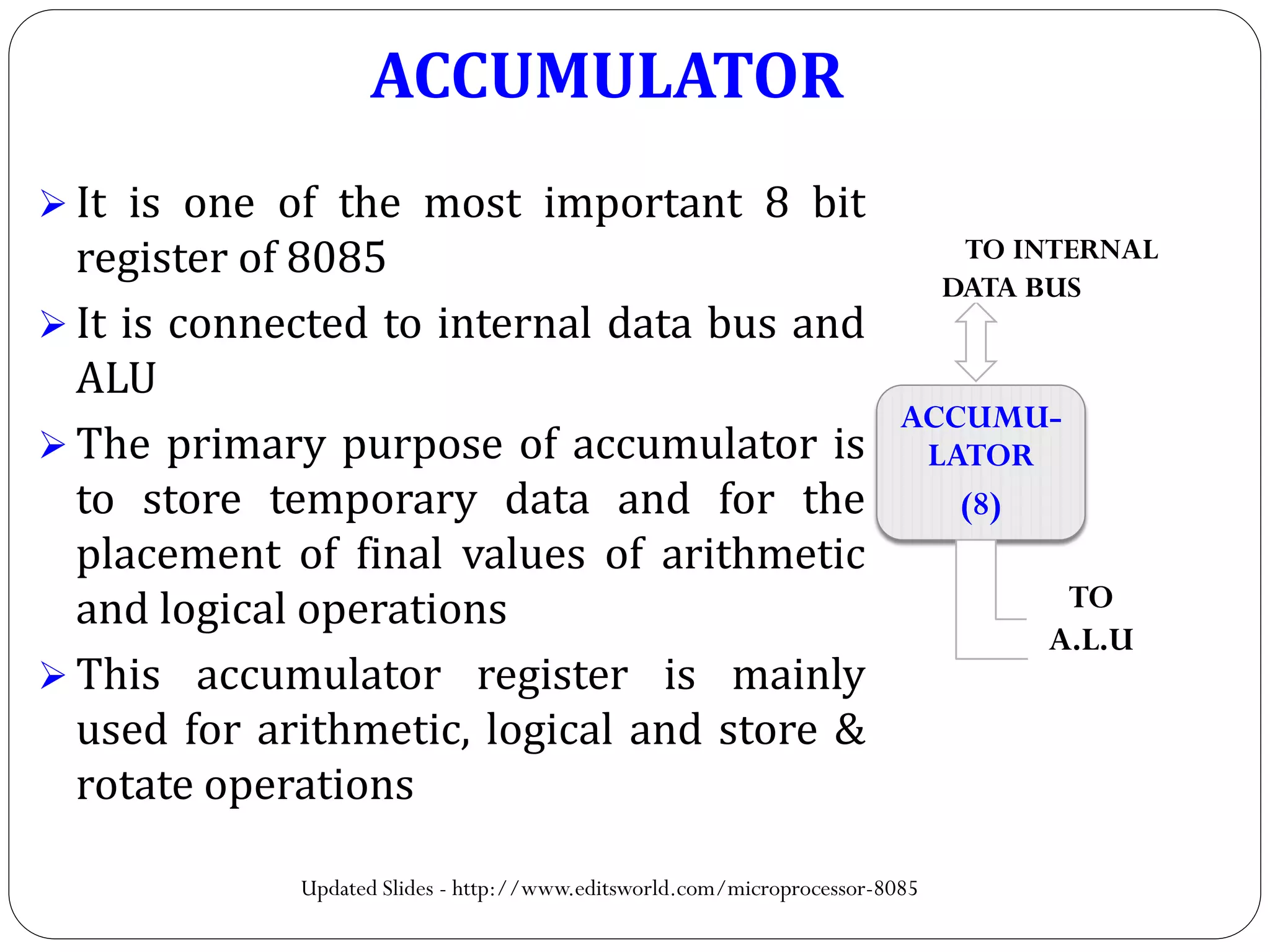
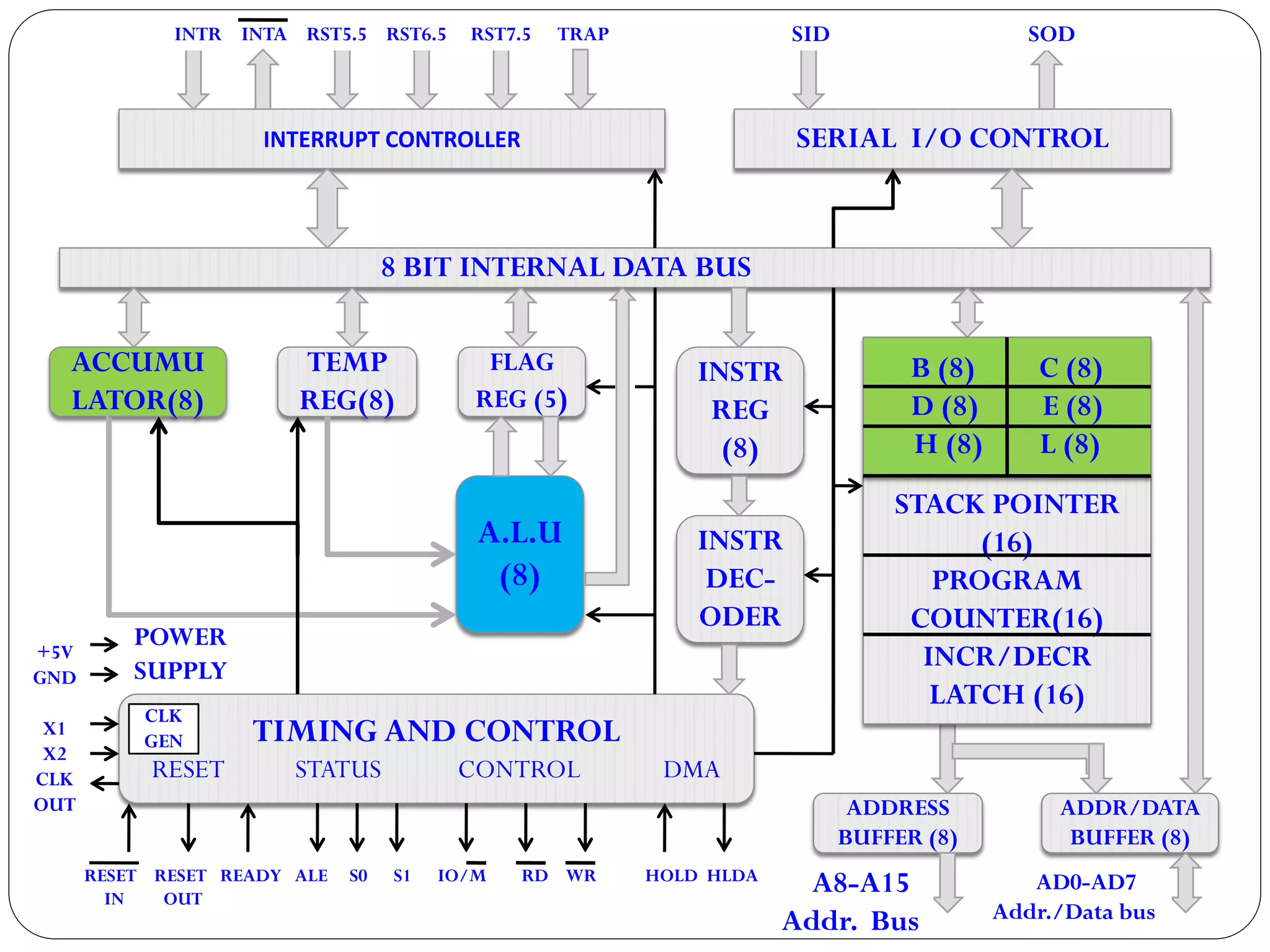
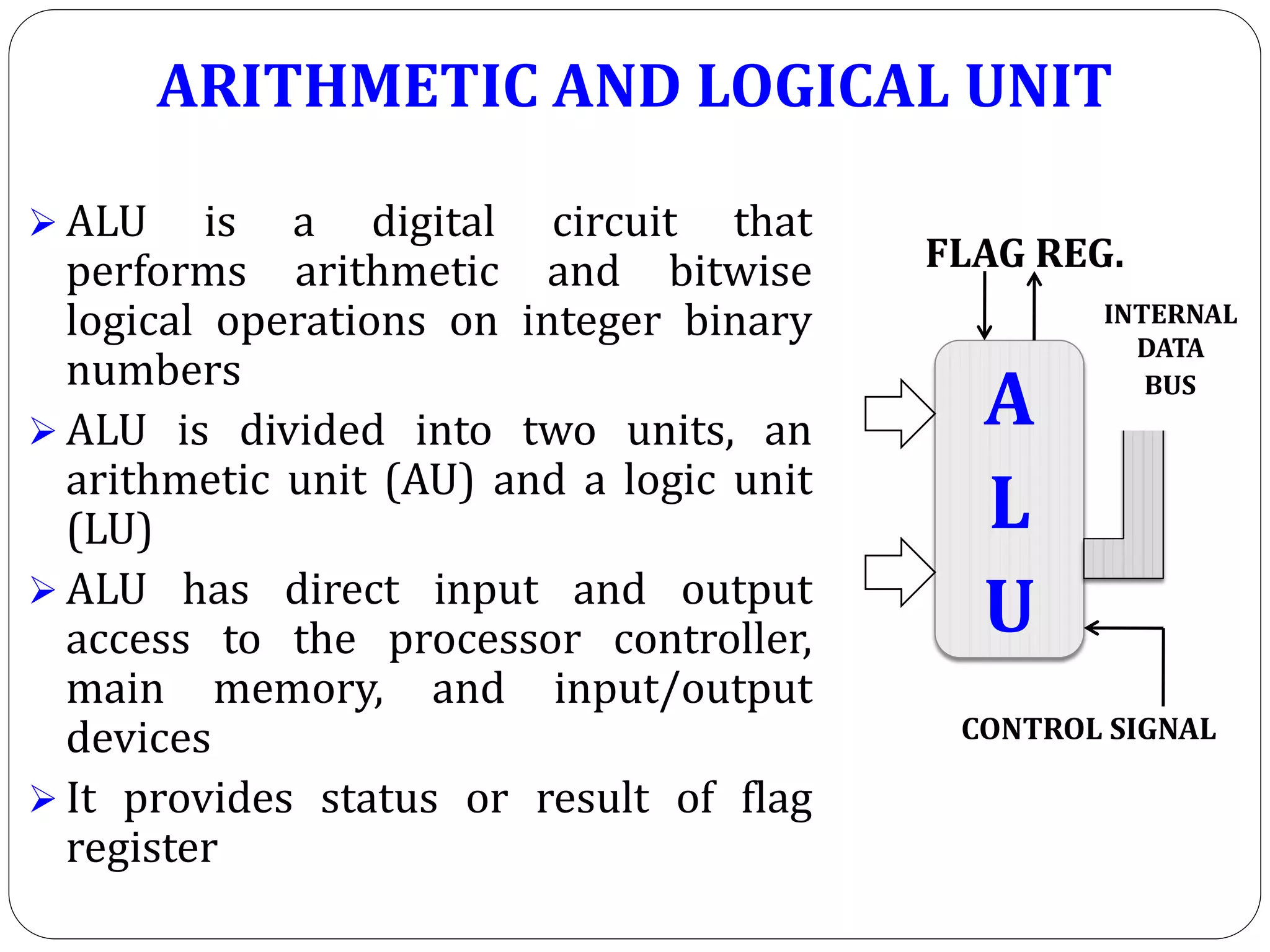
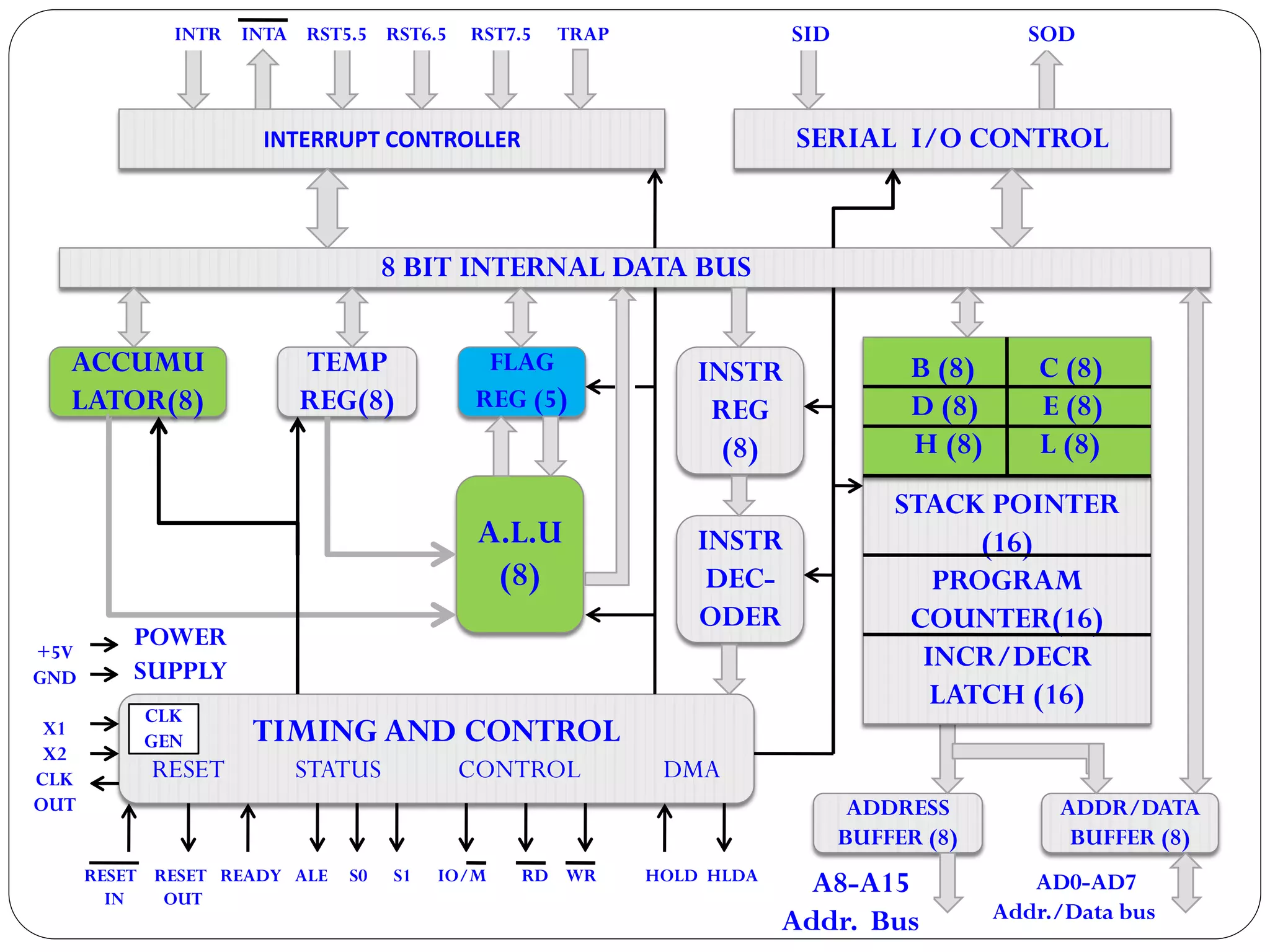
The document describes the architecture of the 8085 microprocessor. It introduces the 8085 and its key specifications. It then describes the main parts of the 8085 including the arithmetic/logical group, register group, interrupt controller, serial I/O control, and instruction register/decoder/timing and control group. It provides details on the general purpose registers, accumulator, flags register, and special purpose registers used in the 8085 architecture.



