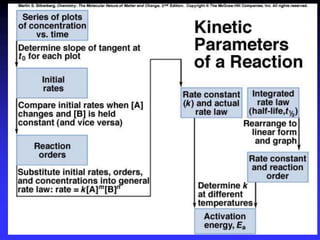
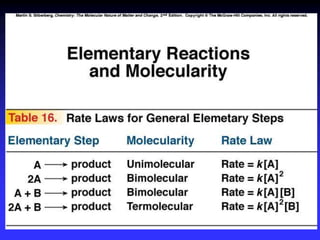
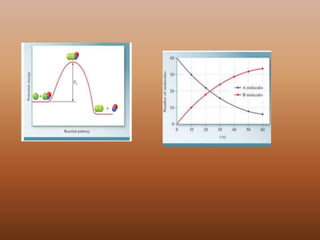
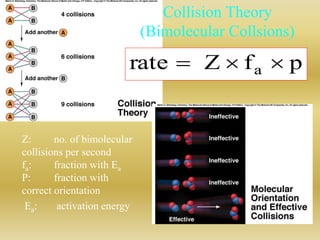
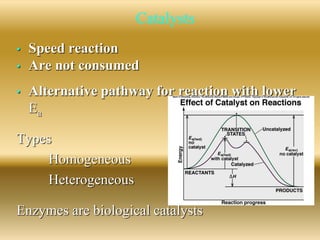
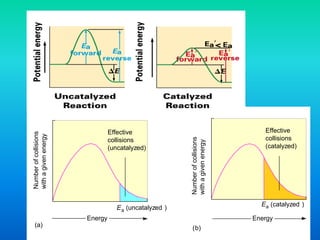
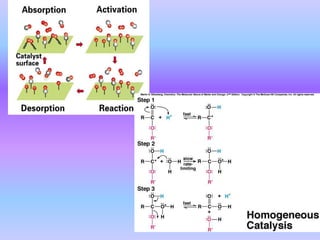
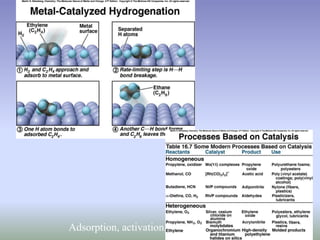
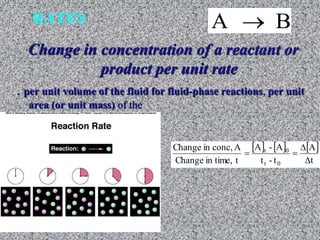
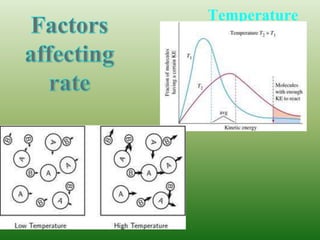
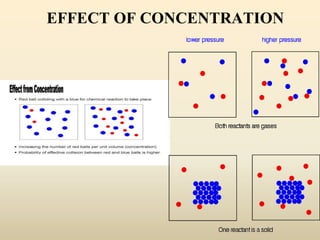
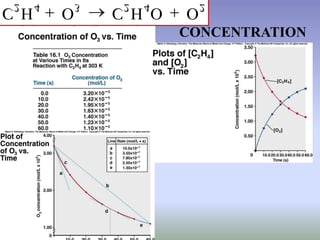
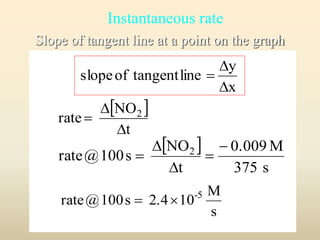
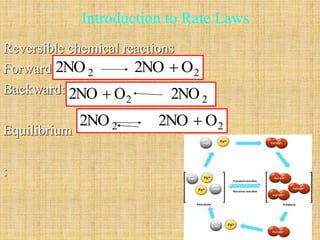
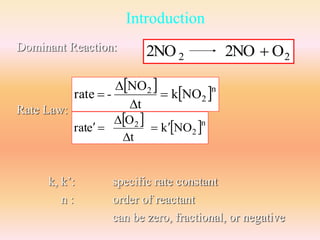
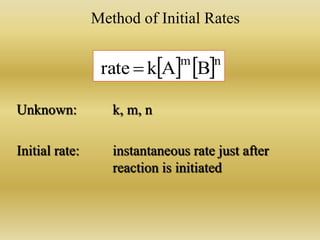
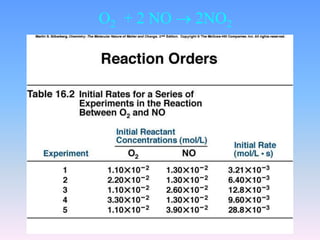
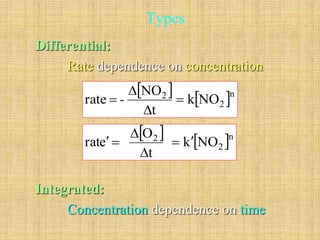
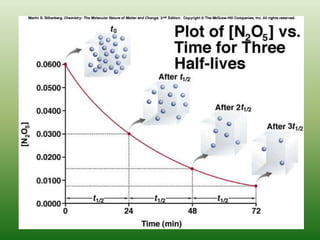
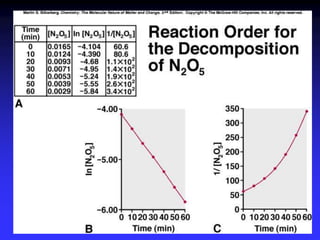
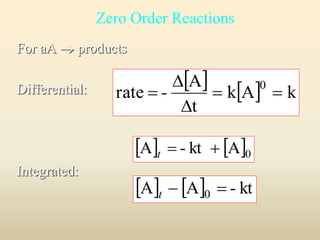
The document discusses chemical kinetics and reaction rates. It defines zero, first, and second-order reactions based on how the reaction rate depends on reactant concentrations. For zero-order reactions, the rate is independent of concentration. For first-order reactions, the rate is directly proportional to one reactant concentration. For second-order reactions, the rate is proportional to the product of two reactant concentrations or the square of one reactant concentration. It also presents the integrated rate laws and methods for determining the order of a reaction from experimental data by plotting concentrations versus time.



![Time(s) [NO2] [NO] [O2]
0 0.0100 0.0000 0.0000
50 0.0079 0.0021 0.0011
100 0.0065 0.0035 0.0018
150 0.0055 0.0045 0.0023
200 0.0048 0.0052 0.0026
250 0.0043 0.0057 0.0029
300 0.0038 0.0062 0.0031
350 0.0034 0.0066 0.0033
400 0.0031 0.0069 0.0035
2 2 2NO 2NO O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-10-320.jpg)
![Graph: Concentration vs. time
NO - NO
