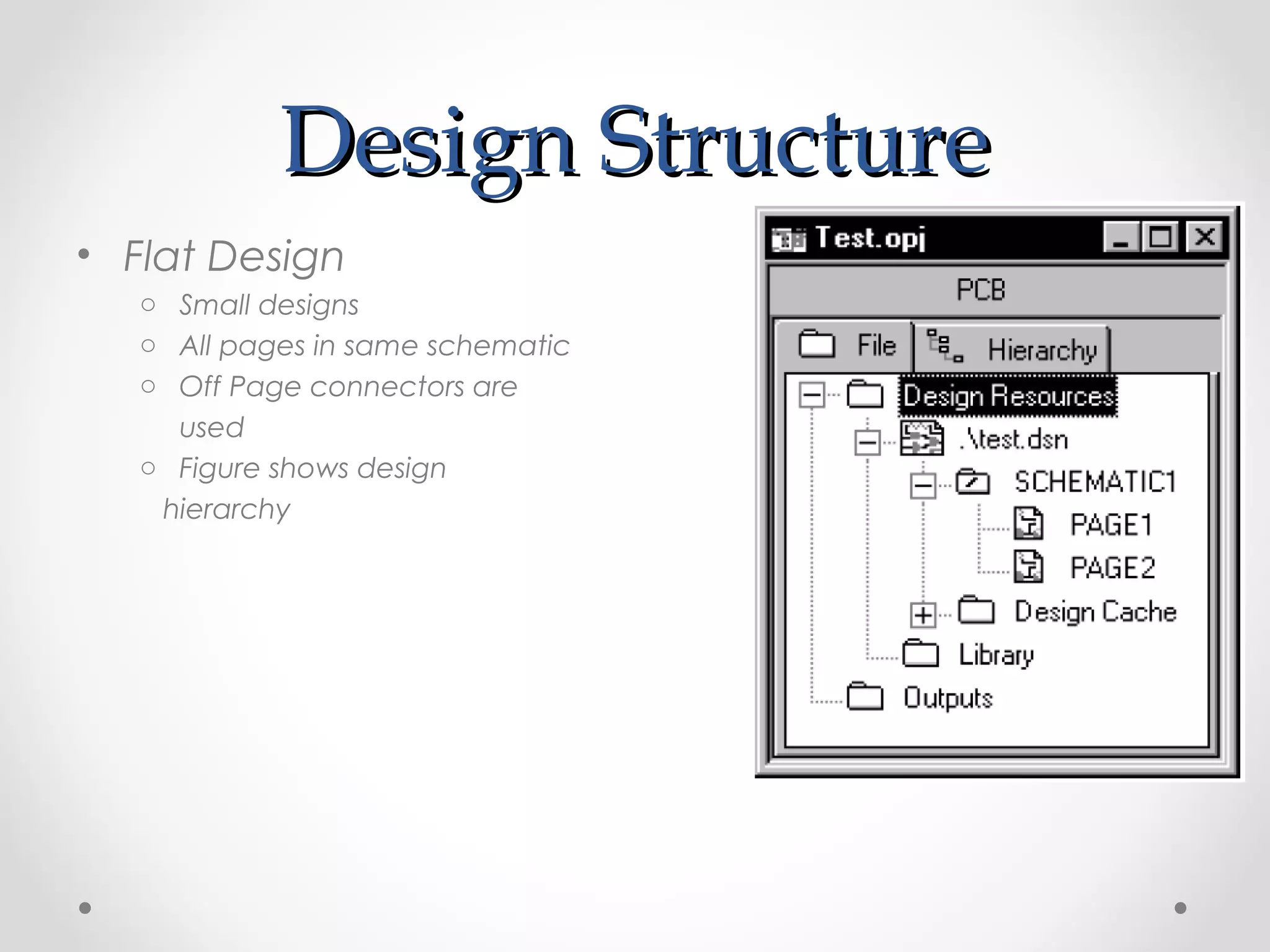
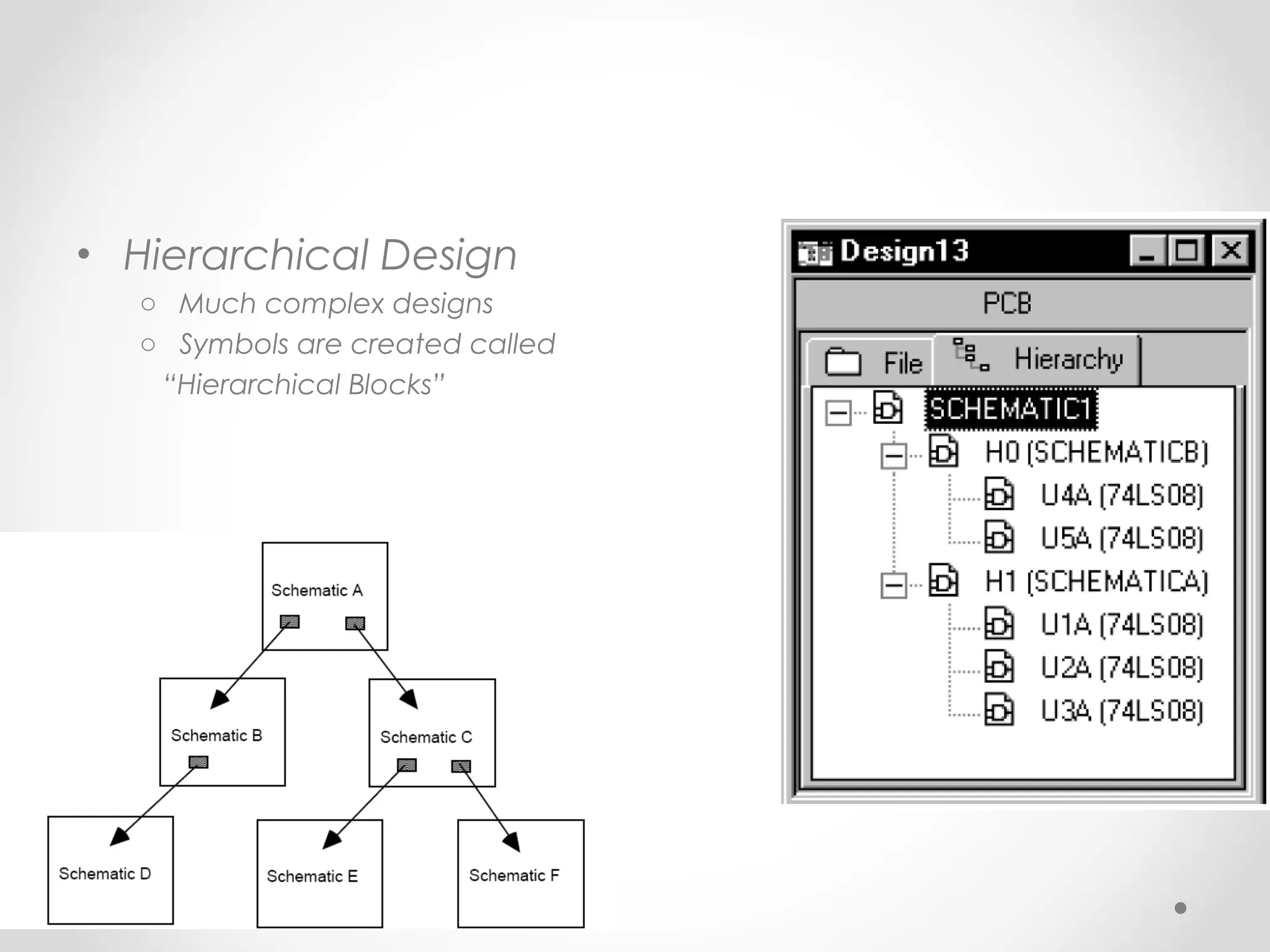
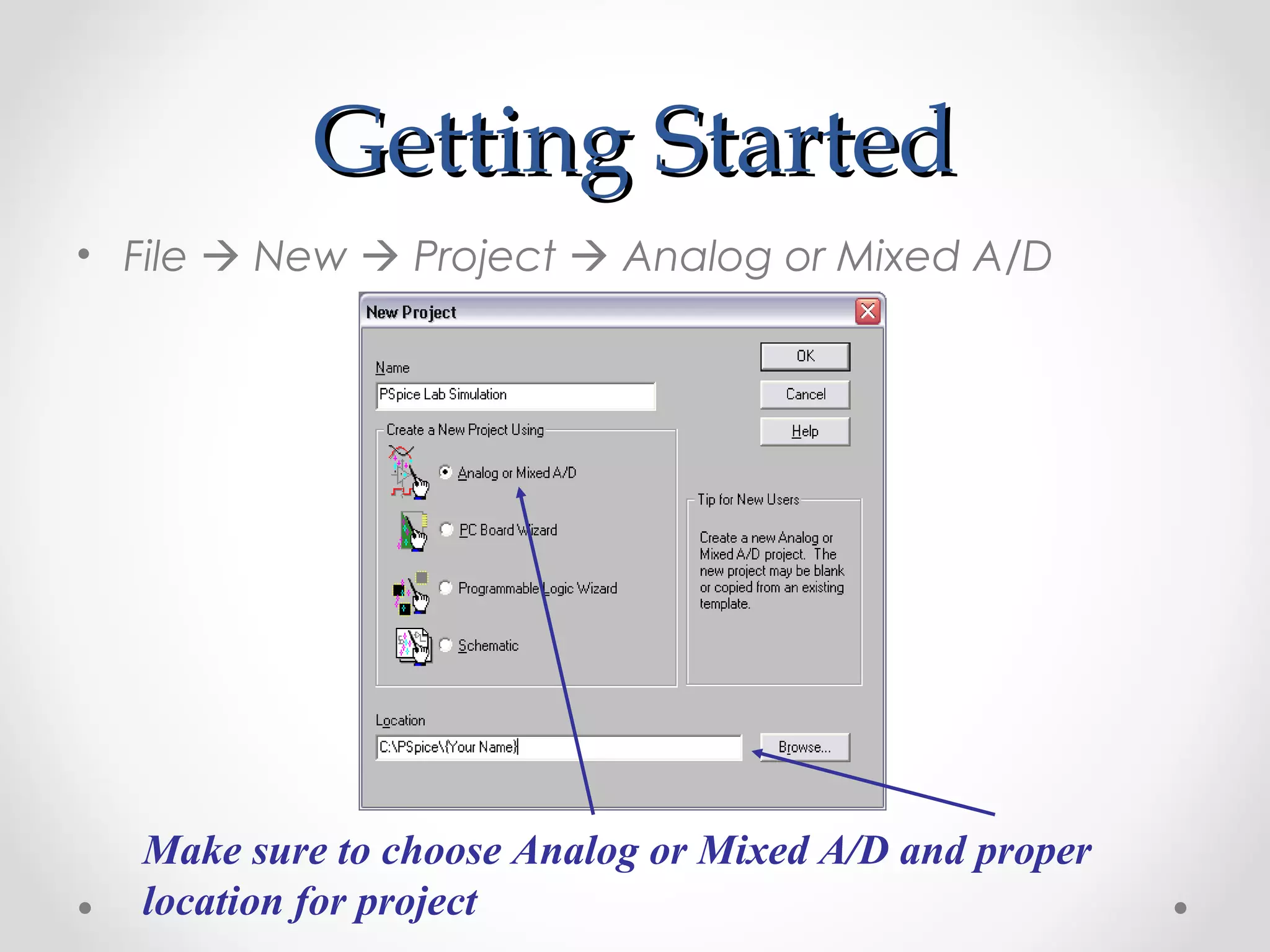
