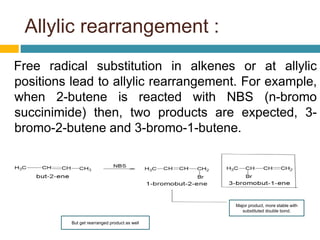
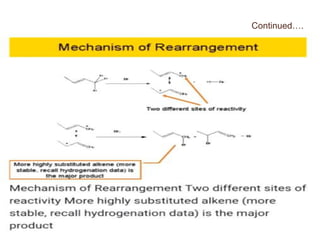
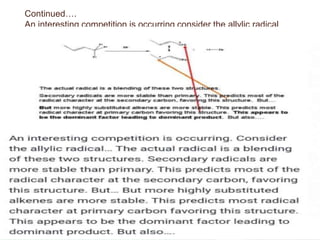
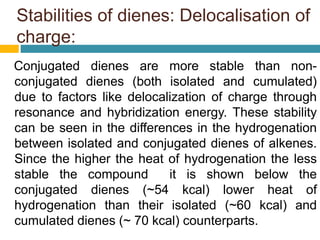
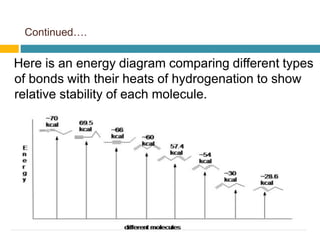
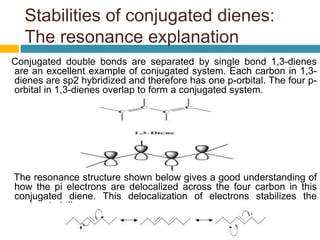
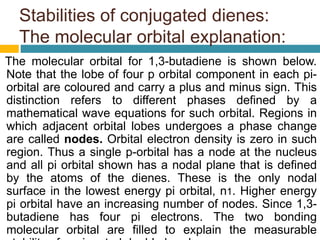
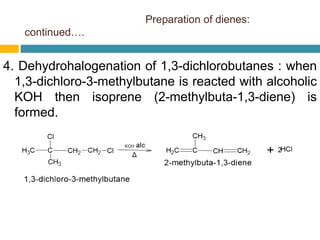
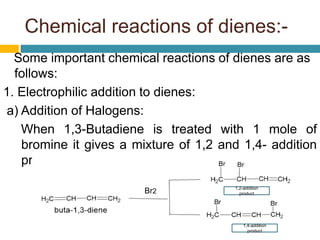
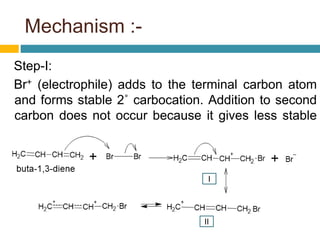
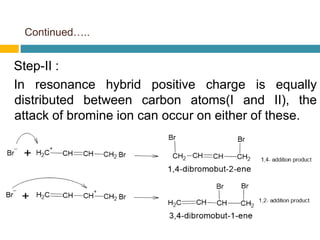
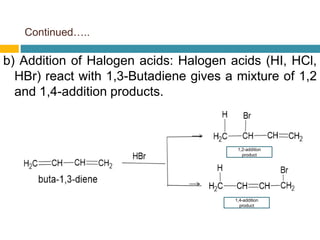
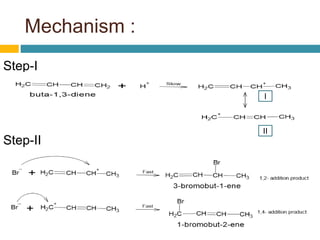
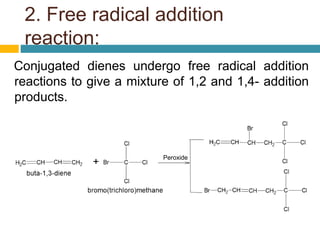
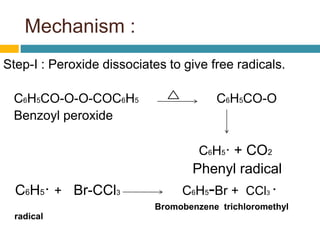
Dienes are hydrocarbons with two carbon pi bonds, classified into cumulated, conjugated, and unconjugated types, with their stability influenced by factors like resonance and hybridization. Conjugated dienes are more stable than their non-conjugated counterparts, and important reactions include electrophilic additions, free radical additions, and Diels-Alder reactions for synthesis. The document also discusses preparation methods for dienes, showcasing their significance in organic chemistry and polymer industries.




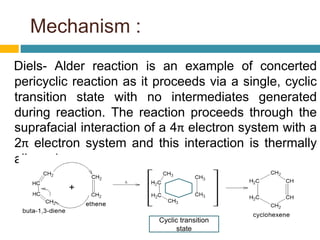
![4. Diels alder reaction:
It is also known as [4+2] cycloaddition reaction. It involves
addition of a conjugated diene (4π electron system) to a
substituted alkene (2π electron system) also known as
dienophile to form a six memebered cyclic alkene. This
reaction is particularly useful in synthetic organic chemistry
as it is reliable method for preparation of six membered
system. Dienophiles may be any acetylenic compound
containing electron withdrawing groups or alpha, ß-
unsaturated, ester, anhydrides, aldehydes, ketones and nitro
compounds. Diels Alder reaction normally do not require any
catalyst and occurs on heating.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conjugateddienes-210722060507/85/Conjugated-dienes-24-320.jpg)