2 2 400 2 0
Concentration vs Time
0.012
0.01
0.008
0.006
0.004
0.002
0
NO
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Time, sec
Conc.,mol/L
[NO2]
[NO]
[O2]
2 2 2NO 2NO O
1.725 10 M
0.0031 - 0.0100
400 - 0
t - t
t
5
400 0
-[NO2]/t time period(s)
–4.20E-05 0 - 50
–2.80E-05 50 - 100
–2.00E-05 100 - 150
–1.40E-05 150 - 200
–1.00E-05 200 - 250
–1.00E-05 250 - 300
–8.00E-06 300 - 350
–6.00E-06 350 - 400
–1.75E-05 0 - 400 Concentration vs Time
0.012
0.01
0.008
0.006
0.004
0.002
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Time, sec
Conc.,mol/L
[NO2]
[NO]
[O2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-11-320.jpg)
![INSTANTANEOUS RATE
Concentration vs Time
0.012
0.01
0.008
0.006
0.004
0.002
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Time, sec
Conc.,mol/L
[NO2]
[NO]
[O2]
12_291
0.0003
70s
O2
0.0100
0.0075
0.005
0.0025
0.0006
70s
0.0026
110 s
NO2
NO
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
Concentrations (mol/L)
Time (s)
[NO2 ]
t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-13-320.jpg)
![Concentration vs Time
0.012
0.01
0.008
0.006
0.004
0.002
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Time, sec
Conc.,mol/L
[NO2]
[NO]
[O2]
NO
rate 2
t
y
x
slope of tangent line
0.010M
225 s
NO
rate @ 0 s 2
t
M
s
rate @ 0 s 4.4 10 -5
Slope of tangent line at time
0 (y intercept)
Initial Rate (t = 0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-14-320.jpg)
![RATE LAWS
m n rate k A B
k = rate constant
m, n = order
2 2 2NO 2NO O
rate = k[NO2]n
Order of Reaction In chemical kinetics, the order of
reaction with respect to a certain reactant, is defined
as the power to which its concentration term.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-15-320.jpg)
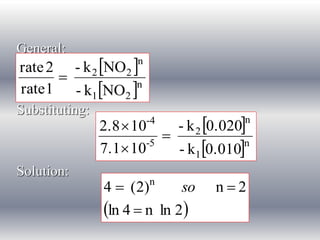
![Initial Rates, NO2 decomposition
2 2 2NO 2NO O
-
rate
Experiment
NO
2 k NO
t
Initial Conc.