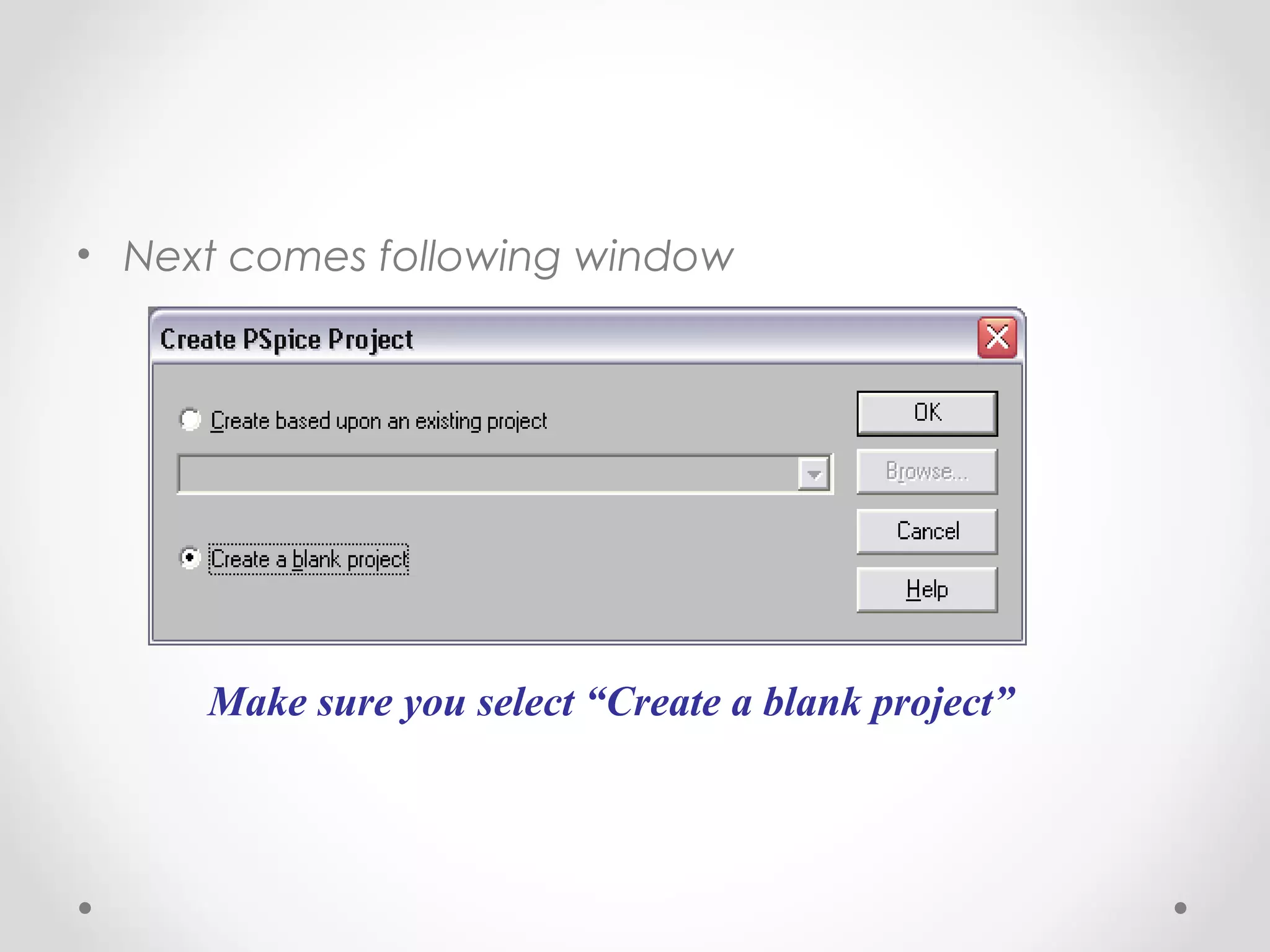
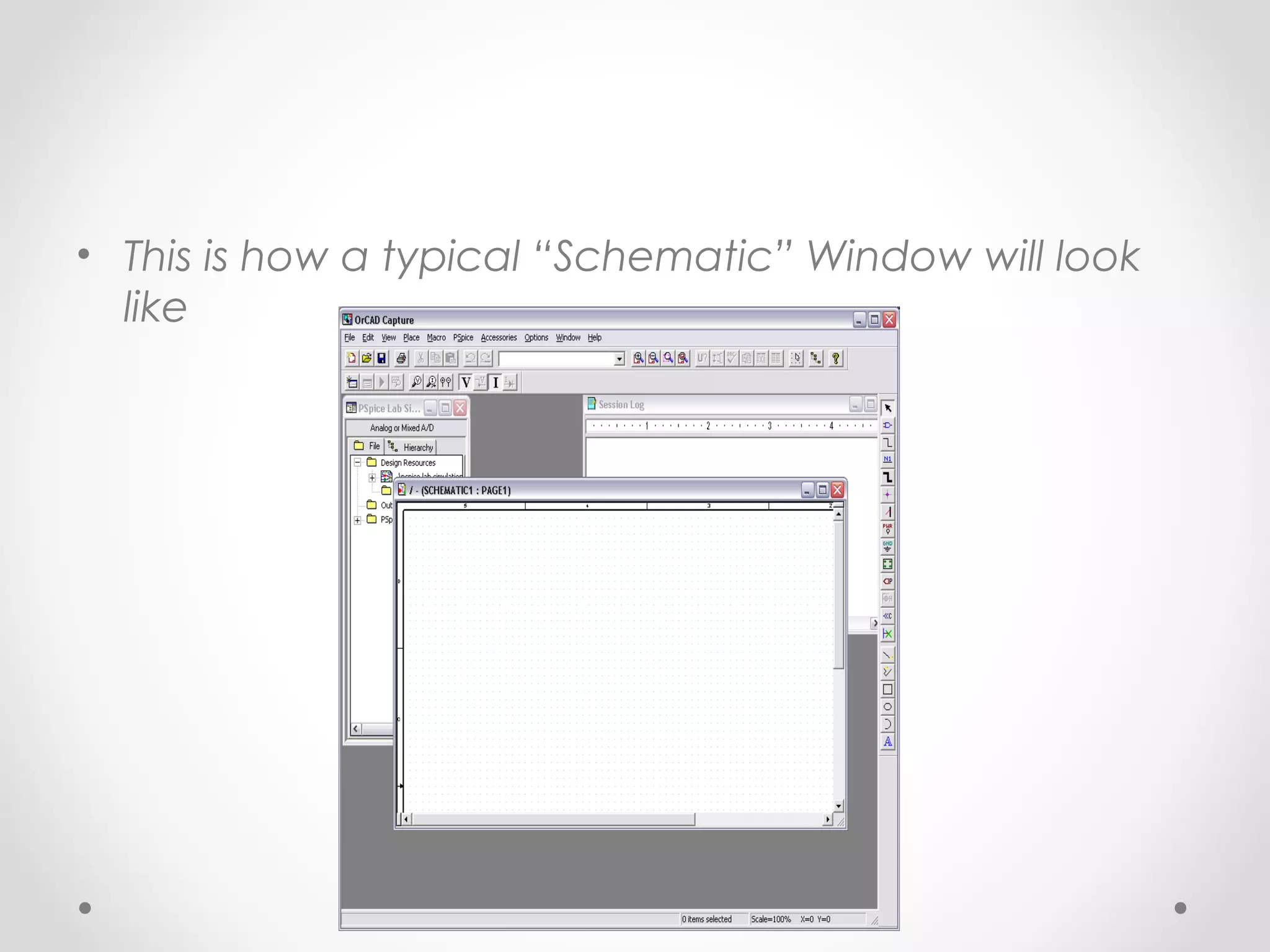
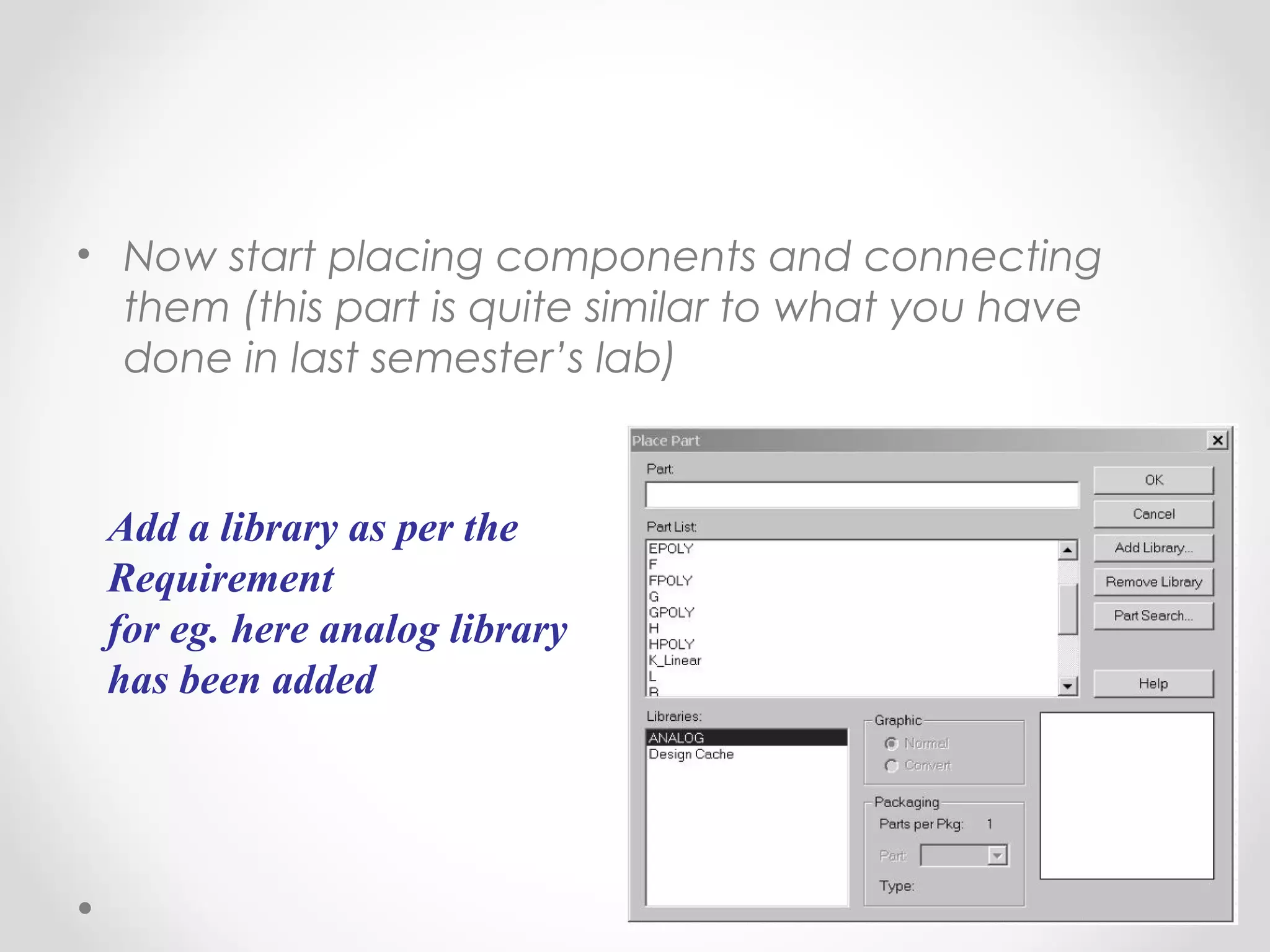