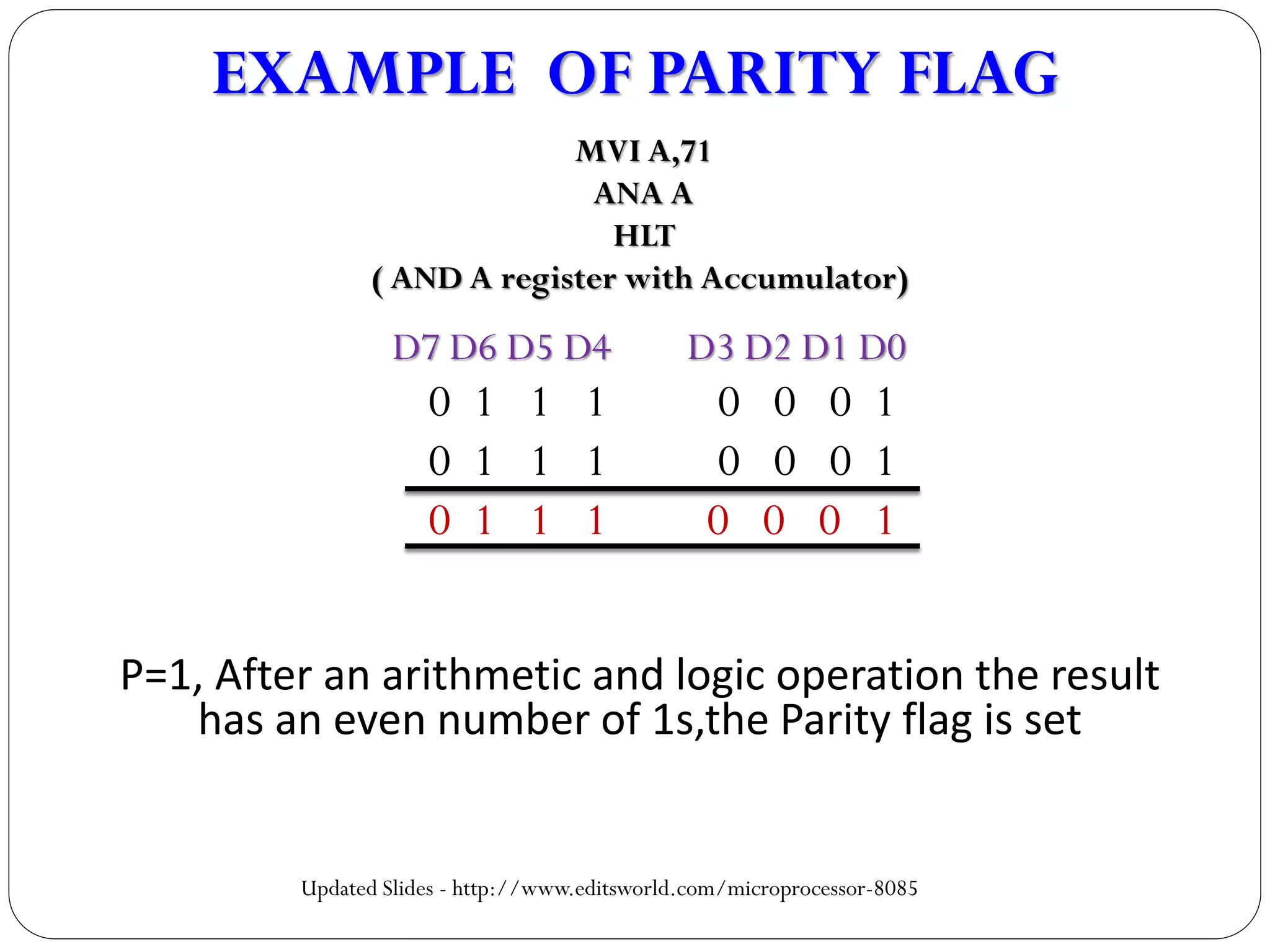
![(Carry) 10 0 10
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
[A] 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
[B] 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 (RESULT)
MSB LSB
AC=1,In an airithmetic operation D3 bit borrow
a carry from D4 bit. So the auxiliary flag is set.
EXAMPLE OF AUXILIARY FLAG
MVI B, A9H
MVI C, 71H
MOV A,C
SBB B
HLT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/architectureof8085-160430102824/75/Architecture-of-8085-14-2048.jpg)