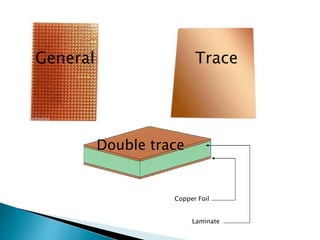
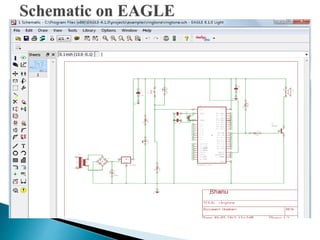
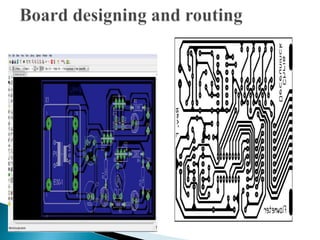
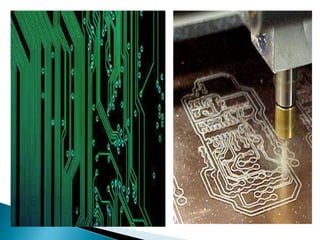
This document discusses printed circuit boards (PCBs). It provides an introduction and overview of what a PCB is, the need for PCBs, types of PCBs including general, trace, single layer and double layer, and the design process for trace PCBs. It also outlines some advantages like lower costs for mass production and reduced wiring, and disadvantages such as difficulty repairing or redesigning a PCB. Finally, it provides some examples of PCB applications.