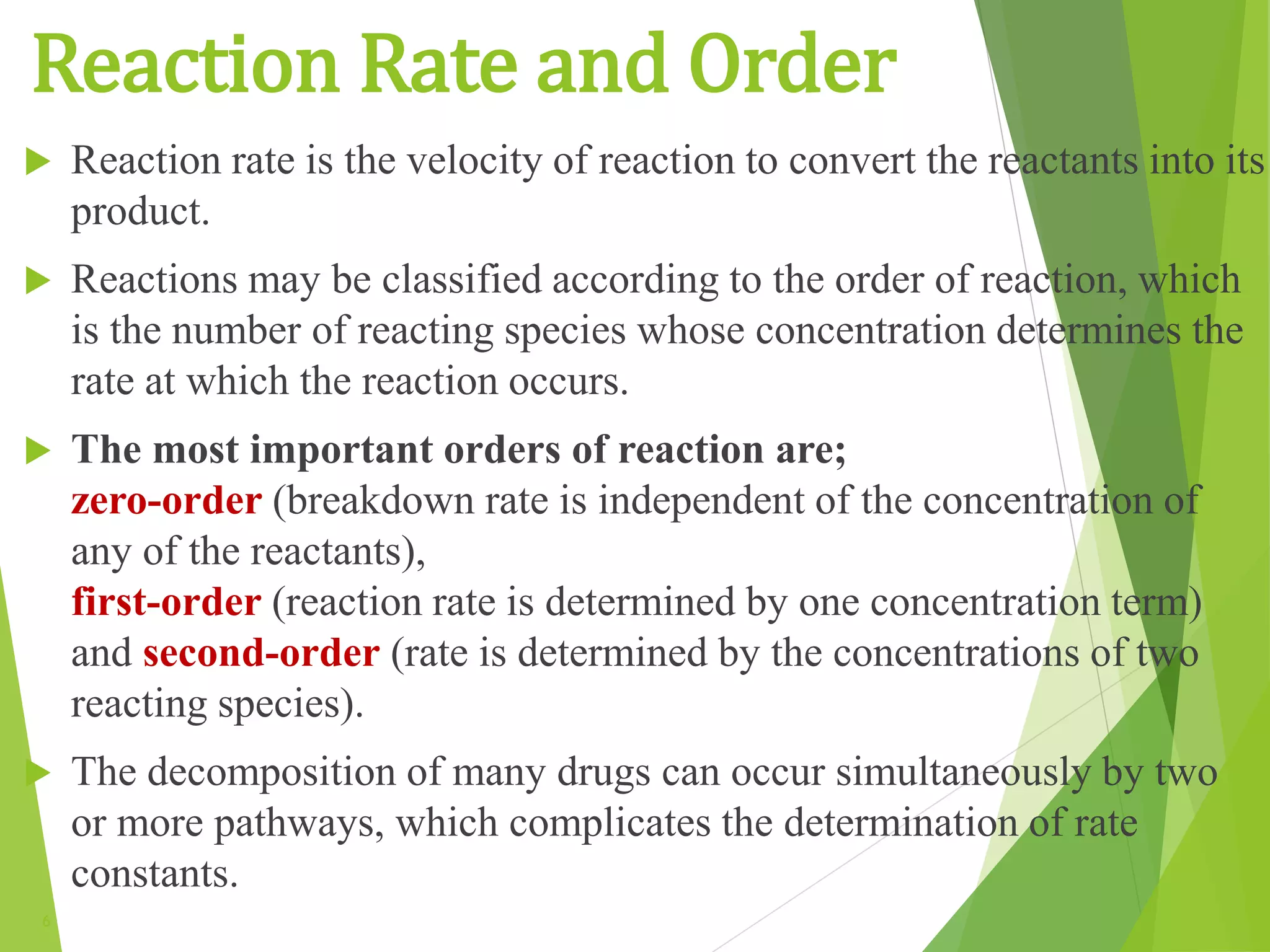
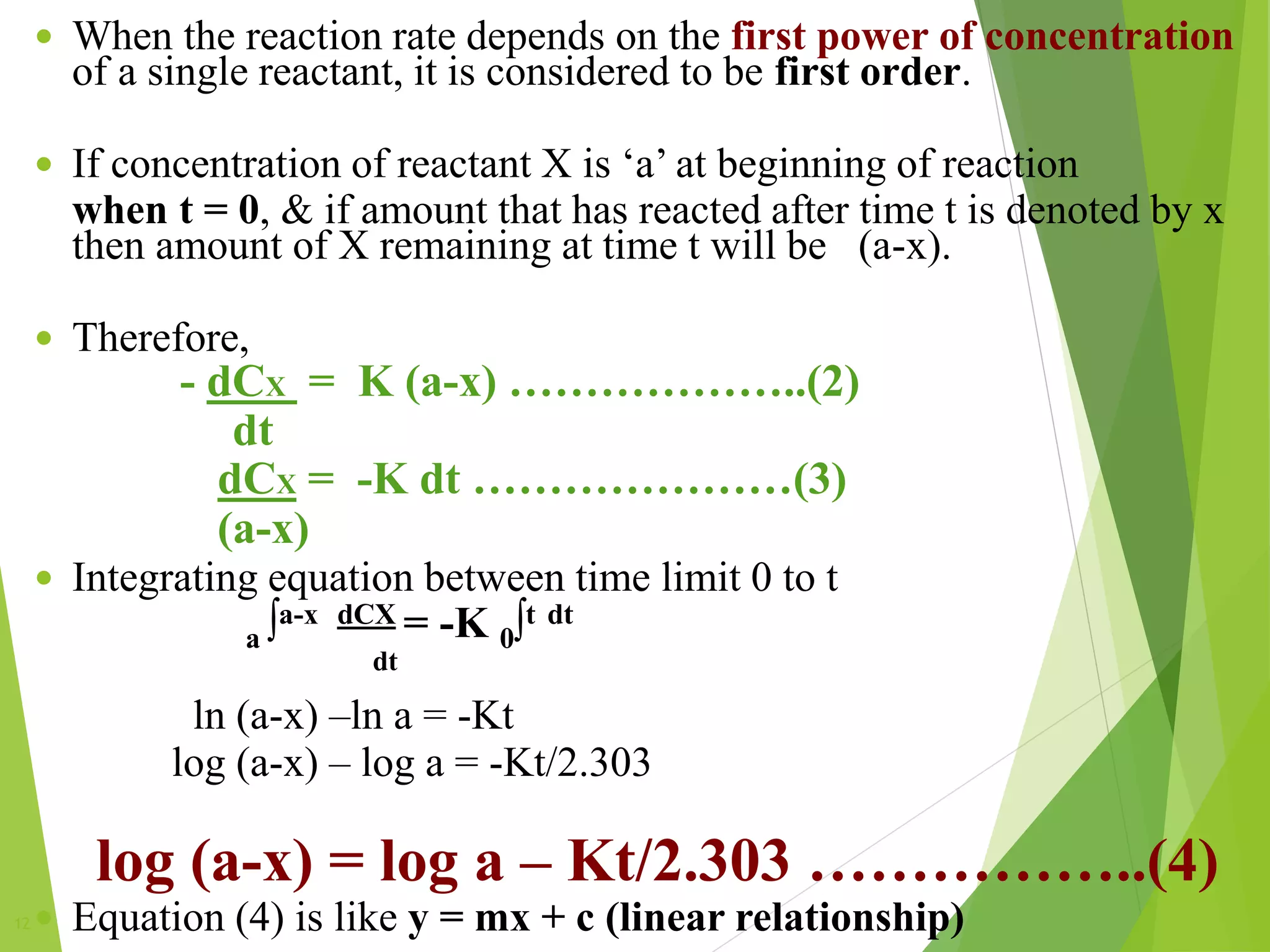
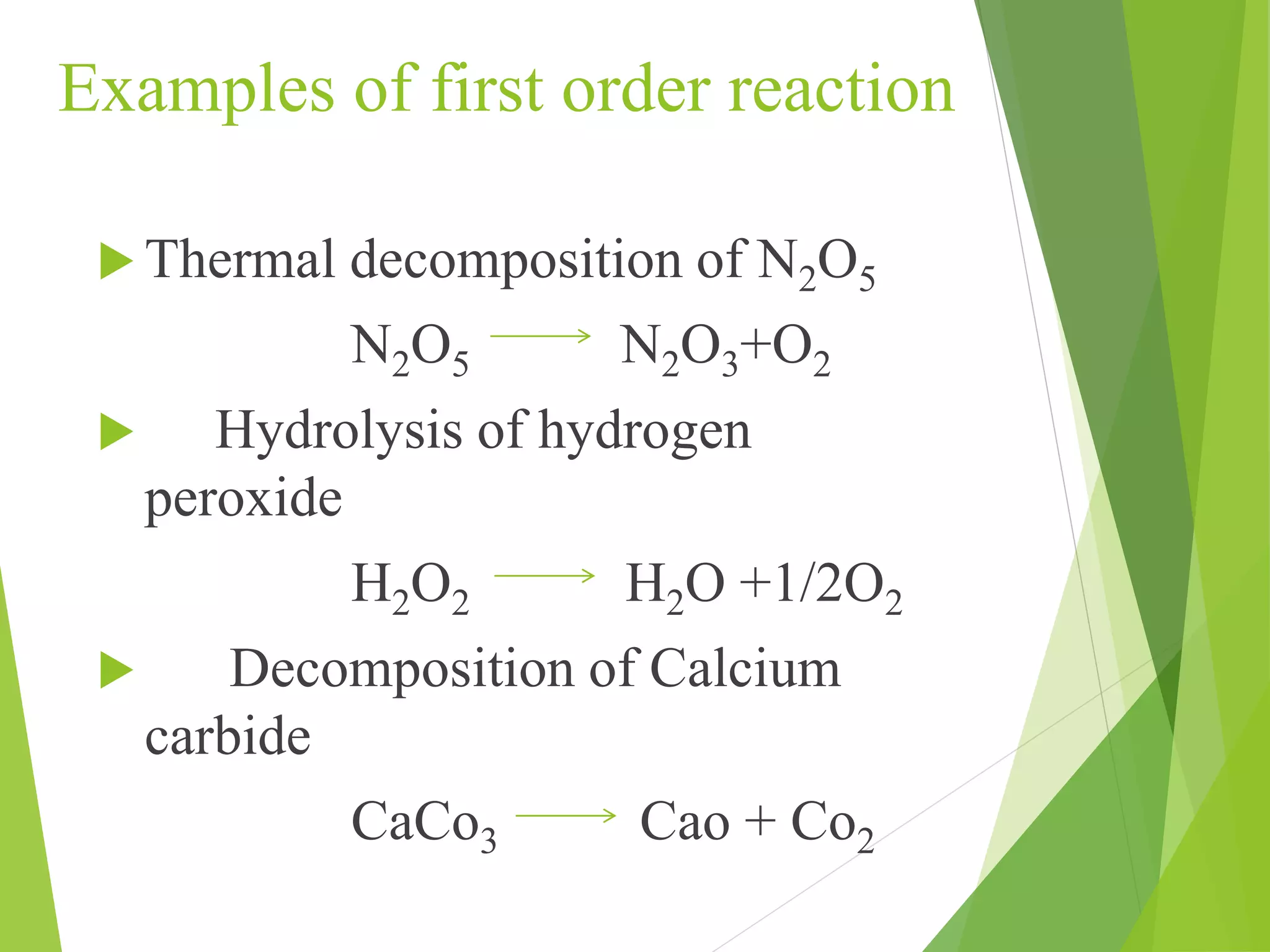
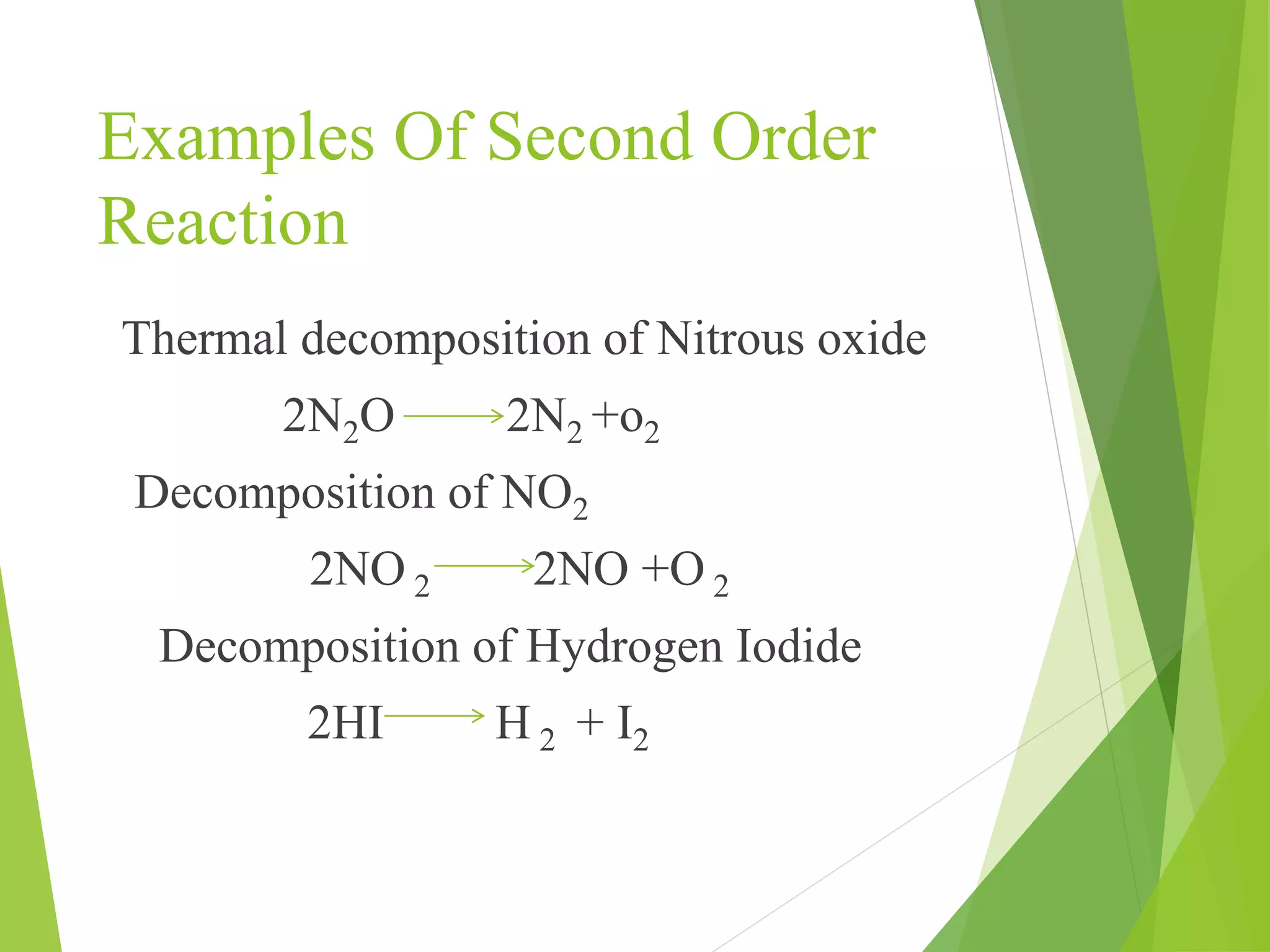
Chemical kinematics deals with the rates of chemical reactions and their mechanisms. The rate constant in a rate law, such as the rate law d[A]/dt = k[A], is independent of concentration but depends on factors like temperature. The order of a reaction is the sum of the powers of the concentration terms in its rate equation. Common orders of reaction include zero-order, where the rate is independent of reactant concentration, first-order, where the rate depends on one concentration term, and second-order, where the rate depends on two concentration terms. Higher order reactions are also possible but are more complex.


![3
RATE CONSTANT
A rate constant is a proportionality constant that
appears in a rate law. For example, k is the rate
