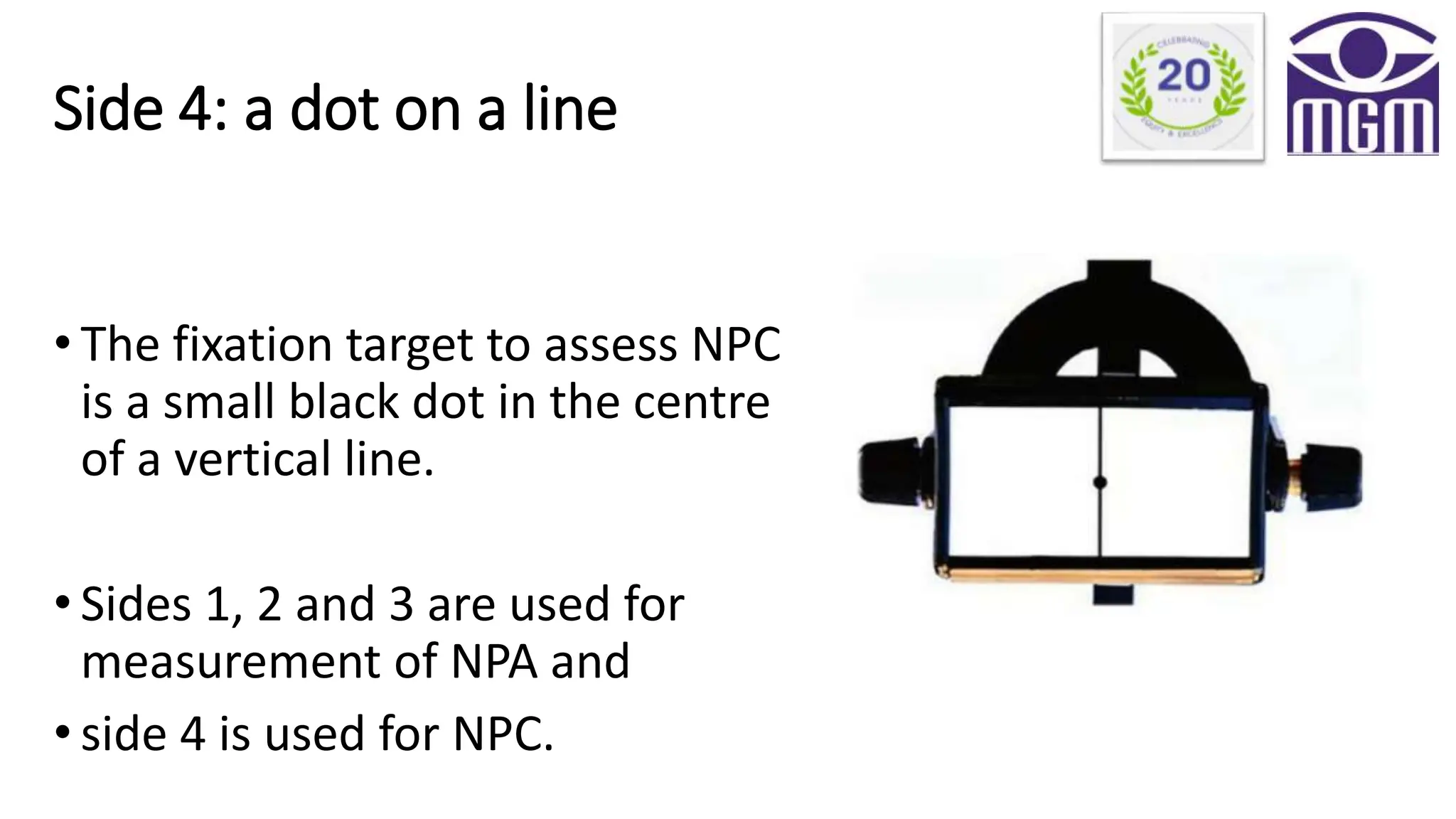
The document discusses the RAF Near Point Rule (RNPR), an instrument used in ophthalmology to measure near point of convergence (NPC) and near point of accommodation (NPA). It describes the history, components, and procedures for measuring NPC and NPA, including the use of a cheek rest and various target charts. Normal ranges for NPC and NPA are provided, along with indications of convergence issues.






![Side 3: Times Roman typeface
•The Faculty of Ophthalmologists [1951]
suggested that.
• Based on these recommendations one
face consists of four lines: N5, N8, N10
and N12;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rafrular-240325184630-18fcd18e/75/RAF-RULAR-PPT-PRESENTATION-Near-point-of-Accommodation-Near-point-of-Convergence-7-2048.jpg)