[NO2]
n
2
Rate [O2]
Formation
1 0.01 7.1 x 10-5
2 0.02 2.8 x 10-4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-19-320.jpg)
![Rate constant
Rate 1
n
2
NO
2 k NO
t
-
rate
7.1 x 10-5 M s-1 = -k[0.01 M]2
k = 0.71 M-1 s-1
Rate 2
2.8 x 10-4 M s-1 = -k[0.02 M]2
k = 0.70 M-1 s-1
2
2
NO
2 0.70 NO
t
rate law
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-21-320.jpg)
![Experiment
H I 2HI 2 2
Initial Conc.
[H2]
Initial Conc.
[I2] Rate
1 0.0113 0.0011 1.9 x 10-23
2 0.0220 0.0033 1.1 x 10-22
3 0.0550 0.0011 9.3 x 10-23
4 0.0220 0.0056 1.9 x 10-22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-22-320.jpg)
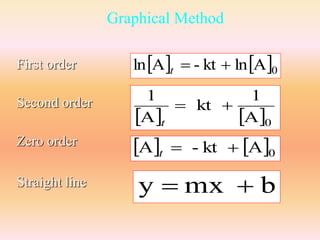
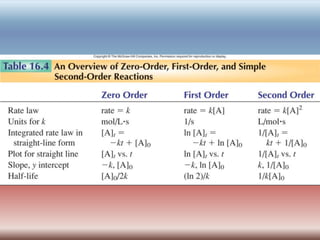
![First Order Reactions
For aA products
Differential:
kA
A
-
rate
t
0 ln A - kt ln A t
Integrated: first order reaction (order = 1) has a
rate proportional to the concentration of one of
the reactants. A common example of a first-order
reaction is the phenomenon of A
radioactive
0 decay.
The rate law is:
ln
kt
A
rate = k[A] (or B instead of A), with t
k having the
The rate of reaction is proportional to the
concentration of A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-25-320.jpg)
![Half-life, first order reactions
Integrated law:
Half-life:
Half of initial reacted
[A]t = ½[A]0
Independent of [A]0
kt
A
ln 0
A
t
ln2
0.693
k
t
k
t
2
1
2
1
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-26-320.jpg)
![First order
Plot:
ln[A] vs. time
ln[A]
ln[A]0
slope = -k
time
lnA - kt lnA0 t
y mx b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-27-320.jpg)
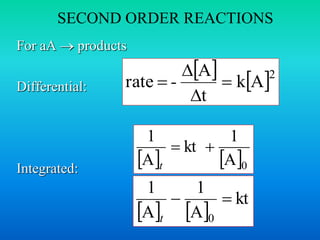
![SECOND-ORDER REACTION
A second-order reaction (order = 2) has a rate
proportional to the concentration of the square
of a single reactant or the product of the
concentration of two reactants:
rate = k[A]2 (or substitute B for A or k multiplied
by the concentration of A times the
concentration of B), with the units of the rate
constant M-1sec-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-30-320.jpg)
![SECOND ORDER
1
kt
1
0 A
Plot:
1 vs. time
[A]
1
[A]o
slope = k
time
y mx b
A
t
1
[A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-31-320.jpg)
![HALF-LIFE, SECOND ORDER
REACTIONS
Integrated law:
Half-life:
Half of initial reacted
[A]t = ½[A]0
1
1
Inversely proportional to [A]0
kt
A
A
0
t
1
0 k A
t
2
1
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-33-320.jpg)

![Zero order
0 A - kt A t
Plot:
[A] vs. time
[A]
[A]0
slope = -k
time
y mx b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch16kinetics-1-141212022344-conversion-gate01/85/Ch16-kinetics-1-36-320.jpg)