constant in the rate law
d[A]/dt = k[A].
Rate constants are independent of concentration
but depend on other factors, most notably
temperature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-3-2048.jpg)
![Order Of Reaction
The sum of the powers
of concentration terms in rate equation is
known as order of reaction.
Consider a reaction mA+nB product
Rate eq (R)=k[A]m[B]n
Order = m + n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-4-2048.jpg)
![ This is the number of concentration terms that determine
the rate.
Consider the reaction:
A + B C + D
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the
concentration of A to the power of x, [A]x
and also the rate may be proportional to the
concentration of B to the power of y, [B]y.
The overall equation is,
Rate = k [A]x [B]y
The overall order of reaction is x+y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-5-2048.jpg)








![SECOND ORDER REACTION
‘’Rate of change in conc. of product and reactant is dependent on
second power of conc. of single reactant or to first powers of the
conc. of two reactants.’’
i.e. - dCX = K [X] [Y]-------------------------------------(1)
dt
or -dCX = K [X]2 ----------------------------------------(2)
dt
- dCX = K [X] [Y]
dt
Here decrease in conc. of Y is similar to X. If conc. of X and Y at
time t = 0 are a and b respectively, and conc. of each substance that
has reacted after time t is equal to x then conc. of X and Y remaining
will be (a-x) & (b-x) respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-17-2048.jpg)


![20
b) In case when (a=b)
-dCX = K [X] 2
dt
Integration gives,
Kt = x ------------------------------------(6)
a(a-x)
Rearrangement of equation (6) gives us
Kt = 1 - 1 -----------------------------(7)
a-x a
So if second order reaction is observed then graph of 1/a-x vs t
gives straight line with slope K and intercept 1/a at t = 0.
Unit of second order reaction is conc.-1 time-1 and
SI unit is mol-1 sec-1
Half-life in this case is t1/2 = 1/ak.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-20-2048.jpg)
![HIRD ORDER REACTION & HIGHER
Rate of change in conc. is proportional to three
concentration terms. However such reactions are
rare and their analysis is complex. Reaction of
even higher order is unlikely to occur.
Rate equation for third order reaction is as follows
K = 1/2t [1/(a-x) 2 -1/a2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-22-2048.jpg)
![Half Life Time
Half life time for third order reaction
t ½ = 1/a n-1
= 1/a 3-1 = 1/ a2
[as n=3]
Units:
k = mol -2 lit 2 sec -1
= conc. -2 sec -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofareaction2302-151029150927-lva1-app6892/75/Order-of-a-reaction-2302-23-2048.jpg)

