This document provides an introduction to optometry, including:
1. Optics is the scientific study of light, categorized into geometrical, physical, and quantum optics.
2. Radiometry measures electromagnetic radiation including light. Photometry measures perceived brightness.
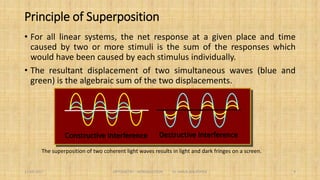
3. Theories of light include the corpuscular, wave, electromagnetic, quantum, and dual theories. Light exhibits both wave and particle properties.