This document discusses key concepts in chemical kinetics including:
1) Chemical kinetics deals with the rates of chemical reactions and their mechanisms.
2) The rate of a reaction is defined as the decrease in reactant concentration or increase in product concentration over time.
3) The order of a reaction refers to the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate law expression.





![6
CONTIN……
• EXAMPLES:
mA+rB product
rate = K[A] ͫ [B] ͫ
The oder of reaction= (m+r)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofreaction-150322072808-conversion-gate01/85/Order-of-reaction-6-320.jpg)

![8
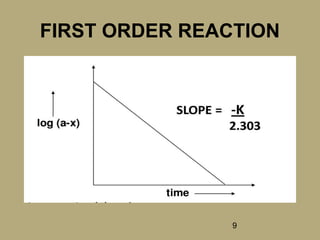
FIRST ORDER REACTION
• If a reaction rate depends on a single
reactant and the value of the exponent is
one, then the reaction is said to be first
order.
• r = k [A]
• FORMULA:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofreaction-150322072808-conversion-gate01/85/Order-of-reaction-8-320.jpg)
![10
SECOND-ORDER REACTION
• the rate of reaction is directly proportional
to the square of the concentration of one
of the reactants.
• r = k [A]2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orderofreaction-150322072808-conversion-gate01/85/Order-of-reaction-10-320.jpg)