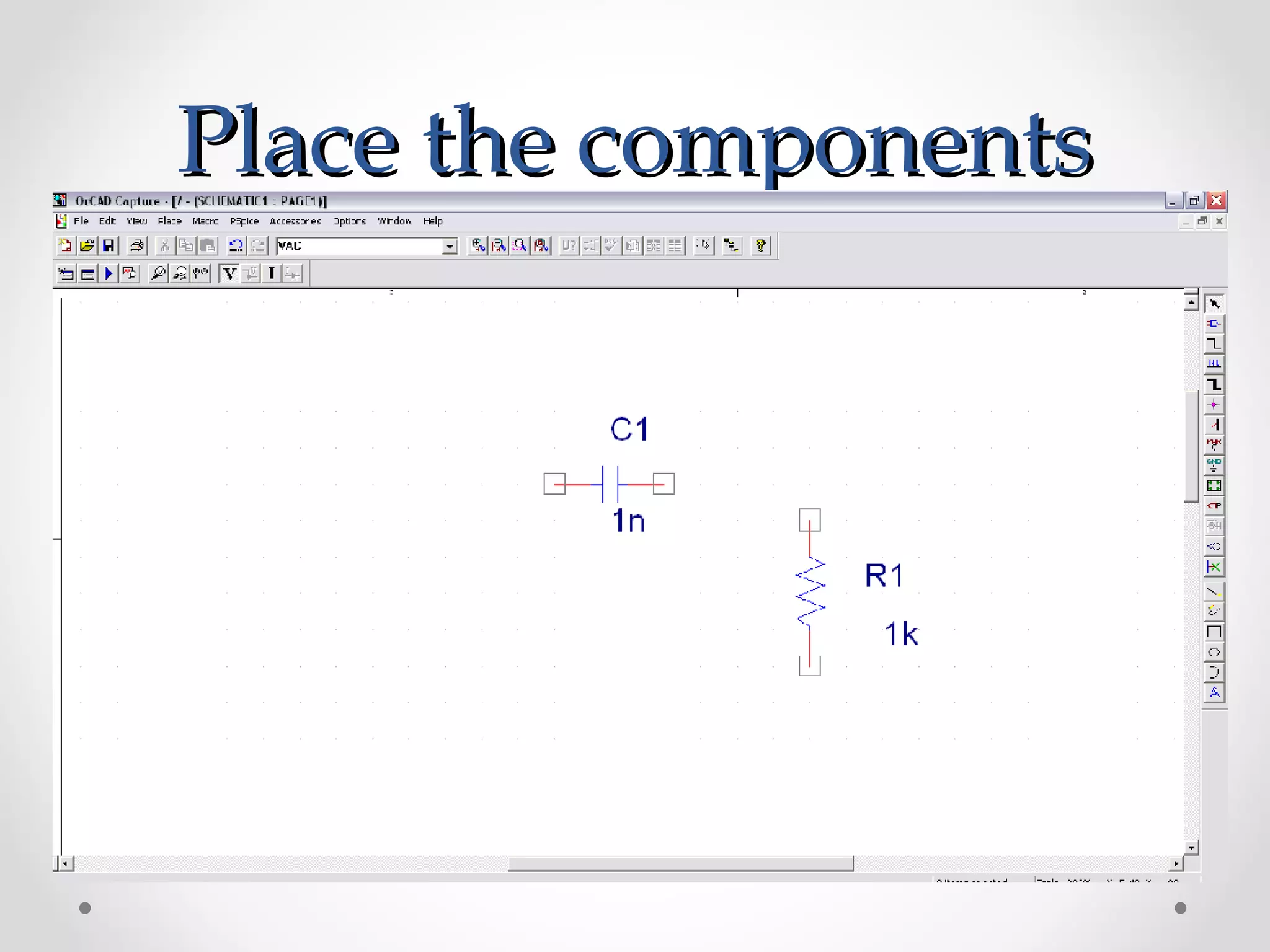
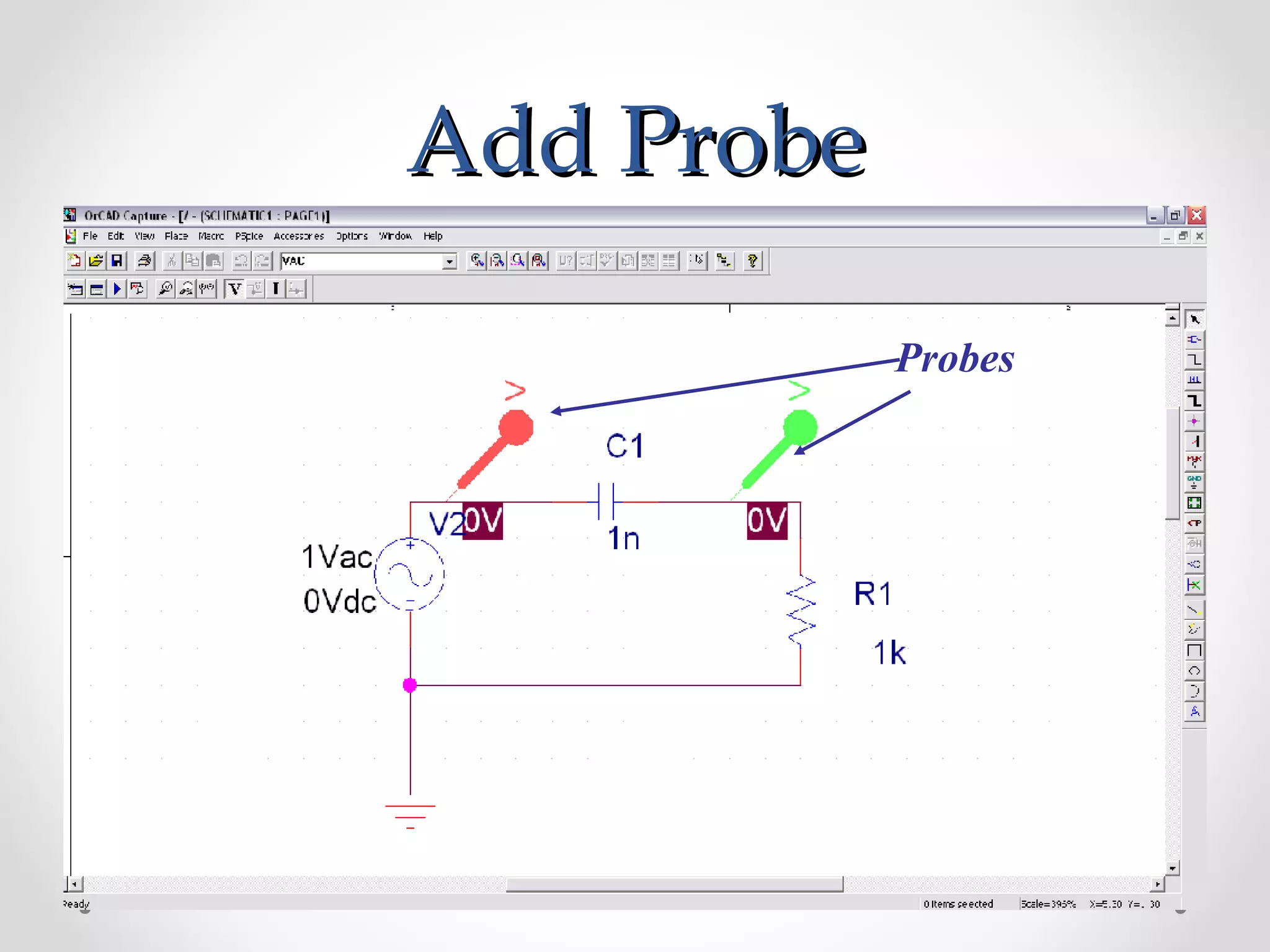
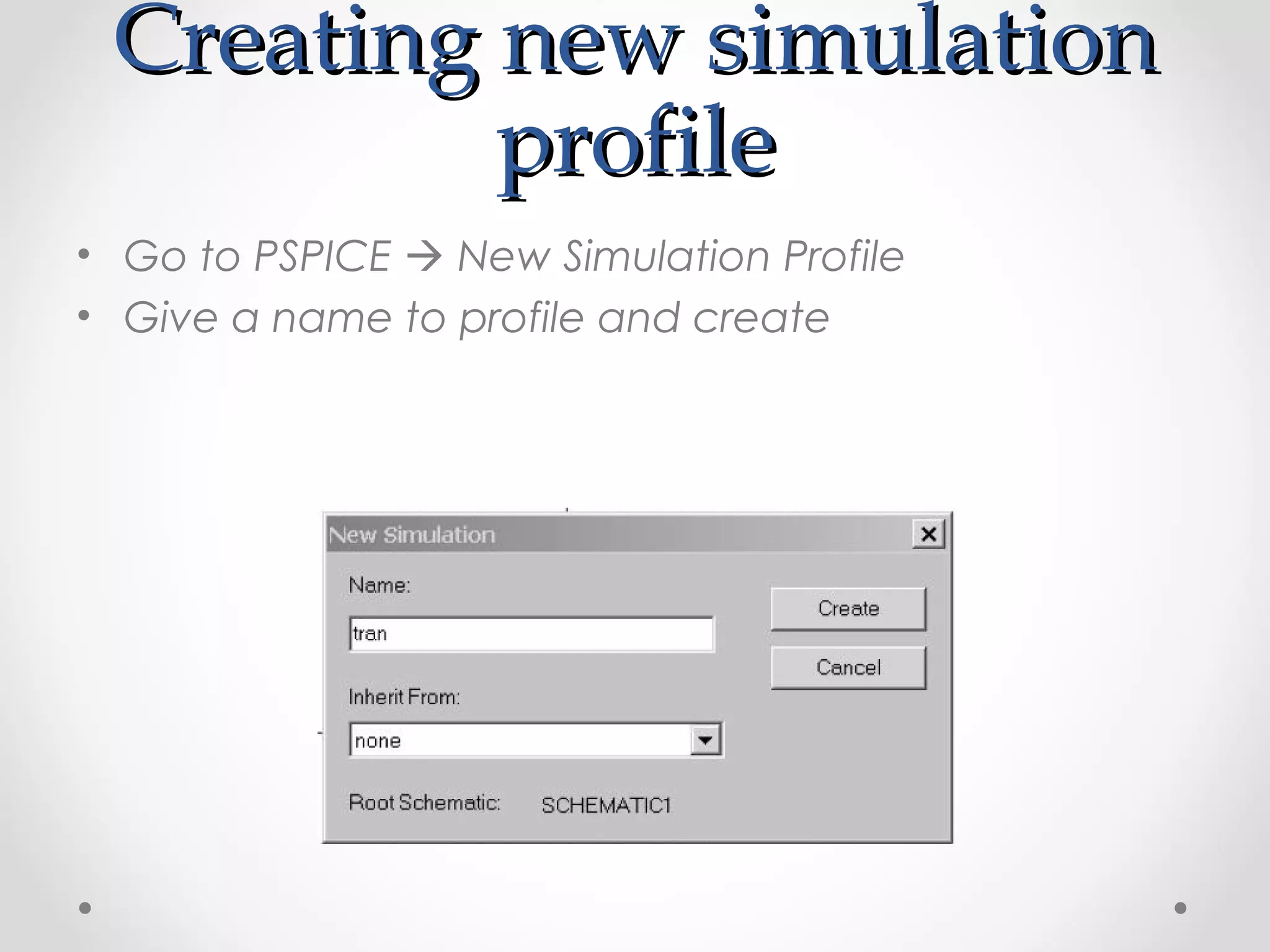
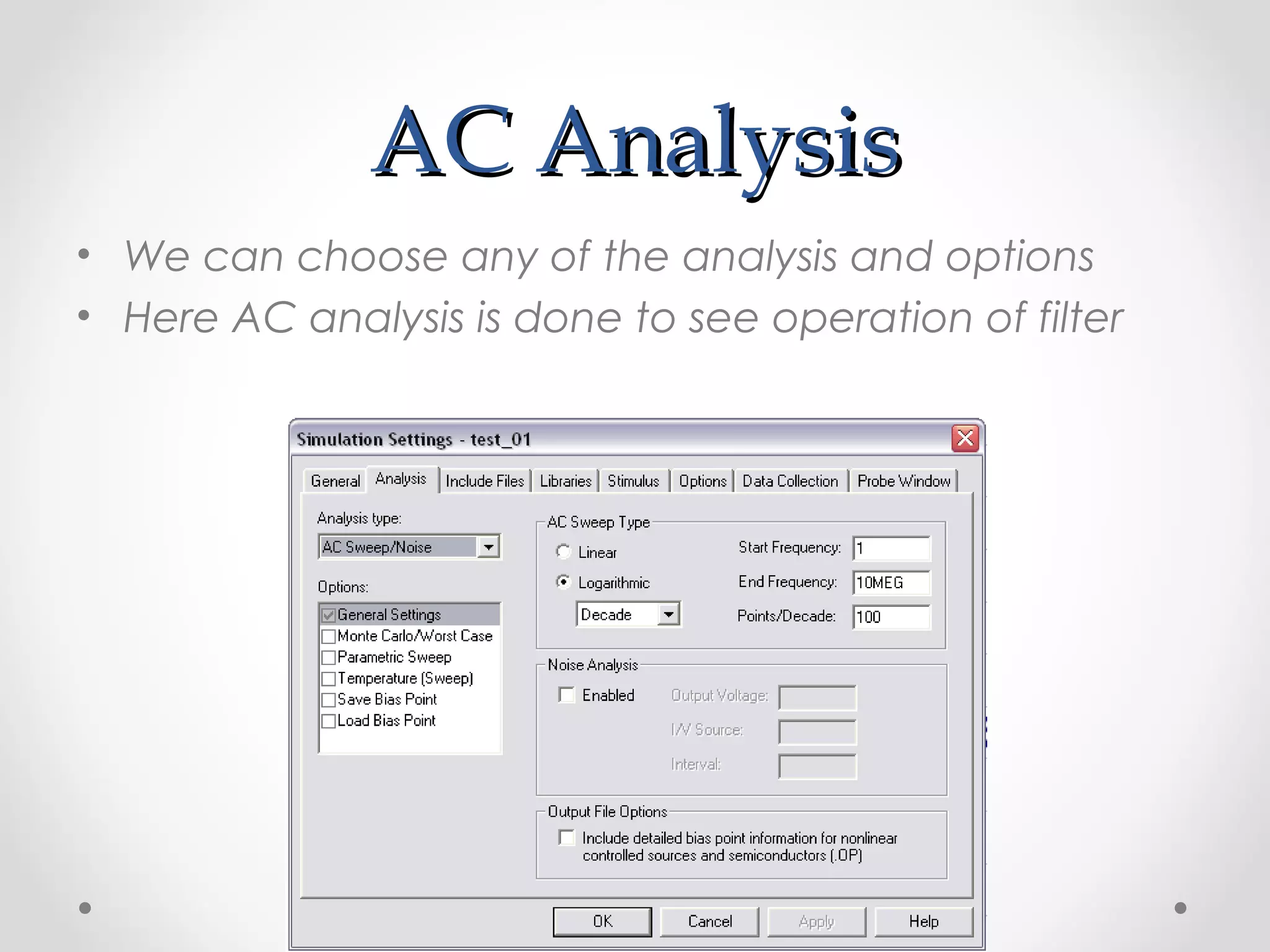
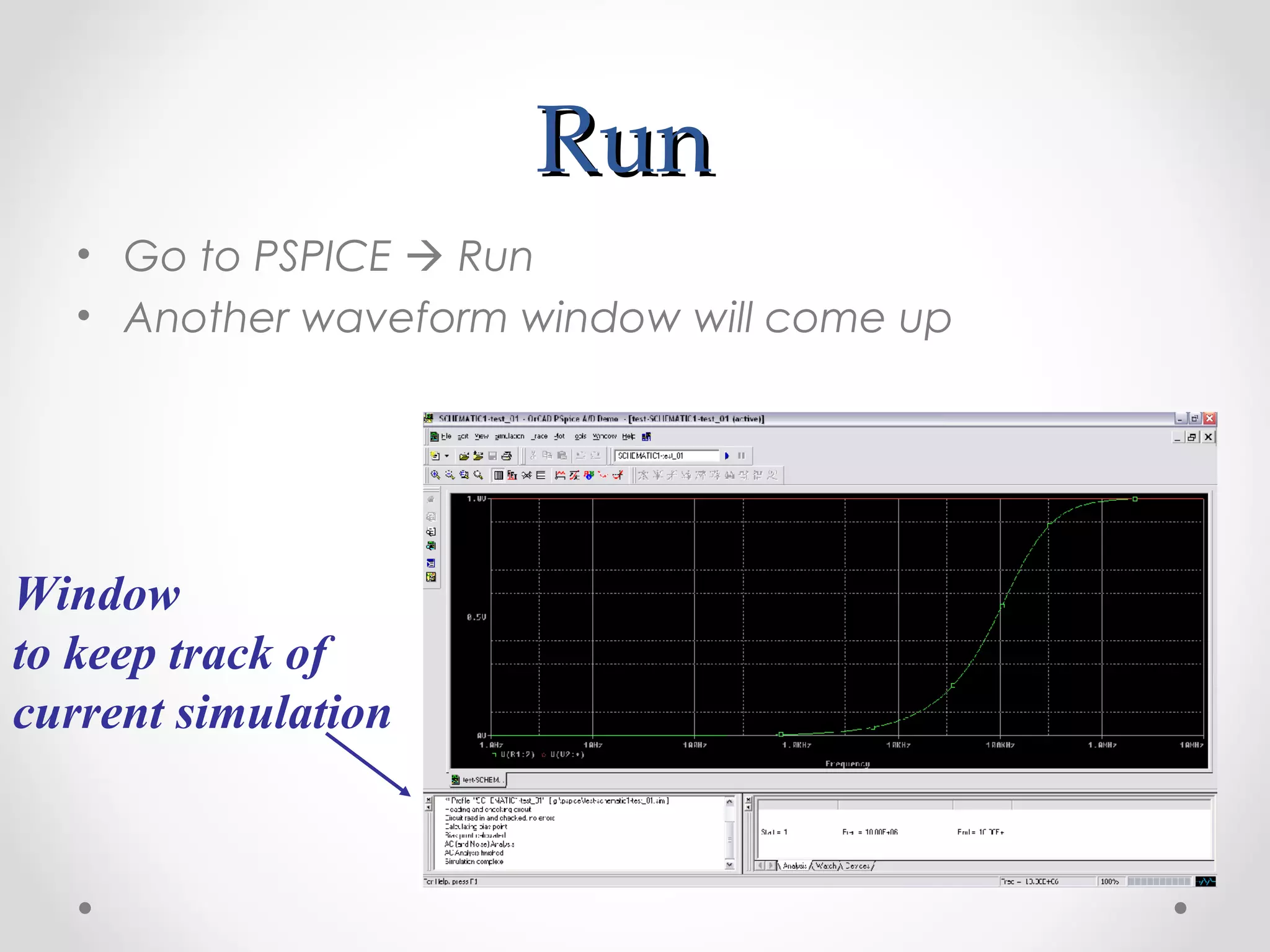
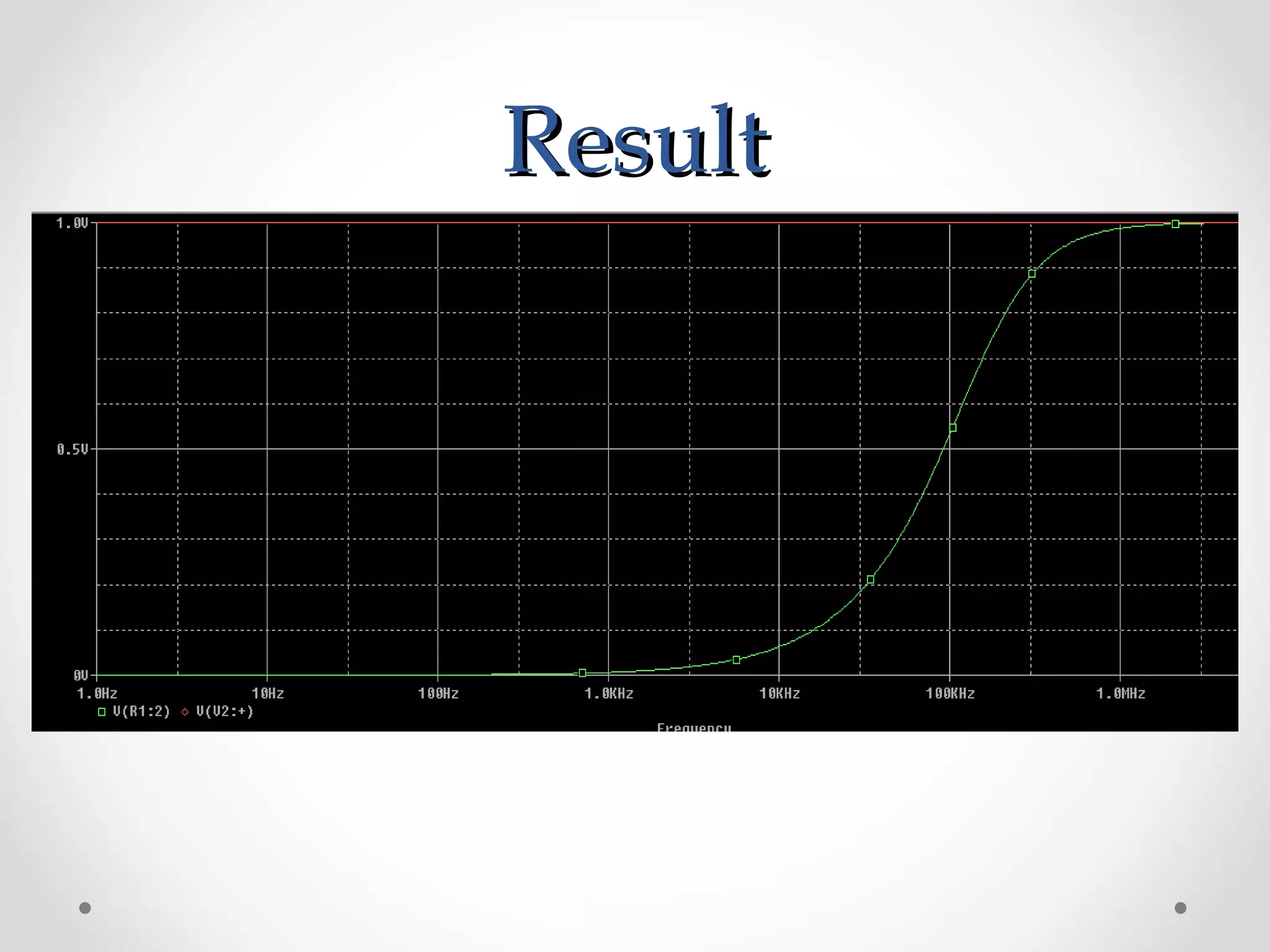
The document introduces PSpice, a PC-based version of the SPICE analog circuit simulator, emphasizing its utility in verifying circuit designs and predicting behavior with a wide range of analysis types. It covers essential components, file structures, libraries, and design methodologies, including flat and hierarchical designs. The conclusion highlights PSpice as an easy-to-use tool for circuit simulation and analysis.